Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Faraday
Caricato da
janszhamDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Faraday
Caricato da
janszhamCopyright:
Formati disponibili
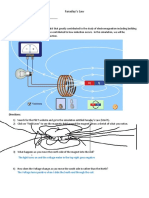
Faradays Experiment Conventions:
Names:
1. What charge do electrons have? Electrons are 2. What direction is direct current? Electric current moves from the Therefore, direct current is (electron flow). 3. How are magnetic poles labeled? Magnetic Poles are labeled and . electrode to the electrode. the direction that electrons are moving
4. What is the magnetic polarity of the geographic North Pole of the Earth? The geographic north end of the Earth is the pole of a magnetic field. A compass needle is a magnetits end is marked NORTH. 5. Historically the Earths Magnetic Field was defined as moving in the direction of Polaris, the Pole Star. Therefore, what is the convention of the direction of a magnetic field? Magnetic field is defined as going from the end. end of a magnet to the
Magnetic Fields: Go to: http://phet.colorado.edu/simulations/sims.php?sim=Magnet_and_Compass 6. What are the two factors that determine the strength of the magnetic field? What determines the direction of the magnetic field?
Electromagnets: a. Go to: http://phet.colorado.edu/simulations/sims.php?sim=Faradays_Electromagnetic_Lab b. Click the tab for electromagnet 7. Notice that the electrons moving through the wire loops create a magnetic field. What happens to the magnetic field if the direction of current in the wire loop is reversed? What happens to the strength of the magnetic field as more electrons move (as current increases)?
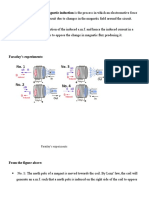
8. When there is no voltage the electrons are still moving randomly. Since the number of electrons moving one direction is balanced by electrons moving the opposite direction then there is no net magnetic field. There is no magnetic field because there is no net flow of electrons. Predict what you think will happen if a magnet approaches a wire loop. Will the movement of electrons producing the same magnetic field be encouraged or discouraged? Will the movement of electrons producing the opposite magnetic field be encouraged or discouraged?
Pickup Coil: a. Go to: http://phet.colorado.edu/simulations/sims.php?sim=Faradays_Electromagnetic_Lab b. Click the tab for pickup coil 9. Slowly move the north end of the magnet towards the coil, what happens to the electrons in the wire as the field from the north pole of the magnet increases in strength?
10. Slowly move the south end of the magnet towards the coil, what happens to the electrons in the wire as the field from the south pole of the magnet increases in strength?
11. Slowly move the north end of the magnet away from the coil, what happens to the electrons in the wire as the field from the north pole of the magnet decreases in strength?
12. Slowly move the south end of the magnet away from the coil, what happens to the electrons in the wire as the field from the south pole of the magnet decreases in strength?
13. Consider your prediction from question number eight. A general rule for how a pickup coil will respond to a magnetic field might be: Electrons in a pickup coil will move to minimize the disturbance in a changing magnetic field. They will tend to move so that the polarity of the coil is opposite the change in the field. Explain, in your own words, what you think is happening to cause the electrons to move.
Generator: a. Go to: http://phet.colorado.edu/simulations/sims.php?sim=Faradays_Electromagnetic_Lab b. Click the tab for generator 14. How does a generator use the effect you noticed in the pickup coil to generate electrical energy? What energy transformations are taking place? Why does a generator make alternating current? What change would have to be made to make direct current? (Hint a generator that makes direct current is called and alternator)
Transformer: a. Go to: http://phet.colorado.edu/simulations/sims.php?sim=Faradays_Electromagnetic_Lab b. Click the tab for transformer. 15. Describe how the energy from the battery reaches the light bulb.
