Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
STA1
Caricato da
Nayan PastagiyaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
STA1
Caricato da
Nayan PastagiyaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
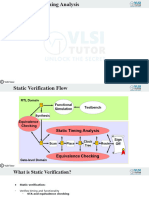
Basic of Timing Analysis in Physical Design
Lots of people asked me to write over timing analysis. Though a lot of material is present but still most of the people are not 100% sure about all these concepts. I am trying to put few of the things here in a simpler language and hope that it will help (beginner and professional). Please let me know if anybody thinks that I should add few more things here. Its difficult to put everything in one blog so just consider this as the first part of Timing analysis. What is Timing Analysis?? Before we start anything at least we should know what exactly we mean by Timing Analysis. Why these days its so important? There are a couple of reasons for performing timing analysis. We want to verify whether our circuit meet all of its timing requirements (Timing Constraints) o There are 3 types of design constraints- timing, power, area. During designing there is a trade-offs between speed, area, power, and runtime according to the constraints set by the designer. However, a chip must meet the timing constraints in order to operate at the intended clock rate, so timing is the most important design constraint. We want to make sure that circuit is properly designed and can work properly for all combinations of components over the entire specified operating environment. "Every Time".
Timing analysis can also help with component selection. o An example is when you are trying to determine what memory device speed, you should use with a microprocessor. Using a memory device that is too slow may not work in the circuit (or would degrade performance by introducing wait states), and using one that is too fast will likely cost more than it needs to. So I can say Timing analysis is the methodical analysis of a digital circuit to determine if the timing constraints imposed by components or interfaces are met. Typically, this means that you are trying to prove that all set-up, hold, and pulse-width times are being met. Note: Timing analysis is integral part of ASIC/VLSI design flow. Anything else can be compromised but not timing! Types of Timing Analysis: There are 2 type of Timing Analysis Static Timing Analysis: o Checks static delay requirements of the circuit without any input or output vectors.
Dynamic Timing Analysis. o verifies functionality of the design by applying input vectors and checking for correct output vectors Basic Of Timing Analysis: The basis of all timing analysis is the clock and the sequential component (here we will discuss with the help of Flip-flop) . Following are few of the things related to clock and flip-flop which we usually wants to take care during Timing analysis. Clock related:
It must be well understood parametrically and glitch-free. Timing analysis must ensure that any clocks that are generated by the logic are clean, are of bounded period and duty cycle, and of a known phase relationship to other clock signals of interest. The clock must, for both high and low phases, meet the minimum pulse width requirements. Certain circuits, such as PLLs, may have other requirements such as maximum jitter. As the clock speeds increase, jitter becomes an increasingly important parameter.
When "passing" data from one clock edge to the other, ensure that the worst-case duty cycle is used for the calculation. A frequent source of error is the analyst assuming that every clock will have a 50% duty cycle. Flip-Flop related: All of the flip-flops parameters are always met. The only exception to this is when synchronizers are used to synchronize asynchronous signals For asynchronous presets and clears, there are two basic parameters that must be met. All setup and hold times are met for the earliest/latest arrival times for the clock. Setup times are generally calculated by designers and suitable margins can be demonstrated under test. Hold times, however, are frequently not calculated by designers.
