Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Red Eye
Caricato da
Rodha Bint HamadDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Red Eye
Caricato da
Rodha Bint HamadCopyright:
Formati disponibili
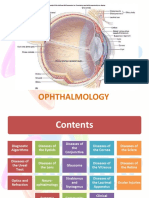
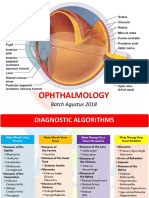
OPHTHALMOLOGY (ABC)
RED EYE
The red eye is one of the most common ophthalmic problems CAUSES OF RED EYE 1. Conjunctivitis 2. Episcleritis & scleritis 3. Corneal ulceration 4. Uveitis 5. Acute closed angle glaucoma 6. Subconjunctival hemorrhage 7. Inflamed pterygium & pingueculum Red eye may be associated with Pain Itching Discomfort Discharge Visual loss
CONJUNCTIVITIS
Most common cause of uncomfortable red eye Causes: Viral Bacterial Allergy Chlamydia
BACTERIAL CONJUNCTIVITIS
Symptoms Discomfort, red eye Purulent discharge ( difficult to open in the morning because of the stickiness of eye lashes because of the discharge) Exam Clear vision Red eye No eye cornea staining after putting the flurescein Management Topical drops antibiotics ( chloramphenicol) Ointment ( chloramphenicol) at night to prevent the stickiness of eye lashes in the morning Advice Good hygiene ( no sharing face towels)
SAJEDA SABT
OPHTHALMOLOGY (ABC)
SAJEDA SABT
OPHTHALMOLOGY (ABC)
VIRAL CONJUNCTIVITIS
Epidemic of red eye Common with URTI Usually caused by adenovirus Symptoms Bilateral eye redness + uncomfortable Watery discharge Begins in one eye then goes to the next eye History of presence of cold & cough Photophobia Exam Presence of follicles ( white lymphoid aggregation) on the conjunctiva Management Lasts longer than bacterial conjunctivitis, for many weeks Self limiting condition Antibiotics eye drops FOR Symptomatic relieve Prevent secondary bacterial infection Highly contagious strict hygiene for BOTH the doctor & the patient Chronic infection needs steroids eye drops1
CHLAMYDIAL CONJUNCTIVITIS (Chlamydia trachomatis)
Major cause of blindness Symptoms Young patients Bilateral conjunctivitis Mucopurulent discharge May be associated with venereal disease Exam Bilateral diffuse conjunctival injection Presence of follicles under the eyelids Keratitis Management Difficult to diagnose clinically, should do culture
Steroids must be prescribed with ophthalmologist supervision, because the risk of glaucoma & cataract
SAJEDA SABT
OPHTHALMOLOGY (ABC)
Tetracycline2 for one month Poor compliance recurrence
Complications Severe scarring of the conjunctiva underlying the tarsal plate that may also cause: Entropion, damage to the cornea
CONJUNCTIVITIS IN INFANTS
EXTREMLY IMPORTANT, because it may causes Blindness Immature eye deafness Severe corneal disease In an infant less than 1 month old ( ophthalmia neonatorum) is a notifiable disease Venereal diseases in parents should be excluded.
ALLERGIC CONJUNCTIVITIS
Symptoms History (+) family history History of contact with chemicals or eye drops Acute Vs. chronic EXAM Red eye Large papillae due to edema in the conjunctiva that covers the eyelids (cobblestone appearance) Management Mainly ITCHING Binocular red eye Clear discharge
Topical Antihistamines Vasoconstrictor eye drops Steroids can be used ( risk of glaucoma and cataract)
Tetracycline affects the growth of bone & teeth in children ( contraindicated), also not used in pregnancy
SAJEDA SABT
OPHTHALMOLOGY (ABC)
EPISCLERITIS & SCLERITIS
Localized area of redness & inflammation Causes : Rheumatoid arthritis ( mainly), idiopathic Symptoms : red, sore eye
IRITIS, IRIDOCYCLITIS (ANTERIOR UVEITIS) & PANUVEITIS
DEFINITIONS Uvea: iris + ciliary body + choroids Iritis: inflammation of the iris Cyclitis: inflammation of the ciliary body Iridocyclitis ( anterior uveitis): both iritis + cyclitis Risk people to develop anterior uveitis Who have HLA B27 ( Autoimmune) Ankylosing spondylitis adults Seronegative RA children Infectious Syphilis, TB, sarcoidosis, herpes zoster ophthalmaticus Causes of Panuveitis SLE polyarthritis nodosa, toxoplasmosis, wegner's granulomatosis Symptoms Pain Exam Increases during reading due to contracting the ciliary muscle Photophobia due to inflammation and ciliary spasm Impaired vision & accomodation Inflammatory cells in the ant. Chamber ( hypopyon) The eye is red around the cornea, circumcorneal redness Small pupil spasm of the sphincter Inflammatory cells deposits behind the cornea ( keratic precipitates)
Management Treat underlying disease 5
SAJEDA SABT
OPHTHALMOLOGY (ABC)
Steroids for inflammation Ciliary body paralysis to decrease the pain Dilatation of the pupil prevents adhesions between the iris and the lens ( posterior synechia) glaucoma3 Complications Glaucoma Cataract Edema of the macula