16. What effect does changing the number of coils or the size of the coils have on the brightness of the light bulb?
17. Describe how this principle could be used to change the voltage of AC current.
18. Explain why this device is not effective when used with DC current. (hint look at the changes of the magnetic field.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Faraday Phet Lab The Other Did Not Go inDocumento3 pagineFaraday Phet Lab The Other Did Not Go inNicholas Barresi50% (2)
- Q4 - General Physics 2 - For PrintingDocumento40 pagineQ4 - General Physics 2 - For PrintingAron paul San MiguelNessuna valutazione finora
- Floyd ED10 Part1 SolutionsDocumento188 pagineFloyd ED10 Part1 SolutionsJung KiyoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 08 - FaradaysLawsDocumento5 pagineLab 08 - FaradaysLawsChristopher SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Q4 STEM General Physics 2 Week 1Documento3 pagineQ4 STEM General Physics 2 Week 1John Russel LanozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic InductionDocumento6 pagineUnderstanding Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic InductionN-Jay MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Faraday's Law ExplainedDocumento6 pagineFaraday's Law Explainedhope100% (1)
- State Whether The Following Statements Are True or FalseDocumento11 pagineState Whether The Following Statements Are True or Falsearohi90% (1)
- Faraday's Experiment: Objective: Induce Current in A Wire With A MagnetDocumento1 paginaFaraday's Experiment: Objective: Induce Current in A Wire With A MagnetAnahita SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-13: Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocumento71 pagineChapter-13: Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentKakoli RoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction Is The Process in Which An Electromotive ForceDocumento3 pagineFaraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction Is The Process in Which An Electromotive ForceJoy OrellanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ac Generator: Faraday's ExperimentDocumento4 pagineAc Generator: Faraday's ExperimentAnjannAnjannaNessuna valutazione finora
- CompLab6 Magnetic EffectsDocumento3 pagineCompLab6 Magnetic EffectsChristina ValeriaNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 Electromagnetic Induction May Nakalagay Na Na SagotDocumento9 pagine04 Electromagnetic Induction May Nakalagay Na Na SagotVircan EstoconingNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current ExplainedDocumento13 pagineMagnetic Effects of Electric Current ExplainedMai ka ChachaNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetic Field Lines and Electric Motors ExplainedDocumento6 pagineMagnetic Field Lines and Electric Motors ExplainedsvsvsvsvNessuna valutazione finora
- General Physics 2: Quarter 4 - Week 1Documento21 pagineGeneral Physics 2: Quarter 4 - Week 1Ralph QuiambaoNessuna valutazione finora
- CK-12 Physics Magnetic Fields Answer KeyDocumento4 pagineCK-12 Physics Magnetic Fields Answer KeyMxloNessuna valutazione finora
- Electromagnetic Induction LecturesDocumento9 pagineElectromagnetic Induction LecturesDoyen DanielNessuna valutazione finora
- NCERT Solutions Magnetic Effects of Current (In Text Questions) PDFDocumento6 pagineNCERT Solutions Magnetic Effects of Current (In Text Questions) PDFRanjit SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Class: X Subject: PHYSICS: Magnetic Effect of Current (Exercise) Prepared by - Jitender V SkariaDocumento5 pagineClass: X Subject: PHYSICS: Magnetic Effect of Current (Exercise) Prepared by - Jitender V SkariaShamik GhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- q3 Sci10 Lesson1 Pic1Documento47 pagineq3 Sci10 Lesson1 Pic1Tash Marcelo Olo-anNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetic Effect of Current 2020-21Documento6 pagineMagnetic Effect of Current 2020-21Rgpadma NathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 7 Part 2 ElectromagnetismDocumento12 pagineUnit 7 Part 2 Electromagnetism123yousss2222Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pajunar J Jonna P. - Assignment 2Documento4 paginePajunar J Jonna P. - Assignment 2Jonna PajunarNessuna valutazione finora
- P7 Recall Qs - FoundationDocumento1 paginaP7 Recall Qs - FoundationHayleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Electromagnetic Induction GuideDocumento22 pagineElectromagnetic Induction GuideKunal AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet 04 06Documento6 pagineWorksheet 04 06BadeekhNessuna valutazione finora
