Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Rabies
Caricato da
geryel_21Descrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Rabies
Caricato da
geryel_21Copyright:
Formati disponibili
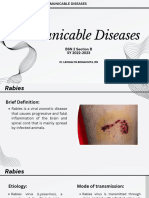
VALDEZ, Brainer VALIN, Gerielle VALMOCENA, Arvi RABIES (Hydrophobia, Lyssa) Rabies is an acute viral encephalomyelitis caused by the
rabies virus, a rhabdovirus, of the genus lyssavirus. It is fatal once signs and symptoms appear. There are two kinds: urban or canine rabies is transmitted by dogs while sylvatic rabies is a disease of wild animals and bats which sometimes spread to dogs, cats and livestock. Approximately 300 to 600 Filipinos die of rabies every year. Mode of Transmission Usually by bites of a rabid animal whose saliva has the virus. The virus may also be introduced into a scratch or in fresh breaks in the skins (very rare). Transmission from man to man is possible. Airborne spread in a cave with millions of bats have occurred, although rarely. Organ transplant (corneal) taken from a person dying of diagnosed central nervous system disease have resulted in rabies in the recipients. Incubation Period The usual incubation period is 2 to 8 weeks. It can be as long as a year or several years depending on the severity of the wounds, site of wound as distance from the brain, amount of virus introduced and protection provided by clothing. Period of Communicability In dogs and cats, for 3 to 10 days before onset of clinical signs (rarely over 3 days) and throughout the duration of the disease. Susceptibility and Resistance All warm-blooded mammals are susceptible. Natural immunity in man is unknown. Signs and Symptoms in Man Sense of apprehension Headache Fever Sensory change near site of animal bite Spasms of muscles or deglutition on attempts to swallow (hydrophobia) Paralysis Delirium and convulsions Without medical intervention, the rabies victim would usually last for only 2 to 6 days. Death is often due to respiratory paralysis.
Management and Prevention The wound must be immediately and thoroughly washed with soap and water. Antiseptics such as povidone iodine or alcohol may be applied. The patients may be given antibiotics and anti-tetanus immunization. Post-exposure treatment is given to persons who are exposed to rabies. It consists of local wound treatment, active immunization (vaccination) and passive immunization (administration of rabies immunoglobulin). a.) Active immunization aims to induce body to develop antibodies against rabies up to 3 years. b.) Passive immunization the process of giving an antibody to persons in order to provide immediate protection against rabies which should be administered within the first 7 days of active immunization. The effect of the immunoglobulin is only short term. Consult a veterinarian or trained personnel to observe your pet for 14 days to observe for signs of rabies. Be a responsible pet owner a.) Have pet immunized at 3 months of age and every year thereafter. b.) Never allow pet to roam the streets. c.) Bathe, feed them regularly with adequate food, provide them with clean sleeping quarters.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Rabies Case StudyDocumento6 pagineRabies Case StudySheryll Almira HilarioNessuna valutazione finora
- AIC - AirROCT35 - Spare Parts ManualDocumento153 pagineAIC - AirROCT35 - Spare Parts ManualMuhammad Arqam Al Ajam67% (3)
- Rabies: by Zakariya Al-NuaimiDocumento16 pagineRabies: by Zakariya Al-Nuaimi123 sasNessuna valutazione finora
- The Moon That Embrace The SunDocumento36 pagineThe Moon That Embrace The SunNorma PuspitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pitman SolutionDocumento190 paginePitman SolutionBon Siranart50% (2)
- History of RabiesDocumento23 pagineHistory of Rabiescolicot100Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies: Reporter: Angelica A. Baes BSN 2-CDocumento9 pagineRabies: Reporter: Angelica A. Baes BSN 2-CElex KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies PDFDocumento8 pagineRabies PDFKathryne May JinonNessuna valutazione finora
- RabiesDocumento25 pagineRabiesAdindapauliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies: A Case Study by Hannah IgniDocumento15 pagineRabies: A Case Study by Hannah IgniHannah Clarisse Monge IgniNessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies: NAME: Duaa Amer Abed U.O.A C.O.PharmacyDocumento8 pagineRabies: NAME: Duaa Amer Abed U.O.A C.O.PharmacyTee bagNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Rabies? How Do People and Animals Get The Disease?Documento14 pagineWhat Is Rabies? How Do People and Animals Get The Disease?lea nicole iglesiasNessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies ContentDocumento3 pagineRabies ContentKim AquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies: 1 and 3 PeopleDocumento6 pagineRabies: 1 and 3 PeopleDumapis RichardNessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies: Clinical FeaturesDocumento3 pagineRabies: Clinical FeaturessivaNessuna valutazione finora
