Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Book Resume
Caricato da
Pratika AyuningtyasDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Book Resume
Caricato da
Pratika AyuningtyasCopyright:
Formati disponibili
DISCOURSE ANALYSIS AND LANGUAGE TEACHING ASSIGNMENTS
Lecturer: Dr. Sujoko, M. A
Book Resume: Text and Discourse by Raphael Salkie
by Pratika Ayuningtyas S891102034
ENGLISH EDUCATION GRADUATE PROGRAM SEBELAS MARET UNIVERSITY 2011
BOOK RESUME TEXT AND DISCOURSE BY RAPHAEL SALKIE
Text and Discourse Analysis was firstly published in London in 1995 by Routledge. The author of the book is Raphael Salkie. This book consists of 128 pages including the cover page. There are three main parts of the book: (a) Part 1. Lexical Cohesion, (b) 2. Part Other Kinds of Cohesion, and (c) Part 3. Beyond Cohesion. In details please look at the list below: Part 1. Lexical Cohesion: 1. Word repetition 2. Using synonyms 3. Superordinals and generals 4. Opposites and related words Part 2. Other Kinds of Cohesion 1. Substitutes 2. More substitution 3. Ellipsis 4. Reference words 5. Connectives Part 3. Beyond Cohesion Larger patterns
I choose this book because this book covers all the materials discussed in the Discourse Analysis class. This book is not a normal textbook but a workbook. It does not try to tell details things, but this book tries to help to ask interesting questions about language- especially on discourse matter. This book introduces the reader to analyze one part of language- text and discourse. This book explains enough about: What terms text and discourse mean Issues deals with those two terms How to use analytical tool to help exploring the issues This book covers some basic ideas and techniques in analyzing text and discourse. Text and discourse analysis is one area of linguistics, the systematic study of language. A text, or a discourse, is a stretch of language that may be longer than one sentence. Thus text and discourse analysis is about how sentences combine to forms texts. The sentences are combined to make an acceptable text. Take a look on these two paragraphs. (a) Its practically impossible to restrain children when they get to grips with technology. Which is why the computer equipment used in schools has to be designed and built to a standard above and beyond the normal call of duty. A standard thats set by Research Machines. (b) Which is why the computer equipment used in schools has to be designed and built to a standard above and beyond the normal call of duty. Its practically impossible to restrain children when they get to grips with technology. A standard thats set by Research Machines.
The first paragraph (a) may not be very interesting or exciting text, but it is certainly all right. It doesnt break any rules or sound wrong of give the impression that whoever who wrote it hasnt learned English properly. But when we combine the sentences differently, as in (b) we can see that the sentences dont fit together in sensible way. Theres nothing wrong if the words are not bind together but when the words are put in one paragraph, the way of combining the sentences is wrong. In (b), as we analyze it in text and discourse, we say it doesnt work incoherent. One of the key issues in test and discourse analysis is to find exactly what it is that makes some texts hang together while other texts are incoherent. We can see from the examples above that a coherent text has certain words and expressions in it which link the sentences together. Expressions like which is why, and the use of repetition, are known as cohesive devices: they are like glue which holds different parts of a text together. Cohesive devices are only one factor in making a text coherent, but they are a good place to start studying of text and discourse because they are quite easy to identify. Just as important in making texts coherent are the intentions, expectations and background knowledge of the text producer and the text receiver. We should make sure that grammar in linguistics means describing how people actually do combine words into sentences, without passing judgment about whether these sentences are correct, meaning socially approved of. Linguistics takes the same kind of approach in text and discourse analysis. The aim of the book is to find out how to make a text coherent.
