Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Extra Capsular Cataract Extraction
Caricato da
Tintin PoncianoDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Extra Capsular Cataract Extraction
Caricato da
Tintin PoncianoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
EXTRACAPSULAR CATARACT
EXTRACTION
INTRODUCTION
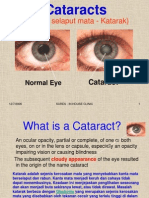
Extracapsular cataract extraction (ECCE) is a category oI eye surgery in which
the lens oI the eye is removed while the elastic capsule that covers the lens is partially
intact to allow implantation oI the intraocular lense (IOL).
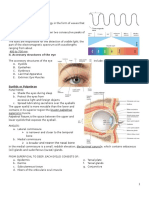
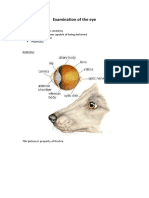
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
Sclerotic Sclerotic is the outer coating oI the eye which is white in colour that protects
the interior oI the eye and provides the shape to the eye.
Cornea The Iront part oI sclerotic is transparent to light and is termed as cornea. The
light coming Irom an object enters the eye through cornea
Iris Iris is just at the back oI cornea. This controls the size oI the pupil. It acts like
a shutter oI a photographic camer and allows the regulated amount oI light to
enter the eye.
Eye Lens Eye lens is a double convex lens with the help oI which image is Iormed at
retina by reIraction oI light.
Ciliary Muscles The eye lens is held by ciliary muscles. Ciliary muscles help the eye lens to
change its Iocal length.
Pupil At the centre oI the iris there is a hole through which light Ialls on the lens,
which is called pupil.
Aqueous Humour The space between cornea and eye lens is Iilled with a transparent Iluid called
aqueous humour.
Vitreous Humour The space between eye lens and retina is Iilled with a jelly like transparent
Iluid called vitreous humour.
ETIOLOGY
O () Family History oI:
4 laucoma
4 Hypertension
4 iabetes Mellitus
O Aging (Usually 40 y/o and above)
O enetics
O Sex/ender (Females)
O Smoking
O Excessive rinking oI Alcohol
O Long Term-Ultra Violet Exposure
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Retina Retina serves the purpose oI a screen in the eye, wherethe images oI the
objects are Iormed. Retina is at the back oI the eye lens. Retins is made oI
light sensitive cells, which are connected to the optical nerve.
Optic Nerve Optic nerve carries the inIormation to brain.
Blind Spot The region oI eye containing the optic nerve is not at all sensitive to light and
is called blind spot. II the image oI an object is Iormed in the blind spot, it is
not visible.
Yellow Spot The central part oI retina lying on the optic axis oI eye is most sensitive to
light and is called yellow spot
Eye Lids Eye lids are provided to control the amount oI light Ialling on the eye. They
also protect the eye Irom dust particles etc
Predisposing/Non-Modifiable Factors
O () Family History oI:
4 laucoma
4 Hypertension
4 iabetes Mellitus
O Aging (Usually 40 y/o and above)
O enetics
O Sex/ender (Females)
Precipitating/ Modifiable Factors
Smoking
Excessive rinking oI Alcohol
Unhealthy iet
Sedentary LiIestyle
Lack oI Exercise
Long Term-Ultra Violet Exposure
Exposure to Radiation
ob/Work
Usage oI Corticosteroids & Ezetimibe
Secondary to other iseases like Uveitis or
InIlammation oI the Inner Layer oI the Eye.
Progressive Oxidative Damage to the Lens
Antioxidants, Vitamins, & Enzymes
H
2
O Content
estruction &
Breakdown oI CHON
Sodium (Na)
DIAGNOSTIC TEST
1he Snellen Jisual Acuity 1est
Slit-Lamp Biomicroscopic Examination(Opthalmoscopy)
An instrument equipped with a special lighting systems and a binocular
microscope.
Allows visualizing in details the anterior segment oI the eye, which
includes the eyelids, eyelashes, conjunctiva, sclera, cornea, tear Iilm,
anterior chamber, iris, lens and anterior portion oI vitreous humor.
!rovides magniIication and conIirms diagnosis oI opacity.
#efraction
eIined as the bending oI light rays by the cornea, aqueous humor,
lens, and vitreous humor in the eye, reIraction enables images to Iocus
in the retina and directly aIIects visual acuity.
This test is done routinely during a complete eye examination or
whenever a patient complains oI a change in vision.
It deIines the degree oI impairment (reIractive error) and determines
the degree oI correction required to improve visual acuity with glasses
or contact lenses.
