Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
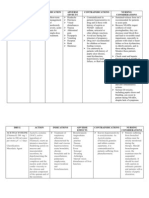
Drug Rationale
Caricato da
Yolanda WilliamsDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Drug Rationale
Caricato da
Yolanda WilliamsCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Allergies:_NO KNOWN DRUG ALLERGIES______________
Time Drug 0.9% NS NACL Dose/Route/ Frequency Specific Classification Mineral and electrolyte replacement supplement Mineral and electrolyte replacement supplement Chemical Action of Drug Maintaining acid-base balance and electrophysiologic balance of the cell Maintaining acid-base balance and electrophysiologic balance of the cell Why is your patient taking the drug Incompatibilities No known incompatibilities. May cause hypernatremia. Hyperkalemia can result with the use of potassium sparing diuretics or ace inhibitors Major Side Effects or Nursing Implications Monitor signs of hydration. Monitor Sodium lab values.
1\2 NS 20 MEQ KCL
Side effects include abdominal pain and diarrhea nausea and vomitingassess patient for signs and symptoms of hypokalemia and hyperkalemia Monitor pulse blood pressure and ECG throughout IV therapy Side effects include: abdominal pain, diarrhea, flatulence. Assess for signs of hypoglycemia, monitor glucose and A1C levels. Does not cause hypoglycemia when taken while fasting. Administer with first bite of each meal 3 times a day. Side effects include fatigue, weakness, blurred vision, brochospasm, wheezing, and impotence. Administer with meals or directly after eating. Take apical pulse, if <50bpm withhold medication. Monitor for bradycardia, dizziness, dyspnea and seizures. Assess I and O monitor for pulmonary edema. Administer atropine if pulse <40 bpm. Side effects include liver failure liver damage rash renal failure assess type location and intensity of pain before and 30 minutes after administration assess fever
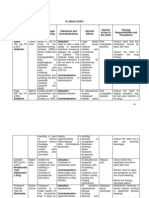
Acarbose Precose
Antidiabetics Alpha glucosidase inhibitors
Lowers blood glucose by inhibiting the enzyme alpha glucosidase in the GI tract. Delays and reduces glucose absorption.
CI in hypersensitivity, diabetic ketoacidosis, cirrhosis, pregnancy, lactation, or children. General anesthesia and verapamil may cause decrease in myocardial depression. CI in pulmonary disease and renal disease, bradycardia and heart block.
Acebtolol sectral
Antianginal Antiarrhythmics Antihypertensive Beta blocker selective
Block stimulation of beta1 adrenergic receptors, usually without affecting beta2 receptor sites.
Acetaminophen
Antipyretics Nonopiod analgesic
Inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins that may serve as mediators of pain and fever
Hepatotoxicity is additive with other hepatotoxic substances
Tylenol
Acyclovir Avirax
Antiviral Purine analogue
Interferes with the viral DNA synthesis.
Probenecid increases blodd levels, Nephrotoxic drugs increases renal effects, Zidovudine and IT methotrexate may increase CNS side effects. CI in hypersensitivity and pregnancy. Y site incomp 0.9%nacl and lr. Temp discontinue other solutions when admin. Flush line before and after administration. Concurrent use with other adrenergic agents will cause increased adrenergic effects beta-blockers may decrease effects. Use with herbs and caffeine containing ephedra may increase stimulant effect.
Alatrofloxacin Trovan
Anti infective Fluoroquinolone
Inhibit bacterial DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA gyrase.
Albuterol sulfate 0.083%
Bronchodilators Adrenergics
Result in the accumulation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate at beta adrenergic receptor. Produces bronchodiliation. Inhibits the release of mediators of immediate hypersensitivity reactions form mast cells.
Alendronate Fosamax
Bone resorption inhibitors Biphosphonates
Inhibits resorption of bone by inhibiting osteoclast activity.
Calcium supplements, antacids, and other oral medications lowers the absorption of alendronate. Increased GI events with NSAIDS. Food, Caffeine, mineral water, and orange juice significantly lowers absorption.
Seizure, dizziness, headache, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, Renal failure, thrombocytopenic prpura/ hemolytic uremic syndrome, pain and phlebitis may occur. Advise patient that this therapy is not a cure. Avoid sexual contact while lesions are present. Use condoms in the absence of lesions. Side effects include: dizziness, drowsiness, headache, insomnia, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea hypoglycemia and phlebitis at IV site. Assess patient for signs of infection, obtain culture before therapy is started, and observe for signs of anaphylaxis. Administer over 60 minutes. Side effects include nervousness restlessness tremor palpitations or tachycardia angina hypertension assess lung sounds, respiratory pattern and blood pressure before administration and during peak of medication Observe for bronchospasm. If condition occurs, withhold medication and notify physician immediately. for nebulizer compressed air or oxygen flows should be 6 to 10 L a minute a single treatment of 3 mL last about 10 minutes. Headahe, blurred vision, abdominal distention, and musculoskeletal pain may occur. Administer first thing in the a.m with 6-8 oz plain water 30 min before other meds, beverages, or food. Instruct patient to remain upright for 30 min following dose to facilitate passage to stomach. Advise patient to wear sunscreen and protective clothing to prevent photosensitivity.
Amikacin Amikin
Antiinfective Aminoglycoside
Inhibits protein synthesis in bacteria at level of 30s ribosome. Has a bactericidal action.
CI in hypersensitivity. Inactivated by penicillins and cephalosporins when administered in renal insufficiency.
Side effects include: ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity, muscle paralysis and hypersensitivity. Assess patient for signs of infection, obtain culture before admin. Evaluate hearing and balance before admin therapy. Keep patient well hydrated, may be admin without meals, IM should be deep into well developed muscle, IV infuse over 30-60 min. Triamterene: bluish urine. Hyperkalemia is most frequent side effect. Potassium levels should be monitored before and during therapy. Administer in the a.m to avoid sleep pattern interruption. Caution patient to avoid using salt substitutes.
Amiloride (Midamor) Spironolactone (Aldactone) Triamterene (Dyrenium)
Potassium sparing diuretics
Cause loss of sodium bicarbonate and calcium while saving potassium and hydrogen ions.
Amino Acid Prostat 64
Amino acid replacement
Aminophylline
Bronchodilators Phosphodiesterase inhibitors
Pro-Stat 64 liquid protein formula is an enzymehydrolyzed concentrated protein fortified with Ltryptophan. Per serving, ProStat 64 has 15 grams of protein and 60 k/cal per 30 ml (one ounce) and is sugar and carbohydrate free. Pro-Stat 64 is rich in Arginine, Glycine, Proline and Hydroxyproline, with high nitrogen donor capability to accelerate tissue healing, a critical factor in replenishing depleted protein stores in patients with pressure ulcers, malnutrition, and low albumin levels. Inhibits phosphodiesterase, producing increased tissue concentrations of CAMP. Increased levels of Camp result in bronchodilation, cns
Increased hypotension with use of alcohol and other antihypertinsives, or nitrates. Increased risk of hyperkalemia with ACE inhibitors, angiotension II receptor antagonist, indomethacin, potassium supplements, or cyclosporine. Decreased effectiveness with NSAIDS. Increases effects of digoxin. Do not add prostate with any other substance. Must irrigate before and after administration.
Feeding tubes should be flushed prior to administration. Flush the tube with 30-50 mL water. Do NOT add Pro-Stat (or any other substance) to an open or closed system of the tube feeding formula or into a container of enteral feeding prior to administering.
Do not use in uncontrolled arrhythmias. Additive cv and cns side effects
Side effects include: anxiety, tachycardia, nausea, vomiting. Assess bp, pulse, RR before therapy. Monitor I & O. monitor drug levels and
Xanthines
stimulation, diuresis and gastric acid secretion.
with adrenergic agents. Phenytoin and rifampin may decrease effectiveness
Amitriptyline
Antidepressant Tricyclic antidepressant
Potentiates the effect of serotonin and norepinephrine in the CNS and also has anticholinergic properties.
CI in pregnancy and lactation and narrow angle glaucoma.
Amlodipine Norvasc
Antianginal Antihypertensive Antiarrhythmics Calcium channel blocker
Inhibits the transport of calcium into myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cells resulting in inhibition of excitationcontraction coupling and subsequent contraction
Amoxicillin
Anti infective Antiulcer Aminopenicillins
Binds to bacterial cell wall, causing cell death.
Additive hypotension may occur when used with other antihypertensives bradycardia may result when used with betablockers. Concurrent ingestion of grapefruit juice increases blood levels and effects. CI in hypersensitivities to penicillins, contains aspartame, avoid in patients with PKU.Probenecid decreases renal excretion and increases blood levels of amoxicillin. Probenecid decreases renal excretion. May increase effects of warfarin. May decrease effectiveness of oral
observe for toxicity signs such as anorexia, vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, confusion, headache, flushing or seizures. Administer over 30 minutes Advise patient to drink plenty of fluids, avoid otc cough, cold, or breathing preparations, minimize caffeine intake and to have serum levels tested periodically. Side effects include: fatigue, sedation, blurred vision, dry eyes, constipation, dry mouth and weight gain. Monitor BP and Pulse before giving, monitor mental status, suicidal tendencies, and assess for pain. Administer with or immediately after a meal, do not administer IV. Side effects include anxiety confusion peripheral edema diarrhea nausea vomiting hyperglycemia arrhythmias nocturia. Monitor blood pressure and pulse before administration.
Amoxicillin Amoxil
Anti-infective Anti-ulcer
Binds to bacterial cell wall, causing cell death. Active against H.pylori
Side effects include: diarrhea, rashes, anaphylaxis, pseudomembranous colitis. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before starting therapy. Observe for signs of anaphylaxis; evaluate renal and hepatic function, cbc, k levels, and bleeding times. Monitor bowel function for pseudomembranous colitis. Administer around the clock, may be given without regard to meals. Seizure, Psuedomembranous colitis, diarrhea, rash, and anaphylaxis/ serum sickness may occur. Monitor bowel function. May be given without regard to meals.
contraceptives. Amoxicillin/clavul anate Anti infective Aminopenicillins Beta lactamase inhibitors Binds to bacterial cell wall, causing cell death. CI in hypersensitivities to penicillins, contains aspartame, avoid in patients with PKU.Probenecid decreases renal excretion and increases blood levels of amoxicillin. CI in hypersensitivity and lactation. Increased risk of renal toxicity if used with antineoplastics. Side effects include: diarrhea, rashes, anaphylaxis, pseudomembranous colitis. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before starting therapy. Observe for signs of anaphylaxis; evaluate renal and hepatic function, cbc, k levels, and bleeding times. Monitor bowel function for pseudomembranous colitis. Administer around the clock, may be given without regard to meals. Side effects include: headache, hypotensiion, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, nephrotoxicity, hypokalemia, chills and fever. Assess injection site for thrombophlebitis may need to add heparin. Assess RR and status, monitor CBC and platelet counts. See drug card for info on each drug. Side effects include: diarrhea, rashes, anaphylaxis, pseudomembranous colitis. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before starting therapy. Observe for signs of anaphylaxis; evaluate renal and hepatic function, cbc, k levels, and bleeding times. Monitor bowel function for pseudomembranous colitis. IV may be administered over 10-15 min within 1 hr of reconstitution. More rapid administration may cause seizures. Intacranial Hemorrhage, reperfusion arrythmias, anaphylaxis, Gi bleed, retroperitoneal bleeding, GU tract bleeding. Assess for bleeding every 15-30 min during the next 8 hr, and at least every 4 hr for the duration of therapy. Assess neuro status throughout therapy (changes may indicate
Amphotericin b deoxycholate Amphotericin b cholesteryl sulfate Amphotericin b lipid complex Amphotericin b liposome Ampicillin/sulbact am Unasyn
Antifungal
Binds to fungal cell membrane, allowing leakage of cellular contents. Toxicity is less with lipid formulations.
Anti infective Aminopenicillins Beta lactamase inhibitors
Binds to bacterial cell wall, causing cell death.
Anistreplase
thrombolytic agents
Converts plasminogen to plasmin, which then degrades fibrin clots.
CI in hypersensitivities to penicillins,.Probe necid decreases renal excretion and increases blood levels of ampicillin. Y site incompatibility if aminoglycosides and penicillins must be given concurrently, administer in separate sites at least 1 hr apart. Asprin, NSAIDS, warfarin, heparin and heparin like agents. Y site: Do not admix or administer with any other med
Aprepitant Emend
Antiemectic Neurokinin antagonists
Acts as a selective antagonist at substance p receptors in the brain.
CI in lactation, hypersensitivity
Ascorbic acid
Vitamin C
Involved in oxidation reduction reactions;tyrosine, folic acid iron, and carbohydrate metabolism; lipid and protein synthesis; cellular respiration; and resistance to infection
Recurrent kidney stones Avoid chronic use of large doses in pregnant women
Intracranial hemorrhage) Administer over 2-5 min. Reconstitute with 5ml Sterile water. Side effects include: dizziness fatigue, weakness, diarrhea, hiccups. Assess nausea, vomiting, appetite, bowel sounds, and abdominal pain prior to and following administration. Monitor hydration and nutritional status. May be administered without regard to food. drowsiness, fatigue, headache, insomnia, cramps, diarrhea, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, kidney stones, flushing, deep vein thrombosis, hemolysis (in G6PD deficiency), sickle cell crisis, If urinary acidification occurs, may increase excretion and decrease effects of mexiletine , amphetamine , or tricyclic antidepressants, Large doses (>10 g/day) may decrease response to warfarin Anaphylaxis, Laryngeal edema, and reyes syndrome (in children) may be fatal if they occur. Dyspepsia, epigastric distress, heartburn, and nausea are common. Patients who have asthma, allergies, and nasal polyps or who are allergic to tartrazine are at increased risk for developing hypersensitivity reactions. Administer after meals or with food or an antacid to minimize gastric irritation. Do not use alcohol. Report unusual bleeding to doctor. Take with a full glass of water. Report tinnitus.
Antipyretics Nonopioid analgesics Salicylates
Produce analgesia and reduce inflammation and fever by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins.
Aspirin
Antipyretics
Produce analgesia and reduce
Increased risk of bleeding with warfarin, heparin, heparin like agents, thrombolytics, ticlopidine, clopidogrel, tirofiban, or eptifibatide. May increase the activity of penicillins, phenytoin, methotrexate, valppoic acid, oral hypoglycemic agents and sulfonamides. Corticosteroids may decrease levels. May blunt the therapeutic response to diuretics, antihypertensives and NSAIDS. Increased risk of
Anaphylaxis, Laryngeal
Nonopioid analgesics Salicylates
inflammation and fever by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins.
Atenolol Tenormin
Antianginal Antiarrhythmics Antihypertensive Beta blocker selective
Block stimulation of beta1 adrenergic receptors, usually without affecting beta2 receptor sites.
bleeding with warfarin, heparin, heparin like agents, thrombolytics, ticlopidine, clopidogrel, tirofiban, or eptifibatide. May increase the activity of penicillins, phenytoin, methotrexate, valppoic acid, oral hypoglycemic agents and sulfonamides. Corticosteroids may decrease levels. May blunt the therapeutic response to diuretics, antihypertensives and NSAIDS. General anesthesia and verapamil may cause decrease in myocardial depression. CI in pulmonary disease and renal disease, bradycardia and heart block.
edema, and reyes syndrome (in children) may be fatal if they occur. Dyspepsia, epigastric distress, heartburn, and nausea are common. Patients who have asthma, allergies, and nasal polyps or who are allergic to tartrazine are at increased risk for developing hypersensitivity reactions. Administer after meals or with food or an antacid to minimize gastric irritation. Do not use alcohol. Report unusual bleeding to doctor. Take with a full glass of water. Report tinnitus.
Atropine
Antiarrhythmics Anticholinergics Antimuscarinics
Atrovastatin (Lipitor)
Lipid lowering agent HGM-CoA reductase inhibitor
Inhibits action of acetylcholine in smooth muscle, secretory glands, and CNS. Low doses decrease sweating, salivation, and respiratory secretions. Intermediate doses produce mydriasis, cycloplegia, and tachycardia. Larger doses decrease GI and GU tract motility. Inhibits 3-hydroxy-3 methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, which is responsible for an early step in the synthesis of cholesterol. Lowers LDL, Increases HDL, decreases VLDL and triglycerides. Slows the progression of CAD with a
CI in hypersensitivity, glaucoma, cardiac insufficiency or hemorrhage. Antacids decrease absorption. Additive cholesterol lowering effect or decreased effectiveness with bile acid sequestrants, May slightly increase
Side effects include fatigue, weakness, blurred vision, brochospasm, wheezing, and impotence. Administer with meals or directly after eating. Take apical pulse, if <50bpm withhold medication. Monitor for bradycardia, dizziness, dyspnea and seizures. Assess I and O monitor for pulmonary edema. Administer atropine if pulse <40 bpm. Side effects include: drowsiness, blurred vision, tachycardia, dry mouth, urinary hesitancy or retention. Assess vital signs and ECG. Intense flushing of the face and trunk may occur 15-20 min after admin. Is expected. Give iv undiluted or dilute in 10 ml of sterile water. Abdominal cramps, constipation, diarrhea, flatus, heartburn, rashes and rhabdomyolysis may occur. Ophthalmologic exams are recommended before and yearly during therapy. If patient develops muscle
decrease in MI and need for myocardial revascularization.
Azathioprine Azasan Imuran
Immunosuppresa nts
Antagonizes purine metabolism with subsequent inhibition of DNA and RNA synthesis. Suppression of cell mediated immunity and altered antibody formation.
digoxin levels, May increase effects of warfarin. Grapefruit juice increases blood levels and increases risk of toxicity. Additive myelosuppressio n with antineoplastics, cyclosporine, and myleosuppressive agents. Allopurinol increases toxicity. Echinacea and melatonin may interfere with immunosuppressi on.
tenderness during therapy, monitor CPK levels. If CPK levels are markedly increased or myopathy occurs, therapy should be discontinued.
Azithromycin Zithromax
Anti infective Macrolides
Inhibits protein synthesis at the level of the 50s bacterial ribosome.
