Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Week-3.1 Line Balancing
Caricato da
projjal.gnit7378Descrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Week-3.1 Line Balancing
Caricato da
projjal.gnit7378Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Work Analysis and Design Line Balancing
Ay e AKBALIK-RAPINE s
January 2011
End 202 - Work analysis and design
Line Balancing
Problem solving steps
Select project (Pareto, Fish diagram, Gantt, PERT, Job/Worksite analysis guide) Get and present data (charts, computations) Analyze data (operation analysis) Develop ideal method (motion, work, equipment design) Present and install method (decision making tools) Develop job analysis Establish time standards (time study) Follow up
2 3 4 5 6 7 8
End 202 - Work analysis and design
Line Balancing
Line Balancing -ideal case-
See Beyond Lean page Everyone is doing the same amount of work Variation is smoothed No one overburdened No one waiting Everyone working together in a balanced fashion
End 202 - Work analysis and design
Line Balancing
Line Balancing
Example 1 Operation 1 = 5 min Operation 2 = 15 min Operation 3 = 10 min Questions What is the cycle time of this system? If each operation was 15 min, what happens? If we consider Operation 2 = 10 min ?
End 202 - Work analysis and design
Line Balancing
Line Balancing
Example 1 What is the system efciency? What is the idle time percentage?
End 202 - Work analysis and design
Line Balancing
Line Balancing
Example 1 What is the system efciency? efciency % = ( total actual standard minutes )% total allowed standard minutes
lead time efciency % = ( number of machines )% bottleneck time
End 202 - Work analysis and design
Line Balancing
Line Balancing
Example 2 We want 960 pieces a day (with 8h a day) See the standard minutes for each operation below Operation Op 1 Op 2 Op 3 Standard minutes 1.2 min 2.4 min 1.9 min Number of operators ? ? ?
End 202 - Work analysis and design
Line Balancing
Line Balancing
Operation Op 1 Op 2 Op 3
Standard minutes 1.2 min 2.4 min 1.9 min
Number of operators 3 5 4
End 202 - Work analysis and design
Line Balancing
How to increase the efciency of the operation 2?
Reassign some of the work of operation 2 to the other operations Improve the method at operation 2 to decrease the cycle time Utilize a part-time worker
End 202 - Work analysis and design
Line Balancing
Line Balancing, Example 3
Operation Op 1 Op 2 Op 3 Op 4 Op 5 Op 6 Op 7 Op 8
Standard minutes 1.25 min 1.38 min 2.58 min 3.84 min 1.27 min 1.29 min 2.48 min 1.28 min
Number of operators
End 202 - Work analysis and design
Line Balancing
Line Balancing
Example 3 nd the number of operators to assign to each operation for a production of 700 pieces per day minimization of the storage costs are of high importance! no stock level is required at the end of day which operation determines the output from the line? nd the total number of pieces produced at the end of the day
End 202 - Work analysis and design
Line Balancing
Assembly line improvement
End 202 - Work analysis and design
Line Balancing
Disadvantages of element sharing
sharable parts, tasks Increase in material handling (parts are delivered to more than one location) Duplication of tooling, additional costs If any competence or experience is required from the operators, training periods... divisible tasks not very economical two times setup time, setup cost decrease on the efciency
End 202 - Work analysis and design
Line Balancing
Assembly line balancing -a precedence chart-
Operation times are given as follows: 0.46, 0.35, 0.25, 0.22, 1.10, 0.87, 0.28, 0.72, 1.32, 0.49, 0.55.
End 202 - Work analysis and design
Line Balancing
Kilbridge and Websters Heuristic
Rank operations according to their number of predecessors Assign rst operations with least number of predecessors In case of tie, choose operation with longest operation time Total time at each work station cannot exceed the total cycle time Precedence relationships must be satised
End 202 - Work analysis and design
Line Balancing
Helgeson and Birnie (1961) method
Compute "Positional weight = Operation time + Total time of all operations that must follow it" Begin by assigning the operation with highest positional weight If there is a tie, break it by
higher operation time lower operation number
Total time at a station cannot exceed the total cycle time Precedence relationship must be satised
End 202 - Work analysis and design
Line Balancing
Assembly line balancing -a precedence chart-
End 202 - Work analysis and design
Line Balancing
Assembly line balancing -precedence matrix-
End 202 - Work analysis and design
Line Balancing
Assembly line balancing -positional weights-
The system cycle time = 1.5 min is given.