Disrupts the Normal Fibers in the Eyes
Density of Lens
Opacity/Clouding of the Lens
CATARACT FORMATION
Vision Loss oI Transparency
BLINDNESS
SIGN & SYMPTOMS (MANIFESTATION)
O iminished visual acuity
O isabling sensitivity to glare
O !ainless
O immed or blurred vision with distortion oI images
O poor night vision
O other eIIects include myopic shiIt astigmatism
O Monocular diplopia (double vision)
O color shiIt (aging lens becomes progressively more absorbent at the blue end oI the
spectrum)
O Brunescence (color values shiIt to yellow brown) and reduced light transmission.
Yellowish, gray, or white pupil
develops gradually over a period oI years; as the cataract worsens, stronger glasses no
longer improve sight
may develop in both eyes, although one is more compromised than the other
NURSING MANAGEMENT
O Caution him to avoid activities that increase intraocular pressure, such as straining with
coughing, bowel movements, or liIting
O Clients Iitted with cataract eyeglasses need inIormation about altered spatial perception.
The eyeglasses should be Iirst used when the patient is seated, until the patient adjusts to
the distortion. Instruct the client to look through the center oI the corrective lenses and to
turn the head, rather than only the eyes, when looking to the side. Clear vision is possible
only through the center oI the lens. Hand-eye coordination movements must be practiced
with assistance and relearned because oI the altered spatial perceptions.
O Teach the patient or Iamily member how to instill ophthalmic ointment or drops.
O riving, sports, and machine operation can be resumed when permission is granted by
the eye surgeon.
O II the patient has increased eye discharge, sharp eye pain, or deterioration in vision,
instruct him to immediately notiIy the physician.
O because surgery is perIormed on an outpatients basis, instruct patient to make
arrangements Ior transportation home, care that evening, and a Iollow-up visit to the
surgeon the next day.
O Withhold any anticoagulants the patient is receiving, iI medically appropriate. Aspirin
should be withheld Ior 5 to 7 days, nonsteroidal anti-inIlammatory drugs (NSAIs) Ior 3
to 5 days, and warIarin (Coumadin) until the prothrombin time oI 1.5 is almost reached.
O Administer dilating drops every 10 minutes Ior Iour doses at least 1 hour beIore surgery.
Antibiotic, corticosteroid, and NSAI drops may be administered prophylactically to
prevent postoperative inIection and inIlammation.
O Instruct patient to wear a protective eye patch Ior 24 hours aIter surgery to prevent
accidental rubbing or poking oI the eye. AIter 24 hours, eyeglasses (sunglasses in bright
light) should be worn during the day and a metal shield worn at night Ior 1 to 4 weeks.
O Instruct patient to restrict bending and liIting heavy objects.
O Caution patient that vision may blur Ior several days to weeks.
O InIorm patient that vision gradually improves as the eye heals; IOL implants improve
vision Iaster than glasses or contact lenses.
O ReinIorce that vision correction is usually needed Ior remaining visual acuity deIicit.
DISCHARGE PLAN
O Anti-inIlammatory drop containing an antibiotic ex: G betamethasone (a corticosteroid)
combined with antibiotic neomycin.
O A cycloplegic may also be prescribed to prevent ciliary spasm: G. cyclopentolate twice
daily and should be stored in a reIrigerator between uses.
O ModiIied or structured environment to ensure patient`s saIety because vision may be
blurry Ior several weeks aIter the surgery.
O !rotective eye patch to avoid accidental rubbing or poking oI the eye.
O Continuation oI prescribed medications.
O Wearing oI eye patch 24 hours aIter surgery.
O Sunglasses should be worn while outdoors during the day because the eye is sensitive to
light.
O Slight morning discharge, some redness, and a scratchy Ieeling may be expected Ior a
Iew days.
O Because cataract surgery increases the risk Ior retinal detachment, the patient must know
to notiIy the surgeon iI new Iloaters (dots) in vision, Ilashing lights, decrease in vision,
pain or increase in redness occurs.
O The patient needs to have a scheduled check up to see the progress oI vision or detection
oI any complications.
O There are no dietary restrictions. However, the restrictions as per pre-existing medical
problems, iI any, are to continue.
O The patient must avoid constipation by taking high Iiber diet and plenty oI Iluids.
