Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Bio Labb
Caricato da
Anyss Hasni Al-banjariDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Bio Labb
Caricato da
Anyss Hasni Al-banjariCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Questions 1. Describe the major differences between gram positive and gram negative bacteria cell walls.
The gram negative bacteria cell wall is a thin peptidoglycan layer and an outer cell membrane with a lipopolysaccharide layer. The gram positive bacteria cell wall is a single thick peptidoglycan layer. This wall forms in a mesh like formation of three layers of alternating material.
2. From the procedure that you have carried out,do you feel that the Gram positive stain
is a simple procedure? No, because there are many procedure to do and more complex than simple ones and use more than one stain to differentiate cellular components. Discussion The Gram stain procedure uses 3 different stains. These are crystal violet, Grams iodine, and safranin. The cells are first stained with crystal violet, then Grams iodine. Following a rinse in alcohol, to de-colorize the cells, the cells are then stained with safranin. The Gram stain procedure separates almost all bacteria into two large groups: the Grampositive bacteria that stain blue and the Gram-negative bacteria that stain pink. Bacteria take up the Gram stain differently because they differ in cell wall composition. Gram-positive bacteria have a thick cell wall layer. Alcohol does not readily penetrate to decolorize the cell wall of the previously applied crystal violet stain. Gram-negative cells have a thinner cell wall through which the alcohol readily penetrates. The crystal violet is removed from these cell walls that are then stained with the safranin counterstain. Staphylococcus aureus, and Bacillus subtillis are Gram-positive and stain blue. E. coli is Gram-negative and stain pink. Conclusion Differential stains are more complex than simple ones and use more than one stain to differentiate cellular components. They are used to examine structural differences between bacterial groups or to provide contrast to different structures within the same organism.
Preparation Of Films For Staining Title: preparation of films for staining Objective: to produce a thin smear of bacteria adhering to a clean microscope slide as preparatory to staining. Procedure: A. From broth cultures 1. Inoculating loop was sterilized using Bunsen burner and let to be cool before use it to obtain bacterial suspension from the tube. 2. The bacterial then placed in the center of the clean microscope slide. It also speared to produce thin films. 3. The films are set to air dry before wafting the slide gently on the Bunsen flame to fix and kill pathogenic bacteria. 4. The slide was place on a rack then the stain were apply. B. From agar cultures. 1. A drop of water was place in the center of the glass slide. 2. With sterilized inoculating loop to obtain a minute of bacterial culture from the agar cultures 3. It then mix with the drop of water and then proceeds as broth cultures. SIMPLE STAINING TECHNIQUES Material: 1. 24 hours broth cultures of a. E. coli b. Staph. aureus 2. 24 hours nutrient agar slants of a. Bacillus subtilis b. Pseudomonas aeruginosa 3. Slides 4. Inoculating loop 5. Dye solution a. Crystal violet b. Methylene blue c. Carbol fuchsin 6. Test tubes Procedure: 1. By using inoculating loop a minute of bacterial was transferred onto the glass slide. 2. Then a film of slide was prepared. 3. The prepared film then flooded with crystal violet, methylene blue,and carbol fuchsin. All of the stain it let to react about 30 seconds. 4. The excess stained was wash with slow running water. The excess water then blot before dry with Bunsen flame. 5. The slide then examine without the cover slip under the objective lens (x100) 6. The observation then recorded.
Question 1. In preparing a slide from a colony growing on an agar medium, why is it necessary to place only a minute portion of the colony on the slide? To obtain a good slide from a colony growing on an agar medium it is necessary to place only a minute portion of the colony on the slide. Discussion From the experiment,a simple stain consists of a solution of a single dye. Some of the most commonly used dyes are methylene blue, carbol fuchsin, and crystal violet. Simple stains allow one to distinguish the shape of the bacteria. For example, E. coli and Bacillus Subtillus are bacilli or rod-shaped bacteria. Many bacilli occur singularly, but chains may also be observed. Bacilli very greatly in length and diameter.Staphylococcus aureus is cocci or spherical bacteria. Cocci may occur singularly.
