Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
PDC
Caricato da
marykamalaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
PDC
Caricato da
marykamalaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Academic Year: 2011-2012
PDC lecture plan
UNIT-I
LINEAR WAVE SHAPING
Learning Objective:
After the completion of this unit students should be able to
1. Analyze the response of high pass RC circuit for sinusoidal and non sinusoidal inputs.
2. Analyze the response of low pass RC circuit for sinusoidal and non sinusoidal inputs. 3. Explain how a RC circuit can be used as differentiator and integrator. 4. Explain how the double differentiation can be done using RC coupling networks.
5. Explain what is attenuation, how it can be done using attenuators and its applications. 6. Draw the response curves of RL and RLC circuits for step input. 7. Explain how a ringing circuit can provide undamped oscillations. Lecture plan:
S.No. 1. 2. 3. 4.
Topic Name High pass RC circuit, its response for sinusoidal, step, pulse, square and ramp inputs Low pass RC circuit, its response for sinusoidal, step, pulse, square and ramp inputs RC network as differentiator and integrator, double differentiation Attenuators, RL and RLC circuits and their response for step input, Ringing circuit Total No. of periods
No. of Periods 3 2 1 3 9
Assignment questions:
1. (a) Explain the response of RC low pass circuit for exponential input signal (b) Derive the expression for percentage till for a square wave output of RC high pass circuit 2. A symmetrical square wave whose peak-to-peak amplitude is 2V and whose average value is zero as applied to on RC integrating circuit. The time constant is equals to half -period of the square wave find the peak to peak value of the output amplitude
UNIT-II NON- LINEAR WAVE SHAPING
Academic Year: 2011-2012
Learning Objective:
PDC lecture plan
After the completion of this unit students should be able to 1. Explain the operation of a clipping circuit.
2. Explain the types of clipping circuits.
3. Draw the transfer characteristics of diode clippers and transistor clippers
4. Distinguish the comparator circuit and clipping circuit 5. Explain the operation of a clamping circuit.
6. Draw the transfer characteristics of clampers. 7. State the clamping circuit theorem.
8. Explain the types of clamping circuits. Lecture plan:
S.No. 1. 2. 4. 5.
6.
Topic Name Diode clippers and its transfer characteristics Transistor clippers, Transfer characteristics of clippers, Emitter coupled clipper clamping operation, clamping circuits using diode with different inputs, Transfer characteristics of clampers Clamping circuit theorem, practical clamping circuits, effect of diode characteristics on clamping voltage, Transfer characteristics of clampers Comparators, applications of voltage comparators Total No. of periods
No. of Periods 2 2 2 2
2 10
Assignment questions: 1. (a) Draw the circuit diagram of slicer circuit using Zener diodes and explain its
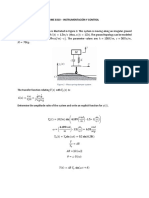
operation with the help of its transfer characteristic. (b) Draw the circuit diagram of emitter coupled clipper. Draw its transfer characteristics indicating all intercepts, slopes and voltage levels derive the necessary equations. 2. (a) State and prove clamping -circuit theorem. (b) Determine Vo for the network shown for the given waveform. Assume ideal Diodes.
Academic Year: 2011-2012
PDC lecture plan
UNIT-III
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS OF DEVICES
Learning Objective:
After the completion of this unit students should be able to
1. Explain how the electronic devices like diode and transistor can be used as switches.
2. Explain the switching characteristics of transistor, saturation parameters and their variation with temperature.
3. Explain about the realization of logic gates using different logic circuits. Lecture plan:
S.No. 1. 2.
3. 4. 5. 6.
Topic Name Diode and Transistor as switches Break down voltage consideration of transistor, saturation parameters of Transistor and their variation with temperature Design of transistor switch, transistorswitching times Realization of Logic Gates using DTL, TTL logic circuits Realization of Logic Gates using ECL and CMOS logic circuits Comparison of logic families Total No. of periods
No. of Periods 1 2
1 2 2 1 9
Assignment questions: 1. Write Short notes on: (a) Diode switching times (b) Switching characteristics of
transistors (c) FET as a switch. 2. Explain the terms pertaining to transistor switching characteristics. Rise time, Delay time, Turn-on time, Storage time, Fall time, Turnoff time
Academic Year: 2011-2012
UNIT-IV MULTIVIBRATORS
PDC lecture plan
Learning Objective:
After the completion of this unit students should be able to 1. Analyze the Bistable multivibrator. 2. Explain the design of Bistable multivibrator.
3. Explain the concept of triggering circuits. Lecture plan:
S.No. 1. 2. 4.