CI in hypersensitivity to macrolides. Nelfinavir increases serum levels, increases serum levels and effects of digoxin, theophylline, ergotamine, triazolam phenytoin, and warfarin.
Beclomethasone
Antiasthmatics Corticosteroids
Potent, locally acting anti inflammatory and immune modifier.
Use cautiously in diabetes and glaucoma, underlying immunosuppressi on.
Anorexia, hepatotoxicity, nausea, vomiting, anemia, leucopenia, pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia, chills, and fever may occur. Assess for infection. Monitor I&O, and daily weight. Decreased urine output may lead to toxicity. A decrease in hemoglobin may indicate bone marrow suppression. Monitor renal, hepatic, and hematologic functions before therapy, weekly during first month, bi-weekly for the next 2-3 months, and monthy thereafter. Advise patient to stay away people with know contagious diseases. Side effects include: abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, hyperglycemia, hyperkalemia, angioedema. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before starting therapy. observe for signs of anaphylaxis, evaluate renal and hepatic function, cbc, k levels, and bleeding times. Administer 1 hr before or 2 hr after meals. Do not administer as a bolus. Administer the 1mg/ml solution over 3 hr or the 2mg/ml solution over 1 hr. Side effects include: headache, dysphonia, hoarseness, oropharyngeal fungal infections, and flu like syndrome. Monitor RR and lung sounds. Assess for adrenal insufficiency such as anorexia, nausea, weakness, fatigue, hypotension and hypoglycemia. May cause increase in serum glucose levels. Teach that this should not be used to treat an attack. Assess for signs and
Benazepril Lotensin
Antihypertensive ace inhibitor
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors block the conversion of angiotensin one to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin two.
Excessive hypotension may occur with use of other antihypertensive. Y site incompatibility amphotericin b, cefepime, phenytoin.
symptoms of infection. Side effects include cough hypotension taste disturbances proteinuria monitor blood pressure and pulse frequently during dose adjustments and periodically during therapy. Monitor weight and assess for fluid overload, monitor cbc, wbc and urine protein prior and during therapy. Teach patient to change positions slowly to reduce orthostatic hypotension and avoid excessive salt intake. Side effects include:blurred vision, dry eyes, constipation, dry mouth, and urinary retention. Assess bowel function daily, monitor I & O, monitor pulse and bp and maintain bedrest for 1 hr after administration. Teach patient to change positions slowly to avoid orthostatic hypotension. Administer with food o after meals. Administer at a rate of 1mg over 1 min. Side effects include: depression, euphoria, hypertension, anorexia, nausea, acne, decreased wound healing, adrenal suppression, cusingoid appearance. Only betamethasone sodium phosphate may be given IV. Administer undiluted and over at least 1 min. Monitor I & O, teach patient not to stop medication abruptly, assess glucose and K levels. Side effects include fatigue, weakness, blurred vision, brochospasm, wheezing, and impotence. Administer with meals or directly after eating. Take apical pulse, if <50bpm withhold medication. Monitor for bradycardia, dizziness, dyspnea and seizures. Assess I and O monitor for pulmonary edema. Administer atropine if pulse
Benztropine Cogentin
Antiparkinson agent Anticholinergic
Blocks cholinergic activity in the CNS, which is partially responsible for the symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Restores the natural balance of neurotransmitters in the CNS.
CI in hypersensitivity, glaucoma, and tardive dyskinesia.
Betamethasone
Antiasthmatics Long acting Corticosteroids
Suppress inflammation and the normal immune response. Suppresses adrenal function. Has negligible mineralocorticoid activity.
CI in active infections, lactation, stress, and pregnancy. Use with NSAIDS increases risk of adverse GI effects.
Betaxolol kerlone
Antianginal Antiarrhythmics Antihypertensive Beta blocker selective
Block stimulation of beta1 adrenergic receptors, usually without affecting beta2 receptor sites.
General anesthesia and verapamil may cause decrease in myocardial depression. CI in pulmonary disease and renal disease, bradycardia and heart block.
Bisacodyl Dulcolax
Laxative Stimulant laxative
Stimulates peristalsis by altering fluid and electrolyte transport, producing fluid accumulation in the colon.
Bisoprolol Zebeta
Antianginal Antiarrhythmics Antihypertensive Beta blocker selective
Block stimulation of beta1 adrenergic receptors, usually without affecting beta2 receptor sites.
Antacids, histamine H2receptor agonists, and gastric acid pump inhibitors may remove enteric coating on tablet. May decrease absorption of other oral meds. Milk may remove enteric coating. General anesthesia and verapamil may cause decrease in myocardial depression. CI in pulmonary disease and renal disease, bradycardia and heart block.
<40 bpm. Abdominal cramps and nausea may occur. Assess for abdominal distention, presence of bowel sounds, and usual pattern of function.
Budesonide pulmicort
Antiasthmatics Corticosteroids
Potent, locally acting anti inflammatory and immune modifier.
Use cautiously in diabetes and glaucoma, underlying immunosuppressi on.
Bupropion Wellbutrin
Antidepressant Smoking deterrent
Decreases neuronal reuptake of dopamine in the CNS. Diminished neuronal uptake of serotonin and norepinephrine.
CI in hypersensitivity, MAOI use, history of seizures, bulimia or anorexia nervosa.
Side effects include fatigue, weakness, blurred vision, brochospasm, wheezing, and impotence. Administer with meals or directly after eating. Take apical pulse, if <50bpm withhold medication. Monitor for bradycardia, dizziness, dyspnea and seizures. Assess I and O monitor for pulmonary edema. Administer atropine if pulse <40 bpm. Side effects include: headache, dysphonia, hoarseness, oropharyngeal fungal infections, and flu like syndrome. Monitor RR and lung sounds. Assess for adrenal insufficiency such as anorexia, nausea, weakness, fatigue, hypotension and hypoglycemia. May cause increase in serum glucose levels. Teach that this should not be used to treat an attack. Do not shake inhaler, inhale forcefully and do not blow back into inhaler. Assess for signs and symptoms of infection. Side effects include: agintation, headache, dry mouth, nausea, vomiting and tremor. Monitor mood changes, suicidal tendencies and hepatic and renal function closely. Admin. Doses in equally spaced time increments throughout day to minimize the risk of seizures. May be admin with food to lessen GI irritation.
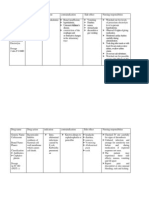
Calcium acetate gelcaps, calcium citrate calcium gluceptate Phoslogelcap Calcium Carbonate Caltrate Calcium glucanate Calcium lactate Tricalcium phosphate
Mineral and electrolyte replacement
Acts as an activator in the transmission of nerve impulses and in the contraction of cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle.
Calcium acetate should not be given concurrently with other calcium supplements.
Side effects include syncope, arrhythmias, constipation and vomiting. Monitor serum calcium or ionized calcium levels. Follow oral doses with a full glass of water. Administer with meals for patients with hyperphosphatemia.
Mineral and electrolyte replacement/ supplement
Essential for nervous, muscular and skeletal systems. Maintains cell membrane and capillary permeability. Essential for bone formation and blood coagulation.
Use cautiously with cardiac disease.
Side effects include: arrhythmias, constipation, nausea and vomiting. Observe for symptoms of hypocalcemia. Monitor serum calcium. Patients calcium level on 10/26/07 9.1. Administer after meals and at bedtime. Follow oral dose with full glass of water.
Candesartan Atacand
Antihypertensive Angiotensin II receptor antagonist
Blocks vasoconstrictor and aldosterone-produing effects of angiotensin II at receptor sites, including vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal glands.
NSAIDS may decrease drug effects. Risk of hypotension when used with diuretics.
Captopril capoten
Antihypertensive ace inhibitor
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors block the conversion of angiotensin one to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin two.
Excessive hypotension may occur with use of other antihypertensive. Y site incompatibility amphotericin b, cefepime, phenytoin.
Side effects include: dizziness, fatigue, headache, hypotension, renal failure and hyperkalemia. Assess bp and pulse before administering. Assess patient for signs of angioedema (dyspnea and facial swelling), monitor I & O, auscultate lungs for rales or crackles, monitor labs. May be administered with or without meals. Side effects include cough hypotension taste disturbances proteinuria monitor blood pressure and pulse frequently during dose adjustments and periodically during therapy. Monitor weight and assess for fluid overload, monitor cbc, wbc and urine protein prior and during therapy. Teach patient to change positions slowly to reduce orthostatic hypotension and avoid excessive salt intake. Administer 1 hr before or 2 hr after meals. Tabs may be crushed and may have a sulfurous odor.
Carbamazepine
Anticonvulsant
Decreases synaptic transmission in the CNS.
CI in bone marrow suppression, hypersensitivity and pregnancy.
Carboplatin
Antineoplastics Alkylating agents
Inhibits DNA synthesis by producing cross linking of parent DNA strands.
Carteolol cartrol
Antianginal Antihypertensive Antiarrhythmics Beta Blocker Non selective
Block stimulation of beta adrenergic and beta two adrenergic receptor sites Decreases heart rate and blood pressure, produces less bradycardia than other beta blockers.
Increased nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity with other nephrotoxic and ototoxic drugs. Increased bone marrow depression with other bone marrow depressing drugs or radiation therapy. May decrease antibody response to livevirus vaccines. Hypotension may occur with other antihypertensives NSAIDs may decrease antihypertensive actions. CI in uncompensated CHF or pulmonary edema.
Side effects include: ataxia, drowsiness and blurred vision. Assess for seizure, trigeminal neuralgia, monitor cbc, platelet count and iron levels, LFT and thyroid tests. Implement seizure precautions, admin with food, do not crush extended release tabs. Anemia, leucopenia, thrombocytopenia, and anaphylactic like reactions may be fatal if they occur. Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and hyponatremia are common. Assess for nausea and vomiting. Monitor for bone marrow suppression. Monitor for signs of anaphylaxis. Monitor electrolyte balance.
Side effects include fatigue, weakness, anxiety, blurred vision, arrhythmias, impotence, constipation, and diarrhea. May be administered with food. Patients receiving IV must have continuous ECG monitoring. Take apical pulse, if <50bpm withhold medication. Tell patient to change positions slowly to avoid orthostatic hypotension. Side effects include fatigue, weakness, anxiety, blurred vision, arrhythmias, impotence, constipation, and diarrhea. May be administered with food. Patients receiving IV must have continuous ECG monitoring. Take apical pulse, if <50bpm withhold medication. Tell patient to change positions slowly to avoid orthostatic hypotension.
Carvedilol coreg
Antianginal Antihypertensive Antiarrhythmics Beta Blocker Non selective
Block stimulation of beta adrenergic and beta two adrenergic receptor sites Decreases heart rate and blood pressure, produces less bradycardia than other beta blockers.
Hypotension may occur with other antihypertensives NSAIDs may decrease antihypertensive actions. CI in uncompensated CHF or pulmonary edema.
Cefaclor Ceclor
Anti infective Second generation cephalosporin
Binds to bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics. Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics.
Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Admin around the clock, can be on empty stomach, IM may be diluted with lidocaine to min. injection discomfort, inject deep into well developed muscle, massage well, administer IV slowly over 3-5 min.
Cefadroxil Duricef
Anti infective First generation cephalosporin
Binds to bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Cefazolin ancef
Anti infective First generation cephalosporin
Binds to bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Cefdinir Omnicef
Anti infective Third generation cephalosporins
Bind to the bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics. Y site incom amphotericin B cholesteryl sulfate complex, idarubicin, pentamidine, vinorelbine. Syringe incom lidocaine. Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics.
Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Administered over 30-60min.
Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Do not administer within 2 hrs of an antacid or 2 hrs after an iron supplement.
Cefditoren Spectracef
Anti infective Third generation cephalosporins
Bind to the bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics.
Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Administer with meals to enhance absorption. Do not administer concomitantly with antacids. Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Administer over 30 minutes.
Cefepime Maxipime
Anti infective Third generation cephalosporins
Bind to the bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Cefmetazole Zefazone
Anti infective Second generation cephalosporin
Binds to bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Cefonicid Monocid
Anti infective Second generation cephalosporin
Binds to bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics. Y site incomp acyclovir, amphotericin b, amphotericin b cholesteryl sulfate, chlordiazepoxide, chlorpromazine, cimetidine, ciprofloxacin, diphenhydramine. Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics. Y site imcomp diphenhydramine, dobutamine,drope ridol, erythromycin lactobionate, haloperidol, prochlorperazine, promethazine. Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop
Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Administer over 1060 min.
Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Administer over 20-
Cefoperazone Cefobid
Anti infective Third generation cephalosporins
Bind to the bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Cefotaxime Claforan
Anti infective Third generation cephalosporins
Bind to the bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Cefotetan Cefotan
Anti infective Second generation cephalosporin
Binds to bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Cefoxitin Mefoxin
Anti infective Second generation cephalosporin
Binds to bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
diuretics. Y site incomp filgrastim, sargramostim. Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics. Y site incomp amifostine, filgrastim, labetalol, meperidine, ondansetron, promethazine. Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics. Y site incomp allopurinol, filgrastim, fluconazole, gemcitabine, hetastarch, pentamidine Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics. Y site incomp. Promethatzine, vinorelbine. Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics. Y site incomp. Stop other mediations
30 minutes. Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Administer over 1530 minutes. Syringe compatibility is heparin.
Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Syringe comp. is heparin and ofloxacin. Administer over 20-30 minutes.
Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Administer over 2030 minutes.
Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Administer over 1530 minutes.
Cefpodoxime Vantin
Anti infective Third generation cephalosporins
Bind to the bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
during infustion, filgrastim, gatifloxacin, pentamidine. Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics. Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics. Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics. Y site incomp amphotericin b, doxorubicin, fluconazole, midazolam and warfarin. Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics. Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop
Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Do not administer within 2 hr of an antacid. Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Syringe compatibility is hydromorphone. Administer over 15-30 minutes.
Cefprozil Cefzil
Anti infective Second generation cephalosporin
Binds to bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Ceftazidime
Anti infective Third generation cephalosporins
Bind to the bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Ceftibuten Cedax
Anti infective Third generation cephalosporins
Bind to the bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Administer over 15-
Ceftizoxime Cefizox
Anti infective Third generation cephalosporins
Bind to the bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Ceftriaxone rocephin
Anti infective Third generation cephalosporins
Bind to the bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Cefuroxime Ceftin, zinacef
Anti infective Second generation cephalosporin
Binds to bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Celecoxib
Antiheumatics, NSAID COX-2 inhibitors
Inhibits the enzyme COX-2. This enzyme is required for the synthesis of prostaglandins. Has analgesic, antiinflammatory, and antipyretic properties.
Cephadrine velosef
Anti infective First generation cephalosporin
Binds to bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
diuretics. Y site incomp filgrastim. Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics. Y site incomp amphotericin b cholesteryl sulfate, filgrastim, fluconazole, labetalol, pentamidine, vinorelbine. Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics. Y site incomp discontinue primary solution when administering cefuroxime via y site. Filgrastim, fluconazole, midazolam, vinorelbine. May decrease the effectiveness of ACE inhibitors, thiazide diuretics, and furosemide. May increase risk of bleeding wth warfarin. May increase levels of lithium. Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics.
30 inutes. Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Administer over 1530 minutes.
Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Administer over 1560 minutes
GI bleeding. Assess patients range of motion, degree of swelling, and pain in affected joints before and periodically throughout therapy.
Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy.
Cephalexin keflex
Anti infective First generation cephalosporin
Binds to bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Cephapirin cefadyl
Anti infective First generation cephalosporin
Binds to bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics. Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics.
Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy. Administer over at least 15-20 min. solution may be diluted in 500-1000 ml.
Chlordiazepoxide
Sedative/ Hypnotic Barbiturate Antianxiety agent
Depresses the CNS, probably by potentiating GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter.
Chlorothiazide (Diuril) Chlorthalidone Hydrochlorothiazi de
Thiazide diuretic Antihypertensive
Increases excretion of sodium and water by inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the distal tubule.
Additive CNS depression with alcohol, antihistamines, opoid analgesics. Decreased effectiveness with: levodopa, barbiturates or rifampin Increased risk of hypotension with other antihypertinsives, or nitrates. Hypokalemia is increased with the use of amphotericin B, mezlocillin, stimulant laxatives, piperacillin, or ticarcillin. Decreased effectiveness with NSAIDS.
Dizziness, drowsiness, pain at IM site. Monitor CBC and liver function tests. May cause increased bilirubin, AST, and ALT.
Hypokalemia and hyperuricimia is common. Monitor electrolytes, blood glucose, BUN, creatinine, and uric acid levels before and periodically through therapy. Monitor blood pressue before and periodically throughout therapy. Assess I&O, daily weights, and feetlegs and sacral area for edema daily.
Choline and magnesium salicylate
Antipyretics Nonopioid analgesics Salicylates
Produce analgesia and reduce inflammation and fever by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins.
May increase the activity of penicillins, phenytoin, methotrexate, valppoic acid, oral
Anaphylaxis, Laryngeal edema, and reyes syndrome (in children) may be fatal if they occur. Dyspepsia, epigastric distress, heartburn, and nausea are common.
hypoglycemic agents and sulfonamides. Corticosteroids may decrease levels. May blunt the therapeutic response to diuretics, antihypertensives and NSAIDS.
Patients who have asthma, allergies, and nasal polyps or who are allergic to tartrazine are at increased risk for developing hypersensitivity reactions. Administer after meals or with food or an antacid to minimize gastric irritation.
Choline Salicylate Arthropan
Antipyretics Nonopioid analgesics Salicylates
Produce analgesia and reduce inflammation and fever by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins.
Cimetidine
Antiulcer agents Histamine H2 antagonist
Inhibits the action of histamine at the H2-receptor site located primarily in gastric parietal cells, resulting in inhibition of gastric acid secretion.
May increase the activity of penicillins, phenytoin, methotrexate, valppoic acid, oral hypoglycemic agents and sulfonamides. Corticosteroids may decrease levels. May blunt the therapeutic response to diuretics, antihypertensives and NSAIDS. May increase levels of toxicity with benzodiazepines and some beta blockers, caffeine, calcium channel blockers, carbamazepine, chloroquine, lidocaine and warfarin. Lowers absorption of ketoconazole Concurrent use with corticosteroids may increase the risk of tendon rupture.