Conclusion A simple stain employs a single stain that is used primarily to examine shape and arrangement of cells. Basic stains such as methylene blue, crystal violet, or carbolfuchsin, are often used for this type of staining because they will react with negatively-charged molecules in the cell,example, nucleic acids and cell wall components.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- BIO461 Practical 2Documento7 pagineBIO461 Practical 2NURUL AIHAN AHMAD HILMINessuna valutazione finora
- Gram Stain Procedure and Additional Information - Practical 1Documento6 pagineGram Stain Procedure and Additional Information - Practical 1kamvajavasNessuna valutazione finora
- BI103 Practical 2 HandoutDocumento5 pagineBI103 Practical 2 HandoutStephane FongNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet 1 Microscopic Visualization of Bacteria Differential and Structural StainingDocumento6 pagineWorksheet 1 Microscopic Visualization of Bacteria Differential and Structural StainingKyra ErniNessuna valutazione finora
- Microbiology ExperimentDocumento9 pagineMicrobiology Experiment门门Nessuna valutazione finora
- Microbiology Lab Test 2 Review: Acid Fast Stain, KOH, India Ink, LPCB, Gram StainDocumento5 pagineMicrobiology Lab Test 2 Review: Acid Fast Stain, KOH, India Ink, LPCB, Gram StainRoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Exercise 6 SIMPLE STAININGDocumento5 pagineLab Exercise 6 SIMPLE STAININGArianne Jans MunarNessuna valutazione finora
- Staining Techniques in Microbiology.Documento9 pagineStaining Techniques in Microbiology.rajendraprasadreddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Report 1 Bio460 PDFDocumento15 pagineLab Report 1 Bio460 PDFNURUL AIHAN AHMAD HILMI100% (2)
- Experiment 4 MicrobiologyDocumento5 pagineExperiment 4 MicrobiologyFrancis TagnongNessuna valutazione finora
- Gram Stain Final DraftDocumento6 pagineGram Stain Final Draftcxs5278Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bacterial Staining TechniquesDocumento13 pagineBacterial Staining TechniquesDara KwonNessuna valutazione finora
- Staining MethodsDocumento8 pagineStaining MethodsMd Arshad100% (1)
- Laboratory Exercise 4. Microscopic Observation of MicroorganismsDocumento9 pagineLaboratory Exercise 4. Microscopic Observation of MicroorganismsNesly Joy CaballeganNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential Staining Techniques MCB 222Documento6 pagineDifferential Staining Techniques MCB 222osibomu41Nessuna valutazione finora
- Simple and Differential Staining of Bacteria: Figure1 Principles Behind Gram StainingDocumento4 pagineSimple and Differential Staining of Bacteria: Figure1 Principles Behind Gram StainingNurulJazirohNessuna valutazione finora
- LAB 2: Staining and Streaking: Series of Stains and Chemical Reagents To Increase Contrast and Reveal Information AboutDocumento10 pagineLAB 2: Staining and Streaking: Series of Stains and Chemical Reagents To Increase Contrast and Reveal Information AboutrabkaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Mic125Documento8 pagine3 Mic125nadiazkiNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Gram Stain.111Documento6 pagineAssignment Gram Stain.111premium Shopping centreNessuna valutazione finora
- Stm3102-Lab Manual 3Documento14 pagineStm3102-Lab Manual 3muhammad mirzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction and Conclusion Lab2Documento6 pagineIntroduction and Conclusion Lab2NURMIZA SYAZWANI MOHD SANINessuna valutazione finora
- Spherical Rod: 2 Lab Microbiology 3 Grade Dentistry MSC. Elaf Mohammed The Morphology and Fine Structure of BacteriaDocumento3 pagineSpherical Rod: 2 Lab Microbiology 3 Grade Dentistry MSC. Elaf Mohammed The Morphology and Fine Structure of BacteriaMohammed Yousif AbdualjabbarNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Staining: The Simple StainDocumento4 pagineCell Staining: The Simple StainAitlas KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- BACTERIAL STAININGDocumento3 pagineBACTERIAL STAININGalmirarepollo015Nessuna valutazione finora
- Microorganism staining techniques explainedDocumento5 pagineMicroorganism staining techniques explainednadiazkiNessuna valutazione finora