Topic Name Analysis & Design of Bistable Multivibrators - Fixed bias& self biased transistor binary Commutating capacitors, Triggering in binary Schmitt trigger circuit, Applications Total No. of periods
No. of Periods 2 2 2 6
Assignment questions: 1. Explain the working of a Bistable multivibrator circuit with the help of neat waveforms.
What are its applications?
2. Design a collector coupled one-shot multivibrator circuit using n-p-n transistors. Neglect
ICBO. Assume VCE(sat) to be 0V., hFE(min) = 20. In the stable state, the OFF transistor has VBE = -1V. The on transistor has base current IB which is 50% in area of the IB(min) value. Vcc = 6V, IC(sat) = 2 mA. Delay time is 3000 sec. Choose R1 = R2.
UNIT-V
MULTIVIBRATORS
Learning Objective: After the completion of this unit students should be able to
1. Analyze the monostable and astable multivibrators.
2. Explain the design of monostable and astable multivibrators.
Academic Year: 2011-2012 3. S.No. 1. Topic Name Analysis & design of Monostable Multivibrator: Collector coupled and Emitter-coupled Monostable multivibrators, Triggering in monostable multi Analysis & design of Astable multivibrator (Collector coupled and Emitter-coupled) using transistors Total No. of periods
PDC lecture plan
No. of Periods 3
2.
Assignment questions:
1. Write short notes on: (a) Gate width of mono-stable multivibrator. (b) Astable multivibrator as a voltage to frequency converter with circuit and waveform. 2. What is a monostable multivibrator? Explain with the help of a neat circuit diagram the principle of operation of a monostable multivibrator, and derive an expression for pulse width. Draw the wave forms at collector and Bases of both transistors.
UNIT-VI TIME BASE GENERATORS
Learning Objective:
After the completion of this unit students should be able to
1. Know how the time base wave forms are generated
2. Know the different types of time base generators
S.No. 1. 2. 4.
Topic Name General features of a time base signal, methods of generating time base waveform Miller and Bootstrap time base generators Transistor miller time base generator, Transistor Bootstrap time base generator, Current time base generators. Total No. of periods
No. of Periods 1 3 3 7
Assignment questions:
Academic Year: 2011-2012
PDC lecture plan
1. (a) Draw and clearly indicate the restoration time and flyback time on the typical waveform of a time base voltage.(b) Derive the relation between the slope, transmission and displacement errors(c) Explain how UJT is used for sweep circuit? 2. (a) Explain the basic principles of Miller and bootstrap time base generators. (b) A transistor bootstrap ramp generator is to produce a 15V, 5ms output to a 2kohms load resistor. The ramp is to be linear within 2%. Design a suitable circuit using Vcc = 22V, -VEE = -22V and transistor with hfe(min) = 25. The input pulse has an amplitude of -5V, pulse width = 5ms and space width = 2.5ms.
UNIT-VII SYNCHRONIZATION AND FREQUENCY DIVISION
Learning Objective: After the completion of this unit students should be able to
1. Know how the multivibrator circuits can be used as frequency dividers
2. Know about the phase delay and phase jitters S.No. 1. 2. 3. 4. Topic Name Principles of Synchronization, Frequency division in sweep circuit Astable relaxation circuits, Monostable relaxation circuits Phase delay & phase jitters Synchronization of a sweep circuit with symmetrical signals, Sine wave frequency division with a sweep circuit Total No. of periods No. of Periods 1 1 2 3 7
Assignment questions: 1. With the help of a circuit diagram and waveforms, explain the frequency division by an
astable multivibrator? 2. (a) Explain how monostable multivibrator is used as frequency divider? (b) Draw and explain the block diagram of frequency divider without phase jitter.
