Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Exercise Chp9
Caricato da
Siti NorhayatiDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Exercise Chp9
Caricato da
Siti NorhayatiCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Exercise chapter 9 Manufacture of sulphuric acid 1 Figure 1 shows the stages in the process where sulphuric acid is manufactured
ed industrially. (a) Name the process shown in Figure 1. (b) Suggest two ways to prepare sulphur dioxide in stage I. (c) Name the following substances in the process shown in Figure 1. (i) X: (ii) Y: (iii) Z: (d) State the optimum conditions in stage II. (e) Write the chemical equation to represent the pro4uction of X from sulphur dioxide. (f) Write the chemical equation to represent the reaction between substance X and concentrated sulphuric acid. (g) Gives 3 uses of sulphuric acid. 2. Give two effects of acid rain
Manufacture of ammonia
The equation below represents the production of ammonia. (a) Name the process used in the industrial manufacture of ammonia. (b) State the optimum conditions for this process. (i)Temperature: (ii)Pressure (iii)Catalyst: (c) What is the function of the catalyst in this process? (d) State one way to increase the amount of ammonia produced. (e) How is urea produced from ammonia? (f) Give two uses of ammonia
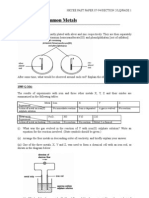
ALLOY 1. What is the meaning of alloy ? 2. Give 3 reasons why pure metals are alloyed before used 3. Draw the arrangement of atoms in (i) pure metal (ii) alloy 4. Relate the arrangement of atoms in metals to their ductile and malleable properties 5. Explain why an alloy is stronger than its pure metal in terms of the arrangement of atoms in metals and alloys 6. Explain why bronze harder tham pure copper ? 7. Complete the table below ALLOY COMPOSITION USAGE Steel Brass Bronze Duralumin Cupronickel Pewter
Exercise chapter 9 Manufacture of sulphuric acid 1 Figure 1 shows the stages in the process where sulphuric acid is manufactured industrially. (a) Name the process shown in Figure 1. (b) Suggest two ways to prepare sulphur dioxide in stage I. (c) Name the following substances in the process shown in Figure 1. (i) X: (ii) Y: (iii) Z: (d) State the optimum conditions in stage II. (e) Write the chemical equation to represent the pro4uction of X from sulphur dioxide. (f) Write the chemical equation to represent the reaction between substance X and concentrated sulphuric acid. (g) Gives 3 uses of sulphuric acid. 2. Give two effects of acid rain
Manufacture of ammonia
The equation below represents the production of ammonia. (a) Name the process used in the industrial manufacture of ammonia. (b) State the optimum conditions for this process. (i)Temperature: (ii)Pressure (iii)Catalyst: (c) What is the function of the catalyst in this process? (d) State one way to increase the amount of ammonia produced. (e) How is urea produced from ammonia? (f) Give two uses of ammonia
ALLOY 1. What is the meaning of alloy ? 2. Give 3 reasons why pure metals are alloyed before used 3. Draw the arrangement of atoms in (i) pure metal (ii) alloy 4. Relate the arrangement of atoms in metals to their ductile and malleable properties 5. Explain why an alloy is stronger than its pure metal in terms of the arrangement of atoms in metals and alloys 6. Explain why bronze harder tham pure copper ? 7. Complete the table below ALLOY COMPOSITION USAGE Steel Brass Bronze Duralumin Cupronickel Pewter
Exercise chapter 9 Manufacture of sulphuric acid 1 Figure 1 shows the stages in the process where sulphuric acid is manufactured industrially. (a) Name the process shown in Figure 1. (b) Suggest two ways to prepare sulphur dioxide in stage I. (c) Name the following substances in the process shown in Figure 1. (i) X: (ii) Y: (iii) Z: (d) State the optimum conditions in stage II. (e) Write the chemical equation to represent the pro4uction of X from sulphur dioxide. (f) Write the chemical equation to represent the reaction between substance X and concentrated sulphuric acid. (g) Gives 3 uses of sulphuric acid. 2. Give two effects of acid rain
Manufacture of ammonia
The equation below represents the production of ammonia. (a) Name the process used in the industrial manufacture of ammonia. (b) State the optimum conditions for this process. (i)Temperature: (ii)Pressure (iii)Catalyst: (c) What is the function of the catalyst in this process? (d) State one way to increase the amount of ammonia produced. (e) How is urea produced from ammonia? (f) Give two uses of ammonia