Anaphylaxis, Laryngeal edema, and reyes syndrome (in children) may be fatal if they occur. Dyspepsia, epigastric distress, heartburn, and nausea are common. Patients who have asthma, allergies, and nasal polyps or who are allergic to tartrazine are at increased risk for developing hypersensitivity reactions. Administer after meals or with food or an antacid to minimize gastric irritation. Confusion, Agranulocytosis, and aplastic anemia may occur. Asses for abdominal or epigastric pain and occult blood. Monitor CBC and Diff periodically throughout therapy. Avoid administration of antacids within 30 min-1hr of administration. Sucralfate 2hrs after administration. Administer with meals or immediately afterward and at bedtime to prolong effect. Side effects include: Dizziness, drowsiness, headache, insomnia, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea. Ciprofloxacin should not be taken with milk or
Ciprofloxacin Cipro
Anti-infective fluoroquinolone
Inhibit bacterial DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA gyrase. Causes death of susceptible bacteria.
yogurt alone. May be administered with meals. Monitor for signs of infection. Cisplatin Plantinol Antineoplastics Alkylating agents Inhibits DNA synthesis by producing cross linking parent DNA strands. Increased nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity with other nephrotoxic and ototoxic drugs. Increased bone marrow depression with other bone marrow depressing drugs or radiation therapy. May decrease antibody response to livevirus vaccines. History of mania, history of suicide attempt during dose adjustment, history of seizure disorder, hepatic impairment or geriatric pts. pregnancy and lactation Seizures, leukopenia, and thrombocytopenia may be deadly if they occur. Ototoxicity, tinnitus, sever nausea, vomiting, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and anemia are common. Encourage patient to drink 2000-3000 ml/day to promote excretion of uric acid. Administer antiemetics 30-45 min before therapy.
Citalopram Hydrobromide Celexa
Treatment of depression, often in conjunction with psychothereapy
Inhibits the reuptake of serotonin in the CNS
Clarithromycin biaxin
Anti infective Antiulcer macrolides
Inhibits protein synthesis at the level of the 50s bacterial ribosome.
CI in hypersensitivity to macrolides. May increase risk of arrhythmias with pimozide.
Clonidine
Antihypertensive
Stimulates alpha adrenergic
Additive sedation
Apathy, confusion, drowsiness, insomnia, weakness, agitation, amnesia, anxiety, decreased libido, dizziness, fatigue, impaired concentration, depression, migrane, abnormal accommodation, cough, postural hypotension, abdominal pain, anorexia, diarrhea, dry mouth, dyspepsia, flatulence, increased saliva, nausea, altered taste, increased appetite, vomiting, increased sweating, tremor. Side effects include: abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, dyspepsia, ventricular arrhythmias, headache and abnormal taste. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before starting therapy. observe for signs of anaphylaxis, evaluate renal and hepatic function, cbc, k levels, and bleeding times. Administeraround the clock, without regard to meals. Food slows but does not decrease the extent of absorption. Do not administer within 4 hr of zidovudine. Side effects include
Catapres
receptors in the CNS which result in decreased sympathetic outflows inhibiting cardio acceleration and vasoconstriction centers
Clopidogrel
Antiplatelet agents Platelet aggregation inhibitors
Inhibits platelet aggregation by irreversibly inhibiting the binding of adenosine triphosphate to platelet receptors.
with CNS depressants additive bradycardia with myocardial depressant including betablockers Increased risk of bleeding with abciximab, eptifibatide, tirofiban, aspirin, NSAIDS, heparin, heparinoids, thrombolytic agents, ticlopidine, or warfarin.
drowsiness dry mouth withdrawal phenomenon dizziness hypotension Patch - administer to hairless site on chest or upper arm. Wash area with soap and water dry before application. GI Bleeding, Bleeding, neutropenia, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura may be deadly if they occur. Assess for signs and symptoms of stroke, PVD, or MI periodically during therapy. Discontinue clopidogrel 5-7 days before planned surgerical procedures. Advise patient to notify health care provider if fever, chills, sore throat, or unusual bleeding or bruising occurs. Confusion, sedation, hypotension, constipation, nausea, vomiting. Increase intake of fluids, bulk, stool softeners and laxatives.
Codeine Paveral
Opioid antagonists Allergy, cold, and cough remedies, antitissives
Binds to the opiate receptors in the CNS-alters perception and response to painful stimuli. Produces CNS depression.
Use extreme caution if patient takes MAOI. Increases CNS depression when used with other sedatives.
Colchicine
Anti gout agent
Interferes with the functions of WBC in initiating and perpetuating the inflammatory response to monosodium urate crystals.
Additive bone marrow depression if used with bone marrow depressants.
Diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting are common.
Conazepam Klonopin
Anticonvulsants Benzodiazepine
Anticonvulsant effects may be caused by presynaptic inhibition. Produces sedative effects in the CNS, probably by stimulating inhibitory GABA receptors.
Alcohol, antidepressants and other benzos may have additive CNS depression.
Side effects include behavioral changes, drowsiness and ataxia. Observe for seizure activity, assess mental status and for drowsiness. Institute seizure precautions, administer with food to minimize gastric irritation. Side effects include hypoglycemia, lipdystrophy, anaphylaxis. Assess for signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, blood glucose
Concentrated regular insulin Regular Iletin II U500
Antidiabetics, hormones Pancreatics
Lower blood glucose by increasing transport into cells and promoting the conversion of glucose to glycogen. Promote the conversion of
CI in hypersensitivity to insulin, infection.
amino acids to proteins in muscle and stimulate triglyceride formation. Inhibit the release of free fatty acids.
and ketones. Must be verified by another nurse, use only insulin syringes to draw up dose. Draw up clear insulin before mixed. Administer SQ at 45 degree angle. Should not be administered IV :Onset 30-60 min Peak 2-4 hr Duration 5-7 hr
Conjugated Estrogen Premarin
Hormone
Promote the growth and evelopment of female sex organs and the maintenance of secondary sex characteristics in women. Restoration of hormonal balance in various deficiency states
Thromboembolic disease undiagnosed vaginal bleeding Pregnancy lactation
Cortisone
Antiasthmatics short acting corticosteroids
Suppress inflammation and the normal immune response. Suppresses adrenal function. Replaces endogenous cortisol in deficiency states. Also has potent mineralocorticoid activity.
CI in active infections, lactation, stress, and pregnancy. Use with NSAIDS increases risk of adverse GI effects. Phenobarbitol or Rifanpin may increase toxicity. Allopurinol or thiazide diuretics may increase bone marrow suppression. Cardiotoxicity may be increased with other cardiotoxic agents. May potentiate the effects of warfarin.
Cyclophosphamid e
Antineoplastics Immunosuppress ant Alkylating agent
Interferes with protein synthesis (cell-cycle phase specific). Death of rapidly replicating cells, particularly malignant ones. Immunosuppressant action in small doses.
MI Thromboembolism edema htn headache intolerance to contact lenses worsening of myopia or astigmatism nausea weight changes amenorrhea breakthrough bleeding dysmenorrheal impotence testicular atrophy acne oily skin gynecomastia breast tenderness Side effects include: depression, euphoria, hypertension, anorexia, nausea, acne, decreased wound healing, adrenal suppression, cusingoid appearance. Monitor I & O, teach patient not to stop medication abruptly, assess glucose and K levels. Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, alopecia, leucopenia, thrombocytopenia, pulmonary fibrosis, myocardial fibrosis, hemorrhagic cystitis and anemia may occur. Monitor urinary output. Fluid intake should be > 3000 ml/day. Assess for fever chills, sore throat, and signs of infection. Assess for bleeding. Avoid IM injections or rectal temps. Antimedics may be given 30min before to minimize GI effects. Monitor CBC and Diff before and throughout therapy.
Cyclosporine
Immunosuppress Anti antirheumatic
Inhibits normal immune responses (cellular and humoral) by inhibiting interleukin-2.
D5 NS
Nutritional supplement
Increases the intake of calories for patients who are unable to eat or are on NPO status.
Risk of toxicity with amphotericin B, aminoglycosides, amiodarone, anabolic steroids, and sone calcium channel blockers, NSAIDS, hormonal contraceptives and sone HIV protease inhibitors. Increased immunosuppressi on with other immunosuppresa nts. Grapefruit or grapefruit juice increases absorption and should be avoided. May increase glucose levels in patients with diabetes.
Seizure, tremor, hypertension, diarrhea, hepatotoxicity, nausea, vomiting, nephrotoxicity, hirsutism, gingival hyperplasia, hypersensitivity reactions and infections may occur. Monitor I&O and B/P closely. Monitor for increased BUN and Creatinine for Nephrotoxicity. Monitor for increased AST, ALT, alkaline phosphate, amylase, and biliruben levels for hepatotoxicity. Patient should be isolated from other sick patients and visitors. Patient should have frequent mouth care and dental examinations every 3 months.
Side effects include confusion, loss of consciousness, dizziness, hypertension, chf, pulmonary edema and hyperglycemia. Monitor electrolyte levels and blood glucose.
D5 1\2 NS 20 MEQ KCL
Mineral and electrolyte replacement supplement
Maintaining acid-base balance and electrophysiologic balance of the cell
Hyperkalemia can result with the use of potassium sparing diuretics or ace inhibitors
Side effects include abdominal pain and diarrhea nausea and vomiting Assess patient for signs and symptoms of hypokalemia and hyperkalemia Monitor pulse blood pressure and ECG throughout IV therapy Side effects include: fever, trouble breathing, and swelling.
D5 Lactated Ringers
Electrolyte supplement/ replacement
This medication is an intravenous (IV) solution used to supply water and electrolytes (e.g., calcium, potassium, sodium, chloride), either with or without calories (dextrose), to the body.
Binds specifically to interleukin-
Use cautiously with diabetes and heart disease. Monitor for fluid overload.
Daclizumab
Immunosuppress
AStragalus,
Pulmonary edema may occur.
ant Zenapax Monoclonal antibodies
2 receptor sites on activated lymphocytes, acting as an IL-2 receptor antagonist. This prevents further activation of lymphocytes and allograft rejection.
Echinacea, and melatonin may interfere with immunosuppressi on. Do not admix or administer in line containing other meds.
Darbepoetin Aranesp
Antianemics Hormones rDNA
Stimulates erythropoiesis Maintains and may elevate rbc counts, decreasing the need for transfusions.
CI in uncontrolled htn.
Desirudin Iprivask
Anticoagulant Thrombin inhibitor
Selectively inhibits free and clot bound thrombin. Inhibition of thrombin prevents activation of factor 5, 8, 12, conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin, platelet adhesion and aggregation.
CI in active bleeding and coagulation disorders. Do not mix with other diluents or medications.
dexamethasone
Antiasthmatics Long acting corticosteroids
Suppress inflammation and the normal immune response. Suppresses adrenal function. Has negligible mineralocorticoid activity.
CI in active infections, lactation, stress, and pregnancy. Use with NSAIDS increases risk of adverse GI effects.
Diazepam
Antianxiety Anticonvulsant Sedative/ Hypnotic benzodiazepine
Depresses the CNS, probably by potentiating GABA. Produces skeletal muscle relaxation by inhibiting spinal polysynaptic afferent pathways. Has anticonvulsant properties because of enhanced presynaptic inhibition.
Additive CNS depression with alcohol, antihistamines, opoid analgesics. Decreased effectiveness with: levodopa, barbiturates or
Assess for fluid overload. Monitor I&O, daily weights, and lung sounds. Obtain chest x-ray within 24hrs of first dose. Monitor for anaphylactic and hypersensitivity reactions at each dose. Monitor for infection. Flush before and after admin with saline. Administer over 15 min via peripheral or central line. Side effects include: dizziness, fatigue, headache, cough, dyspnea, htn, hypotension, abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting and fever. Monitor BP before and during therapy. Monitor cbc for anemia. Monitor iron levels and renal function throughout therapy. IV administer undiluted and do not administer in conjunction with other drugs or solutions. Side effects include: nausea, bleeding, anemia, wound secretion. Assess patient for signs of bleeding, thrombosis, cbc and aptt. Rotate sites for SQ injection. Do not rub site , inject entire length of needle while pinching skin between thumb and forefinger. Side effects include: depression, euphoria, hypertension, anorexia, nausea, acne, decreased wound healing, adrenal suppression, cusingoid appearance. May be given undiluted do not administer suspension IV, administer over 1 min. Monitor I & O, teach patient not to stop medication abruptly, assess glucose and K levels. Dizziness, drowsiness, lethargy. Avoid driving or other activities that require alertness. Abrupt withdrawl may cause insomnia, irritability, nervousness, or seizure.
rifampin
Diclofenac
Nonopioid analgesics NSAID
Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis.
Aspirin may decrease effectiveness. Increased GI effects with aspirin, NSAIDS, colchicines, corticosteroids or alcohol. Additive hypotension may occur when used with other antihypertensives bradycardia may result when used with betablockers. Concurrent ingestion of grapefruit juice increases blood levels and effects. Increased risk of CNS depression with other antihistamines, opiod analgesics and sedative hypnotics.
Diltiazem Cardizem
Antihypertensive Antiarrhythmics Calcium channel blocker
Inhibits the transport of calcium into myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cells resulting in inhibition of excitationcontraction coupling and subsequent contraction
GI bleeding, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, heartburn, and anaphylaxis. May cause increased BUN, serum creatinine, and electrolytes. Take with full glass of ater. Wear sun protection to prevent photosensitivity reaction. Contact doctor if flu like symptoms occur. Side effects include anxiety confusion peripheral edema diarrhea nausea vomiting hyperglycemia arrhythmias nocturia May be administered undiluted administer each dose as a bolus over two minutes. Monitor blood pressure and pulse before administration.
Diphenhydramine Benadryl
Allergy and antihistamine
Antagonizes effects of histamine at H1 receptors, does not bind to or inactivate histamine. Significant CNS depressant and anticholinergic effects.
Diphenoxylate/atr opine Difenoxin/atropin e
Antidiarrheals Anticholinergics
Inhibits excess GI motility. Structurally related to opioid analgesics but has no analgesic properties. Atropine added to discourage abuse.
Dipyridamole
Antiplatelet agents Platelet adhesion
Decreases platelet aggregation by inhibiting the enzyme phosphodiesterase.
CI in dehydration, liver disease, infectious diarrhea and children <2yo. Additive CNS depression with other CNS depressants including alcohol, and sedatives. Do not use with MAOIs. Additive effects with aspirin. Increased risk of bleeding with heparins,
Side effects include: Drowsiness, anorexia, dry mouth, constipation, and diarrhea. Assess degree of itching. Assess sleep patterns. Administer with meals or milk to minimize GI irritation. Capsule may be emptied and contents taken with water or food. Side effects include: dizziness, constipation, blurred vision, tachycardia and urinary retention and flushing. May be administered with food, teach patient good oral hygiene, take medication exactly as directed. May cause drosiness.
Dissiness, headache, hypotension and nausea are common. PO: Monitor BP and pulse before and during therapy.
warfarin, NSAIDS, thrombolytics, sulfinpyrazone, ticlopidine, clopidogrel, abciximab, tirofiban, epitibatide, valproic acid, or plicamycin. Increased hypotension with alcohol.
Administer with full glass of water at least one hr before or 2 hrs after meals. If GI irritation occurs, administer with meals. IV: Dilute in at least a 12 ratio of 0.45% NaCl, 0.9% NaCl, or D5W for a total volume of 2050ml. Infuse over 4 min. Notify health care provider if dyspnea or chest pain occurs.
Divalproex sodium Valproate sodium Valproic acid
Anticonvulsants Vascular headache suppressants
Increases levels of GABA and inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS.
CI in liver impairment and hypersensitivity. Increased risk of bleeding when used with antiplatelet agents. Ni significant incompatibilities.
Docusate calcium Docusate sodium (Colace)
Laxative Stool softeners
Promotes incorporation of water into stool, resulting in softer fecal mass.
Side effects include: indigestion, nausea, vomiting and hyper salivation. Assess mood and behavior, assess seizure activities, monitor for headaches, and monitor liver function and thyroid tests. Administer with or after meals. Infuse over at least 60 minutes Administer with full glass of water or juice. Faster absorption on empty stomach. Assess for abdominal distention, presence of bowel sounds, and usual pattern of function.
Donepezil (Aricept)
Reversible Cholinesterase Inhibitor
Elevates acetylcholine concentrations by slowing degradation of acetylcholine released in cholinergic neurons, does not alter underlying dementia. Dilates both arteries and veins by blocking postsynaptic alpha adrenergic receptors.
Other anticholerginics may decrease the effects of this drug. CI in hypersensitivity. Increased hypotension with other antihypertensives , alcohol, or nitrates.
Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are common. Atrial fibrillation may be fatal if it occurs.
Doxazosin Cardura
Antihypertensive Peripherally acting antiadrenergics
Side effects include: dizziness, headache, weakness, nasal conogestion, orthostatic hypotension, nausea and vomiting. Assess bp and pulse before administering. Syncope may occur 30-120 mi after administration, monitor I and O. administer initial dose at bedtime.
Doxepin
Antidepressant Antianxiety agent antihistamine Tricyclic antidepressant
Prevents reuptake of norepinephrine serotonin by presynaptic neurons, resultant accumulation of neurotransmitters potentiates activity.
CI in pregnancy and lactation and narrow angle glaucoma.
Doxorubicin hydrochloride
Antineoplastics Anthracyclines
Inhibits DNA and Rna synthesis by forming complex with DNA; action is cell cycle S phase specific.
Doxycycline Minocycline Tetracycline
Anti infectives
Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis at the level of the 30 s bacterial ribosome,
Drotrecogin Xigris
Anti infective Activated protein c, human
Probably acts by suppressing widespread inflammation associated with sepsis.