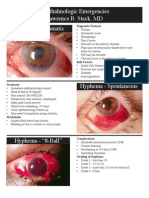
SUBCONJUNCTIVAL HEMORRHAGE
Symptoms Red eye with/ without visual disturbance History of Trauma, foreign body, ocular injury, strain, child birth, HTN Exam Localized / diffused area of subconjunctival blood No discharge Management Role out HTN The patient should be assured and told that the redness may take several weeks to fade Coagulation profile should be checked & platelets
Open angle glaucoma may developed, because inflamed cells may block the trabecular meshwork
SAJEDA SABT
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Red EyeDocumento45 pagineThe Red EyeIsraa AlaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mata MerahDocumento119 pagineMata MerahAzwanHamdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Opthalmic Emergencies PresentationDocumento85 pagineOpthalmic Emergencies PresentationvictoreffiomNessuna valutazione finora
- D.D of Red EyeDocumento116 pagineD.D of Red Eyehassan daacadNessuna valutazione finora
- Opt Halm OlogyDocumento87 pagineOpt Halm OlogyAya MahmoudNessuna valutazione finora
- Eye Disorders in Children: Alka Sara SajuDocumento64 pagineEye Disorders in Children: Alka Sara SajuManisa ParidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Redness Eye TreatmentDocumento52 pagineRedness Eye TreatmentIka HandayaniNessuna valutazione finora
- OphthalmologyDocumento144 pagineOphthalmologyrosaririsNessuna valutazione finora
- Care For Clients With Eye, EarDocumento130 pagineCare For Clients With Eye, Earlovely roan riolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Eye ConditionsDocumento35 pagineCommon Eye ConditionsElukoti BhosleNessuna valutazione finora
- Eye Problems: Dr. Gitalisa Andayani, SPMDocumento88 pagineEye Problems: Dr. Gitalisa Andayani, SPMhasanajNessuna valutazione finora
- The Red EyeDocumento71 pagineThe Red Eyehenok biruk80% (5)
- Glaukoma Dan KonjungtivitisDocumento24 pagineGlaukoma Dan KonjungtivitisAnnisa DeasyNessuna valutazione finora
- Contact Lens-Associated Microbial KeratitisDocumento39 pagineContact Lens-Associated Microbial Keratitisณัช เกษมNessuna valutazione finora
- Ocular Manifestations of Systemic DiseasesDocumento62 pagineOcular Manifestations of Systemic DiseaseslonguseridNessuna valutazione finora
- Ophthalmology NotesDocumento22 pagineOphthalmology NotesdrusmansaleemNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical App Red Eye Without Blurred VisionDocumento38 pagineClinical App Red Eye Without Blurred VisionPriskila SamanthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ophthalmic Manifestation of Systimic DiseaseDocumento45 pagineOphthalmic Manifestation of Systimic DiseaseSarahNessuna valutazione finora
- Eyelid Disorders: Ii. ChalazionDocumento62 pagineEyelid Disorders: Ii. ChalazionFreeburn SimunchembuNessuna valutazione finora
- Red EyeDocumento45 pagineRed EyeDavidVictoriousLukas100% (1)
- Short Notes and Short Cases in Ophthalmology PDFDocumento108 pagineShort Notes and Short Cases in Ophthalmology PDFInna Bujor100% (1)
- Pediatrics OptometryDocumento59 paginePediatrics Optometryendalew mulugetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Oftalmologi Batch November 2017 - UnlockedDocumento153 pagineOftalmologi Batch November 2017 - Unlockeddzulkifli sukriNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute ConjunctivitisDocumento20 pagineAcute ConjunctivitisAhmad Samim AyoubiNessuna valutazione finora
- DT LeukocoriaDocumento44 pagineDT LeukocoriahamzahNessuna valutazione finora
- Mata Merah Penglihatan NormalDocumento28 pagineMata Merah Penglihatan NormalEllen CelciliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ophthalmology Emergencies - 2Documento32 pagineOphthalmology Emergencies - 2navenNessuna valutazione finora
- L9 Cataract and Ocular PharmDocumento26 pagineL9 Cataract and Ocular PharmSofíaGriggsNessuna valutazione finora
- BLEPHARITISDocumento25 pagineBLEPHARITISSrijana MahatoNessuna valutazione finora
- Urgent and Emergent Eye ComplaintsDocumento60 pagineUrgent and Emergent Eye ComplaintsMayank SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Phase 4 Ophthalmology 2021-22Documento62 paginePhase 4 Ophthalmology 2021-22Olivia Genevieve El JassarNessuna valutazione finora
- Uveitis 140205125134 Phpapp02Documento139 pagineUveitis 140205125134 Phpapp02ﻣﻠﻚ عيسىNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 OphthalmologyDocumento37 pagine12 Ophthalmologyayeshafarooq60Nessuna valutazione finora
- BlepharitisDocumento20 pagineBlepharitisNorshahidah IedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Penyakit Pada MataDocumento138 paginePenyakit Pada Matadevi taqiyyahNessuna valutazione finora