- SBL 1023 Lab 9 Exp Gram Staining AsepticDocumento10 pagineSBL 1023 Lab 9 Exp Gram Staining Asepticapi-384057570Nessuna valutazione finora
- UTRA Microbiology Lab Report on Staining TechniquesDocumento7 pagineUTRA Microbiology Lab Report on Staining TechniquesJojoba Chew Fei YanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Report Bio461 Practical 2 (Discussion & Conclusion)Documento4 pagineLab Report Bio461 Practical 2 (Discussion & Conclusion)Allisya NasirNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOL 240 Lab Report 1Documento11 pagineBIOL 240 Lab Report 1Ben CharlesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Report 3Documento5 pagineLab Report 3nurul ainNessuna valutazione finora
- Gram Staining: Course: MCB 103 Lab Section: 1 Name: Noor-E-Khadiza Shama ID: 1921168 Date: 04/02/20Documento5 pagineGram Staining: Course: MCB 103 Lab Section: 1 Name: Noor-E-Khadiza Shama ID: 1921168 Date: 04/02/20ShamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kolawole Bisola Mercy BacteriologyDocumento5 pagineKolawole Bisola Mercy BacteriologyDrizzy MarkNessuna valutazione finora
- Gram StainDocumento7 pagineGram StainYani ManuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt. 3 - StainingDocumento8 pagineExpt. 3 - StainingVaibhav UpadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamental Principles of MicrobiologyDocumento50 pagineFundamental Principles of MicrobiologySONAL SHARMANessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment #6 Galinato, Jewel R. BSN 1ADocumento11 pagineExperiment #6 Galinato, Jewel R. BSN 1AJyzleen SelmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Isolation and Characterization TechniquesDocumento28 pagineIsolation and Characterization TechniquesAsad ButtNessuna valutazione finora
- Observing Bacterial Specimens Under The Light MicroscopeDocumento2 pagineObserving Bacterial Specimens Under The Light MicroscopeEman Hamdy100% (1)
- تقريرDocumento8 pagineتقريرcrtgyhujikNessuna valutazione finora
- Gram Staining TechniqueDocumento26 pagineGram Staining TechniqueGaurav MudaduNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab ReportDocumento24 pagineLab Reportwol aldo0% (1)
- Gram Staining Technique Identifies BacteriaDocumento3 pagineGram Staining Technique Identifies Bacteriadavid5king-3119Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bacterial Staining TechniquesDocumento13 pagineBacterial Staining TechniquesSRUTHI FRANCIS M.Tech Environmental Engineering 2020-2022Nessuna valutazione finora
- G6 Lab 4 Basic Food MicrobiologyDocumento13 pagineG6 Lab 4 Basic Food MicrobiologyNOR SYUHADA BINTI BAHARUDIN / UPMNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles and Types of StainingDocumento42 paginePrinciples and Types of StainingMthandeni KhumaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 5 Microbiology sbl1023Documento9 pagineLab 5 Microbiology sbl1023api-385038701Nessuna valutazione finora
- REPORT ON GRAM STAINING 1Documento7 pagineREPORT ON GRAM STAINING 1Abena FlourishingNessuna valutazione finora
- Bacte_ReadingsDocumento4 pagineBacte_Readingssheilacastillo1222Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Report Bio320 - Practical 1 - As1204eDocumento17 pagineLab Report Bio320 - Practical 1 - As1204eUzma ZulaikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 6 Microscopy and StainingDocumento41 pagineUnit 6 Microscopy and StainingKatisha JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- StainingDocumento5 pagineStainingyuppie_raj2175Nessuna valutazione finora
- FT 112 General MicrobiologyDocumento9 pagineFT 112 General MicrobiologyPrincess Lia SarnoNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of BacteriaDocumento16 pagineClassification of BacteriaJessica Sannoh100% (1)
- Lab Report 6,7,8,9,10,11Documento26 pagineLab Report 6,7,8,9,10,11Rani anak matNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio310 Lab 1Documento19 pagineBio310 Lab 1nursyahirahNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Excercise 5 (Fungi) (2023-2024)Documento7 pagineLab Excercise 5 (Fungi) (2023-2024)ps.pcpc221Nessuna valutazione finora