When passing data from one clock domain to another, ensure that there is either known phase relationships which will guarantee meeting setup and hold times or that the circuits are properly synchronized Now Lets talk about Each type of Timing analysis One by one in the next few blogs.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Sta VlsiDocumento40 pagineSta VlsiSanchitJain100% (1)
- Setup Hold TimeDocumento28 pagineSetup Hold Timeavneesh_singh100% (1)
- Sta Vlsi PDFDocumento40 pagineSta Vlsi PDFRahul YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- StaDocumento91 pagineStaMohd Mayur100% (1)
- Static Timing AnalysisDocumento49 pagineStatic Timing AnalysisedussinNessuna valutazione finora
- Static Timing Analysis 9100Documento32 pagineStatic Timing Analysis 9100Balaji VenkataramanNessuna valutazione finora
- Static Timing AnalysisDocumento100 pagineStatic Timing Analysismrinalmishra100% (2)
- Timing Analysis in Physical DesignDocumento32 pagineTiming Analysis in Physical Designgoud.mahesh0584269100% (2)
- STA Concepts and Interview Questions PDFDocumento173 pagineSTA Concepts and Interview Questions PDFAtul100% (3)
- Assignment 2Documento10 pagineAssignment 2Vishakh BharadwajNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.timing Optimization Techniques: 1. MappingDocumento152 pagine1.timing Optimization Techniques: 1. MappingPraveen Kumar100% (1)
- DFT QuestionsDocumento8 pagineDFT QuestionsAdhi SuruliNessuna valutazione finora
- Interview QuestionsDocumento13 pagineInterview QuestionsVENKATRAMANNessuna valutazione finora
- Static Timing AnalysisDocumento9 pagineStatic Timing AnalysisPradeepdarshan PradeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Clock Skew: Hold Time RequirementsDocumento4 pagineClock Skew: Hold Time Requirementsniranjanpujari25100% (1)
- Designing A Robust Clock Tree StructureDocumento9 pagineDesigning A Robust Clock Tree StructureStudent100% (1)
- DFT QuestionsDocumento8 pagineDFT QuestionsNaga NitheshNessuna valutazione finora
- Consistent Timing Constraints With Primetime: Steve GolsonDocumento31 pagineConsistent Timing Constraints With Primetime: Steve GolsonRajesh SirinomulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Clock Gating: Smart Use Ensures Smart ReturnsDocumento4 pagineClock Gating: Smart Use Ensures Smart Returnskiran_kpNessuna valutazione finora
- Clock Domain Crossing (CDC) Design TechniquesDocumento20 pagineClock Domain Crossing (CDC) Design Techniquesasic_masterNessuna valutazione finora
- STA BasicsDocumento13 pagineSTA BasicsMaulin Sheth100% (1)
- Static and Dynamic Timing AnalysisDocumento5 pagineStatic and Dynamic Timing AnalysisSudhanshu ShekharNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 2 Grandhi Vyasa MaharshiDocumento7 pagineAssignment 2 Grandhi Vyasa MaharshiRAKESH KUMAR SINGHNessuna valutazione finora
- UncertaintyDocumento24 pagineUncertaintyramana459Nessuna valutazione finora
- Scan Insertion Assignment - 1Documento17 pagineScan Insertion Assignment - 1poojithas acharya100% (5)
- STA Basic ConceptsDocumento79 pagineSTA Basic Conceptsmaheshdesh1617Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2003 StabilityAnalysisDocumento58 pagine2003 StabilityAnalysisSettuNessuna valutazione finora
- Scan Insertion Assignment - 2Documento4 pagineScan Insertion Assignment - 2poojithas acharyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Static Timing AnalysisDocumento3 pagineStatic Timing AnalysisHimanshu GomeNessuna valutazione finora
- How Does The Clock Skew Violate Setup and Hold Time Contraints? What Are The Common Errors in Constraints?Documento11 pagineHow Does The Clock Skew Violate Setup and Hold Time Contraints? What Are The Common Errors in Constraints?Sai KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- OS SchedulerDocumento7 pagineOS Schedulers-tasneem.attiaNessuna valutazione finora
- An Optimized Round Robin Scheduling Algorithm For CPU Scheduling PDFDocumento3 pagineAn Optimized Round Robin Scheduling Algorithm For CPU Scheduling PDFccalero78Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vlsi Interview Questions 2Documento15 pagineVlsi Interview Questions 2Ganessh Balaji100% (1)