End 202 - Work analysis and design Line Balancing
Assembly line balancing -balanced assembly line-
End 202 - Work analysis and design
Line Balancing
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- LSCM Course OutlineDocumento13 pagineLSCM Course OutlineDeep SachetiNessuna valutazione finora
- Tesco True Results Casing Running in China Results in Total Depth PDFDocumento2 pagineTesco True Results Casing Running in China Results in Total Depth PDF123456ccNessuna valutazione finora
- 8051 NotesDocumento61 pagine8051 Notessubramanyam62Nessuna valutazione finora
- postedcontentadminuploadsFAQs20for20Organization PDFDocumento10 paginepostedcontentadminuploadsFAQs20for20Organization PDFMohd Adil AliNessuna valutazione finora
- AMULDocumento11 pagineAMULkeshav956Nessuna valutazione finora
- An Evaluation of MGNREGA in SikkimDocumento7 pagineAn Evaluation of MGNREGA in SikkimBittu SubbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Toeic: Check Your English Vocabulary ForDocumento41 pagineToeic: Check Your English Vocabulary ForEva Ibáñez RamosNessuna valutazione finora
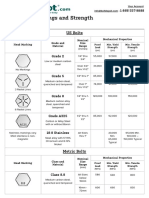
- Bolt Grade Markings and Strength ChartDocumento2 pagineBolt Grade Markings and Strength ChartGregory GaschteffNessuna valutazione finora
- IMCI Chart BookletDocumento43 pagineIMCI Chart Bookletmysticeyes_17100% (1)
- (Jones) GoodwinDocumento164 pagine(Jones) Goodwinmount2011Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fertilization Guide For CoconutsDocumento2 pagineFertilization Guide For CoconutsTrade goalNessuna valutazione finora
- Biography Thesis ExamplesDocumento7 pagineBiography Thesis Examplesreneewardowskisterlingheights100% (2)
- Rom 2 - 0-11 (En)Documento132 pagineRom 2 - 0-11 (En)Mara HerreraNessuna valutazione finora
- Desktop 9 QA Prep Guide PDFDocumento15 pagineDesktop 9 QA Prep Guide PDFPikine LebelgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Peer PressureDocumento13 paginePeer PressuremightymarcNessuna valutazione finora
- Triaxial Shear TestDocumento10 pagineTriaxial Shear TestAfiqah Nu'aimiNessuna valutazione finora
- Configuring BGP On Cisco Routers Lab Guide 3.2Documento106 pagineConfiguring BGP On Cisco Routers Lab Guide 3.2skuzurov67% (3)
- Physics Education Thesis TopicsDocumento4 paginePhysics Education Thesis TopicsPaperWriterServicesCanada100% (2)
- KsDocumento5 pagineKsnurlatifahNessuna valutazione finora
- 6GK74435DX040XE0 Datasheet enDocumento3 pagine6GK74435DX040XE0 Datasheet enLuis CortezNessuna valutazione finora
- Head Coverings BookDocumento86 pagineHead Coverings BookRichu RosarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Public Health ManagementDocumento3 pagineFundamentals of Public Health ManagementHPMA globalNessuna valutazione finora
- Literatura Tecnica 3Documento10 pagineLiteratura Tecnica 3Christian PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- The Influence of Irish Monks On Merovingian Diocesan Organization-Robbins BittermannDocumento15 pagineThe Influence of Irish Monks On Merovingian Diocesan Organization-Robbins BittermanngeorgiescuNessuna valutazione finora
- EPAS 11 - Q1 - W1 - Mod1Documento45 pagineEPAS 11 - Q1 - W1 - Mod1Alberto A. FugenNessuna valutazione finora
- Acer N300 ManualDocumento50 pagineAcer N300 Manualc_formatNessuna valutazione finora
- Recitation Math 001 - Term 221 (26166)Documento36 pagineRecitation Math 001 - Term 221 (26166)Ma NaNessuna valutazione finora
- QuexBook TutorialDocumento14 pagineQuexBook TutorialJeffrey FarillasNessuna valutazione finora
- SASS Prelims 2017 4E5N ADocumento9 pagineSASS Prelims 2017 4E5N ADamien SeowNessuna valutazione finora
- Promotion-Mix (: Tools For IMC)Documento11 paginePromotion-Mix (: Tools For IMC)Mehul RasadiyaNessuna valutazione finora