- Public Health RabbiesDocumento3 paginePublic Health Rabbiesrobertkani2004Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies ADocumento26 pagineRabies ARoy BelenNessuna valutazione finora
- A. Infectious ProcessDocumento22 pagineA. Infectious ProcessKyla Malapit GarvidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Frias, Sid Artemis B. Bsn3ADocumento2 pagineFrias, Sid Artemis B. Bsn3ASid Artemis FriasNessuna valutazione finora
- RabiesDocumento23 pagineRabiesKristoffer Villareal100% (1)
- RabiesDocumento24 pagineRabiesDaniell Lisondra100% (1)
- What Is Rabies?Documento9 pagineWhat Is Rabies?Bijay Kumar MahatoNessuna valutazione finora
- Yellow FeverDocumento31 pagineYellow FeverVibha AvasthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies Is A Viral Infection of Animals That Can Be Transmitted To Humans. ItDocumento4 pagineRabies Is A Viral Infection of Animals That Can Be Transmitted To Humans. ItNoscire RegioNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is RabiesDocumento4 pagineWhat Is RabiesjamNessuna valutazione finora
- RabiesDocumento17 pagineRabiesYanna Habib-MangotaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Project PowerPointDocumento8 pagineScience Project PowerPointamna15033Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies: Unit-5 Anil Kumar Asst. Professor Dept. of VCCDocumento13 pagineRabies: Unit-5 Anil Kumar Asst. Professor Dept. of VCCWanderlust ExplorerNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio ProjDocumento12 pagineBio Projsb132086Nessuna valutazione finora
- RabiesDocumento81 pagineRabiesSujatha J Jayabal100% (1)
- Medical Virology Dr. Saif AL-Mayah: Rabies Virus Disease:This Virus Causes Rabies. Important PropertiesDocumento9 pagineMedical Virology Dr. Saif AL-Mayah: Rabies Virus Disease:This Virus Causes Rabies. Important PropertiesAtheer AlabdyNessuna valutazione finora
- RabiesDocumento50 pagineRabiesMichael John TahadlangitNessuna valutazione finora
- 41 Other - Important - VirusesDocumento22 pagine41 Other - Important - VirusespoojaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies VirusDocumento14 pagineRabies VirusDiane AlecksaNessuna valutazione finora
- RabiesDocumento48 pagineRabiesSarah AliNessuna valutazione finora
- I. Signs and SymptomsDocumento3 pagineI. Signs and SymptomsGeo SolonNessuna valutazione finora
- RabiesDocumento10 pagineRabiesWinda LiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies. Rhabdovirus Can Be Animals. 99% of Rabies Cases Human, It Can Take 1-3 MonthsDocumento5 pagineRabies. Rhabdovirus Can Be Animals. 99% of Rabies Cases Human, It Can Take 1-3 MonthsUserrrrrbistaNessuna valutazione finora
- RABIESDocumento2 pagineRABIESSection_keiNessuna valutazione finora
- Rhabdoviridae: Rabies VirusDocumento13 pagineRhabdoviridae: Rabies Virusميمونه عبد الرحيم مصطفىNessuna valutazione finora
- RABIESDocumento7 pagineRABIESJoyna AlcordoNessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies by DR Najeeb Memon PakistanDocumento23 pagineRabies by DR Najeeb Memon Pakistanmnajeeb807196Nessuna valutazione finora
- RhabdovirusDocumento74 pagineRhabdovirustummalapalli venkateswara raoNessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies-Complete Report - San Lazaro HospitalDocumento13 pagineRabies-Complete Report - San Lazaro HospitalMichelle Palacio-De la Cruz100% (1)
- Rabies DataDocumento4 pagineRabies DataUserrrrrbistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies: Also Known As "Hydrophobia" and Lyssa. Also Known As "Hydrophobia" and LyssaDocumento12 pagineRabies: Also Known As "Hydrophobia" and Lyssa. Also Known As "Hydrophobia" and Lyssalorella_abejuelaNessuna valutazione finora
- RabiesDocumento6 pagineRabiesAnjum AfzalNessuna valutazione finora
- RabiesDocumento2 pagineRabiesChhaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediculosis: Pubis (Pubic Louse)Documento4 paginePediculosis: Pubis (Pubic Louse)christian quiaoitNessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies: Dr. Amany Ahmed IbrahimDocumento31 pagineRabies: Dr. Amany Ahmed IbrahimMohammed Abd ElfattahNessuna valutazione finora
- VaxiRab CME Slides - EnglishDocumento40 pagineVaxiRab CME Slides - EnglishAnand VinayNessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies NOTESDocumento6 pagineRabies NOTESAbynarh PinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dog Bite Show NotesDocumento5 pagineDog Bite Show NotesLakshay ChananaNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study: VIROLOGY: 1.which of The Clinical Features That Jude Is Manifesting Suggest Rabies?Documento4 pagineCase Study: VIROLOGY: 1.which of The Clinical Features That Jude Is Manifesting Suggest Rabies?Kolin N JandocNessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies HE FinalDocumento8 pagineRabies HE FinalRikkimae NaagNessuna valutazione finora