O Increase in Vitamin A, !rotein & Fiber
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Complication of TBDocumento15 pagineComplication of TBTintin PoncianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Submitted By: Christine Grace V. PoncianoDocumento7 pagineSubmitted By: Christine Grace V. PoncianoTintin PoncianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Phenytoin and Protamine SulfateDocumento2 paginePhenytoin and Protamine SulfateTintin Ponciano100% (1)
- ProgrammeDocumento2 pagineProgrammeTintin PoncianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Small Scale Fish FarmingDocumento84 pagineSmall Scale Fish FarmingMike Nichlos89% (9)
- Hypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseDocumento16 pagineHypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseTintin Ponciano100% (1)
- Chole Lithia SisDocumento5 pagineChole Lithia SisSllavko K. KallfaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- PDF Soal Bahasa Inggris Kelas 3 SD Bab 1 Parts of The Body Dan Kunci Jawaban - CompressDocumento6 paginePDF Soal Bahasa Inggris Kelas 3 SD Bab 1 Parts of The Body Dan Kunci Jawaban - CompressPutu Dian PratamawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Comprehensive Eye Exams - What To Expect - AllAboutVisionDocumento8 pagineComprehensive Eye Exams - What To Expect - AllAboutVisionIsniNessuna valutazione finora
- Eye ExaminationDocumento44 pagineEye ExaminationZeenat NazirNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Form 2 Chapter 1Documento9 pagineScience Form 2 Chapter 1Lim Cj100% (2)
- Choroidal Coloboma: Presenter:Dr. Rahul Moderator: Dr. ArchisDocumento48 pagineChoroidal Coloboma: Presenter:Dr. Rahul Moderator: Dr. ArchisjihanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cataract AkkvDocumento22 pagineCataract AkkvAfshan Pt TNessuna valutazione finora
- Eligible Candidates Apr May-15 GP XY N-R PDFDocumento610 pagineEligible Candidates Apr May-15 GP XY N-R PDFAnand sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Elements 1 PDFDocumento6 pagine6 Elements 1 PDFdocbraun100% (1)
- Coloboma Iris PDFDocumento2 pagineColoboma Iris PDFDanielNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM IO3 Eye ExaminationDocumento50 pagineNCM IO3 Eye ExaminationNicole NipasNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 AccommodationDocumento12 pagine06 AccommodationMwanja MosesNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles of Facial ExpressionDocumento63 pagineMuscles of Facial Expressionraphaelyohana140Nessuna valutazione finora
- 05 Aphakia and PseudophakiaDocumento15 pagine05 Aphakia and PseudophakiaMwanja Moses100% (1)
- Cataract and Eye Care DCaDocumento26 pagineCataract and Eye Care DCaSamuil SumpalNessuna valutazione finora
- ConjunctivitisDocumento13 pagineConjunctivitisIdasari DewiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cranial Nerve AssessmentDocumento4 pagineCranial Nerve AssessmentAnonymous h2EnKyDbNessuna valutazione finora
- VisionDocumento12 pagineVisionSonali ChandelNessuna valutazione finora
- Sousa Short Illustrated Arabic Story For Kids With English Translation For PDF DownloadDocumento11 pagineSousa Short Illustrated Arabic Story For Kids With English Translation For PDF DownloadyasirismNessuna valutazione finora
- The Human Eye: Structure and Function: R M F. LDocumento1 paginaThe Human Eye: Structure and Function: R M F. LzodiacgeminyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Solutions Physics Chapter 6Documento72 pagineLakhmir Singh Class 10 Solutions Physics Chapter 6Aishwaria MurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocumento9 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of The EyeJayricDepalobos100% (1)
- The Refracting Media - Human AnatomyDocumento4 pagineThe Refracting Media - Human AnatomyanggastavasthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Tseng 2016Documento12 pagineTseng 2016Amalia Alexandra ZanadNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 2 LS EyeDocumento63 pagine11 2 LS EyeAdhi PandayNessuna valutazione finora
- Ophthalmology For Lawyers PDFDocumento329 pagineOphthalmology For Lawyers PDFAnonymous PYgnwOWKNessuna valutazione finora
- 3800lecture 1 - Eye AnatomyDocumento17 pagine3800lecture 1 - Eye AnatomyAkshay Dhawan100% (1)
- Rheumatic EyeDocumento10 pagineRheumatic EyeDr Dushyant Kamal DhariNessuna valutazione finora
- Chart Book CbimnciDocumento59 pagineChart Book CbimnciBhoja Raj GAUTAMNessuna valutazione finora
- DENT 202 Course SyllabusDocumento7 pagineDENT 202 Course SyllabusMohamed Harun B. SanohNessuna valutazione finora
- Examination of The EyeDocumento16 pagineExamination of The EyeRoxana SurliuNessuna valutazione finora