Increased bone marrow depression with other bone marrow depressing drugs or radiation therapy. May decrease antibody response to livevirus vaccines. CI in hypersensitivity, pregnancy and lactation. May increase the effects of warfarin.. sulcrafate may bind to tetracycline and prevent its absorption form the GI tract. Y sit e incomp. Allopurinol, heparin, piperacillin/taxob actam. CI in hypersensitivity, patients with a high risk of bleeding, stroke, head trauma, epidural catheter, increased chance of bleeding when used with antiplateley, anticoagulants, thrombolytic and other agents that may affect coagulation. Y sit
Side effects include: fatigue, sedation, blurred vision, dry eyes, constipation, dry mouth and weight gain. Monitor BP and Pulse before giving, monitor mental status, suicidal tendencies, and assess for pain. Administer with or immediately after a meal, do not mix with carbonated beverages or grape juice. Cardiomyopathy and ECG changes may be fatal if they occur. Diarrhea, esophagitis, nausea, stomatitis, vomiting, red urine, alopecia, anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, and phlebitis at IV site are common.
Side effects include:dizziness, vestibular reactions, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, photosensitivity and superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before starting therapy. Assess IV site for thrombophlebitis. Administer around the clock. Administer with a full glass of liquid and at least 1 hr before going to bed to avoid esophageal ulceration.
Side effects include: bleeding. Assess patient for signs of bleeding and hemorrhage, assess for infection, monitor apt and pt. discontinue 2 hr prior to invasive surgical procedures.
Efavirenz Sustiva
Anti-retrovirals Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor
Inhibits HIV reverse transcriptase, which results in disruption of DNA synthesis.
eincompatibility administer via a dedicated IV line or a dedicated lumen of a multilumen central venous catheter. Increased CNC depression with other CNS depressants. Ritonavir may increase hepatoxicity. May alter effectiveness of hormonal contraception. May alter effects of warfarin.
Emtricitabine Emtriva
Anti-retrovirals Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor
Phosphorylated intacellularly where it inhibits HIV reverse transcriptase, resulting in viral DNA chain termination.
No incompatibilities noted.
Enalaprilat Vasotec
Antihypertensive ace inhibitor
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors block the conversion of angiotensin one to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin two.
Excessive hypotension may occur with use of other antihypertensive
Enoxacin Penetrex
Anti infective Fluoroquinolone
Inhibit bacterial DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA gyrase.
CI in hypersensitivity and pregnancy.
Nausea and rash are common. Asses for change in severity of HIV symptoms or symptoms of opportunistic infections. Assess for CNS and psychiatric symptoms which may occur 1-2 days after therapy and resolve within 2-4 wks. Monitor CD4 and viral load counts during therapy. Inform patient that this therapy does not cure HIV and the Importance of strict drug adherence. Headache, diarrhea, nausea and rash are common. Severe hepatomegaly with steatosis is fatal if occurs. Asses for change in severity of HIV symptoms or symptoms of opportunistic infections. Assess for signs of lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis ( increased serum lactate levels, elevated liver enzymes, and liver enlargement on palpation. If these signs are present, stop therapy. Contact MD. Side effects include cough hypotension taste disturbances proteinuria monitor blood pressure and pulse frequently during dose adjustments and periodically during therapy may be administered undiluted administer over at least five minutes Side effects include: dizziness, drowsiness, headache, insomnia, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea hypoglycemia and phlebitis at IV site. Assess patient for signs of infection, obtain culture before therapy
is started, observe for signs of anaphylaxis. Enoxaparin sodium Lovenox Dalteparin tinzaparin Anticoagulants Antithrombotic Potentiate the inhibitory effect of antithrombin on factor XA and thrombin Increased risk for bleeding when using warfarin aspirin and drugs that affect platelet function Side effects include anemia thrombocytopenia dizziness headache insomnia constipation nausea administer deep into subcutaneous tissue inject entire length of needle at 45 or 90 angle do not aspirate or massage Side effects include: nervousness, tremor, angina, htn, and tachycardia. Assess lung sounds, PFT, wheezing, BP, Pulse, RR, volume status. SQ massage inj site , avoid IM. IV admin over at least 1 min. Side effects include: dizziness, fatigue, abdominal pain, diarrhea, hyperkalemia, flulike symptoms. . Assess bp and pulse before administering. Syncope may occur 30-120 mi after administration, monitor I and O. Side effects include seizures, headache, and hypertension. Monitor blood pressure before and during therapy. Monitor Hematocrit before and twice weekly during initial therapy for two to six weeks after dose change. Administer undiluted. Side effects include: dizziness, fatigue, headache, hypotension, renal failure and hyperkalemia. Assess bp and pulse before administering. Assess patient for signs of angioedema (dyspnea and facial swelling), monitor I & O, auscultate lungs for rales or crackles, monitor labs. May be administered with or without meals. Bleeding (including GI and intracranial bleeding, hematuria and hematomas) could be fatal if it occurs. Direct Iv:
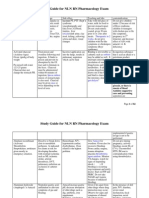
Epinephrine
Bronchodilators Antiasthmatics Vasopressors Adrenergics
Results in the accumulation of cAMP at beta adrenergic receptors. Produces broondhodilation. Inhibits the release of mediators of immediate hypersensitivity reactions from mast cells.
Eplerenone Inspara
Antihypertensive Aldosterone antagonist
Blocks the effects of aldosterone by attaching to mineralocorticoid receptors.
CI in hypersensitivity. Concurrent use with other adrenergic agents will have increased effects. Y site inc. ampicillin thiopental CI in serum k >5.5, use with k sparing diuretics and lactation.
Epoetin Epogen
Anti-anemic Hormones rDNA
Stimulates erythropoiesis.
May increase the requirement for heparin during hemodialysis.
Eprosartan Teveten
Antihypertensive Angiotensin II receptor antagonist
Blocks vasoconstrictor and aldosterone-produing effects of angiotensin II at receptor sites, including vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal glands.
NSAIDS may decrease drug effects. Risk of hypotension when used with diuretics.
Eptifibatide Integrilin
Antiplatelet agent Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors
Decreases platelet aggregation by reversibly antagonizing the binding of fibrinogen to the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa binding site on platelet surfaces.
Increased risk of bleeding with heparins, warfarin, NSAIDS, thrombolytics,
dipyridamole, ticlopidine, clopidogrel, some cephlosporines, valproates, plicamycin.
Erythromycin Erythromycin base Erythromycin estolate Erythromycin ethylsuccinate Erythromycin gluceptate Erythromycin lactobionate Erythromycin stearate Escitalopram
Anti infective Macrolides
Suppresses protein synthesis at the level of the 50s ribosome.
CI in hypersensitivity, hepatic dysfunction
Administer undiluted. Iv push over 1-2 minutes. Intermittent infusion: Based on pt wt. Y site incompatibility: furosemide. Y site compatible: 0.9% NaCl, D5/0.9% NaCl, up to 60 meq KCL. Assess for bleeding. Instruct patient to notify health care provider if bleeding occurs. Minimize use of arterial and venous punctures, IM injections, and use of urinary catherters, nasotracheal intubation, and NG tubes. Side effects include: nausea, vomiting, phlebitis at IV site. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before starting therapy. observe for signs of anaphylaxis, evaluate renal and hepatic function, cbc, k levels, and bleeding times. Administer around the clock at least 1 hr before or 2 hr after meals. Take with a full glass of water. IV administer slowly over 20-60 min to prevent phlebitis.
Antidepressant SSRI
Selectively inhibits the reuptake of serotonin in the CNS.
Esomeprazole Nexium
Antiulcer Proton pump inhibitor
Binds to an enzyme on gastric parietal cells in the presence of acidic gastric pH preventing the final transport of hydrogen ions into the gastric lumen
CI in hypersensitivity and MAOI use, and concurrent use of citalopram. Wait at least 14 days after discontinuing MAOI use to begin using this drug. May increase risk of bleeding with warfarin
Side effects include: insomnia, diarrhea, nausea, hyponatremia, and increased appetite. Monitor mood changes, assess for suicidal tendencies. Administer as a single dose in the morning or evening without regard to meals.
Side effects include headache abdominal pain constipation diarrhea nausea. Administer at least one hour before meals. Assess patient routinely for epigastric or abdominal pain and occult blood in the stool or gastric aspirate.
IV push mix in 5 mL normal saline infused over three minutes flush before and after administration Ezetimible (Zetia) Cholesterol absorption inhibitor Lipid lowering agent Inhibits absorption of cholesterol in the small intestine. Effects may be lowered by cholestyramine or other bile acis sequestrants. Concurrent use of fibrates may increase blood levels of ezetimible and also increases the risk of cholelithiasis. Cyclosporine may increase ezetimible levels. Probenecid increases blodd levels. Increased hepatic transaminases may occur. Administer without regard to meals. May be taken at the same time as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Instruct patient to notify health care professional if unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness occur.
Famciclovir Famvir
Antiviral
Inhibits viral DNA synthesis in herpes infected cells only.
Headaches may occur. Inform the patient that famciclovir does not prevent the spread of infection. Until all lesions have crusted, precautions should be taken around others who have never had chicken pox or varicella vaccine or peole who are immunosuppressed. Advise patient that this therapy is not a cure. Avoid sexual contact while lesions are present. Use condoms in the absence of lesions.
Famotidine
Antiulcer agents Histamine H2 antagonist
Inhibits the action of histamine at the H2-receptor site located primarily in gastric parietal cells, resulting in inhibition of gastric acid secretion.
Lowers the absorption of ketoconazole. Antacids and sucralfate decreases absorption.
Fentanyl
Opiod Analgesic
Bind to opiate receptors in the CNS altering the response to and the perception of pain
Additive CNS depression when used with other CNS depressants
Side effects include confusion sedation weakness anorexia constipation dry mouth vomiting sweating
Duragesic
Apply to flat non-irritated site such as chest back or upper arm. Press firmly in place with palm of hand for 30 seconds. Hematinic Replaces iron stores needed for red blood cell development, energy and oxygen transport, utilization. Contraindicated in hemolytic anemia. Decreased absorption with dairy products, caffeine and eggs. Primary hemochromatosis , Hemolytic anemias and other anemias not due to iron deficiency, Some products contain alcohol, tartrazine, or sulfites and should be avoided in patients with known intolerance or hypersensitivity May increase the activity of warfarin. Side effects include: Nausea, constipation, black and red tarry stools, vomiting, diarrhea and temporary discolored tooth enamel and eyes. Swallow tabs whole. Give between meals for best absorption, do not give with milk or antacids. SEIZURES, dizziness, headache, syncope, hypotension, tachycardia, nausea, constipation, dark stools, diarrhea, epigastric pain, GI bleeding GI bleeding, taste disorder, vomiting, flushing, urticaria, ALLERGIC REACTIONS INCLUDING ANAPHYLAXIS, fever, lymphadenopathy
Ferrous Fumarate Chromagen
Ferrous sulfate
325mg/oral/ bid
Antianemics iron supplements
An essential mineral found in hemoglobin, myoglobin, and many enzymes Parenteral iron enters the bloodstream and organs of the reticuloendothelial system (liver, spleen, bone marrow), where iron is separated out and becomes part of iron stores
Fluconazole Diflucan
Anti-fungal
Inhibit's synthesis of fungal sterols, a necessary component of the cell membrane.
Flunisolide
Antiasthmatics Corticosteroids
Potent, locally acting anti inflammatory and immune modifier.
Use cautiously in diabetes and glaucoma, underlying immunosuppressi on.
Side effects include headache, Hepatotoxicity, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea and vomiting. Monitor BUN levels and serum creatinine before and during therapy, patients with renal dysfunction will require dosage adjustment. Infuse at a maximum rate of 200 mg per hour. Side effects include: headache, dysphonia, hoarseness, oropharyngeal fungal infections, and flu like syndrome. Monitor RR and lung sounds. Assess for adrenal insufficiency such as anorexia, nausea, weakness, fatigue, hypotension and hypoglycemia. May cause increase in serum glucose levels. Teach that this should not be used to treat an attack.
Fluoxetine Prozac
Antidepressant SSRI
Selectively inhibits the reuptake of serotonin in the CNS.
CI in hypersensitivity and MAOI use, and concurrent use of citalopram. Wait at least 14 days after discontinuing MAOI use to begin using this drug.
Fluticasone flovent
Antiasthmatics Corticosteroids
Potent, locally acting anti inflammatory and immune modifier.
Use cautiously in diabetes and glaucoma, underlying immunosuppressi on.
Fluvastatin (Lescol)
Lipid lowering agent HGM-CoA reductase inhibitor
Inhibits 3-hydroxy-3 methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, which is responsible for an early step in the synthesis of cholesterol. Lowers LDL, Increases HDL, decreases VLDL and triglycerides. Slows the progression of CAD with a decrease in MI and need for myocardial revascularization.
Folic Acid
Supplement
Needed for erythropoieses, increases RBCC, WBC, and platlet formation in megaloblastic anemias.
Additive cholesterol lowering effect or decreased effectiveness with bile acid sequestrants, May slightly increase digoxin levels, May increase effects of warfarin. Grapefruit juice increases blood levels and increases risk of toxicity. Increased need for folic acid with the use of Estrogen, glucocorticoids, and hudantoins. Sulfonamides decrease the action of folic acid.
Side effects include: anxiety, drowsiness, sexual dysfunction, excessive sweating, pruritus, tremor, insomnia, diarrhea, nausea, hyponatremia, and increased appetite. Monitor mood changes, assess for suicidal tendencies, and monitor appetitie and nutritional intake. Administer as a single dose in the morning or evening without regard to meals. Side effects include: headache, dysphonia, hoarseness, oropharyngeal fungal infections, and flu like syndrome. Monitor RR and lung sounds. Assess for adrenal insufficiency such as anorexia, nausea, weakness, fatigue, hypotension and hypoglycemia. May cause increase in serum glucose levels. Teach that this should not be used to treat an attack. Assess for signs and symptoms of infection. Abdominal cramps, constipation, diarrhea, flatus, heartburn, rashes and rhabdomyolysis may occur. Administer in the evening. Ophthalmologic exams are recommended before and yearly during therapy. If patient develops muscle tenderness during therapy, monitor CPK levels. If CPK levels are markedly increased or myopathy occurs, therapy should be discontinued.
May cause flushing of the sking or bronchospasm. Offer the patient foods high in folic acid: bran, yeast, dried beans, nuts, fruits, fresh veggies, and asparagus. Assess pt for fatigue, weakness, dyspnea, shortness of breath and activity intolerance, which are signs of megaloblastic anemia.
Fondaparinux Arixtra
Anticoagulant Antithrombotic
Potentiate the inhibitory effect of antithrombin on factor XA and thrombin.
Risk of bleeding may be increased by concurrent use of warfarin, asprin and nsaids. Cannot be used interchangeably with heparin or LMWH.
Formoterol Foradil
Bronchodilators Adrenergics
Result in the accumulation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate at beta adrenergic receptor. Produces bronchodiliation. Inhibits the release of mediators of immediate hypersensitivity reactions form mast cells.
Concurrent use with other adrenergic agents will cause increased adrenergic effects beta-blockers may decrease effects. Use with herbs and caffeine containing ephedra may increase stimulant effect. Excessive hypotension may occur with use of other antihypertensive. Y site incompatibility amphotericin b, cefepime, phenytoin.
Side effects include: headache, edema, constipation, anemia, and thrombocytopenia. Assess for signs of bleeding and hemorrhage. Monitor CBC, platelet count and stools for occult blood during therapy. Administer at least 6 hours after surgery. Do not expel air bubble before injection. Administer deep into SQ tissue into abdominal wall at a 45 to 90 degree angle 1 around umbilicus. Do not massage, administer im or aspirate injection. Side effects include nervousness restlessness tremor palpitations or tachycardia angina hypertension assess lung sounds, respiratory pattern and blood pressure before administration and during peak of medication Observe for bronchospasm. If condition occurs, withhold medication and notify physician immediately. Do not wet capsule. Do not use a spacer. Side effects include cough hypotension taste disturbances proteinuria monitor blood pressure and pulse frequently during dose adjustments and periodically during therapy. Monitor weight and assess for fluid overload, monitor cbc, wbc and urine protein prior and during therapy. Teach patient to change positions slowly to reduce orthostatic hypotension and avoid excessive salt intake. Side effects include dizziness hypotension constipation diarrhea dehydration and increased BUN levels. Monitor daily weight and intake and output. Monitor blood pressure and pulse before and during
Fosinopril monopril
Antihypertensive ace inhibitor
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors block the conversion of angiotensin one to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin two.
Furosemide Lasix
Loop diuretic
Inhibit the reabsorption of sodium and chloride from the loop of Henle and distal renal tubule.
Bumetanide Bumex
Increased hypotension with antihypertensives May increase the effects of warfarin. Increased risk of hypokalemia
when used with other diuretics. Furosemide: Y site incompatibility: ciprofloxacin, diltiazem, droperidol, esmolol, filgrastim, fluconazole, gatifloxacin, gemcitabine, gentamicin, hydralazine, idarubicin, levofloxacin, metoclopramide, midazolam, milrinone, netilmicin, ondansetron, quinidine gluconate, thiopental, vecuronium, vinblastine, vincristine vonorelbine Bumex Y site incompatibility: Midazolam CI in hypersensitivity.
administration. Monitor electrolyte levels. Give undiluted. Administer slowly over two minutes.
Gabapentin Neurontin
Analgesic adjuncts Anticonvulsant
Mechanism of action is not known. May affect transport of amino acids across and stabilize neuronal membranes.
Side effects include: confusion, depression, drowsiness, and anxiety. Assess for seizure activity and chronic pain. May be administered without regard to meals. Should be discontinued gradually over at least 1 wk. Side effects include: dizziness, drowsiness, headache, insomnia, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea hypoglycemia and phlebitis at IV site. Assess patient for signs of infection, obtain culture before therapy is started, observe for signs of anaphylaxis. Administer over 60 minutes, avoid rapid or bolus IV infusion.
Gatifloxacin Tequin
Anti infective Fluoroquinolone
Inhibit bacterial DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA gyrase.
CI in hypersensitivity and pregnancy. Ysite incomp do not mix or administer with other medications. Temp discontinue other solutions. Flush line before and after administration..