- Induced EmfDocumento5 pagineInduced Emftajju_121Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3.3 Analysing Electromagnetic InductionDocumento11 pagine3.3 Analysing Electromagnetic Inductionpanitiafiziksmkb100% (2)
- Physics ProjectDocumento15 paginePhysics ProjectDebkanti Gupta Bhaya0% (1)
- ElectromagnetismDocumento5 pagineElectromagnetismUmer ZubairNessuna valutazione finora
- GenPhysics2 - Q2 Module 1Documento27 pagineGenPhysics2 - Q2 Module 1Jasmin SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic InductionDocumento16 pagineFaraday's Law of Electromagnetic InductionPawan TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetic Induction and Faradays Law in General Physics 2Documento43 pagineMagnetic Induction and Faradays Law in General Physics 2Heidi QuiranteNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 4 Electromagnetic Effects PDFDocumento10 pagineTopic 4 Electromagnetic Effects PDFHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Review of Science Test #4Documento5 pagineReview of Science Test #4Dariana MercadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Document on Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocumento21 paginePhysics Document on Magnetism and ElectromagnetismPhilip MooreNessuna valutazione finora
- Faraday's & Lenz LawDocumento14 pagineFaraday's & Lenz LawPnDeNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF VIP Questions CH 13 Magnetic Effectof Elctric Curent ABK SSJDocumento2 paginePDF VIP Questions CH 13 Magnetic Effectof Elctric Curent ABK SSJsatyabrata sahooNessuna valutazione finora
- Fall 2020 Faraday's Law Phet DC Only - Colorado.eduDocumento4 pagineFall 2020 Faraday's Law Phet DC Only - Colorado.eduKarl MarkNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetic Circuits and TransformersDocumento10 pagineMagnetic Circuits and TransformersSantosh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetism Phet Electromagnetic Induction LabDocumento2 pagineMagnetism Phet Electromagnetic Induction Labapi-394411074Nessuna valutazione finora
- 10 PhysicsDocumento5 pagine10 PhysicsTapas BanerjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- FinalDocumento20 pagineFinalKheerthna GNessuna valutazione finora
- 10th Magnetic Electric Current Test Paper-1Documento6 pagine10th Magnetic Electric Current Test Paper-1ashish gandreNessuna valutazione finora
- Bhavana SDocumento16 pagineBhavana SanyaarajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics ProjectDocumento18 paginePhysics ProjectDevansh SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetic Field p6Documento3 pagineMagnetic Field p6Niña Solijon DoyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Avila Basic EeDocumento6 pagineAvila Basic EeBrian AvilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Electromagnet Teachers Guide 2009Documento257 pagineChapter 8 Electromagnet Teachers Guide 2009ashok100% (2)
- JPN Pahang Physics Module Form 5 Chapter 8: Electromagnetism Guide <40Documento47 pagineJPN Pahang Physics Module Form 5 Chapter 8: Electromagnetism Guide <40kenenathNessuna valutazione finora
- Faraday's Law & Electromagnetic InductionDocumento3 pagineFaraday's Law & Electromagnetic InductionhayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electromagnetic Induction PracticalDocumento4 pagineElectromagnetic Induction PracticalPaing Khant KyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics English 2Documento2 paginePhysics English 2AmyMukaromatunLuthfianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kheerthna 12 SapDocumento19 pagineKheerthna 12 SapKheerthna GNessuna valutazione finora
- Electromagnetic Induction - MagLabDocumento2 pagineElectromagnetic Induction - MagLabChanel FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksDa EverandPhysics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Electromagnetism: Maxwell Equations, Wave Propagation and EmissionDa EverandElectromagnetism: Maxwell Equations, Wave Propagation and EmissionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (18)
- Aqa Sciencea Unit1 PhysicsDocumento8 pagineAqa Sciencea Unit1 PhysicsjanszhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy6t q12 TestDocumento7 paginePhy6t q12 TestjanszhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy6t q12 TestDocumento7 paginePhy6t q12 TestjanszhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Jan11 Unit 4 AnswersDocumento1 paginaJan11 Unit 4 AnswersjanszhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial Class Starts This WeekDocumento32 pagineTutorial Class Starts This WeekChinchili MohitNessuna valutazione finora