This book also make an interchangeably of two terms, text and discourse. Some linguists distinguish between text and discourse, using text to mean what one speaker or writer says, while a discourse for them has two or more speakers or writers interacting. In this book the two terms are interchangeably to refer any stretch of language that may be longer than a single sentence, and which therefore may have structural properties which go beyond the scope of grammar. For the sake of simplicity the book shall usually uses the word text.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Mechanical Engineering Design ProjectsDocumento2 pagineMechanical Engineering Design Projectsanand906Nessuna valutazione finora
- Addie Model Reflection Vanessa LebrasseurDocumento4 pagineAddie Model Reflection Vanessa Lebrasseurapi-394024277Nessuna valutazione finora
- Usability: Lessons Learned and Yet To Be Learned: James R. LewisDocumento22 pagineUsability: Lessons Learned and Yet To Be Learned: James R. LewisLoai F AlzouabiNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning TheoriesDocumento15 pagineLearning TheoriesjordnormNessuna valutazione finora
- Propositional LogicDocumento74 paginePropositional Logicankit saurav100% (1)
- A Comparison of Methods To Teach Foreign Language Targets To Young ChildrenDocumento20 pagineA Comparison of Methods To Teach Foreign Language Targets To Young ChildrenSter SilNessuna valutazione finora
- Educ 533 Final Curriculum As Inquiry ProjectDocumento29 pagineEduc 533 Final Curriculum As Inquiry Projectapi-608917974Nessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Types of Speeches Preparation and DeliveryDocumento12 pagine5 Types of Speeches Preparation and DeliveryRegina Grace Pangilinan ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Minimalist SyntaxDocumento12 pagineMinimalist Syntaxdarbaz rasulNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary Chapter 9Documento2 pagineSummary Chapter 9Owi BenningtonNessuna valutazione finora
- PR2-GROUP-10-IMPACT-OF-TEACHING-STRATEGIES (AutoRecovered)Documento13 paginePR2-GROUP-10-IMPACT-OF-TEACHING-STRATEGIES (AutoRecovered)Insan ReynilNessuna valutazione finora
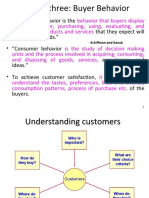
- Ch-3-Buyer-Behavior 8 0Documento16 pagineCh-3-Buyer-Behavior 8 0Hiwot NimanieNessuna valutazione finora
- A Concise Introduction To Reinforcement Learning: February 2018Documento12 pagineA Concise Introduction To Reinforcement Learning: February 2018NirajDhotreNessuna valutazione finora
- Correlational ResearchDocumento12 pagineCorrelational ResearchZahroh SenjhaNessuna valutazione finora
- ESL Lesson Plans-An ESL Teacher's Essential Guide To Lesson PlanningDocumento52 pagineESL Lesson Plans-An ESL Teacher's Essential Guide To Lesson Planningjamalgraduate100% (17)
- The Marzano Teacher Evaluation Model PowerpointDocumento42 pagineThe Marzano Teacher Evaluation Model PowerpointUkulele PrincessNessuna valutazione finora
- SNEd 111-Instructional Guidelines and Accomodation For Teaching Students With Developmental DisabilityDocumento2 pagineSNEd 111-Instructional Guidelines and Accomodation For Teaching Students With Developmental DisabilityDami EmeylNessuna valutazione finora
- Press Kit BLinglesDocumento6 paginePress Kit BLinglesjoanacampossilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz #1 Level 3 A.C 1 Term School Year: Date: 25 / 10 / 2008Documento3 pagineQuiz #1 Level 3 A.C 1 Term School Year: Date: 25 / 10 / 2008ACHRAF DOUKARNENessuna valutazione finora
- Skill Assessment Worksheet: 1 Communication SkillsDocumento2 pagineSkill Assessment Worksheet: 1 Communication SkillsmeklitNessuna valutazione finora
- The Color RedDocumento1 paginaThe Color RedPetru JocuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Mezirow, J. (1985) - A Critical Theory of Self-Directed Learning.Documento14 pagineMezirow, J. (1985) - A Critical Theory of Self-Directed Learning.Piero Morata100% (1)
- Bandura Et Al. 1961Documento5 pagineBandura Et Al. 1961Ghinet BiancaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.01 Writing Assignment A Spark PDFDocumento5 pagine6.01 Writing Assignment A Spark PDFPriya RaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Causes of Day and NightDocumento6 pagineCauses of Day and NightRHEA MARIE REYESNessuna valutazione finora
- Maranao Rido: Implicatiom To Education: Asnifah M. Mimbala Hidaya M. AsalanDocumento1 paginaMaranao Rido: Implicatiom To Education: Asnifah M. Mimbala Hidaya M. AsalanChem R. PantorillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Interview Presentations: Steps For Interview Presentation SuccessDocumento3 pagineInterview Presentations: Steps For Interview Presentation SuccessAditya SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Business English AssignmentDocumento2 pagineBusiness English AssignmentMarialicia MeleanNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis 7 Types of Meaning in AdvertisementDocumento7 pagineAnalysis 7 Types of Meaning in AdvertisementWinda WelanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lexicology Is A Branch of LinguisticsDocumento4 pagineLexicology Is A Branch of LinguisticsGeorge IashviliNessuna valutazione finora