ALLOY 8. What is the meaning of alloy ? 9. Give 3 reasons why pure metals are alloyed before used 10. Draw the arrangement of atoms in (i) pure metal (ii) alloy 11. Relate the arrangement of atoms in metals to their ductile and malleable properties 12. Explain why an alloy is stronger than its pure metal in terms of the arrangement of atoms in metals and alloys 13. Explain why bronze harder tham pure copper ? 14. Complete the table below ALLOY COMPOSITION USAGE Steel Brass Bronze Duralumin Cupronickel Pewter
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- SculptureDocumento38 pagineSculpturelemy100% (1)
- Astm SpecificationDocumento9 pagineAstm SpecificationHARSHANessuna valutazione finora
- Sec 3e Chem My 09 p2 (Ans)Documento14 pagineSec 3e Chem My 09 p2 (Ans)martynchekycNessuna valutazione finora
- Class - 7 English CompactaDocumento67 pagineClass - 7 English CompactaNeelam Yadav75% (4)
- 2012 OLevel Pure Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and AnswersDocumento13 pagine2012 OLevel Pure Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and AnswersMethodology OfStudies100% (6)
- TALAT Lecture 1201: Introduction To Aluminium As An Engineering MaterialDocumento22 pagineTALAT Lecture 1201: Introduction To Aluminium As An Engineering MaterialCORE MaterialsNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Chemistry of Oxides for Emerging ApplicationsDa EverandIndustrial Chemistry of Oxides for Emerging ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of Copper N BronzeDocumento6 pagineProperties of Copper N BronzechiyikomoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Module 11A-Manufactured Substances in IndustryDocumento7 pagineAnswer Module 11A-Manufactured Substances in IndustryYen ZyNessuna valutazione finora
- Tugasan CNY Manufactured SubstancesDocumento4 pagineTugasan CNY Manufactured SubstancesIda Yuni SukadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Olympiard-2015Documento3 pagineChemistry Olympiard-2015LuyandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbon and Its Compounds QDocumento8 pagineCarbon and Its Compounds QMuthoni WachiraNessuna valutazione finora
- 07 JPNT Kim f4 Modul5Documento9 pagine07 JPNT Kim f4 Modul5Abdul ManafNessuna valutazione finora
- ICSE Class 10 Chemistry 1997Documento5 pagineICSE Class 10 Chemistry 1997AshwinNessuna valutazione finora
- Attempt All Questions From This Section.: General InstructionsDocumento5 pagineAttempt All Questions From This Section.: General InstructionsmpkediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry (233) Mind JogDocumento23 pagineChemistry (233) Mind JogNishad EsdorNessuna valutazione finora
- NSS Chemistry Part 3 Metals - LQDocumento25 pagineNSS Chemistry Part 3 Metals - LQNicole ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry PaperDocumento6 pagineChemistry PaperRishikesh YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry (Sem-2) 2022 Set - 1Documento7 pagineChemistry (Sem-2) 2022 Set - 1ejeyapilNessuna valutazione finora
- FORM 3 SULPHUR AND ITS COMPOUNDS QUESTIONS Teacher - Co - .KeDocumento8 pagineFORM 3 SULPHUR AND ITS COMPOUNDS QUESTIONS Teacher - Co - .Keideal writersNessuna valutazione finora
- 0620 w08 QP 2Documento16 pagine0620 w08 QP 2MERCY LAWNessuna valutazione finora
- AMMONIA (1 Hour) - 25 MksDocumento1 paginaAMMONIA (1 Hour) - 25 MkseruchNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem F1 QNDocumento6 pagineChem F1 QNmoisabihelenNessuna valutazione finora
- Sulphuric Acid: Quick Review (A)Documento6 pagineSulphuric Acid: Quick Review (A)Mi MiNessuna valutazione finora
- S3 ChemDocumento3 pagineS3 Chemwww.mpoyamesach.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Section A (Answer ALL Questions.) : 2004-MOCK EXAM.-CHEM 1-2 - 1Documento11 pagineSection A (Answer ALL Questions.) : 2004-MOCK EXAM.-CHEM 1-2 - 1api-19650882Nessuna valutazione finora
- KAMAL Assignment July Phy&ChemDocumento3 pagineKAMAL Assignment July Phy&ChemSHERIFF LAWALNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 3Documento4 pagineChemistry 3Gurman BhatiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Worksheet 1 Year 11Documento8 pagineChemistry Worksheet 1 Year 11fatma.darghouth2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Test 2Documento2 pagineChemistry Test 2Lakshya PiplaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper 3 SPM 2011 Mastery PracticesDocumento30 paginePaper 3 SPM 2011 Mastery Practicesaganbasm100% (1)
- Chemistry f3 Qs Endterm 1Documento11 pagineChemistry f3 Qs Endterm 1Victor OnyangoNessuna valutazione finora
- Bengkel Ambang SPM 2009 Kertas 2Documento31 pagineBengkel Ambang SPM 2009 Kertas 2azharsarahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Grade X Prelim Paper 2019 Changed 123 - 1Documento4 pagineChemistry Grade X Prelim Paper 2019 Changed 123 - 117 Shinjini RanjanNessuna valutazione finora
- JJKDocumento11 pagineJJKAnonymous pa8pSCC15Nessuna valutazione finora
