Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Examination of Abdomen
Caricato da
Syed FareezCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Examination of Abdomen
Caricato da
Syed FareezCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Examination of abdomen 1. Inspection a. From the front i. Symmetry of abdomen b. From the side i.
Hold breath- visible peristalsis ii. Visible pulsation iii. Moves with respiration c. From above i. Scars 1. Site 2. Size 3. Healing (primary intention, secondary intention) ii. Scratch marks iii. Dilated veins (caput medusa) iv. Liver disease stigmata v. Hernia orifice intact? 2. Palpation (all 9 quadrants) a. Superficial- tenderness b. Deep- mass c. Lower border of liver d. Lower pole of spleen e. Kidney ballotable 3. Percussion (all 9 quadrants) a. Tympanic/dull/resonance b. Upper border of liver (liver span) c. Traubs space d. Shifting dullness ascites e. Abdominal thrill 4. Auscultation a. Breath sounds b. Bruit UGIB 1. Investigation a. FBC i. Anemia ii. Leucocytosis b. RP/BUSE i. Electrolyte imbalance ii. Dehydration c. ABG d. Radiological investigation i. Erect plain CXR
1. Ddx of Air under diaphragm a. Perforated viscuspneumatoides cystides intestinalis (gas producing bacteria b. Chilatides sign i. Bowel moves above c. Basal atelectasis d. Tubal inssufflation and per vagina e. Escape air from trachea ii. Differential diagnosis of perforated viscus 1. Perforated gallbladder 2. Perf. Appedicites 3. Perf colon iii. Left lateral decubitus 1. Minimal air under diaphragm 2cc iv. Serum amylase 1. >1000 is acute pancreatitis v. LFT 1. Proteins low- chronic disease 2. Transaminases elevated- hepatocyte destruction 3. Bilirubin- liver/ gallbladder disease 4. ALP- obstruction of CBD 5. GGT- alcoholic vi. Ultrasound 1. Gall bladder thickening 2. CBD dilation 3. gallstone (10% radiopaque) 4. periceolic abcess 2. Tissue perfusion indicators a. CBD- urine output b. CVP Sebaceous cyst 1. Complication a. Infection b. Ulceration c. Calcification d. Serbacoeous whorl e. Sebaceous carcinoma (Arise from cyst) 2. Treatment a. Uncomplicated- no abscess i. Excision of entire sac including underlying of skin ellipse b. Complicated i. I&D 1. 1 mth after i&d review Excision
Ascending cholangitis 1. Definition a. Infection of the biliary tree 2. Signs and symptoms a. Charcot triad i. Fever + chills rigor ii. RUQ pain iii. Jaundice b. Reynods pentad (+ septic shock, mental confusion) 3. Complication of gallstone a. In gallbladder i. Biliary colic ii. Acute cholecystitis iii. Mucocele iv. Empyema b. In biliary system i. Obstructive jaundice ii. Ascending cholangitis iii. Acute pancreatitis c. Outside i. Gallstone ileus 4. investigation a. ERCP i. Diagnostic 1. Gallstone 2. Biopsy- cancer of head of pancreases 3. Brush cytology 4. Sclerosis- primary sclerosing cholangitis ii. Therapeutic 1. Retrieve stone- dornia basket 2. Remove mass 3. Stenting SEMS b. Complication of ERCP i. Perforation of CBD ii. Bleeding 1. Coagulation profile must check prior to procedure 2. Antibiotic cover- pre and post iii. Sepsis iv. Acute pancreatitis v. Stricture- mucosal injury vi. Allergic to dye c. MRCP i. Magnetic ii. Only diagnostic
iii. Not therapeutic d. Management of ascending cholangitis i. conservative 1. IV fluid a. Hydrate patient b. Dilute bilirubin 2. Diuretics a. Flush out bilirubin 3. Antibiotic a. Metorbnidazole b. Ciprofloxacin ii. Surgical 1. Indication a. Fail conservative mx b. Easy dissect in acute d/t fibrouseous i. Fibrous hard to dissect c. 48-72 hours of conservative management iii. Organism 1. E.coli 2. Strp fecalis 3. Klebsiela iv. Differential diagnosis 1. Acute pancreatitis 2. Acute hepatitis 3. R. pyelonephritis 4. Liver abscess 5. Leaking duodenal ulcer
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Abdominal Pain History TakingDocumento8 pagineAbdominal Pain History TakingParth PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Patho1 OBSTRUCTIVE JAUNDICE 2' CHOLEDOLITHIASIS, CHOLELITHIASISDocumento1 paginaPatho1 OBSTRUCTIVE JAUNDICE 2' CHOLEDOLITHIASIS, CHOLELITHIASISKyle Cholo CholoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hepatobiliary DiseaseDocumento60 pagineHepatobiliary DiseaseFirdaus AslamNessuna valutazione finora
- Hirschsprung Disease (Congenital Aganglionic Megacolon) : PathophysiologyDocumento2 pagineHirschsprung Disease (Congenital Aganglionic Megacolon) : PathophysiologyDiane Mary S. Mamenta100% (1)