- 2324 Grade 8 (UAE-GULF) Science Course Revision QuestionsDocumento40 pagine2324 Grade 8 (UAE-GULF) Science Course Revision Questionswritetome.amjadNessuna valutazione finora
- Anharmonic Crystal InteractionsDocumento3 pagineAnharmonic Crystal InteractionsMonika Singh AyamNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 s2.0 S0263224116306157 MainDocumento7 pagine1 s2.0 S0263224116306157 MainbatuhanNessuna valutazione finora
- BS 7th Semester F G RecDocumento30 pagineBS 7th Semester F G RecHussain RanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Dec 01 06Documento168 pagineScience Dec 01 06ABCNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines For VNA Very Narrow Aisle Forklift and Racking System PDFDocumento42 pagineGuidelines For VNA Very Narrow Aisle Forklift and Racking System PDFOxil FarahNessuna valutazione finora
- Dasar Teori FEMDocumento163 pagineDasar Teori FEMNurhidayat Dayat100% (3)
- Yasir Mudakir Khan: Familiarization With The Oscilloscope and Proteus SoftwareDocumento4 pagineYasir Mudakir Khan: Familiarization With The Oscilloscope and Proteus SoftwareSaad AliKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Local Bond Stress-Slip Models For Reinforcing Bars and Prestressing Strands in High-Peformance Fiber-Reinforced Cement CompositesDocumento23 pagineLocal Bond Stress-Slip Models For Reinforcing Bars and Prestressing Strands in High-Peformance Fiber-Reinforced Cement CompositesSameerNessuna valutazione finora
- ASTM F1554 Anchor Bolt Specs & Mechanical PropertiesDocumento1 paginaASTM F1554 Anchor Bolt Specs & Mechanical PropertiesReyuni doankNessuna valutazione finora
- ET302 (Power System) : Politeknik Merlimau, KB No. 1031 Pejabat Pos Merlimau, 77300 MERLIMAU, MelakaDocumento27 pagineET302 (Power System) : Politeknik Merlimau, KB No. 1031 Pejabat Pos Merlimau, 77300 MERLIMAU, Melakahashim_mokhtar9286Nessuna valutazione finora
- B Tech Mech Mech Sandwich Final Year 2023 24 ModifiedDocumento30 pagineB Tech Mech Mech Sandwich Final Year 2023 24 ModifiedShrimant H. NikamNessuna valutazione finora
- Density Measurements Cast IronDocumento20 pagineDensity Measurements Cast IronashokjkhannaNessuna valutazione finora
- YLP V2 series 说明书Documento20 pagineYLP V2 series 说明书王怡鹏Nessuna valutazione finora
- Env68 8 EyDocumento6 pagineEnv68 8 Eythuy linhNessuna valutazione finora
- .0106 Mm/s 0.075 Mm/s .106 Cm/s 0.750 Cm/s .106 Mm/s 0.750 Mm/s .0106 Mm/s 0.075 Cm/sDocumento2 pagine.0106 Mm/s 0.075 Mm/s .106 Cm/s 0.750 Cm/s .106 Mm/s 0.750 Mm/s .0106 Mm/s 0.075 Cm/sReech Aerol AlmendralNessuna valutazione finora
- XR3C 6 Element Triband Yagi 20-15-10MDocumento18 pagineXR3C 6 Element Triband Yagi 20-15-10Msboonuy331Nessuna valutazione finora
- HALF-REACTION METHODBalancing Redox EquationsDocumento8 pagineHALF-REACTION METHODBalancing Redox EquationsJunell TadinaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Kinematics-Motion GraphsDocumento3 pagine3 Kinematics-Motion GraphsRavi LallNessuna valutazione finora
- New Process Performance IE4 Motors: Product NotesDocumento2 pagineNew Process Performance IE4 Motors: Product NotesCali MelendezNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.1. IR SpectrosDocumento56 pagine2.1. IR Spectroshussaini polackNessuna valutazione finora
- Dekton Technical Manual ENDocumento24 pagineDekton Technical Manual ENIzrada FotografijaNessuna valutazione finora
- Applications and Challenges of Carbon-Fibres Reinforced CompositesDocumento13 pagineApplications and Challenges of Carbon-Fibres Reinforced CompositesDinar IstiyantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ship Stability Notes & Examples Kemp & Young 2001, PDFDocumento184 pagineShip Stability Notes & Examples Kemp & Young 2001, PDFSumit Kumar100% (2)
- 7KM21120BA003AA0Documento8 pagine7KM21120BA003AA0jaydeeppanchalNessuna valutazione finora
- WINSEM2018-19 - MEE4007 - ETH - MB310A - VL2018195003564 - Reference Material I - Bevel Gears PDFDocumento22 pagineWINSEM2018-19 - MEE4007 - ETH - MB310A - VL2018195003564 - Reference Material I - Bevel Gears PDFSahil PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- IRM-3 DUO Manual EnglishDocumento33 pagineIRM-3 DUO Manual EnglishThiago Takumi TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11Documento9 pagineChapter 11kiaunaNessuna valutazione finora