Gemfibrozil
Lipid lowering agent Fibric acid derivatives
Inhibits peripheral lipolysis. Decreases triglyceride production by the liver. Decreases production of the triglyceride carrier protein. Increases high-density lipoproteins.
May increase the effects of warfarin or sulfonylurea oral hypoglycemic agent. May decrease the effect of cyclosporine.
Abdominal pain, diarrhea, and epigastric pain may occur. Administer 30 min before breakfast or dinner.
Gemifloxacin Factive
Anti infective Fluoroquinolone
Inhibit bacterial DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA gyrase.
CI in hypersensitivity and pregnancy.
gentamicin
Antiinfective Aminoglycoside
Inhibits protein synthesis in bacteria at level of 30s ribosome. Has a bactericidal action.
CI in hypersensitivity. Inactivated by penicillins and cephalosporins when administered in renal insufficiency. CI in hypersensitivity, insulin dependent diabetics, ketoacidosis, uncontrolled infection.
Glimedpiride Glipizide Glyburide
Antidiabetics Sulfonylureas
Lowers blood glucose by stimulating the release of insulin form the pancreas and increasing the sensitivity to insulin at receptor sites. May also decrease hepatic glucose production.
Granisetron
Antiemetics 5-HT3 antagonists
Blocks the effects of serotonin at receptor sites located in vagal nerve terminals and in the chemoreceptor trigger zone in the CNS,
CI in hypersensitivity. Increased risk of extrapyramidal reactions with
Side effects include: dizziness, drowsiness, headache, insomnia, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea hypoglycemia and phlebitis at IV site. Assess patient for signs of infection, obtain culture before therapy is started, observe for signs of anaphylaxis. Side effects include: ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity, muscle paralysis and hypersensitivity. Assess patient for signs of infection, obtain culture before admin. Evaluate hearing and balance before admin therapy. Do not use solutions that are discolored. Infuse slowly over 30 min-2 hr. Side effects include: photosensitivity, hypoglycemia. Assess for hypoglycemia, monitor cbc. May be administered once in the morning or divided into 2 doses. Glipizide should be taken 30 min before a meal. Glyburide should not be taken wit a meal high in fat. Glimedpiride Onset :unknown Peak 2-3 hr Duration 24 hr Glipizide onset: 15-30 min Peak 1-2 hr Duration: 24hr Glyburide onset 45-60 min Peak 1.5-3hr 24 hr Side effects include: headache and constipation. Assess patient for nausea, vomiting, abdominal distention and bowel sounds
Haloperidon Haldol
Antipsychotics
Alters the effects of dopamine in the CNS. Has anticholinergic and alpha-adrenergic blocking activity.
other agents causing extrapyramidal reactions. Y site amphotericin B incompatable Increases hypotension with antihypertensives , nitrates, or acute ingestion of alcohol. Increased anticholinergic effects with drugs having anticholinergic properties. Increased CNS depression with other CNS depressants. Acute encephalopathic syndrome may occur when used with lithium.
prior to and following administration. Administer undiluted over 30 sec, diluted over 5 minutes. Seizure and neuroleptic malignant syndrome may be fatal if they occur. Extrapyramidal reactions, blurred vision, dry eyes, constipation, and dry mouth are common. Monitor bp and pulse during therapy. Monitor I&O daily. Monitor for alkathisia. Monitor for tardive dyskinesia. Monitor for development of neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
Heparin sodium
Anticoagulants Antithrombotic
Potentiate the inhibitory effect of antithrombin on factor xa and thrombin
Risk of bleeding may be increased by concurrent use of group of drugs that affect platelet function including aspirin and NSAIDs. Additive hypotension with use of other antihypertensive NSAIDs may decrease antihypertensive response Increased CNS depression with sedatives.
Hydralazine hydrochloride Apresoline
Antihypertensive Vasodilator
Direct acting peripheral arteriolar vasodilator.
Hydrocodone
Opiod analgesic
Binds to Opiate receptors in the CNS. Alters perception of and response to painful stimuli while producing generalized CNS depression.
Side effects include bleeding, anemia, thrombocytopenia. Assess patient for signs of bleeding. Monitor PTT and hematocrit. Monitor platelet count. Administer deep into subcutaneous tissue. Inject entire length of needle at a 45 to 90 angle. Do not aspirate or massage. Side effects include tachycardia sodium retention drug induced lupus syndrome Administer undiluted use solution as quickly as possible after drawling through needle into syringe. Monitor blood pressure and pulse during dosage adjustment &during therapy. Side effects include confusion sedation hypotension and constipation. Assess blood pressure pulse and respirations before and
Acetaminophen
Hydrocortisone
Antiasthmatics short acting corticosteroids
Suppress inflammation and the normal immune response. Suppresses adrenal function. Replaces endogenous cortisol in deficiency states. Also has potent mineralocorticoid activity.
CI in active infections, lactation, stress, and pregnancy. Use with NSAIDS increases risk of adverse GI effects.
periodically during administration. Assess bowel function routinely. Assess type location and intensity of pain before and one hour after administration. Side effects include: depression, euphoria, hypertension, anorexia, nausea, acne, decreased wound healing, adrenal suppression, cusingoid appearance. Reconstitute with 2 ml of sterile saline. Monitor I & O, teach patient not to stop medication abruptly, assess glucose and K levels. Side effects include confusion sedation hypotension constipation. Dilute with at least 5 mL of sterile water for injection. Administer slightly at a rate not to exceed 2 mg over three to five minutes. Assess blood pressure pulse and respirations before and after administration Assess bowel function routinely. Assess Thai location and intensity of pain prior to and one hour following administration. Drowsiness, dry mouth. Inform patient that frequent mouth rinses, good oral hygiene, and sugarless gum or candy will help with dry mouth.
Hydromorphone
Opiod Agonist
Dilaudid
Binds to opiate receptors in the CNS alters perception of response to painful stimuli while producing generalized CNS depression.
Amphotericin B diazepam phenobarbital sodium bicarbonate
Hydroxyzine
Sedative/ Hypnotic antihistamine
Acts as a CNS depressant at the subractical level of the CNS. Has anticholinergic, antihistaminic, and antiemedic properties.
Imipramine
Antidepressant Tricyclic antidepressant
Potentiates the effect of serotonin and norepinephrine in the CNS and also has anticholinergic properties.
Additive CNS depression with alcohol, antihistamines, opoid analgesics. Added anticholinergic properties with other drugs possessing anticholingeric properties. CI in pregnancy and lactation and narrow angle glaucoma.
Side effects include: fatigue, sedation, blurred vision, dry eyes, constipation, dry mouth and weight gain. Monitor BP and Pulse before giving, monitor mental status, suicidal tendencies, and assess for pain. Administer with or immediately after a meal, IM may be slightly yellow or red, crystals may
Indapamide (Lozol)
Antihypertensive s Thiazide diuretic
Increases excretion of sodium and water by inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the distal tubule. Promotes excretion of magnesium, chloride, potassium, and bicarbonate. May produce arteriolar dilation.
Indomethacin
Antiheumatics NSAIDS
Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis.
Increased hypotension with use of alcohol and other antihypertinsives, or nitrates. Hypokalemia is increased with the use of amphotericin B, mezlocillin, piperacillin, or ticarcillin. Aspirin, NSAIDS, potassium supplements, corticosteroids and alcohol may decrease effectiveness.
develop, place under warm water for 1 min to dissolve. Hypokalemia and hyperuricimia is common. Monitor electrolytes, blood glucose, BUN, creatinine, and uric acid levels before and periodically through therapy. Monitor blood pressue before and periodically throughout therapy. Assess I&O, daily weights, and feetlegs and sacral area for edema daily. Dizziness, drowsiness, headache, psychic disturbance. GI bleeding, drup induced hepatitis, constipation, dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting, Anaphylaxis. Caution patient to wear sun protection against photosensitivity. May cause an increase in serum tests: potassium, BUN, creatinine, AST, ALT. Lipodystrophy, pruritus, rash, allergic reactions, and hypoglycemia, Assess for signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, blood glucose and ketones. Must be verified by another nurse, use only insulin syringes to draw up dose. Draw up clear insulin before mixed. Administer SQ at 45 degree angle. DO NOT MIX ANY OTHER IINSULINS USE A SEPARTATE SYRINGE TO ADMINISTER. Administer once daily at the same time each day. Side effects include hypoglycemia, lipdystrophy, anaphylaxis. Assess for signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, blood glucose and ketones. Must be verified by another nurse, use only insulin syringes to draw up dose. Draw up clear insulin before mixed. Administer SQ at 45 degree angle. Onset 15 min
Insulin Humulin R
Antidiabetics, hormones Pancreatics
Regular Insulin
Lower blood glucose by increasing transport into cells and promoting the conversion of glucose to glycogen. Promote the conversion of amino acids to proteins in muscle and stimulate triglyceride formation. Inhibit the release of free fatty acids.
Insulin aspart novolog
Antidiabetics, hormones Pancreatics
Lower blood glucose by increasing transport into cells and promoting the conversion of glucose to glycogen. Promote the conversion of amino acids to proteins in muscle and stimulate triglyceride formation. Inhibit the release of free fatty acids.
CI in hypersensitivity to insulin, infection. Beta blockers Thiazide diuretics , corticosteroids , acetazolamide , morphine , diltiazem , dobutamine , thyroid preparations , estrogens , nicotine , protease inhibitor antiretrovirals , alcohol CI in hypersensitivity to insulin, infection.
Peak 1-3 hr Insulin glargine Lantus Pancreatics Antidiabetics, hormones Lower blood glucose by increasing transport into cells and promoting the conversion of glucose to glycogen. Promote the conversion of amino acids to proteins in muscle and stimulate triglyceride formation. Inhibit the release of free fatty acids. CI in hypersensitivity to insulin, infection. Duration 3-5 hr Side effects include hypoglycemia, lipdystrophy, anaphylaxis. Assess for signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, blood glucose and ketones. Must be verified by another nurse, use only insulin syringes to draw up dose. Draw up clear insulin before mixed. Administer SQ at 45 degree angle. DO NOT MIX ANY OTHER IINSULINS USE A SEPARTATE SYRINGE TO ADMINISTER. Administer once daily at the same time each day. Do not administer IV. :Onset 1.1 hr Peak 5 hr Duration 24 hr
Insulin lispro Humalog
Antidiabetics, hormones Pancreatics
Lower blood glucose by increasing transport into cells and promoting the conversion of glucose to glycogen. Promote the conversion of amino acids to proteins in muscle and stimulate triglyceride formation. Inhibit the release of free fatty acids.
CI in hypersensitivity to insulin, infection.
Side effects include hypoglycemia, lipdystrophy, anaphylaxis. Assess for signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, blood glucose and ketones. Must be verified by another nurse, use only insulin syringes to draw up dose. Draw up clear insulin before mixed. Administer SQ at 45 degree angle. Use only U-100 syringes to draw up this insulin. Administer within 15 min before a meal. Onset 15 min Peak 30-90 min
Insulin lispro/protamine insulin lispro mixture Humalog 75/25, humalog 50/50
Antidiabetics, hormones Pancreatics
Lower blood glucose by increasing transport into cells and promoting the conversion of glucose to glycogen. Promote the conversion of amino acids to proteins in muscle and stimulate triglyceride formation. Inhibit the release of free fatty acids.
CI in hypersensitivity to insulin, infection.
Duration 6-8 hr Side effects include hypoglycemia, lipdystrophy, anaphylaxis. Assess for signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, blood glucose and ketones. Must be verified by another nurse, use only insulin syringes to draw up dose. Draw up clear insulin before mixed. Administer SQ
at 45 degree angle. Use only U-100 syringes to draw up this insulin. Administer within 15 min before a meal. Onset 15 min Peak 30-90 min Insulin zinc suspension extended ultralente insulin Humulin U Antidiabetics, hormones Pancreatics Lower blood glucose by increasing transport into cells and promoting the conversion of glucose to glycogen. Promote the conversion of amino acids to proteins in muscle and stimulate triglyceride formation. Inhibit the release of free fatty acids. CI in hypersensitivity to insulin, infection. Duration 6-8 hr Side effects include hypoglycemia, lipdystrophy, anaphylaxis. Assess for signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, blood glucose and ketones. Must be verified by another nurse, use only insulin syringes to draw up dose. Draw up clear insulin before mixed. Administer SQ at 45 degree angle. :Onset 4-6 hr Peak 18-24hr Duration 36 hr Side effects include hypoglycemia, lipdystrophy, anaphylaxis. Assess for signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, blood glucose and ketones. Must be verified by another nurse, use only insulin syringes to draw up dose. Draw up clear insulin before mixed. Administer SQ at 45 degree angle. :Onset 1-3 hr Peak 8-12 hr Duration 18-28 hr Side effects include dizziness headache blurred vision bronchospasm hypotension when administering with other inhalation medications administer adrenergic bronchodilator's first Assess respiratory status before administration and at peak of medication. Assess bowel function daily, monitor I & O, monitor pulse and bp and maintain bedrest for 1 hr after administration. Teach patient to change positions slowly to avoid orthostatic hypotension. Side effects include: dizziness, fatigue, headache,
Insulin zinc suspension lente insulin Humulin l
Antidiabetics, hormones Pancreatics
Lower blood glucose by increasing transport into cells and promoting the conversion of glucose to glycogen. Promote the conversion of amino acids to proteins in muscle and stimulate triglyceride formation. Inhibit the release of free fatty acids.
CI in hypersensitivity to insulin, infection.
Ipratropium Atrovent
Bronchodilator
Inhibit cholinergic receptors in bronchial smooth muscle resulting in decreased concentrations of cyclic guanosine monophosphate
Increased anticholinergic properties with other drugs having Anticholinergic properties
Irbesartan
Antihypertensive
Blocks vasoconstrictor and aldosterone-produing effects of
NSAIDS may decrease drug
Avapro
Angiotensin II receptor antagonist
angiotensin II at receptor sites, including vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal glands.
effects. Risk of hypotension when used with diuretics.
Isoniazid INH
Antitubercular
Inhibits mycobacterial cell wass synthesis and interferes with metabolism.
Additive CNS toxicity with other antituberculars. Aluminum containing antacids may decrease absorption. Increased risk of hypatotaxicity with other hypatotoxic drugs. Avoid foods with tyramine.
hypotension, renal failure and hyperkalemia. Assess bp and pulse before administering. Assess patient for signs of angioedema (dyspnea and facial swelling), monitor I & O, auscultate lungs for rales or crackles, monitor labs. May be administered with or without meals. Drug induced hepatitis may be fatal if occurs. Peripheral neuropathy is common. May be administered with food or antacids if GI irritation occurs. Have Pyrodoxine (vitamin B) on hand in case of overdose. Do not use alcohol during therapy.
Isosorbide dinitrate
Antianginal Nitrates
Produces vasodilatation (venous greater than arterial). Decreases left ventricular end diastolic pressure and left ventricular end diastolic volume; net effect is reduced myocardial oxygen consumption. Increases coronary blood flow by dilating coronary arteries and improving collateral flow to ischemic regions.
Use cautiously with head Injuries or cerebral hemorrhage. Additive hypotension when used with other antihypertensives.
Isosorbide mononitrate
Antianginal Nitrates
Produces vasodilatation (venous greater than arterial). Decreases left ventricular end diastolic pressure and left ventricular end diastolic volume; net effect is reduced myocardial oxygen consumption. Increases coronary blood flow by dilating coronary arteries and improving
Use cautiously with head Injuries or cerebral hemorrhage. Additive hypotension when used with other antihypertensives.
Side effects include: dizziness, headache, hypotension and tachycardia. Assess location, duration, intensity, and precipitating factors of anginal pain. Monitor blood pressure and pulse routinely during period of dosage adjustment. Administer 1 hr or 2 hr after meals with a full glass of water for faster absorption. Teach patient to change position slowly, headache is common and can be treated with asprin or Tylenol. Side effects include: dizziness, headache, hypotension and tachycardia. Assess location, duration, intensity, and precipitating factors of anginal pain. Monitor blood pressure and pulse routinely during period of dosage adjustment.
collateral flow to ischemic regions.
Itraconazole
Antifungal
Inhibits enzymes necessary for integrity of the fungal cell membrane.
CI in hypersensitivity. Increased risk of myopathy when used with simvastatin or lovastatin.
Ketoconazole
Anti-fungal
Disrupts fungal cell membrane. Interferes with fungal metabolism. Also inhibits the production of adrenal steroids.
CI in hypersensitivity, concurrent astemizon\le, pregnancy and lactation.
Administer on empty stomach with a full glass of water for faster absorption. Teach patient to change position slowly, headache is common and can be treated with aspirin or Tylenol. Side effects include: dizziness, fatigue, nausea, toxic epidermal necrolysis, rhabdomyolysis and fever. Assess for signs of infection before and throughout therapy. Cultures should be taken before therapy is started. Monitor liver function tests, monitor serum k levels may cause hypokalemia. Admin. Capsules with meals. Admin. Oral solution without food. IV administer 60 ml over 60 min. Side effects include: dizziness, nausea, vomiting abdominal pain and diarrhea. Administer with meals, do not administer within 2 hr of antacids. Assess for signs of infection. Monitor lft.
Ketorolac Tromethamine
NSAID, Nonopiod analgesic
Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis, producing peripherally mediated analgesia and also has anti-inflammatory properties.
Concurrent use with aspirin may decrease effects.
Toradol
Side effects include: Drowsiness, GI bleeding, pruritus, urticaria, nausea and diarrhea. Assess pain before and 1-2 hours after administration. Insert needle at 90 degree angle, aspirate and apply pressure at site after administration. Side effects include: Drowsiness, GI bleeding, pruritus, urticaria, nausea and diarrhea. Assess pain before and 1-2 hours after administration. Insert needle at 90 degree angle, aspirate and apply pressure at site after administration. Side effects include fatigue, weakness, anxiety, blurred vision, arrhythmias, impotence, constipation, and diarrhea.
Ketorolac Tromethamine
NSAID, Nonopiod analgesic
Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis, producing peripherally mediated analgesia and also has anti-inflammatory properties.
Concurrent use with aspirin may decrease effects.