- Medical Surgical Nursing:Gastrointestinal DisorderDocumento89 pagineMedical Surgical Nursing:Gastrointestinal DisorderMinlik-alew Dejenie100% (8)
- Volume 15, Number 5 May 2011Documento188 pagineVolume 15, Number 5 May 2011Nicolai BabaliciNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Presentation VolvulusDocumento34 pagineCase Presentation Volvulusanjawi5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Volvulus: Volvulus Is When A Loop ofDocumento7 pagineVolvulus: Volvulus Is When A Loop ofranshNessuna valutazione finora
- 200 (Gandor, Patricia Lacy)Documento26 pagine200 (Gandor, Patricia Lacy)Anh PhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Ped Gi Handbook For Doctor, Medical Student, NurseDocumento62 paginePed Gi Handbook For Doctor, Medical Student, NurseLikoh TimothyNessuna valutazione finora
- Surgery Pretest. QuestionsDocumento6 pagineSurgery Pretest. QuestionsMariana UngurNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Management of Gastro Intestinal Problem 2Documento20 pagineNursing Management of Gastro Intestinal Problem 2wyneNessuna valutazione finora
- GIT - Dr. Allam 2021 PDFDocumento47 pagineGIT - Dr. Allam 2021 PDFMohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomi Radiologi Barium Studies For GITDocumento52 pagineAnatomi Radiologi Barium Studies For GITRio ArbiansyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Approach To Peritoneal Fluid AnalysisDocumento10 pagineApproach To Peritoneal Fluid AnalysisLady BugNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar Pustaka: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Andalas 60Documento5 pagineDaftar Pustaka: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Andalas 60Eka TamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hiatus Hernia - Chinese Herbs, Chinese Medicine, AcupunctureDocumento6 pagineHiatus Hernia - Chinese Herbs, Chinese Medicine, AcupunctureCarlCordNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Surgical Nursing Study GiudeDocumento5 pagineMedical Surgical Nursing Study GiudeRexson Alcantara DalanginNessuna valutazione finora
- TextDocumento17 pagineTextnaser zoabiNessuna valutazione finora
- Adult Idiopathic Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis A Common Presentation With An Uncommon DiagnosisDocumento5 pagineAdult Idiopathic Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis A Common Presentation With An Uncommon DiagnosiszapomannNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of The 2018 NASPGHAN-ESPGHAN Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Clinical Practice GuidelineDocumento4 pagineSummary of The 2018 NASPGHAN-ESPGHAN Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Clinical Practice GuidelineAyu KendranNessuna valutazione finora
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Ibd)Documento28 pagineInflammatory Bowel Disease (Ibd)suhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Git PathologyDocumento113 pagineGit PathologyanggitaNessuna valutazione finora
- (A) K14 - Dispepsia FungsionalDocumento44 pagine(A) K14 - Dispepsia FungsionaljeihanalkhairNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation of GERD Diagnosis, Management, and OutcomesDocumento8 pagineEvaluation of GERD Diagnosis, Management, and Outcomesakhil fahri atalahNessuna valutazione finora
- Visceral Pain Somatic Pain Referred Pain: 9. Acute AbdomenDocumento4 pagineVisceral Pain Somatic Pain Referred Pain: 9. Acute AbdomenLenard BangugNessuna valutazione finora
- Right Upper Quadrant Pain: William MiddletonDocumento14 pagineRight Upper Quadrant Pain: William MiddletonAmalia Gh,Nessuna valutazione finora
- Giant Choledochal Cyst in Infant A Rare Case.99963Documento2 pagineGiant Choledochal Cyst in Infant A Rare Case.99963Monica JubaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Hubungan Pola Makan Dan Tingkat Stres Dengan Kejadian Dispepsia Di Rumah Sakit Umum Sundari Medan Tahun 2019Documento11 pagineHubungan Pola Makan Dan Tingkat Stres Dengan Kejadian Dispepsia Di Rumah Sakit Umum Sundari Medan Tahun 2019Muhammad Anugrah RamadhanNessuna valutazione finora
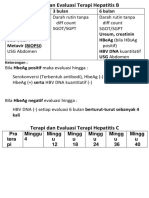
- Pra Terapi 3 Bulan 6 Bulan Hbsag Hbeag HBV Dna Kuantitatif Metavir (Biopsi) Ureum, Creatinin Hbeag (Bila Hbsag HBV Dna Kuantitatif Usg AbdomenDocumento24 paginePra Terapi 3 Bulan 6 Bulan Hbsag Hbeag HBV Dna Kuantitatif Metavir (Biopsi) Ureum, Creatinin Hbeag (Bila Hbsag HBV Dna Kuantitatif Usg AbdomenAhmad JazmiNessuna valutazione finora