- RabiesDocumento1 paginaRabiesKevin WalshNessuna valutazione finora
- Tagum Doctor'S College, Inc. Mahogany St. Rabe Subdivision, Tagum City Bachelor of Science in NursingDocumento5 pagineTagum Doctor'S College, Inc. Mahogany St. Rabe Subdivision, Tagum City Bachelor of Science in NursingreginawilsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies An OverviewDocumento6 pagineRabies An OverviewShahzad ZakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Rabies: UnderstandingDocumento17 pagineRabies: UnderstandingMzsvtm MacapagalNessuna valutazione finora
- Production of Animal-Based Vaccines - Animal LeptospirosisDocumento7 pagineProduction of Animal-Based Vaccines - Animal Leptospirosisjefina agnesNessuna valutazione finora
- The 10 Deadliest and Most Dangerous Viruses in the WorldDa EverandThe 10 Deadliest and Most Dangerous Viruses in the WorldNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Advice and Immunizations for TravelersDa EverandHealth Advice and Immunizations for TravelersNessuna valutazione finora
- Canine Parvovirus: Everything You Need to KnowDa EverandCanine Parvovirus: Everything You Need to KnowNessuna valutazione finora
- Smith KJ Student Mathematics Handbook and Integral Table ForDocumento328 pagineSmith KJ Student Mathematics Handbook and Integral Table ForStrahinja DonicNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1 - Reinforced Concrete - IntroductionDocumento62 pagineLecture 1 - Reinforced Concrete - IntroductionChristopher PaladioNessuna valutazione finora
- Inverse Curve Trip Time Calculation: Enter Values in White CellDocumento3 pagineInverse Curve Trip Time Calculation: Enter Values in White CellVijay FxNessuna valutazione finora
- Biasing Opamps Into Class ADocumento11 pagineBiasing Opamps Into Class AsddfsdcascNessuna valutazione finora
- Notice - Appeal Process List of Appeal Panel (Final 12.1.24)Documento13 pagineNotice - Appeal Process List of Appeal Panel (Final 12.1.24)FyBerri InkNessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd Stage ComplicationsDocumento84 pagine3rd Stage ComplicationsDream100% (1)
- No Client Too Far: Flexible Antenna Options TDMA GPS Sync ClientDocumento2 pagineNo Client Too Far: Flexible Antenna Options TDMA GPS Sync ClientFelix MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Benefits of OTN in Transport SDNDocumento9 pagineBenefits of OTN in Transport SDNGhallab AlsadehNessuna valutazione finora
- Company Profile Pt. KPT PDFDocumento23 pagineCompany Profile Pt. KPT PDFfery buyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4th Semester Electrical Engg.Documento19 pagine4th Semester Electrical Engg.Bhojpuri entertainmentNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of CEB BuildingDocumento20 pagineDesign of CEB BuildingVishalya Nipuni Lankeshi100% (1)
- May New 2011 NYBMA (Web)Documento15 pagineMay New 2011 NYBMA (Web)Erik HooverNessuna valutazione finora
- AeonDocumento4 pagineAeonsancsa_74Nessuna valutazione finora
- Boundary ScanDocumento61 pagineBoundary ScanGéza HorváthNessuna valutazione finora
- Unemployment in IndiaDocumento9 pagineUnemployment in IndiaKhushiNessuna valutazione finora
- Nitofloor NDocumento3 pagineNitofloor Nkiranmisale7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Curso VII Lectura 2. New Rural Social MovementsDocumento12 pagineCurso VII Lectura 2. New Rural Social MovementsFausto Inzunza100% (1)
- Water Chemistry - An Introduction To The Chemistry of Natural and Engineered Aquatic Systems-Páginas-483-492Documento10 pagineWater Chemistry - An Introduction To The Chemistry of Natural and Engineered Aquatic Systems-Páginas-483-492jhonier guevaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Head N Neck-MCQsDocumento57 pagineHead N Neck-MCQsbhargavi pasagadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aesa Based Pechay Production - AbdulwahidDocumento17 pagineAesa Based Pechay Production - AbdulwahidAnne Xx100% (1)
- SVR Neuro Quote 2 PROvidoDocumento3 pagineSVR Neuro Quote 2 PROvidoChejarla Naveen KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Science7 q2 Mod6of8 Asexual Sexualrep v2Documento26 pagineScience7 q2 Mod6of8 Asexual Sexualrep v2Ishi OcheaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cho Gsas - Harvard 0084L 11462Documento503 pagineCho Gsas - Harvard 0084L 11462Claudemiro costaNessuna valutazione finora
- IMCI UpdatedDocumento5 pagineIMCI UpdatedMalak RagehNessuna valutazione finora
- International Travel Insurance Policy: PreambleDocumento20 pagineInternational Travel Insurance Policy: Preamblethakurankit212Nessuna valutazione finora
- Problem-Based Learning ReportDocumento24 pagineProblem-Based Learning Reporterdayu86Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6.003 Homework #12 Solutions: ProblemsDocumento9 pagine6.003 Homework #12 Solutions: ProblemsSamu PacurucuNessuna valutazione finora