Toradol
Labetalol Trandate
Antihypertensive Beta blocker
Block stimulation of beta adrenergic and beta two adrenergic receptor sites Decreases heart rate and blood pressure
Hypotension may occur with other antihypertensives NSAIDs may decrease
antihypertensive actions
Lactated Ringers
Electrolyte supplement/ replacement
This medication is an intravenous (IV) solution used to supply water and electrolytes (e.g., calcium, potassium, sodium, chloride), either with or without calories (dextrose), to the body.
Increases water content and softens stool. Lowers the ph of the colon, which inhibits the diffusion of ammonia from the colon into the blood, thereby reducing blood ammonia levels.
Use cautiously with diabetes and heart disease. Monitor for fluid overload.
administer undiluted slowly over two minutes assess blood pressure and pulse before and after administration. Take apical pulse, if <50bpm withhold medication. patients must be supine during and for 3 hr after admin. Monitor vital signs every 5-15 min after admin. For several hours. Side effects include: fever, trouble breathing, and swelling.
Lactulose
Laxative Osmotic
Lamivudine Epivir
Anti-retrovirals Antivirals Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor
Inhibits viral DNA by inhibiting the enzyme reverse transcriptase.
Lansoprazole Prevacid
Antiulcer Proton pump inhibitor
Binds to an enzyme on gastric parietal cells in the presence of acidic gastric pH preventing the final transport of hydrogen ions into the gastric lumen.
Should not be used with other laxatives in hepatic encephalopathy. Anti infectives may diminish effectiveness in hepatic encephalopathy. Trimethoprim/ sulfamethoxazole increases blood levels. Increased risk of pancreatitis with other drugs that cause pancreatitis. Increased risk of neuropathy with other drugs that cause neuropathy. Tenofovir and abacavir should not be used, they may lead to virologic nonresponse. Sucralfate lowers absorption. May increase risk of bleeding with warfarin.
Cramps, belching, distention, and flatulence may occur. Mix with fruit juice, water, milk, or carbonated citrus beverage to improve taste. Take with full glass of liquid. Assess for abdominal distention, presence of bowel sounds, and usual pattern of function. Seizures, hepatomegaly with steatosis, Pancreatitis, anaphylaxis, and stevensjohnson syndrome may be fatal if occurs. Fatigue, headache, insomnia, malaise, cough, anorexia, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, musculoskeletal pain, and neuropathy are common. Asses for change in severity of HIV symptoms or symptoms of opportunistic infections. Assess liver function tests. Inform patient that this therapy does not cure HIV and the Importance of strict drug adherence. Dizziness, headache, and rash may occur. Assess patient routinely for epigastric or abdominal pain and occult blood in the stool or gastric aspirate. Administer before
meals. Do not crush or chew capsules.
Levalbuterol Xopenex
Bronchodilators Adrenergics
Result in the accumulation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate at beta adrenergic receptor. Produces bronchodiliation. Inhibits the release of mediators of immediate hypersensitivity reactions form mast cells.
Concurrent use with other adrenergic agents will cause increased adrenergic effects beta-blockers may decrease effects. Use with herbs and caffeine containing ephedra may increase stimulant effect.
Side effects include nervousness restlessness tremor palpitations or tachycardia angina hypertension assess lung sounds, respiratory pattern and blood pressure before administration and during peak of medication Observe for bronchospasm. If condition occurs, withhold medication and notify physician immediately. Protect vial from sun, do not mix other drugs in nebulizer. Do not inject or administered orally. Side effects include seizures dizziness drowsiness headache insomnia abdominal pain diarrhea and nausea. Administer by infusion over at least 60 minutes, avoid rapid bolus injections. Insomnia, irritability, nervousness, CV collapse, arrythmias, tachycardia, weight loss may occur. Assess apical pulse and blood pressure periodically during therapy. Monitor thyroid function prior to and during therapy. Administer with breakfast. Instruct patient to take medication as directed at same time every day. Therapy is lifelong. Instruct patient to notify physician if nervousness, diarrhea, heat intolerance, headache, excessive sweating, chest pain, increased HR, palpitations, wt loss >2lb/wk, or ant unusual symptoms.
Levofloxacin Levaquin
Anti-infective Fluoroquinolone s
Inhibits bacterial DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA gyrase.
Administration with antacids iron salts and zinc salts decreases absorption of fluoroquinolones. Bile acid sequestrants lower the absorption of oral thyroid preparations. May alter effects of Warfarin. May increase insulin requirement or hypoglycemic agents, concurrent estrogen therapy may increase thyroid replacement requirements. Increased CV effects with adrenergics, May decrease response to beta blockers. Excessive hypotension may
Levothyroxine Liothryronine Liotrix Thyroid
Hormones Thyroid preparations
Principle effect is increasing metabolic rate of body tissues: Promotes gluconegenesis, Increases utilization and mobilization of glycogen stores, Stimulates protein synthesis, Promotes cell growth and differentiation, Aids in the development of the brain and CNS, Contains T3 and T4 activity.
Lisinopril
Antihypertensive ace inhibitor
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors block the conversion
Side effects include cough hypotension taste
Prinivil zestril
of angiotensin one to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin two.
occur with use of other antihypertensive. Y site incompatibility amphotericin b, cefepime, phenytoin.
disturbances proteinuria monitor blood pressure and pulse frequently during dose adjustments and periodically during therapy. Monitor weight and assess for fluid overload, monitor cbc, wbc and urine protein prior and during therapy. Teach patient to change positions slowly to reduce orthostatic hypotension and avoid excessive salt intake. Side effects include: dizziness, drowsiness, headache, insomnia, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea hypoglycemia and phlebitis at IV site. Assess patient for signs of infection, obtain culture before therapy is started, observe for signs of anaphylaxis. Side effects include: drowsiness, constipation, dry mouth and nausea. Assess frequency and consistency of stools and bowel sounds before and throughout therapy. Assess fluid and electrolyte balance and skin turgor for dehydration. Administer with clear fluids to help prevent dehydration that may accompany diarrhea. Diarrhea, and taste aversion (in children) are common. Asses for change in severity of HIV symptoms or symptoms of opportunistic infections. Assess for pancreatitis. Assess liver function tests. May cause hyperglycemia. Inform patient that this therapy does not cure HIV and the Importance of strict drug adherence.
Lomefloxacin Maxaquin
Anti infective Fluoroquinolone
Inhibit bacterial DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA gyrase.
CI in hypersensitivity and pregnancy.
Loperamide
Antidiarrheal
Inhibits peristalsis and prolongs transit time by a direct effect on nerves in the intestinal muscle wall. Reduces fecal volume and increases fecal viscosity and bulk while diminishing loss of fluid and electrolytes.
CI in hypersisitivity, in patients whom constipation must be avoided, alcohol intolerance. Additive CNS depression with other CNS depressants. Life threatening drug interactions may occur with concurrent use of flecainide, amiodarone, propafenone, dihydroergotamin e, ergonovine, ergotamine, methylergonovine , pimozide, midazolam, and triazolam.
Lopinavir/ Ritonavir
Anti-retrovirals Protease inhibitors Metabolic inhibitors
Lopinavir: inhibita HIV viral protease. Ritonavir: Inhibits the action of HIV protease and prevents the cleavage viral polyproteins, it is combines with Lopinavir to inhibit the metabolism of lopinavir thus increasing plasma levels.
Loracarbef lorabid
Anti infective Second generation
Binds to bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death.
Probenecid decreases excretion and increases blood
Side effects include: pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rashes and
cephalosporin
levels. Increased risk of renal toxicity when used with loop diuretics. Blocks peripheral effects of histamine released during allergic reactions. Decrease symptoms of allergic reactions Incompatible with lactation hepatic impairment use cautiously in geriatrics pregnancy or children younger than 2 Additive CNS depression with alcohol, antihistamines, opoid analgesics. Decreased effectiveness with: levodopa, barbiturates or rifampin NSAIDS may decrease drug effects. Risk of hypotension when used with diuretics.
superinfection. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before initiating therapy.
Loratadine Claritin
Antihistamine
Confusion, drowsiness, paradoxical excitation, blurred vision, dry mouth, gi upset, photosensitivity, rash, weight gain.
Lorazepam Ativan
Antianxiety Anticonvulsant
Depresses the CNS, probably by potentiating GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter.
Dizziness, drowsiness, lethargy are common. Abrupt withdrawl may cause insomnia, irritability, nervousness, or seizure. Hold med if the patient is lethargic per doctors orders.
Losartan Cozaar
Antihypertensive Angiotensin II receptor antagonist
Blocks vasoconstrictor and aldosterone-produing effects of angiotensin II at receptor sites, including vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal glands.
Side effects include: dizziness, fatigue, headache, hypotension, renal failure and hyperkalemia. Assess bp and pulse before administering. Assess patient for signs of angioedema (dyspnea and facial swelling), monitor I & O, auscultate lungs for rales or crackles, monitor labs. May be administered with or without meals. Blurred vision, Abdominal cramps, constipation, diarrhea, flatus, heartburn, rashes and rhabdomyolysis may occur. Administer with food. Ophthalmologic exams are recommended before and yearly during therapy. If patient develops muscle tenderness during therapy, monitor CPK levels. If CPK levels are markedly increased or myopathy occurs, therapy should be discontinued. Anaphylaxis, Laryngeal edema, and reyes syndrome (in children) may be fatal if
Lovastatin
Lipid lowering agent HGM-CoA reductase inhibitor
Inhibits 3-hydroxy-3 methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, which is responsible for an early step in the synthesis of cholesterol. Lowers LDL, Increases HDL, decreases VLDL and triglycerides. Slows the progression of CAD with a decrease in MI and need for myocardial revascularization.
Magnesium salicylate
Antipyretics Nonopioid
Produce analgesia and reduce inflammation and fever by inhibiting the production of
Additive cholesterol lowering effect or decreased effectiveness with bile acid sequestrants, May slightly increase digoxin levels, May increase effects of warfarin. Grapefruit juice increases blood levels and increases risk of toxicity. May increase the activity of penicillins,
analgesics Salicylates
prostaglandins.
Meperdine Demerol
Opioid antagonists
Binds to the opiate receptors in the CNS-alters perception and response to painful stimuli. Produces CNS depression.
phenytoin, methotrexate, valppoic acid, oral hypoglycemic agents and sulfonamides. Corticosteroids may decrease levels. May blunt the therapeutic response to diuretics, antihypertensives and NSAIDS. Use extreme caution if patient takes MAOI or procarbazine. Increases CNS depression when used with other sedatives. Concurrent use with other adrenergic agents will cause increased adrenergic effects beta-blockers may decrease effects. Use with herbs and caffeine containing ephedra may increase stimulant effect. Onset several days Peak 2-4 wk Duration 12 hr CI in hypersensitivity, metabolic acidosis, dehydration, sepsis, renal dysfunction and CHF. The following may increase toxicity: salicylates, NSAIDS, oral hypoglycemic agents, phenytoin, tertracyclines,
they occur. Dyspepsia, epigastric distress, heartburn, and nausea are common. Patients who have asthma, allergies, and nasal polyps or who are allergic to tartrazine are at increased risk for developing hypersensitivity reactions. Administer after meals or with food or an antacid to minimize gastric irritation. Confusion, sedation, hypotension, constipation, nausea, vomiting. Advise patient to rise slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension.
Metaproterenol
Bronchodilators Adrenergics
Result in the accumulation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate at beta adrenergic receptor. Produces bronchodiliation. Inhibits the release of mediators of immediate hypersensitivity reactions form mast cells.
Side effects include nervousness restlessness tremor palpitations or tachycardia angina hypertension assess lung sounds, respiratory pattern and blood pressure before administration and during peak of medication Observe for bronchospasm. If condition occurs, withhold medication and notify physician immediately. Do not use if solution is brown. Side effects include: bloating, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting. Whithold med before or at time of studies requiring IV administration of iodinated contrast media and for 48 hr after study. Administer with meals. Arachnoiditis, Pulmonary fibrosis, anorexia, hepatotoxicity, nausea, stomatitis, vomiting, Aplastic anemia, anemia, leucopenia, thrombocytopenis, and nephropathy may occur. Monitor I&O, daily weights,
Metformin Glucophage
Antidiabetic Biguanide
Decreases hepatic production of glucose. Decreases intestinal absorption of glucose. Increases sensitivity to insulin.
Methotrexate
Immunosuppress ants Antineoplastics Antirheumatics
Interferes with folic acid metabolism. Results in inhibition of DNA synthesis and cell reproduction (cell cycle S phase-specific). Also has immunosuppressant activity.
prebenecid. Radiation therapy may increase the risk of soft tissue necrosis.
Methylprednisolo ne
Antiasthmatics Intermediate acting corticosteroids
Suppress inflammation and the normal immune response. Suppresses adrenal function. Has minimal mineralocorticoid activity.
CI in active infections, lactation, stress, and pregnancy. Use with NSAIDS increases risk of adverse GI effects.
Metoclopramide
Antiemetic
Blocks dopamine receptors in chemoreceptor trigger zone of the CNS. Stimulates motility of the upper GI tract and accelerates gastric emptying.
CI in GI obstruction, seizures, Parkinsons. additive CNS depression with alcohol, antidepressants and sedatives. Increased risk of hypotension with other antihypertinsives, or nitrates. Hypokalemia is increased with the use of amphotericin B, mezlocillin, stimulant laxatives, piperacillin, or ticarcillin. Food mat increase the extent of absorption. General anesthesia and verapamil may cause decrease in myocardial depression. CI in pulmonary disease and renal disease, bradycardia and
Metolazone (Mykrox) (Zaroxolyn)
Antihypertensive s Thiazide diuretic
Increases excretion of sodium and water by inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the distal tubule. Promotes excretion of magnesium, chloride, potassium, and bicarbonate. May produce arteriolar dilation.
and lung sounds. Monitor for bone marrow suppression. Assess for bleeding. Avoid IM injections and rectal temps. Monitor methotrexate levels every 12-24hrs during high dose therapy until levels are <5X10M. Side effects include: depression, euphoria, hypertension, anorexia, nausea, acne, decreased wound healing, adrenal suppression, cusingoid appearance. May be admin. Direct IV push over 1 to several minutes. Monitor I & O, teach patient not to stop medication abruptly, assess glucose and K levels. Side effects include: drowsiness, eps, restlessness, arrhythmias. Assess patient for nausea, vomiting, abdominal distention and bowel sounds before and after administration. Monitor for tardive dyskinesia. Administer IV dose undiluted slowly over 1-2 minutes. Hypokalemia and hyperuricimia is common. Monitor electrolytes, blood glucose, BUN, creatinine, and uric acid levels before and periodically through therapy. Monitor blood pressue before and periodically throughout therapy. Assess I&O, daily weights, and feetlegs and sacral area for edema daily.
Metoprolol Succinate
Antianginal Antiarrhythmic Beta Blocker
Block stimulation of beta1 adrenergic receptors, usually without affecting beta2 receptor sites.
Side effects include fatigue, weakness, blurred vision, brochospasm, wheezing, and impotence. Administer with meals or directly after eating. Take apical pulse, if <50bpm withhold medication. Monitor for bradycardia, dizziness, dyspnea and seizures.
heart block.
Metronidazole With Saline PGBK
Anti-infective Antiprotozoal Antiulcer
Disruptes DNA and protein synthesis in susceptible organisms
Midazolam
Antianxiety agent Sedative/ Hypnotic
Acts at many levels of the CNC to produce generalized CNS depression. Effects may be mediated by GABA.
Increases effects of warfarin do not mix with other medications discontinue primary IV during metronidazole infusion Additive CNS depression with alcohol, antihistamines, opoid analgesics. Increased risk of hypotension with alcohol or nitrates.
Assess I and O monitor for pulmonary edema. Administer atropine if pulse <40 bpm. Side effects include dizziness headache abdominal pain anorexia diarrhea assess patient for infection monitor intake and output and daily weight Apnea, Laryngospasm, respiratory depression, Cardiac arrest, phlebitis at IV site.
Midodrine HCL
Antihypotensive, Vasopressor
Increases vascular resistance and ultimately raises blood pressure
Hypotension
Severe coronary aretery disease, acute renal disease, urinary retention, thyrotoxicosis
Miglitol Glyset
Antidiabetics Alpha glucosidase inhibitors
Lowers blood glucose by inhibiting the enzyme alpha glucosidase in the GI tract. Delays and reduces glucose absorption.
CI in hypersensitivity, diabetic ketoacidosis, cirrhosis, pregnancy, lactation, inflammatory bowel disease or impaired absorption.
Paresthesia, vasodilation,bradycardia, supine hypertension, dry mouth, urinary retention, frequency, or urgency. Monitor Kidney studies. Stay alert for paresthesias. Pt should report dizziness pounding in ears blurred vision, and headache. Side effects include: abdominal pain, diarrhea, flatulence. Assess for signs of hypoglycemia, monitor glucose and A1C levels. Does not cause hypoglycemia when taken while fasting. Administer with first bite of each meal 3 times a day. Onset rapid Peak 1 hr
Mineral oil
Used to soften impacted feces in the management of constipation
Coats surface of stool and intestine with lubricant film to allow passage of stool through intestine. Improves water retention of stool
Appears on Beers list due to increased risk of aspiration resulting in lipid pneumonia and other adverse effects. Chronic use during pregnancy
Duration unknown Lipid pneumonia, Diarrhea, anal irritation, rectal seepage of mineral oil. Decreases absorption of fat soluble vitamins ADE and K. Concurrent use with stool softeners may increase absorption of mineral oil or produce more diarrhea
decreases absorption of fatsoluble vitamins and may cause hypoprothrombin emia in newborn Mirtazapine Remeron Antidepressant Tetracyclic and tidepressant Potentiates the effects of norepinephrine and serotonin. CI in hypersensitivity and MAOI use. Side effects include: drowsiness, constipation, dry mouth, increased appetite and weight gain. Assess mental status, bp and pulse rate, and monitor for seizure activity. May be given at bedtime to decrease drowsiness. Can be taken without regard to meals. Side effects include cough hypotension taste disturbances proteinuria monitor blood pressure and pulse frequently during dose adjustments and periodically during therapy. Monitor weight and assess for fluid overload, monitor cbc, wbc and urine protein prior and during therapy. Teach patient to change positions slowly to reduce orthostatic hypotension and avoid excessive salt intake. Administer on an empty stomach, 1 hr before a meal. Side effects include confusion sedation hypotension constipation Administer 2.5 to 15 mg over four to five minutes dilute with at least 5 mL of sterile water. Side effects include: dizziness, drowsiness, headache, insomnia, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea hypoglycemia and phlebitis at IV site. Assess patient for signs of infection, obtain culture before therapy is started, observe for signs of anaphylaxis. Administer over 60 minutes avoid rapid or bolus infusion. No known side effects at recommended dosage.