- Edited - 7 On Chip Clock ControllerDocumento8 pagineEdited - 7 On Chip Clock ControllerJayesh Popat0% (1)
- An Overview of The Logic Analyzer Used For Monitoring Digital SignalsDocumento7 pagineAn Overview of The Logic Analyzer Used For Monitoring Digital SignalshemantsomanNessuna valutazione finora
- DFT Notes PrepDocumento13 pagineDFT Notes PrepBrijesh S D100% (2)
- 05 TimingDocumento7 pagine05 TimingAditya SoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Driven Clock Gating: Bar Ilan University School of Engineering Vlsi LabDocumento34 pagineData Driven Clock Gating: Bar Ilan University School of Engineering Vlsi LabaanbalanNessuna valutazione finora
- PrimeTime SlidesDocumento47 paginePrimeTime SlidesRamakrishnaRao SoogooriNessuna valutazione finora
- Static Timing AnalysisDocumento4 pagineStatic Timing AnalysisballisticanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Negative Skew For Setup: Propagation Delays Load Delays Interconnect DelaysDocumento25 pagineNegative Skew For Setup: Propagation Delays Load Delays Interconnect DelaysRajni100% (1)
- SynthesisDocumento41 pagineSynthesisFeroz AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- ASIC Interview Question & Answer: Prime Time QuestionsDocumento5 pagineASIC Interview Question & Answer: Prime Time Questionsprodip7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Logic and EmulatorDocumento7 pagineLogic and EmulatorSheik GowsNessuna valutazione finora
- Clock Domain Crossing BasicsDocumento9 pagineClock Domain Crossing BasicsRapolu SushmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Interview QuestionsDocumento155 pagineInterview Questionspravallika vysyaraju100% (9)
- STA Prime TimeDocumento125 pagineSTA Prime TimeNishanth GowdaNessuna valutazione finora
- DFT FlowDocumento18 pagineDFT Flowsenthilkumar100% (1)
- Timing SimulationDocumento3 pagineTiming SimulationKarthik Sharma100% (1)
- Clock Tree Design ConsiderationsDocumento4 pagineClock Tree Design Considerationscontscribd11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Clock Tree Synthesis: Presentation by Sudhir Kumar MadhiDocumento69 pagineClock Tree Synthesis: Presentation by Sudhir Kumar Madhisudhir100% (2)
- How To Solve Setup & Hold Violations in The Design: PowerDocumento20 pagineHow To Solve Setup & Hold Violations in The Design: PowerSujit Kumar100% (1)
- Constraining Designs 1.0Documento17 pagineConstraining Designs 1.0bvrboseNessuna valutazione finora
- A Tutorial On Timing Equations by S Schwartz (TUG 2000 Paper)Documento16 pagineA Tutorial On Timing Equations by S Schwartz (TUG 2000 Paper)domingouclarayNessuna valutazione finora
- HSE-3 Soc Chip Basics - ClearDocumento50 pagineHSE-3 Soc Chip Basics - ClearUdayaJasperNessuna valutazione finora
- (Word To PDF Converter - Unregistered) : 1) Top of FormDocumento83 pagine(Word To PDF Converter - Unregistered) : 1) Top of FormsarathynalNessuna valutazione finora
- PLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsDa EverandPLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- PLC Programming Using RSLogix 500 & Industrial Applications: Learn ladder logic step by step with real-world applicationsDa EverandPLC Programming Using RSLogix 500 & Industrial Applications: Learn ladder logic step by step with real-world applicationsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Order - 57 Confined Space ProcedureDocumento38 pagineOrder - 57 Confined Space ProcedureJay PrasanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Rehan Overseas - Just Another WordPress SiteDocumento1 paginaRehan Overseas - Just Another WordPress SiteRaunaq SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2Documento84 pagineUnit 2Ashok (Ak)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shaqra University-Costing Sajjad V1Documento4 pagineShaqra University-Costing Sajjad V1Moody KhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- 09 - Erosion Mechanisms Which Cause Boiler Tube FailureDocumento40 pagine09 - Erosion Mechanisms Which Cause Boiler Tube Failuremahati munnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nil Report EP LabDocumento6 pagineNil Report EP LabCHANDRAPRAKASHNessuna valutazione finora
