Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
IEEE Networking Standards
Caricato da
Zainab TariqDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
IEEE Networking Standards
Caricato da
Zainab TariqCopyright:
Formati disponibili
IEEE NETWORKING STANDARDS
IEEE 802 refers to a family of IEEE standards dealing with local area networks and metropolitan area networks. The IEEE 802 standards are restricted to networks carrying variable-size packets. The services and protocols specified in IEEE 802 map to the lower two layers (Data Link and Physical) of the seven layer OSI networking reference model. In fact, IEEE 802 splits the OSI Data Link Layer into two sub-layers named Logical Link Control (LLC) and Media Access Control (MAC), so that the layers can be listed like this: The IEEE 802 family of standards is maintained by the IEEE 802 LAN/MAN Standards Committee (LMSC). The most widely used standards are for the Ethernet family, Token Ring, Wireless LAN, Bridging and Virtual Bridged LANs. An individual Working Group provides the focus for each area.
Name IEEE 802.1 IEEE 802.2 IEEE 802.3 IEEE 802.4 IEEE 802.5 IEEE 802.6 IEEE 802.7 IEEE 802.8 IEEE 802.9 IEEE 802.10 IEEE 802.11 a/b/g/n
Description Bridging (networking) and Network Management LLC (Logical Link Control) Sub layer Ethernet Networks Token Bus A Token Ring Network MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) Broadband LAN using Coaxial Cable Fiber Optic TAG Integrated Services LAN Interoperable LAN Security Wireless LAN (WLAN) & Mesh (Wi-Fi certification)
IEEE 802.1 IEEE 802.1 is a working group of the IEEE 802 project of the IEEE Standards Association. It is concerned with: 802 LAN/MAN architecture.
Internetworking among 802 LAN, MAN and other wide area networks. 802 Link Securities. 802 overall network management. Protocol layers above the MAC & LLC layers.
IEEE 802.2 IEEE 802.2 is the IEEE 802 standard defining Logical Link Control (LLC), which is the upper portion of the data link layer of the OSI Model. The LLC sub layer presents a uniform interface to the user of the data link service, usually the network layer. Beneath the LLC sub layer is the Media Access Control (MAC) sub layer, which is dependent on the particular medium being used (Ethernet, token ring, FDDI, 802.11, etc.). I EEE 802.3 IEEE 802.3 is a working group and a collection of IEEE standards produced by the working group defining the physical layer and data link layer's media access control (MAC) of wired Ethernet. This is generally a local area network technology with some wide area network applications. Physical connections are made between nodes and/or infrastructure devices (hubs, switches, routers) by various types of copper or fiber cable. IEEE 802.4 Token bus is a network implementing the token ring protocol over a "virtual ring" on a coaxial cable. A token is passed around the network nodes and only the node possessing the token may transmit. If a node doesn't have anything to send, the token is passed on to the next node on the virtual ring. Each node must know the address of its neighbor in the ring, so a special protocol is needed to notify the other nodes of connections to, and disconnections from, the ring. It is mainly used for industrial applications. Token bus was used by GM (General Motors) for their Manufacturing Automation Protocol (MAP) standardization effort and flexible manufacturing system (FMS). IEEE 802.5 Token Ring is a LAN protocol defined in the IEEE 802.5 where all stations are connected in a ring and each station can directly hear transmissions only from its immediate neighbor. Permission to transmit is granted by a message (token) that circulates around the ring. Token Ring is originated from the IBM Token Ring LAN technologies. Both are based on the Token Passing technologies. IEEE 802.6 IEEE 802.6 is a standard governed by the ANSI for Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN). It is an improvement of an older standard (also created by ANSI) which used the Fiber distributed data interface (FDDI) network structure. The FDDI-based standard failed due to its expensive implementation and lack of compatibility with current LAN standards. The IEEE 802.6 standard uses the Distributed Queue Dual Bus (DQDB) network form.