Moexipril univasc
Antihypertensive ace inhibitor
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors block the conversion of angiotensin one to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin two.
Excessive hypotension may occur with use of other antihypertensive. Y site incompatibility amphotericin b, cefepime, phenytoin.
Morphine sulfate
Opiod analgesics
Binds to opiate receptors in the CNS. Alters perception of and response to painful stimuli while producing generalized CNS depression
Increased CNS depression with sedatives. May increase the anticoagulant effect of warfarin.
Moxifloxacin Avelox
Anti infective Fluoroquinolone
Inhibit bacterial DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA gyrase.
CI in hypersensitivity and pregnancy. Do not dilute premixed bags. Temp discontinue other solutions. Flush line before and after administration.. There are no oral Incompatibilities.
Multi-vitamin
Vitamins
Needed for adequate metabolism
Neprocaps
Assess for vitamin deficiencies. Take oral with glass of water.
Multiple vitamins Theragran
1tab Oral Daily
Treatment and prevention of vitamin deficiencies. Special formulations are available for patients with particular needs
Contain fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, and E) and most watersoluble vitamins, These vitamins are a diverse group of compounds necessary for normal growth and development. Many act as coenzymes or catalysts in numerous metabolic processes
Mycophenolate
Immunosuppress ants
Inhibits the enzyme inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase, which is involved in the purine synthesis. This inhibition results in suppression of T and B lymphocyte proliferation.
Nabumetone
Antiheumatics NSAIDS
Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis.
Hypersensitivity to preservatives, colorants, or additives, including tartrazine, saccharin, and aspartame, Some products contain alcohol and should be avoided in patients with known intolerance Magnesium and aluminum hydroxide antacids lower the absorption. Toxicity may be increased with salicylates. May interfere with the action of oral contraceptives. Aspirin, NSAIDS, potassium supplements, corticosteroids and alcohol may decrease effectiveness.
Urin discoloration, allergic reactions to preservatives, additives or colorants, Large amounts of vitamin B may interfere with the beneficial effect of levodopa
GI bleeding, diarrhea, vomiting, leucopenia, sepsis may occur. Monitor CBC and Diff weekly during first week, twice monthly for 2-3 months, and then monthly for 1st year of therapy.
GI bleeding, andominal pain, diarrhea, anaphylaxis, angioneurotic edema. Assess patients range of motion, degree of swelling, and pain in affected joints before and periodically throughout therapy. Side effects include fatigue, weakness, anxiety, blurred vision, arrhythmias, impotence, constipation, and diarrhea. May be administered with food. Patients receiving IV must have continuous ECG monitoring. Take apical pulse, if <50bpm withhold medication. Tell patient to change positions slowly to avoid orthostatic
Nadolol corgard
Antianginal Antihypertensive Antiarrhythmics Beta Blocker Non selective
Block stimulation of beta adrenergic and beta two adrenergic receptor sites Decreases heart rate and blood pressure, produces less bradycardia than other beta blockers.
Hypotension may occur with other antihypertensives NSAIDs may decrease antihypertensive actions. CI in uncompensated CHF or pulmonary edema.
hypotension. Naloxone Antidote Completely blocks the effects of opioids, including CNS and repiratory depression, without producing any agonist effects. Can precipitate withdrawal in patients physically dependent on opioid analgesics. Side effects include: Hypertension, hypotension, ventricular fibrillation, nausea and vomiting. Monitor RR, rhythm, depth, pulse, BP and level of consciousness. Administer undiluted for opioid overdose. For RR depression, dilute 0.4 mg in 10 ml of Normal saline. Administer at a rate of 0.5 ml direct IV push every 2 minutes. Titrate dose to avoid withdrawal and severe pain. Dizziness, drowsiness, headache, Drug induced hepatitis, GI bleeding, constipation, dyspepsia, nausea, anaphylaxis. More effective if given before pain becomes severe. Administer 30 min before or 2 hrs after meals. May take with food, milk, or antacids to decrease GI irritation. Side effects include: dizziness, insomnia, somnolence, constipation, dry mouth, nausea. Monitor mood changes, suicidal tendencies, bp and pulse before and during therapy, monitor liver function. Administer doses twice a day. Seizure can be fatal if occur. Diarrhea is common. Asses for change in severity of HIV symptoms or symptoms of opportunistic infections. Assess liver function tests. May cause hyperglycemia. Inform patient that this therapy does not cure HIV and the Importance of strict drug adherence. Administer with meals.
Narcan
Opioid antagonists
Naproxen
NSAID Non opioid analgesic
Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis.
Nefazodone Serzone
Antidepressant
Inhibits the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine by neurons. Antagonizes alpha adrenergic receptors.
Aspirin may decrease effectiveness. Increased risk of bleeding with anticoagulants, and thrombolytics. May increase serum levels of lithium. CI in hypersensitivity, MAOI use and active liver disease.
Nefinavir Viracept
Anti-retrovirals Protease inhibitors
Inhibits the action of HIV protease and prevents the cleavage viral polyproteins.
Neomycin sulfate
Anti infective aminoglycosides
Decrease the number of ammonia producing bacteria in the gut. Inhibits prtein synthesis in bacteria at level of 30S
Life threatening drug interactions may occur with concurrent use of amiodarone, dihydroergotamin e, ergonovine, ergotamine, methylergonovine , pimozide, midazolam, quinidine, simvastatin, lovastatin and triazolam. Food increases absorption. Hypersensitivity to neomycin or other aminoglycosides
N/V diarrhea, hypersensitivity reactions. Enhance possible respiratory paralysis after inhalation anesthetics. Or
Netilmicin netromycin
Antiinfective Aminoglycoside
ribosome Inhibits protein synthesis in bacteria at level of 30s ribosome. Has a bactericidal action.
Nicardipiine Cardene
Antianginal Antihypertensive Antiarrhythmics Calcium channel blocker
Inhibits the transport of calcium into myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cells resulting in inhibition of excitationcontraction coupling and subsequent contraction
Nifedipine Procardia
Antianginal Antihypertensive Antiarrhythmics Calcium channel blocker
Inhibits the transport of calcium into myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cells resulting in inhibition of excitationcontraction coupling and subsequent contraction
Nitrofurantoin
Anti infective
Interferes with bacterial enzumes.
CI in hypersensitivity. Inactivated by penicillins and cephalosporins when administered in renal insufficiency. Additive hypotension may occur when used with other antihypertensives. bradycardia may result when used with beta-blockers. Concurrent ingestion of grapefruit juice increases blood levels and effects. Additive hypotension may occur when used with other antihypertensives. bradycardia may result when used with beta-blockers. Concurrent ingestion of grapefruit juice increases blood levels and effects. CI in hypersensitivity, oliguria, anuruia. Probenedcid and sulfinpyrazone prevent high urinary concentration may decrease effectiveness.
neuromuscular blockers Side effects include: ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity, muscle paralysis and hypersensitivity. Assess patient for signs of infection, obtain culture before admin. Evaluate hearing and balance before admin therapy. Infuse slowly over 30 min-2 hr. Side effects include anxiety confusion peripheral edema diarrhea nausea vomiting hyperglycemia arrhythmias nocturia. Monitor blood pressure and pulse before administration. Monitor I & O and for peripheral edema.
Side effects include anxiety confusion peripheral edema diarrhea nausea vomiting hyperglycemia arrhythmias nocturia. Monitor blood pressure and pulse before administration.
Side effects include: anorexia, nausea, vomiting, hypersensitivity reactions and dizziness. Assess for signs and symptoms of urinary tract infection before and during therapy. Obtain specimens for culture and sensitivity before and during administration, monitor intake and output, cbc. Administer with food or milk to minimize GI irritation and to delay and increase absorption. Do not crush tablets.
Nitroglycerin Nitrostat
Anti-anginal Nitrates
Acute and long-term prophylactic management of angina pectoris.
Additive hypotension with antihypertensives
Side effects include dizziness, headache, hypotension, tachycardia. Inform patient that the tablets should be kept in original glass container. Replace tablet after six months of opening. Ensure patient correctly places tablet under the tongue.
Nizatidine
Antiulcer agents Histamine H2 antagonist
Inhibits the action of histamine at the H2-receptor site located primarily in gastric parietal cells, resulting in inhibition of gastric acid secretion.
Lowers the absorption of ketoconazole. Antacids and sucralfate decreases absorption.
Norepinephrine
Cardiac stimulant
Stimulates beta1 and alpha1 receptors in sympathetic nervous system, causing vasoconstriction, increased blood pressure, enhanced contractility, and decreased heart rate
In case of anaphylactic episode
Hypotension, thrombosis, cardiac disease, peripheral vascular disease, hypertension.
Norfloxacin Noroxin
Anti infective Fluoroquinolone
Inhibit bacterial DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA gyrase.
CI in hypersensitivity and pregnancy.
Headache, anxiety, bradycardia, severe hypertension, arrhythmias, respiratory difficulty. Check blood pressure every 2 minutes until desired pressure is achieved. Maintain continuous ecg monitoring. Headache may signal extreme hypertension and overdose. Watch for signs and symptoms of peripheral vascular insufficiency. Side effects include: dizziness, drowsiness, headache, insomnia, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea hypoglycemia and phlebitis at IV site. Assess patient for signs of infection, obtain culture before therapy is started, observe for signs of anaphylaxis.
NPH insulin Humulin N
Antidiabetics, hormones Pancreatics
Humulin 50/50, humulin 70/30, novolin 70/30
Lower blood glucose by increasing transport into cells and promoting the conversion of glucose to glycogen. Promote the conversion of amino acids to proteins in muscle and stimulate triglyceride formation. Inhibit the release of free fatty acids.
CI in hypersensitivity to insulin, infection.
Side effects include hypoglycemia, lipdystrophy, anaphylaxis. Assess for signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, blood glucose and ketones. Must be verified by another nurse, use only insulin syringes to draw up dose. Draw up clear insulin before mixed. Administer SQ
at 45 degree angle. :Onset 3-4 hr Peak 6-12 hr Duration 18-24 hr Nystatin Powder Antifungal Inteferes with fungal cell-wall synthesis causing osmotic instability Fungal infection between folds Renal or hepatic disease pregnant or breastfeeding in patients younger than 2 use cautiously. CI in hypersensitivity and pregnancy. Y site incomp amphotericin b cholesteryl sulfate, cefepime, doxorubicin liposome. Effects may be decreased by carbamazepine, omeprazole, or rifampin. Increased hypotension with antihypertensives Increased CNS depression with CNS depressants. May antagonize the effects of levodopa or dopamine antagonist. Can cause pruritus increases corticosteroid absorption. Monitor area of use for increase in redness, swelling, or irritation. Side effects include: dizziness, drowsiness, headache, insomnia, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea hypoglycemia and phlebitis at IV site. Assess patient for signs of infection, obtain culture before therapy is started, observe for signs of anaphylaxis. Administer over 60 minutes. Seizure and neuroleptic malignant syndrome may be fatal if they occur. Agitation, dizziness, headache, restlessness, sedation, weakness, amblyopia, rhinitis, orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia, constipation, dry mouth, weight gain, and tremor are common. Monitor bp and pulse during therapy. Monitor I&O daily. Monitor for alkathisia. Monitor for tardive dyskinesia. Monitor for development of neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Advise patient to protect against photosensitivity. Side effects include: injection site reactions and anaphylaxis. Assess lung sounds and RR, assess for allergic reactions within 2 hr of first injection, monitor for injection site reactions. Solution is viscous and may take 5-10 sec. to administer. Side effects include headache constipation diarrhea administer undiluted immediately before induction of anesthesia or postoperatively if nausea and
Ofloxacin Floxin
Anti infective Fluoroquinolone
Inhibit bacterial DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA gyrase.
Olanzapine Zyprexia
Antipsychotic
Antagonizes dopamine and serotonin type 2 in the CNS. Also has anticholinergic, antihistaminic, and anti alpha adrenergic effects.
Omalizumab Xolair
Antiasthmatics Monoclonal antibodies
Inhibits binding of IgE to receptors on mast cells and eosinophils, preventing the release of mediators of the allergic response. Also decreases amount of IgE receptors on basophils.
CI in hypersensitivity and acute bronchospasm.
Ondansetron Zofran
Anti-emetic
Blocks the effects of serotonin at receptor sites located in vagal nerve terminals and the chemoreceptor trigger zone in the CNS.
Lorazepam piperacillin sodium bicarbonate ampicillin
Oxycodone HCL
Opiod Analgesic
Tylox
Binds to opiate receptors in the CNS. Alters perception of and response to painful stimuli while producing generalized CNS depression.
Increases CNS depression when used with other sedatives.
vomiting occur shortly after surgery Assess patient for nausea and vomiting abdominal distention in bowel sounds prior to and following administration. Side effects include confusion sedation hypotension constipation. Administer tables with food or milk to minimize GI irritation. Assess pain, BP, pulse and respirations before administration. Do not give is RR <10bpm.
Oxybutynin Chloride Ditropan
Antispasmodic anticholinergic
Oxytocin
Hormone Oxytocics
Inhibits the action of acetylcholine at postganglionic receptors. Has direct spasmolytic action on smooth muscle, including smooth cuscle lining the GU tract without affecting vascular smooth muscle Stimulates uterine and mammary gland smooth muscle, producing uterine contractions similar to spontaneous labor contractions.
Increases bladder capacity Delayed desire to void Decreases urge incontinence urgency and frequency Severe hypertension may occur if given with vasopressors. Concurrent use with cyclopropane anesthesia may result in excessive hypotension
Side effects include dizziness, drowsiness, hallucinations, insomnia, weakness, blurred vision, increased intraocular pressure palpitations dry mouth urinary retention nausea and vomiting Maternal: coma, seizure, increased uterine motility, painful contractions. Fetal: Intracranial hemorrhage, asphyxia. Advise patient to expect contractions similar to menstrual cramps after administration. Assess aharecter, frequency, and duration of uterine contractions; resting uterine tone; and fetal heart rate. If contractions occur ,2min apart and are .50-65mm Hg on monitor, if they last 60-90 sec or longer, or change in fetal heart tone develops, stop the infusion and turn patient on her left side to prevent fetal anoxia. Notify physician immediately. Side effects include: headache and constipation. Assess patient for nausea, vomiting, abdominal distention and bowel sounds prior to and following administration. Administer undiluted over 30 sec,
palonosetron
Antiemetics 5-HT3 antagonists
Blocks the effects of serotonin at receptor sites located in vagal nerve terminals and in the chemoreceptor trigger zone in the CNS,
CI in hypersensitivity. Concurrent diuretic or antiarrhythmic therapy increases risk of arrhythmias. Do not mix with other
drugs.
Pantoprazole
Antiulcer agent
Protonix
Gastric acidpump inhibitor
Binds to an enzyme in the presence of acidic gastric PH, preventing the final transport of hydrogen ions into the gastric lumen.
May alter bioavailability of drugs for which absorption is PH dependant.
Side effects include: Headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea and hyperglycemia. Assess for epigastric pain. May be administered with or without food. Do not break, crush or chew tablets.
Paroxetine Paxil
Antidepressant SSRI
Selectively inhibits the reuptake of serotonin in the CNS.
CI in hypersensitivity and MAOI use, and concurrent use of citalopram. Wait at least 14 days after discontinuing MAOI use to begin using this drug.
Penbutolol Levatol
Antianginal Antihypertensive Antiarrhythmics Beta Blocker Non selective
Block stimulation of beta adrenergic and beta two adrenergic receptor sites Decreases heart rate and blood pressure, produces less bradycardia than other beta blockers.
Hypotension may occur with other antihypertensives NSAIDs may decrease antihypertensive actions. CI in uncompensated CHF or pulmonary edema.
Side effects include: anxiety, drowsiness, sexual dysfunction, excessive sweating, pruritus, tremor, insomnia, diarrhea, nausea, hyponatremia, and increased appetite. Monitor mood changes, assess for suicidal tendencies, and monitor appetitie and nutritional intake. Administer as a single dose in the morning or evening without regard to meals. Side effects include fatigue, weakness, anxiety, blurred vision, arrhythmias, impotence, constipation, and diarrhea. May be administered with food. Patients receiving IV must have continuous ECG monitoring. Take apical pulse, if <50bpm withhold medication. Tell patient to change positions slowly to avoid orthostatic hypotension. Side effects include: diarrhea, epigastric distress, nausea, vomiting, rashes, and pain at IM site, phlebitis, anaphylaxis and serum sickness. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before starting therapy. Observe for signs of anaphylaxis; administer around the clock. Pen v may be administered without regard to meals. Inject penicillin deep into muscle.
Penicillins Penicillin g potassium Penicillin v Procaine penicillin g Benzathine penicillin g
Anti infective Penicillins
Bind to bacterial cell wall, resulting in cell death.
CI in hypersensitivities to penicillin, procaine or benzathine. Penicillin v may decrease the effectiveness of oral contraceptive agents. Neomycin may decrease the absorption of penicillin v. y sit
Perindopril aceon
Antihypertensive ace inhibitor
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors block the conversion of angiotensin one to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin two.
e incomp. If aminoglycosides and penicillins must be administered concurrently, administer in separate sites at least 1 hr apart. Excessive hypotension may occur with use of other antihypertensive. Y site incompatibility amphotericin b, cefepime, phenytoin.
Change iv sites every 48 hr to prevent phlebitis. Administer slowly and observe for hypersensitivity.