- Paper 3 SPM 2011 Mastery PracticesDocumento30 paginePaper 3 SPM 2011 Mastery PracticesaganbasmNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem Form 4Documento2 pagineChem Form 4Okumu KevinsNessuna valutazione finora
- A1 10 ChemistryDocumento6 pagineA1 10 ChemistrySuvadip SanyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem F3 QS2Documento6 pagineChem F3 QS2Okumu KevinsNessuna valutazione finora
- HKCEE2Documento4 pagineHKCEE2api-3739994Nessuna valutazione finora
- ChemistryDocumento6 pagineChemistrySRIJANessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry QuestionsDocumento6 pagineChemistry Questionshotbytecyber991Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electrochemistry and Oxidation and ReductionDocumento32 pagineElectrochemistry and Oxidation and ReductionHajar Norasyikin Abu BakarNessuna valutazione finora
- 0620 s04 QP 3Documento24 pagine0620 s04 QP 3G M Ali KawsarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Prefinal PaperDocumento4 pagineChemistry Prefinal Paperkuldeep9034.patelNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem Form 2 End Term 3Documento8 pagineChem Form 2 End Term 3DenisNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework For Grade 10Documento5 pagineHomework For Grade 10SavithaBroonanNessuna valutazione finora
- QBank 1C StructuredQDocumento82 pagineQBank 1C StructuredQCharles Borromeo LiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Mocks 2016 Questions Champions ExamsDocumento383 pagineChemistry Mocks 2016 Questions Champions ExamskandeabigaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Section B: Structured Questions (65 Marks) : F.4 Chemistry Final Exam (2010-2011)Documento8 pagineSection B: Structured Questions (65 Marks) : F.4 Chemistry Final Exam (2010-2011)harrynghomanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry IGCSEDocumento16 pagineChemistry IGCSENadine Kanyange100% (1)
- Murang'A High School: Chemistry Form 4 April Holiday Assignment 2024Documento4 pagineMurang'A High School: Chemistry Form 4 April Holiday Assignment 2024j96410457Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry PaperDocumento12 pagineChemistry PaperRitambhara BhattacharyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry F1T2 QSDocumento11 pagineChemistry F1T2 QSAugustine stertNessuna valutazione finora
- B M E E, 2012: Achelor OF Etallurgical Ngineering XaminationDocumento3 pagineB M E E, 2012: Achelor OF Etallurgical Ngineering XaminationChayon MondalNessuna valutazione finora
- Florence Public School Chemistry Important Questions 2018-19Documento5 pagineFlorence Public School Chemistry Important Questions 2018-19Shashank K BNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry (Sem-2) 2022 Set - 3Documento8 pagineChemistry (Sem-2) 2022 Set - 3ejeyapilNessuna valutazione finora
- ICSE-Science 2 (Chemistry) 2007: Attempt All Questions From This SectionDocumento8 pagineICSE-Science 2 (Chemistry) 2007: Attempt All Questions From This SectionSantanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Practise Questions For Prelims Section A Set1Documento6 paginePractise Questions For Prelims Section A Set1Dony GregorNessuna valutazione finora
- 032 FIV CHEMISTRY 1 Tanganyika DC Mock 2023Documento5 pagine032 FIV CHEMISTRY 1 Tanganyika DC Mock 2023tl561746Nessuna valutazione finora
- ISC Board Question Paper Class XII - 2009Documento5 pagineISC Board Question Paper Class XII - 2009Biswajit GhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Al-based Energetic Nano Materials: Design, Manufacturing, Properties and ApplicationsDa EverandAl-based Energetic Nano Materials: Design, Manufacturing, Properties and ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyrdogen Storage TechnologiesDa EverandHyrdogen Storage TechnologiesMehmet SankirNessuna valutazione finora
- Acid Bases 2018Documento2 pagineAcid Bases 2018Siti NorhayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Objective Questions: SMJK Sin Min Form 5Documento11 pagineObjective Questions: SMJK Sin Min Form 5Siti NorhayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Class: 4S7 Time /duration: 10.15am - 11.25 AmDocumento1 paginaClass: 4S7 Time /duration: 10.15am - 11.25 AmSiti NorhayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Objective Content Form 5 Sin MinDocumento3 pagineObjective Content Form 5 Sin MinSiti NorhayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Combustion 2. Substitution: AlkaneDocumento2 pagineCombustion 2. Substitution: AlkaneSiti NorhayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Science SPM Module 2Documento9 pagineScience SPM Module 2Siti NorhayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Title ChemistryDocumento11 pagineTitle ChemistrySiti NorhayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Wow Module: Analysing Four Stroke Petrol and Diesel EnginesDocumento3 pagineWow Module: Analysing Four Stroke Petrol and Diesel EnginesSiti NorhayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparing Alkanes and AlkenesDocumento2 pagineComparing Alkanes and AlkenesSiti NorhayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Science CHAPTER 4 Form 4Documento3 pagineScience CHAPTER 4 Form 4Siti Norhayati100% (2)