This form supports 150 Mbit/s transfer rates. It consists of two unconnected unidirectional buses. DQDB is rated for a maximum of 160 km before significant signal degradation over fiber optic cable with an optical wavelength of 1310 nm. This standard has also failed, mostly for the same reasons that the FDDI standard failed. Most MAN now use Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) or Asynchronous Transfer Mode(ATM) network designs, with recent designs using native Ethernet or MPLS. IEEE 802.7 IEEE 802.7 is a sub-standard of the IEEE 802 which covers broadband local area networks. The working group did issue a recommendation in 1989, but is currently inactive and in hibernation. IEEE 802.8 The Fiber Optic Technical Advisory Group was to create a LAN standard for fiber optic media used in token passing computer networks like FDDI. This was part of the IEEE 802group of standards. IEEE 802.9 The 802.9 Working Group of the IEEE 802 networking committee developed standards for integrated voice and data access over existing Category 3 twisted-pair network cable installations. Its major standard was usually known as isoEthernet. IEEE 802.10 IEEE 802.10 is a former standard for security functions that could be used in both local area networks and metropolitan area networks based on IEEE 802 protocols. 802.10 specify security association management and key management, as well as access control, data confidentiality and data integrity. IEEE 802.11 IEEE 802.11 is a set of standards for implementing wireless local area network (WLAN) computer communication in the 2.4, 3.6 and 5 GHz frequency bands. They are created and maintained by the IEEE LAN/MAN Standards Committee (IEEE 802). The base version of the standard IEEE 802.11-2007 has had subsequent amendments. These standards provide the basis for wireless network products using the Wi-Fi brand name.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Reports On VlanDocumento25 pagineReports On Vlanshiva200100% (2)
- Construction Standards For Small Vessels PDFDocumento170 pagineConstruction Standards For Small Vessels PDFTihomir MarkovicNessuna valutazione finora
- IEEE STD ANSI-IEEE STD C37.23-1987Documento38 pagineIEEE STD ANSI-IEEE STD C37.23-1987abdou sami100% (2)
- Substation Automation System Using IEC 61850: S.Roostaee, R.Hooshmand, and Mohammad AtaeiDocumento5 pagineSubstation Automation System Using IEC 61850: S.Roostaee, R.Hooshmand, and Mohammad AtaeiDeddy Ardyansyah Regz GedanganNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 PDFDocumento43 pagineChapter 1 PDFKavya ParasharNessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless NetworkingDocumento200 pagineWireless NetworkingVamsikrishna PanugantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networks - Physical LayerDocumento40 pagineComputer Networks - Physical LayerChandana PamidimukkalaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3000 Standards Collection 2015 Sale SheetDocumento2 pagine3000 Standards Collection 2015 Sale Sheetajalbornoz100% (1)
- Power System Restructuring and Deregulation Trading, Performance and Information TechnologyDocumento499 paginePower System Restructuring and Deregulation Trading, Performance and Information Technologyhareesh.makesu100% (8)
- Network Monitoring and Control SystemDocumento75 pagineNetwork Monitoring and Control SystemkaranNessuna valutazione finora
- College Network ScenarioDocumento18 pagineCollege Network ScenarioSaad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Toaz - Info Ieee 1474 2 PRDocumento26 pagineToaz - Info Ieee 1474 2 PRJay JayNessuna valutazione finora
- EE Engg SOPDocumento2 pagineEE Engg SOPapi-19509948Nessuna valutazione finora
- Iec62271-111 (Ed1 0) en PDFDocumento8 pagineIec62271-111 (Ed1 0) en PDFAle0% (1)
- IoT Connectivity Part 1Documento28 pagineIoT Connectivity Part 1Dr. Hitesh MohapatraNessuna valutazione finora
- Missile Detection and Auto Destroy System DocumentDocumento61 pagineMissile Detection and Auto Destroy System Documentdileeppatra100% (6)
- Table of Contents - Computer NetworksDocumento3 pagineTable of Contents - Computer NetworksJit AggNessuna valutazione finora
- For Data Sharing in Cloud Computing Using Revocable EncryptionDocumento23 pagineFor Data Sharing in Cloud Computing Using Revocable EncryptionKalyan Sai Tirumani0% (1)
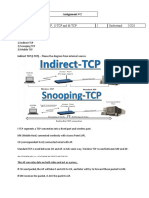