- 079 Muhammad Khairul Nizam Bin Khir 7.1Documento30 pagine079 Muhammad Khairul Nizam Bin Khir 7.1Ilham RafisNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Eye Problems and DiagnosisDocumento84 pagineCommon Eye Problems and Diagnosisvivekrajbhilai5850Nessuna valutazione finora
- Opthalmology For AiimsDocumento25 pagineOpthalmology For AiimssureshNessuna valutazione finora
- Pemeriksaan Dasar MataDocumento103 paginePemeriksaan Dasar Mataandhie_soyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ophthalmology Clinical Cases pixOpOpDocumento61 pagineOphthalmology Clinical Cases pixOpOpUsman ImtiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Ophthalmology: by Dr. Laraib Jameel RPHDocumento75 pagineOphthalmology: by Dr. Laraib Jameel RPHDhivya SekarNessuna valutazione finora
- (Mantap) Slide Materi Mata Batch 3 2018Documento164 pagine(Mantap) Slide Materi Mata Batch 3 2018fifinnurfina50% (2)
- K.15 Ophtalmologic EmergenciesDocumento35 pagineK.15 Ophtalmologic EmergenciesZikri Putra Lan Lubis100% (1)
- Staphylococcal Blepharitis Treatment: Try Our Search!Documento9 pagineStaphylococcal Blepharitis Treatment: Try Our Search!reniNessuna valutazione finora
- Allergic Conjunctivitis: Ascia Information For Patients, Consumers and CarersDocumento4 pagineAllergic Conjunctivitis: Ascia Information For Patients, Consumers and CarersElrach CorpNessuna valutazione finora
- Optic Disc: Symptoms of The Optic Nerve DiseasesDocumento11 pagineOptic Disc: Symptoms of The Optic Nerve DiseasesDilawar JanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ophthalmology Emergencies HandoutDocumento9 pagineOphthalmology Emergencies HandoutMutiara SazkiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Disease of UveaDocumento21 pagineDisease of UveaMarshet GeteNessuna valutazione finora
- Eye Osce 3Documento39 pagineEye Osce 3epic sound everNessuna valutazione finora
- Dry Eye SyndromeDocumento69 pagineDry Eye Syndromeendalew mulugetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sore Eyes (Conjunctivitis/Pink Eyes)Documento21 pagineSore Eyes (Conjunctivitis/Pink Eyes)Diana MaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Eye Adnexa Diseases: Catedra OftalmologieDocumento39 pagineEye Adnexa Diseases: Catedra OftalmologieDanielaNessuna valutazione finora
- ABC of Red EyeDocumento5 pagineABC of Red Eyeakmar887Nessuna valutazione finora
- KeratitisDocumento14 pagineKeratitismalathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Blefaritis EarlyDocumento28 pagineBlefaritis EarlyPaomo Zhixia EarlyNessuna valutazione finora
- Visual ImpairmentDocumento57 pagineVisual ImpairmentNavami KrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Eye Manifestations in Systemic Diseases - AudioDocumento22 pagineEye Manifestations in Systemic Diseases - AudioPerfect GirlNessuna valutazione finora
- Eye DisordersDocumento68 pagineEye DisordersYasmeen zulfiqarNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Article: Visual Impairment Among Primary School Children in Gondar Town, Northwest EthiopiaDocumento6 pagineResearch Article: Visual Impairment Among Primary School Children in Gondar Town, Northwest EthiopiaManaye MengisteNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice Questions 1Documento15 pagineMultiple Choice Questions 1safna saleemNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyesDocumento3 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of The EyesNkk Aqnd MgdnglNessuna valutazione finora
- Visual AcuityDocumento20 pagineVisual AcuityJúnior AlvesNessuna valutazione finora
- A Guide: To Choose Right IOL - Cataract SurgeryDocumento25 pagineA Guide: To Choose Right IOL - Cataract SurgeryChristopherJamesNessuna valutazione finora
- CATARACTDocumento1 paginaCATARACTYan SolivenNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Orthoptics 2019Documento97 pagineClinical Orthoptics 2019Joseph IsraelNessuna valutazione finora
- CataractDocumento5 pagineCataractcarls burg a. resurreccionNessuna valutazione finora
- Corneal Stining 2Documento4 pagineCorneal Stining 2kameliasitorusNessuna valutazione finora
- Student's Name: - Roll No: - Date: - Subject: Special Senses Class: 2Documento4 pagineStudent's Name: - Roll No: - Date: - Subject: Special Senses Class: 2Priya bhattiNessuna valutazione finora
- Worldwide Distribution of Visual Refractive Error1Documento8 pagineWorldwide Distribution of Visual Refractive Error1Rian AprizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sure Success in Ophthalmology Viva Voce & Practical Examination - 2013 PDFDocumento300 pagineSure Success in Ophthalmology Viva Voce & Practical Examination - 2013 PDFKaran Kumarswamy79% (14)