- 4/3 Directional High-Response Control Valves, Direct Operated, With Integrated Control Electronics (OBE)Documento14 pagine4/3 Directional High-Response Control Valves, Direct Operated, With Integrated Control Electronics (OBE)yasin çakırNessuna valutazione finora
- JCB 550-80 & 560-80 Brochure - Set96414422 PDFDocumento20 pagineJCB 550-80 & 560-80 Brochure - Set96414422 PDFYutub RichardxdNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Install AutoCAD 2010 Without ErrorsDocumento2 pagineHow To Install AutoCAD 2010 Without ErrorsmaicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Low-Temperature Multichip-To-Wafer 3D Integration Based On Via-Last TSV With OER-TEOS-CVD and Microbump Bonding Without Solder ExtrusionDocumento6 pagineLow-Temperature Multichip-To-Wafer 3D Integration Based On Via-Last TSV With OER-TEOS-CVD and Microbump Bonding Without Solder ExtrusionIvan HuNessuna valutazione finora
- Eticket - Rohit Gupta 5892137278569Documento3 pagineEticket - Rohit Gupta 5892137278569Rohit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Service Manual: PCG-FXA32/FXA33/ /FXA36Documento28 pagineService Manual: PCG-FXA32/FXA33/ /FXA36Frank ElizaldeNessuna valutazione finora
- Pegasus PDFDocumento103 paginePegasus PDFbospanker100% (1)
- OP Lifting Equipment 1006Documento1 paginaOP Lifting Equipment 1006Sinead1990Nessuna valutazione finora
- To Determine The Specific Resistance of The Given Wires, Using Ohm's LawDocumento13 pagineTo Determine The Specific Resistance of The Given Wires, Using Ohm's LawSivaRamaKrishnan R.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ipses d2xx Usermanual enDocumento27 pagineIpses d2xx Usermanual enLojze MiškovičNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 MAS Distributed Constraint OptimizationDocumento124 pagine05 MAS Distributed Constraint Optimizationhai zhangNessuna valutazione finora
- FOI Finder - Rev01Documento90 pagineFOI Finder - Rev01Muhammad Fahmmi Bin MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- BMW 1 Series Coupé/Cabrio (E81/E82/E87/E88), 3 Series (E90/E92/E93), Z4 (E89) OBDII + ECU ConnectionDocumento7 pagineBMW 1 Series Coupé/Cabrio (E81/E82/E87/E88), 3 Series (E90/E92/E93), Z4 (E89) OBDII + ECU Connectionabdull rehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- ML PPT On Laptop Price PredictionDocumento17 pagineML PPT On Laptop Price PredictionSsvg SumanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Recomendaciones de Meta para Contenido de CampañasDocumento85 pagineRecomendaciones de Meta para Contenido de Campañasemanuelgermano90Nessuna valutazione finora
- KEI - Cable List Price - April 2021Documento5 pagineKEI - Cable List Price - April 2021smithNessuna valutazione finora
- McIntosh EF-1080I Information - My BlogDocumento38 pagineMcIntosh EF-1080I Information - My Blogcck4251Nessuna valutazione finora
- DIP167 Engineering Graphics Marathi Diploma 284Documento284 pagineDIP167 Engineering Graphics Marathi Diploma 284CIVIL ENGINEERINGNessuna valutazione finora
- Research 2 Week 1-2 LessonsDocumento62 pagineResearch 2 Week 1-2 LessonsJenn Imperial100% (1)
- IIOTDocumento15 pagineIIOTSangeeta PandaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-571 Study Guide - 1000+ QADocumento112 pagine1-571 Study Guide - 1000+ QAMahmoud Hagag100% (3)
- Digital Marketing and CommunicationDocumento9 pagineDigital Marketing and CommunicationKezaiahNessuna valutazione finora
- RB - A5D2x - Rev1P1 - CARRIER BOARD - SCHEMATICDocumento16 pagineRB - A5D2x - Rev1P1 - CARRIER BOARD - SCHEMATICPrajwalNessuna valutazione finora
- John Collier, Malcolm Collier Visual Anthropology Photography As A Research Method 1986Documento135 pagineJohn Collier, Malcolm Collier Visual Anthropology Photography As A Research Method 1986Paul Alexandru ChirilăNessuna valutazione finora