- 1 Compare I-TCP, S-TCP and M-TCP 2 Understand CO3: Assignment # 2Documento8 pagine1 Compare I-TCP, S-TCP and M-TCP 2 Understand CO3: Assignment # 2wexidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Iec 61850 - Communication Networks and Systems in SubstationsDocumento16 pagineIec 61850 - Communication Networks and Systems in SubstationsCamiloNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Goals of Transport Layer ProtocolDocumento1 paginaDesign Goals of Transport Layer ProtocolSwamy NallabelliNessuna valutazione finora
- Disease Drug Prediction Using MLDocumento72 pagineDisease Drug Prediction Using MLsumathi100% (1)
- Cordect: Wireless Access SystemDocumento24 pagineCordect: Wireless Access Systemarjun c chandrathil100% (1)
- Project Synopsis On LAN ConnectionDocumento15 pagineProject Synopsis On LAN ConnectionডৰাজবংশীNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth Protocol StackDocumento3 pagineBluetooth Protocol StackKrishanu Modak100% (2)
- Case StudyDocumento17 pagineCase StudySumeet KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- CND Practical 1 To 12Documento26 pagineCND Practical 1 To 12PALLAV MANDVENessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless Lan PresentationDocumento19 pagineWireless Lan Presentationapi-3765549Nessuna valutazione finora
- San 18Cs822 Mod 5 Short NotesDocumento28 pagineSan 18Cs822 Mod 5 Short NotesJacob DragonetteNessuna valutazione finora
- Wired Lans: Ethernet: Mcgraw-HillDocumento41 pagineWired Lans: Ethernet: Mcgraw-Hillprince keshriNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar Report (Networking)Documento17 pagineSeminar Report (Networking)jbhamarNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Electronics & Computer OrganisationDocumento17 pagineDigital Electronics & Computer Organisationabhishek125Nessuna valutazione finora
- WiFi TechnologyDocumento35 pagineWiFi TechnologySmitesh MukaneNessuna valutazione finora
- IOT NetworkingDocumento61 pagineIOT Networkinglalit24006Nessuna valutazione finora
- AWT Viva Questions and Answer Mca Sem5Documento11 pagineAWT Viva Questions and Answer Mca Sem5vinayakgar100% (1)
- Campus ProjectDocumento17 pagineCampus ProjectOsama MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Wi-Fi: Seminar Report OnDocumento19 pagineWi-Fi: Seminar Report OnSeshasai Nandi Raju50% (2)
- Telecom Business Information System AbstractDocumento5 pagineTelecom Business Information System AbstractTelika RamuNessuna valutazione finora
- CN Unit1 8-7-10Documento20 pagineCN Unit1 8-7-10nallapatiharika0% (1)
- Macro MicroDocumento48 pagineMacro MicroRiajimin100% (1)
- Assignment 1 Network SecurityDocumento5 pagineAssignment 1 Network SecuritySaeed AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- The Network Devices FunctionDocumento2 pagineThe Network Devices FunctionJhea ArponNessuna valutazione finora
- Apple TalkDocumento17 pagineApple Talkgandla SowmyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Synopsis VPNDocumento4 pagineSynopsis VPNRoop Goswami100% (2)
- Unit 1 CN MCQDocumento5 pagineUnit 1 CN MCQSanskar PawarNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation Layer & Session LayerDocumento51 paginePresentation Layer & Session LayerAnonymous fp8NP80% (1)
- Te CN Lab ManualDocumento58 pagineTe CN Lab Manualenggeng7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Embedded IoT Assignment Answers TemplateDocumento5 pagineEmbedded IoT Assignment Answers TemplateMuhannad TahaNessuna valutazione finora
- An Academic Seminar On Wireless Fidelity: B.Tech (Ece)Documento21 pagineAn Academic Seminar On Wireless Fidelity: B.Tech (Ece)baluchandrashekar4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Role of IEC 61850 & GOOSE in Substation Automation: A ReviewDocumento4 pagineRole of IEC 61850 & GOOSE in Substation Automation: A ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- BCT Mini ProjectDocumento20 pagineBCT Mini ProjectDnyaneshwar JarandeNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.high Speed LANDocumento29 pagine5.high Speed LANUtsav Kakkad100% (1)
- CN PPT-Unit IDocumento63 pagineCN PPT-Unit ISashikanth BethaNessuna valutazione finora
- Difference Between Web of Things and Internet of ThingsDocumento8 pagineDifference Between Web of Things and Internet of ThingsPreeti AnandNessuna valutazione finora
- Zigbee Technology Cse Ieee Seminar Topic Idea AbstractDocumento10 pagineZigbee Technology Cse Ieee Seminar Topic Idea AbstractVidya Hiremath100% (1)