UNIT-VIII BLOCKING OSCILLATORS AND SAMPLING GATES
After the completion of this unit students should be able to 1. Know about the sampling gates
Academic Year: 2011-2012 2. Design the sampling gates using diodes 3. Know about the blocking oscillators S.No. 1. 2. 3. 4. Topic Name Monostable blocking oscillators (Base timing& Emitter timing) Astable blocking oscillators (DiodeControlled & RC controlled), Applications Basic operating principles of sampling gates, Unidirectional and Bidirectional sampling gates Reduction of pedestal in gate circuits, Four-diode sampling gates; Applications of sampling gates. Total No. of periods
PDC lecture plan
No. of Periods 1 2 2 2 7
Assignment questions:
1. Write the different capacitances which effect on the operation of the sampling gates. 2. (a) Draw and explain the unidirectional diode sampling gate for more that one input signal and also explain how to overcome the loading effect on control signal? (b) What are the advantages and disadvantages of unidirectional diode sampling gate?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- SIFANG - CSC-326G - V1.00 - Numerical Transformer Protection Equipment Technical Manual - 2012-02Documento54 pagineSIFANG - CSC-326G - V1.00 - Numerical Transformer Protection Equipment Technical Manual - 2012-02MarkusKunNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ - Unit No - 1 and 2 B.X.EDocumento30 pagineMCQ - Unit No - 1 and 2 B.X.ERohit GhereNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 Bus Timings & Communication With PeripheralsDocumento22 pagineChapter 5 Bus Timings & Communication With Peripheralsshubhankar palNessuna valutazione finora
- 745-b5 - 7 Modbus MultilinDocumento68 pagine745-b5 - 7 Modbus MultilinJorge William Bermudez GaviriaNessuna valutazione finora
- DE10-Lite User Manual: June 5, 2020Documento56 pagineDE10-Lite User Manual: June 5, 2020SferreiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Scott Baxter TotalDocumento721 pagineScott Baxter TotalSatish BabuNessuna valutazione finora
- DG1 Application Manual MN040004EN PDFDocumento270 pagineDG1 Application Manual MN040004EN PDFcosmin75Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3 DicDocumento18 pagine3 DicPhanindra BodduNessuna valutazione finora
- DSC9000 Tech ManualDocumento178 pagineDSC9000 Tech ManualAlan TanNessuna valutazione finora
- BH4000 BH6000 Upgrade Instruction PDFDocumento2 pagineBH4000 BH6000 Upgrade Instruction PDFUziel HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Can Angle Sensor 424cDocumento5 pagineCan Angle Sensor 424cAleksei ChvilevNessuna valutazione finora
- Frequency Response Exercise - SolDocumento2 pagineFrequency Response Exercise - SolLuis SarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- Arm7 FamilyDocumento4 pagineArm7 FamilydanielNessuna valutazione finora
- f2 2 - PJM - User Handbook Emu M BusDocumento101 paginef2 2 - PJM - User Handbook Emu M BusemresuzerNessuna valutazione finora
- Sony Kv-21fs150 Bx1sDocumento76 pagineSony Kv-21fs150 Bx1sJose Luis Martìnez MachucaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sunny Highpower Peak3 125-Us / 150-UsDocumento2 pagineSunny Highpower Peak3 125-Us / 150-UsBen Clark100% (1)
- C.Abdul Hakeem College of Engineering & Technology Ec 2403 - RF & Microwave EngineeringDocumento1 paginaC.Abdul Hakeem College of Engineering & Technology Ec 2403 - RF & Microwave EngineeringJanani MunisamyNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 RADWIN 2000 C PTP SE1Documento85 pagine1 RADWIN 2000 C PTP SE1Vero DuranNessuna valutazione finora
- Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan: College of EngineeringDocumento2 pagineDhanalakshmi Srinivasan: College of Engineeringhamsalakshmi cNessuna valutazione finora
- FXon-3A AnalogicoDocumento24 pagineFXon-3A AnalogicoiuctmeNessuna valutazione finora
- CLI Temperatura y Cold Restart Ericsson TNDocumento11 pagineCLI Temperatura y Cold Restart Ericsson TNandres1988maturin67% (9)
- G 05Documento10 pagineG 05JoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution of Homeworks: Homework For Aug. 26Documento14 pagineSolution of Homeworks: Homework For Aug. 26ZulkarnineNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar Power Auto Irrigation SystemDocumento36 pagineSolar Power Auto Irrigation Systemakshay sajwan100% (1)
- Equipment Manual: Monarch 9416 XL Thermal Transfer PrinterDocumento32 pagineEquipment Manual: Monarch 9416 XL Thermal Transfer PrinterJuan Carlos Llanes MantillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Migrating Teleprotection Application Ipmpls Networks PDFDocumento15 pagineMigrating Teleprotection Application Ipmpls Networks PDFLuiss SelvasNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 10 - Unit 2.2.1a-1Documento50 pagineScience 10 - Unit 2.2.1a-1marisNessuna valutazione finora
- NGX BlueBoard LPC1768 H v2.0 PDFDocumento8 pagineNGX BlueBoard LPC1768 H v2.0 PDFGuille RivasNessuna valutazione finora
- TL 9000 Quality Management System Measurements Handbook NPR ExamplesDocumento7 pagineTL 9000 Quality Management System Measurements Handbook NPR ExamplesMani Rathinam RajamaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Ra890f ManualDocumento11 pagineRa890f ManualbenjaminNessuna valutazione finora