- Anatomy of EyeDocumento26 pagineAnatomy of EyeANI REHMNessuna valutazione finora
- Ocular Penetrans Trauma and It EditDocumento11 pagineOcular Penetrans Trauma and It EditTamsilNessuna valutazione finora
- Eyelid Surgery Los AngelesDocumento2 pagineEyelid Surgery Los AngelesVeronica HinmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Coleman - Understanding PrescriptionDocumento8 pagineColeman - Understanding PrescriptionThomas ChapelNessuna valutazione finora
- KMKP 2 BookDocumento499 pagineKMKP 2 BookgigaslayerxNessuna valutazione finora
- BlepharitisDocumento4 pagineBlepharitisnan623Nessuna valutazione finora
- Medi 97 E0094Documento5 pagineMedi 97 E0094greenNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Evaluation of Corneal Ulcer Among Patients Attending Teaching Hospital PDFDocumento4 pagineClinical Evaluation of Corneal Ulcer Among Patients Attending Teaching Hospital PDFYosiita KartinaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Diplopia PDFDocumento4 pagineDiplopia PDFSelvina SheillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric CataractDocumento8 paginePediatric CataractDayang SayalamNessuna valutazione finora
- Reoperations For Complications Within 90 Days After Glaucoma SurgeryDocumento3 pagineReoperations For Complications Within 90 Days After Glaucoma SurgeryMuhammad Imam NoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Ophthalmology Second Long Exam 2014aDocumento13 pagineOphthalmology Second Long Exam 2014acbac19900% (1)
- Advances in The Surgical Treatment of KeratoconusDocumento20 pagineAdvances in The Surgical Treatment of Keratoconuspepe_garces_2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lapkas Glaukoma Pemasangan Implan GDD Lapkas Glaukoma (AutoRecovered)Documento14 pagineLapkas Glaukoma Pemasangan Implan GDD Lapkas Glaukoma (AutoRecovered)Vincent RoorohNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Lesson 38 Eyes, Vision (2) : Medical EnglishDocumento10 pagineChapter 2 Lesson 38 Eyes, Vision (2) : Medical EnglishAngel Manuel HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 - Objective RefractionDocumento11 pagine12 - Objective RefractionSumon SarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- CataractDocumento38 pagineCataractruhulcoc1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar Pustaka Makalah Tahap IDocumento2 pagineDaftar Pustaka Makalah Tahap IAulina Refri RahmiNessuna valutazione finora
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDDa EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDa EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (30)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDa EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeValutazione: 2 su 5 stelle2/5 (1)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Da EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Valutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionDa EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (404)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsDa EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (4)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (42)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsDa EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsDa EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDa EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (81)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsDa EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (170)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDa EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Da EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (110)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDa EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (8)
- Empath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainDa EverandEmpath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (95)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeDa EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (253)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessDa EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (328)
- Summary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDa EverandSummary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (61)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDa EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlDa EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (59)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesDa EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (1412)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryDa EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)