- Body Coordination FORM 4 SCIENCEDocumento15 pagineBody Coordination FORM 4 SCIENCESiti NorhayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Changes in Male and Female During PubertyDocumento1 paginaChanges in Male and Female During PubertySiti NorhayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- ThermochemistryDocumento5 pagineThermochemistrySiti NorhayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- TEST - THERMOCHEMISTRY - Answer All The QuestionsDocumento3 pagineTEST - THERMOCHEMISTRY - Answer All The QuestionsSiti NorhayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2: Blood Circulation and Transport 2.1 Transport System in HumansDocumento4 pagineChapter 2: Blood Circulation and Transport 2.1 Transport System in HumansSiti NorhayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- RespirationDocumento4 pagineRespirationSiti NorhayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Taper and Deburring CountersinkersDocumento33 pagineTaper and Deburring CountersinkersTuyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 7Documento18 pagineLecture 7Iftekhar ArefinNessuna valutazione finora
- Katalog ARITA - 2019Documento68 pagineKatalog ARITA - 2019Sugeng Arief Van'tbowoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tecnofil 2016Documento42 pagineTecnofil 2016Josue David Junior Salazar RosadioNessuna valutazione finora
- Earthing Rod ClampsDocumento2 pagineEarthing Rod ClampsgreenwiresolutionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Worm GearingDocumento37 pagineWorm GearingAnonymous Hy5Ir9QXNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem f3 Question BankDocumento63 pagineChem f3 Question BankAnonymous 8JBi3DANessuna valutazione finora
- Chapters On Nonferrous MetalsDocumento17 pagineChapters On Nonferrous MetalsMohmmad ShaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Semester 4 - 2019 - November - Engineering Metallurgy em Pattern 2015Documento4 pagineSemester 4 - 2019 - November - Engineering Metallurgy em Pattern 2015AYUSHNessuna valutazione finora
- KONE Materials and Accessories-Brochure SOC 21 2 Tcm238-98201Documento12 pagineKONE Materials and Accessories-Brochure SOC 21 2 Tcm238-98201Bill GetsNessuna valutazione finora
- ASTM E747-04 - Design, Manufacture and Material Grouping Classification of Wire Image Quality Indicators (IQI) Used For RadiologyDocumento14 pagineASTM E747-04 - Design, Manufacture and Material Grouping Classification of Wire Image Quality Indicators (IQI) Used For RadiologyMelissa SammyNessuna valutazione finora
- Valtek Spring Cylinder Linear Actuators: Experience in MotionDocumento12 pagineValtek Spring Cylinder Linear Actuators: Experience in Motionmhidayat108Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction Historical Prospective, Importance of Materials PDFDocumento33 pagineIntroduction Historical Prospective, Importance of Materials PDFsayiramNessuna valutazione finora
- SMI ProfileDocumento24 pagineSMI ProfileAbdul BasithNessuna valutazione finora
- 3a. Isi-B. Survey Dan Cara Pemeriksaan Kapal-31-55Documento25 pagine3a. Isi-B. Survey Dan Cara Pemeriksaan Kapal-31-55MuhammadRiady100% (1)
- DoorknobDocumento8 pagineDoorknobBurn-Man Hiruma VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitsuhiro Okayasu Amr0204004Documento15 pagineMitsuhiro Okayasu Amr0204004pavan_1988Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ziff, Magic Goggles, and Golden PlatesDocumento137 pagineZiff, Magic Goggles, and Golden PlatesJerry D Grover100% (1)
- Hackers Reading SCR 2Documento1 paginaHackers Reading SCR 2Phil AcademyNessuna valutazione finora
- Copper Alloy NotesDocumento5 pagineCopper Alloy NotesSalem GarrabNessuna valutazione finora
- Tin and Tin AlloysDocumento22 pagineTin and Tin AlloysstainedClassNessuna valutazione finora
- Brass Alloys Metalurgija Alloys enDocumento19 pagineBrass Alloys Metalurgija Alloys enebrahimikntuNessuna valutazione finora
- Cast Iron Types PDFDocumento8 pagineCast Iron Types PDFGeorge_Wabag_2014Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Compositions of AlloysDocumento40 pagineChemical Compositions of AlloysSampath Kumar50% (2)
- Galvanic Corrosion ChartDocumento2 pagineGalvanic Corrosion Chartrmartinson8Nessuna valutazione finora