- OSI ModelDocumento18 pagineOSI ModelruletriplexNessuna valutazione finora
- Contention Based - PAMASDocumento2 pagineContention Based - PAMASmurlak37Nessuna valutazione finora
- TIME TABLE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM A Mini Proj PDFDocumento7 pagineTIME TABLE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM A Mini Proj PDFSaranya Sa RaNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison of Data Encryption AlgorithmsDocumento3 pagineComparison of Data Encryption Algorithmskartikrathod10Nessuna valutazione finora
- ch01 FOROUZAN DATA COMMUNICATIONDocumento18 paginech01 FOROUZAN DATA COMMUNICATIONresolution8878Nessuna valutazione finora
- 5G Technology: Danish Amin & MD ShahidDocumento25 pagine5G Technology: Danish Amin & MD ShahidRam PadhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar Report On Fire WireDocumento34 pagineSeminar Report On Fire Wirenjpatel9100% (2)
- Bluetooth, IEEE 802.11, WIMAXDocumento30 pagineBluetooth, IEEE 802.11, WIMAXMukesh71% (7)
- Iare DWDM and WT Lab Manual PDFDocumento69 pagineIare DWDM and WT Lab Manual PDFPrince VarmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networking Viva - MarufDocumento6 pagineComputer Networking Viva - MarufMaruf BillahNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Horizons Emerging Technologies and Applications 2018 - 2019 EditionDa EverandNetwork Horizons Emerging Technologies and Applications 2018 - 2019 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Supervisory control and data acquisition Third EditionDa EverandSupervisory control and data acquisition Third EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- A Set of Network Standards Developed by The IEEEDocumento14 pagineA Set of Network Standards Developed by The IEEEDennis4281989Nessuna valutazione finora
- 811 826Documento16 pagine811 826Alvaro Ginestar RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- AP2610-20 - Install 9034544-01Documento2 pagineAP2610-20 - Install 9034544-01CartoonXNessuna valutazione finora
- IEEE STD 1425-2001Documento51 pagineIEEE STD 1425-2001Peter Jhoan Pulido Nuñez50% (2)
- Proceedings MECO2021 AbbreviatedDocumento17 pagineProceedings MECO2021 AbbreviatedaxyyNessuna valutazione finora
- 514 13 EthernetDocumento22 pagine514 13 EthernetAbhishek SoniNessuna valutazione finora
- DP LAN Others 13115 DriversDocumento2.284 pagineDP LAN Others 13115 DriversSyed AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Ieee Sight 2018 Call For PapersDocumento4 pagineIeee Sight 2018 Call For PapersThushar TomNessuna valutazione finora
- Egyptian Knowledge Bank ResourcesDocumento6 pagineEgyptian Knowledge Bank ResourcesAnonymous tofGENshN9100% (1)
- Ether TypeDocumento4 pagineEther Typeujwala_512Nessuna valutazione finora
- PBB NoticeDocumento69 paginePBB NoticemkamapNessuna valutazione finora
- DWH MiningDocumento6 pagineDWH MiningabdakbarNessuna valutazione finora
- Light Levels CorrectionDocumento2 pagineLight Levels Correctionusama_gculNessuna valutazione finora
- Voice Operated Intelligent LiftDocumento3 pagineVoice Operated Intelligent LiftInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Call For Paper ITEC AP 2023 Extended Deadline 9 July 2023Documento1 paginaFinal Call For Paper ITEC AP 2023 Extended Deadline 9 July 2023syaleafNessuna valutazione finora
- IEEE Networking StandardsDocumento3 pagineIEEE Networking StandardsZainab TariqNessuna valutazione finora
- Ieee Student Branch Funding Opportunities: Dr. V.NandalalDocumento18 pagineIeee Student Branch Funding Opportunities: Dr. V.Nandalalsrijith rajNessuna valutazione finora
- Lista de Precios Ubiquiti 2013Documento3 pagineLista de Precios Ubiquiti 2013Fred Javier Melendez GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology PDFDocumento207 pagineBiology PDFRaihanul islamNessuna valutazione finora
- IEEE STD C57.12.23 - 2002: Recognized As An American National Standard (ANSI)Documento15 pagineIEEE STD C57.12.23 - 2002: Recognized As An American National Standard (ANSI)Ahmed abd el megeedNessuna valutazione finora
- ProgramDocumento52 pagineProgramSantanu SenNessuna valutazione finora
- Resource Sharing Among ISRO Libraries: A Case Study of Consortia ApproachDocumento11 pagineResource Sharing Among ISRO Libraries: A Case Study of Consortia ApproachM S Sridhar100% (3)
- Moduletek SFPDocumento3 pagineModuletek SFPDũng Đào TrungNessuna valutazione finora