- Capsule, Flagella, Pili, EndosporesDocumento21 pagineCapsule, Flagella, Pili, EndosporesabimubNessuna valutazione finora
- Bacteria & FungiDocumento37 pagineBacteria & FungiJessica SannohNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 FP Client AssessmentDocumento54 pagineModule 3 FP Client AssessmentJhunna TalanganNessuna valutazione finora
- Application Sheet: Series CW SeriesDocumento2 pagineApplication Sheet: Series CW SerieskamalNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Proposal ApprovedDocumento2 pagineProject Proposal ApprovedRonnel BechaydaNessuna valutazione finora
- A 231 - A 231M - 15 PDFDocumento4 pagineA 231 - A 231M - 15 PDFأسامة وحيد الدين رمضانNessuna valutazione finora
- Corporate Citizenship, Social Responsibility, Responsiveness, and PerformanceDocumento27 pagineCorporate Citizenship, Social Responsibility, Responsiveness, and Performanceguru2k9100% (1)
- Deed of Sale for 2009 Toyota PickupDocumento1 paginaDeed of Sale for 2009 Toyota PickupRheal P Esmail100% (3)
- Iso 9117-3 2010Documento10 pagineIso 9117-3 2010havalNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 - Subsequent To AcquisitionDocumento8 pagineModule 3 - Subsequent To AcquisitionRENZ ALFRED ASTRERONessuna valutazione finora
- Next-Generation Widebody Conversion: in Service From 2017 ONWARDSDocumento6 pagineNext-Generation Widebody Conversion: in Service From 2017 ONWARDSAgusNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Chapter on Motion and Force EquationsDocumento2 paginePhysics Chapter on Motion and Force EquationsMalikXufyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Markard Et Al. (2012) PDFDocumento13 pagineMarkard Et Al. (2012) PDFgotrektomNessuna valutazione finora
- O Bio Summarize Notes For RevisionDocumento31 pagineO Bio Summarize Notes For RevisionAfifa AmerNessuna valutazione finora
- Martina: Available Colors For This VersionDocumento2 pagineMartina: Available Colors For This VersionUmeshNessuna valutazione finora
- R-101 and D-101 energy balancesDocumento4 pagineR-101 and D-101 energy balancesPuteri MimieNessuna valutazione finora
- Sales TAX FORMATDocumento6 pagineSales TAX FORMATMuhammad HamzaNessuna valutazione finora
- The NF and BNF Charts from the Trading RoomDocumento23 pagineThe NF and BNF Charts from the Trading RoomSinghRaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Geography Lesson PlanDocumento4 pagineGeography Lesson Planapi-204977805100% (3)
- Conflict Analysis Tools PDFDocumento12 pagineConflict Analysis Tools PDFApeuDerrop0% (1)
- Computer Assisted Language LearningDocumento9 pagineComputer Assisted Language Learningapi-342801766Nessuna valutazione finora
- Danfoss DatasheetDocumento74 pagineDanfoss DatasheetzansNessuna valutazione finora
- Newman News January 2017 EditionDocumento12 pagineNewman News January 2017 EditionSonya MathesonNessuna valutazione finora
- Slimline: Switch Disconnector Fuse, SR 63-630 ADocumento46 pagineSlimline: Switch Disconnector Fuse, SR 63-630 AЕвгений МатвеевNessuna valutazione finora
- Environment Health: European Research OnDocumento73 pagineEnvironment Health: European Research OnDaiuk.DakNessuna valutazione finora
- SITXWHS001 Participate in Safe Work Practices - Training ManualDocumento82 pagineSITXWHS001 Participate in Safe Work Practices - Training ManualIsuru AbhimanNessuna valutazione finora
- Return On Marketing InvestmentDocumento16 pagineReturn On Marketing Investmentraj_thanviNessuna valutazione finora
- The 4Ms of Operations: Prepared By: Karla Jane F. BangaysisoDocumento18 pagineThe 4Ms of Operations: Prepared By: Karla Jane F. BangaysisoKarla BangFerNessuna valutazione finora
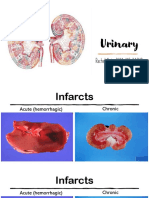
- Urinary: Rachel Neto, DVM, MS, DACVP May 28 2020Documento15 pagineUrinary: Rachel Neto, DVM, MS, DACVP May 28 2020Rachel AutranNessuna valutazione finora
- Knife Gate ValveDocumento67 pagineKnife Gate Valvekrishna100% (1)
- Angel FishDocumento1 paginaAngel FishWilla CrowellNessuna valutazione finora
- VRLA Instruction ManualDocumento11 pagineVRLA Instruction Manualashja batteryNessuna valutazione finora