Phenobarbital
Sedative/ Hypnotic Barbiturate Anticonvulsant
Produces all levels of CNS depression, Inhibits transmission in CNS and increases seizure threshold.
Phenytoin Dilantin
Antiarrhythmics Anticonvulsants Hydantoins
Limits seizure propagation by altering ion transport. Antiarrhythmic properties cause im;provement in AV conduction. May also decrease synaptic transmission.
Additive CNS depression with alcohol, antihistamines, opoid analgesics, and other sedative/hypnotic. MAOIS, valproic acid, or divalproex may decrease metabolism CI in heart block and hypersensitivity. Y site incompatability cipro, diltiazem, enalaprilat, hydromorphone, kcl, sufentanil, vit b complex
Side effects include cough hypotension taste disturbances proteinuria monitor blood pressure and pulse frequently during dose adjustments and periodically during therapy. Monitor weight and assess for fluid overload, monitor cbc, wbc and urine protein prior and during therapy. Teach patient to change positions slowly to reduce orthostatic hypotension and avoid excessive salt intake. Hangover, Laryngospam, angioedema, serum sickness. Assess respiratory status, pulse, and b/p frequently. Equipment for resuscitation and artificial ventilation should be readily available.
Side effects include: ataxia, diplopia, nystagmus, hypotension, gingival hyperplasia, nausea and rashes. Institute seizure precautions, administer with food to minimize gastric irritation. Administer at a rate not to exceed 50 mg over 1 min to minimize hypotension.
Phosphate/ Biphosphate
Laxative Saline
Osmotically active in the lumen of the GI tract. Produces laxative effect by causing water retention and stimulation of peristalsis. Stimulates motility and inhibits fluid and electrolyte absorption from the small intestine.
Visicol: Concurrently administered oral meds may not be absoebed.
Visicol: dizziness, headache, abnominal bloating and pain, vomiting. Arrythmias, cramping, nausea. Assess for abdominal distention, presence of bowel sounds, and usual pattern of function. Do not administer at
bedtime or late in the day. Pindolol Visken Antianginal Antihypertensive Antiarrhythmics Beta Blocker Non selective Block stimulation of beta adrenergic and beta two adrenergic receptor sites Decreases heart rate and blood pressure, produces less bradycardia than other beta blockers. Hypotension may occur with other antihypertensives NSAIDs may decrease antihypertensive actions. CI in uncompensated CHF or pulmonary edema. Side effects include fatigue, weakness, anxiety, blurred vision, arrhythmias, impotence, constipation, and diarrhea. May be administered with food. Patients receiving IV must have continuous ECG monitoring. Take apical pulse, if <50bpm withhold medication. Tell patient to change positions slowly to avoid ortho.hypotension. Side effects include: edema and anemia. Assess for hypoglycemia, monitor cbc, liver studies and cpk levels. May be taken with or without meals. Onset: 30 min Peak: 2-4 hr Piperacillin Tazobactam Zosyn Anti-infective Extended spectrum penicillins Binds to bacterial cell wall causing cell death. Potassium losing diuretics corticosteroids or amphotericin b may increase the risk of hypokalemia Concurrent use with other adrenergic agents will cause increased adrenergic effects beta-blockers may decrease effects. Use with herbs and caffeine containing ephedra may increase stimulant effect. Interferes with the absorption of orally administered drugs. Duration: 24 hr Side effects include hypokalemia pain at IM site anaphylaxis serum sickness reconstitute with 5 mL sterile water for injection. Shake well until dissolved. Administer over at least 30 minutes. Side effects include nervousness restlessness tremor palpitations or tachycardia angina hypertension assess lung sounds, respiratory pattern and blood pressure before administration and during peak of medication Observe for bronchospasm. If condition occurs, withhold medication and notify physician immediately Do not administer within one hour of other oral meds. Abdominal fullness and diarrhea may occur. Patient should fast 3-4 before administration and hold food for 2 hrs after administration. Do not add extra flavoring or ingredients to solution.
Pioglitazone Actos
Antidiabetic Thiazolidnedione s
Improves sensitivity to insulin by acting as an agonist at receptor sites involved in insulin responsiveness and subsequent glucose production and utilization. Requires insulin for activity.
CI in hypersensitivity, insulin dependent diabetics, ketoacidosis, uncontrolled infection.
Pirbuterol maxair
Bronchodilators Adrenergics
Result in the accumulation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate at beta adrenergic receptor. Produces bronchodiliation. Inhibits the release of mediators of immediate hypersensitivity reactions form mast cells.
Polyethylene glycol/electrolyte
Laxative Osmotic
Polyethylene glycol solution acts as an osmotic agent, drawing water into the lumen of the GI tract.
Potassium Chloride
Mineral and electrolyte replacement/ supplement
Maintain acid-base balance, isotonicity, and electrophysiologic balance of the cell. Required fro transmission of nerve impulses.
Use cautiously with cardiac disease and Diabetes Mellitus.
Micro K
Side effects include: Abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting. Assess for signs of hypo and hyperkalemia. Administer with or after meals to reduce GI irritation. These capsules may be opened and sprinkled on soft food and swallowed immediately with water. Abdominal cramps, constipation, diarrhea, flatus, heartburn, rashes and rhabdomyolysis may occur. Administer in the evening, no regard to food. Ophthalmologic exams are recommended before and yearly during therapy. If patient develops muscle tenderness during therapy, monitor CPK levels. If CPK levels are markedly increased or myopathy occurs, therapy should be discontinued.
Pravastatin (Pravachol)
Lipid lowering agent HGM-CoA reductase inhibitor
Inhibits 3-hydroxy-3 methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, which is responsible for an early step in the synthesis of cholesterol. Lowers LDL, Increases HDL, decreases VLDL and triglycerides. Slows the progression of CAD with a decrease in MI and need for myocardial revascularization.
Additive cholesterol lowering effect or decreased effectiveness with bile acid sequestrants, May slightly increase digoxin levels, May increase effects of warfarin. Grapefruit juice increases blood levels and increases risk of toxicity. CI in active infections, lactation, stress, and pregnancy. Use with NSAIDS increases risk of adverse GI effects.
Prednisolone
Antiasthmatics Intermediate acting corticosteroids
Suppress inflammation and the normal immune response. Suppresses adrenal function. Has minimal mineralocorticoid activity.
Prednisone
Antiasthmatics Intermediate acting Corticosteroids
Suppress inflammation and the normal immune response. Suppresses adrenal function. Has minimal mineralocorticoid activity.
CI in active infections, lactation, stress, and pregnancy. Use with NSAIDS increases risk of adverse GI effects. CI in hypersisitivity, bone marrow depression, liver or heart disease. Increased
Prochlorperazine Compazine
Antipsychotics Antiemedics
Alters effects of dopamine in the CNS.
Side effects include: depression, euphoria, hypertension, anorexia, nausea, acne, decreased wound healing, adrenal suppression, cusingoid appearance. Admin. IV push at no more than 10 mg/min. Monitor I & O, teach patient not to stop medication abruptly, assess glucose and K levels. Side effects include: depression, euphoria, hypertension, anorexia, nausea, acne, decreased wound healing, adrenal suppression, cusingoid appearance. Monitor I & O, teach patient not to stop medication abruptly, assess glucose and K levels. Side effects include: epx, blurred vision, constipation, dry mouth, anorexia, photosensitivity and allergic reactions. Monitor bp and pulse during therapy. Assess
Side effe blurred v dry mou photose reaction pulse du
Promethazine
Antiemedic antihistamine sedative/ hypnotic
Blocks the effects of histamine. Has inhibitory effect on chemoreceptor trigger zone in the medulla. Alters the effects of dopamine in the CNS.
hypotension when used withantihypertens ives, nitrates or alcohol. Do not mix with any other meds in the same syringe. Ysite income: allopurinol, amphotericin B, cefepime, peperacillin and tazobactam. Additive CNS depression with alcohol, antihistamines, opoid analgesics. Increased CNS side effects with MAOIS CI in hypersensitivity to drug or soybean oil, egg, and hyperlipidemia.
patient for nausea and vomiting before and 30-60 min after administration. Avoid getting solution on hands. IM keep patient recumbent for at least 30 min after injection to minimize hypotensive effects.
patient f vomiting after adm getting s keep pat least 30 minimize
Confusion, disorientation, sedation, NEUROLEPTIC MALIGNANT SYNDROME. Assess for nausea and vomiting before and after administration.
Propofol Diprivan
General anesthetic
Produces dose dependent CNS depression, action is unknown.
Side effects include:jerking, fever, dizziness, shivering, increased ICP, impaired cerebral flow, seizures, asystole, pancreatitis, apnea, cough and hypoxia. Use d5w to dilute. Give over 3-5 minutes. Use only glass containers when mixing. Side effects include: dizziness, weakness and nausea. May be administered with food or milk to minimize GI irritation. Assess pain for location, intensity and type before and after administration. Side effects include fatigue, weakness, anxiety, blurred vision, arrhythmias, impotence, constipation, and diarrhea. May be administered with food. Patients receiving IV must have continuous ECG monitoring. Take apical pulse, if <50bpm withhold medication. Cramping, nausea and vomiting may occur.
Propoxyphene Napsylate
Opiod Analgesic
Binds to opiate receptors in the CNS. Alters perception of and response to painful stimuli while producing generalized CNS depression.
Increases CNS depression when used with other sedatives.
Davocet-N
Propranolol Inderal
Antianginal Antihypertensive Antiarrhythmics Beta Blocker
Block stimulation of beta adrenergic and beta two adrenergic receptor sites Decreases heart rate and blood pressure
Hypotension may occur with other antihypertensives NSAIDs may decrease antihypertensive actions
Psyllium
Laxative Bulk-forming
Combines with water in the intestinal contents to form an
May decrease the absorption of
agent
emollient gel or viscous solution that promotes peristalsis and reduces transit time.
warfarin, salicylates, or digitalis glycosides.
Assess for abdominal distention, presence of bowel sounds, and usual pattern of function.
Pulmocare
Nutritional supplement
PULMOCARE is a high-fat, lowcarbohydrate formula specifically designed to reduce carbon dioxide production, thereby minimizing CO, retention resulting from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cystic fibrosis or respiratory failure.Appropriate for ambulatory or ventilatordependent patients. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors block the conversion of angiotensin one to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin two.
May cause an increase in blood sugar levels.
IF YOU ARE TAKING FEEDINGS THROUGH A FEEDING TUBE, be sure the product is at room temperature before using. SIDE EFFECTS that may go away during feedings include nausea, vomiting, stomach cramps, diarrhea, and constipation. Side effects include cough hypotension taste disturbances proteinuria monitor blood pressure and pulse frequently during dose adjustments and periodically during therapy. Monitor weight and assess for fluid overload, monitor cbc, wbc and urine protein prior and during therapy. Teach patient to change positions slowly to reduce orthostatic hypotension and avoid excessive salt intake. Side effects include headache abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea and nausea. Assess patient routinely for epigastric or abdominal pain and occult blood in the stool or gastric aspirate.
Quinapril accupril
Antihypertensive ace inhibitor
Excessive hypotension may occur with use of other antihypertensive. Y site incompatibility amphotericin b, cefepime, phenytoin.
Rabeprazole Aciphex
Antiulcer Proton pump inhibitor
Binds to an enzyme on gastric parietal cells in the presence of acidic gastric pH preventing the final transport of hydrogen ions into the gastric lumen.
Lowers blood levels of ketoconazole. Increases digoxin levels. May increase risk of bleeding with warfarin. Cholestyramine decreases absorption. May alter effects of warfarin and other highly proteinbound drugs. It is not recommended to take estrogen concurrently. Excessive
Raloxifene
Bone resorption inhibitors
Binds to estrogen receptors, producing estrogen-like effects on bone, resulting in reduced resorption of bone and decreased bone turnover.
Ramipril
Antihypertensive
Angiotensin converting enzyme
Leg cramps and hot flashes may occur. May be administered without regard to meals. Calcium supplements may be necessary. Emphasize the importance of regular weight bearing exercises. Do not take during prolonged immobilization because of increased risk of thrombosis. Side effects include cough
ace inhibitor altace
inhibitors block the conversion of angiotensin one to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin two.
hypotension may occur with use of other antihypertensive. Y site incompatibility amphotericin b, cefepime, phenytoin.
hypotension taste disturbances proteinuria monitor blood pressure and pulse frequently during dose adjustments and periodically during therapy. Monitor weight and assess for fluid overload, monitor cbc, wbc and urine protein prior and during therapy. Teach patient to change positions slowly to reduce orthostatic hypotension and avoid excessive salt intake. Capsules may be opened and sprinkled on apple sauce, store prepared mixtures for 24 hours at room temp or 48 hrs if refrigerated.
Ranitidine bismuth citrate Tritec
Antiulcer agents Histamine H2 antagonist
Inhibits the action of histamine at the H2-receptor site located primarily in gastric parietal cells, resulting in inhibition of gastric acid secretion. Some antibacterial action against h.pylori.
Lowers the absorption of ketoconazole. Antacids and sucralfate decreases absorption.
Regular insulin Humulin R
Antidiabetics, hormones Pancreatics
Novolin R
Lower blood glucose by increasing transport into cells and promoting the conversion of glucose to glycogen. Promote the conversion of amino acids to proteins in muscle and stimulate triglyceride formation. Inhibit the release of free fatty acids.
CI in hypersensitivity to insulin, infection.
Side effects include hypoglycemia, lipdystrophy, anaphylaxis. Assess for signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, blood glucose and ketones. Must be verified by another nurse, use only insulin syringes to draw up dose. Draw up clear insulin before mixed. Administer SQ at 45 degree angle. This is the only insulin that can be given IV. Do not use if it is cloudy, discolored or viscous. May be administered IV undiluted directly into vein or through Y site. For IV :Onset 10-30 min Peak 15-30 min Duration 30-60 min For SQ:Onset 30-60 min Peak 2-4 hr Duration 5-7 hr
Repaglonide Gluconorm
Antidiabetics Meglitinides
Stimulates the release of insulin from pancreatic beta cells by closing potassium channels,
CI in hypersensitivity, lactation, diabetic
Side effects include: angina, chest pain, hypoglycemia, and hyperglycemia.
Prandin
which results in the opening of calcium channels in beta cells. This is followed by release of insulin.
ketoacidosis, insulin dependent diabetes.
Resperidone Resperdal
Anti-psychotic
Antagonizes dopamine and serotonin in the CNS.
May decrease the antiparkinsonian effects of lovedopa or other dopamine antagonist. Carbamazepine may decrease effects. Clozapine may increase the effects. Increased CNS depression with CNS depressants.
Administer up to 30 min before meals. Assess for signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, blood glucose and ketones. Onset: within 30 min Peak: unknown Duration: unknown Neuroleptic malignant syndrome may be fatal if it occurs. Aggressive behavior, dizziness, extrapyramidal reactions, headache, increased dreams, increased sleep duration, insomnia, sedation, pharyngitis, rhinitis, visual disturbance, cough, constipation, diarrhea, dry mouth, nausea, decreased libido, dysmenorrheal, itching/skin rash and weight gain are common. Monitor bp and pulse during therapy. Monitor I&O daily. Monitor for alkathisia. Monitor for tardive dyskinesia. Monitor for development of neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Advise patient to protect against photosensitivity. Intacranial Hemorrhage, reperfusion arrythmias, anaphylaxis, GI bleed, retroperitoneal bleeding, GU tract bleeding. Assess for bleeding every 15-30 min during the next 8 hr, and at least every 4 hr for the duration of therapy. Assess neuro status throughout therapy (changes may indicate Intracranial hemorrhage) Red discoloration of all body fluids, abdominal pain, diarrhea, flatulence, heart burn, nausea, vomiting. Advise patient to contact physician immediately if signs of hepatitis occur. Do not use alcohol during therapy. Weakness, abdominal pain, diarrhea, rash and arthralgia may occur. Administer first thing in the
Reteplase
thrombolytic agents
Converts plasminogen to plasmin, which then degrades fibrin clots.
Asprin, NSAIDS, warfarin, heparin and heparin like agents. Y site: heparin. No other med should be infused or injected into line used for reteplase.
Rifampin
Antitubercular
Inhibits RNA synthesis by blocking RNA transcription in susceptible organisms.
Increased risk of hypatotoxicity with other hypatotoxic drugs. Lowers the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptive agents. NDAIS or asprin may increase GI irritation. Absorption is
Risedronate Actenel
Bone resorption inhibitors Biphosphonates
Inhibits bone resorption by binding to bone hydroxyapatite, which inhibits osteoclast activity.
lowered by food and calcium supplements or antacids.
rosiglitazone
Antidiabetic Thiazolidnedione s
Rosuvastatin (Crestor)
Lipid lowering agent HGM-CoA reductase inhibitor
Improves sensitivity to insulin by acting as an agonist at receptor sites involved in insulin responsiveness and subsequent glucose production and utilization. Requires insulin for activity. Inhibits 3-hydroxy-3 methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, which is responsible for an early step in the synthesis of cholesterol. Lowers LDL, Increases HDL, decreases VLDL and triglycerides. Slows the progression of CAD with a decrease in MI and need for myocardial revascularization.
Salmeterol Serevent
Bronchodilators Adrenergics
Result in the accumulation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate at beta adrenergic receptor. Produces bronchodiliation. Inhibits the release of mediators of immediate hypersensitivity reactions form mast cells.
CI in hypersensitivity, insulin dependent diabetics, ketoacidosis, uncontrolled infection. Additive cholesterol lowering effect or decreased effectiveness with bile acid sequestrants, May slightly increase digoxin levels, May increase effects of warfarin. Grapefruit juice increases blood levels and increases risk of toxicity. Concurrent use with other adrenergic agents will cause increased adrenergic effects beta-blockers may decrease effects. Use with herbs and caffeine containing ephedra may increase stimulant effect.
a.m with 6-8 oz plain water 30 min before other meds, beverages, or food. Instruct patient to remain upright for 30 min following dose to facilitate passage to stomach. Advise patient to wear sunscreen and protective clothing to prevent photosensitivity. Assess cacium and vitamin D before and periodically during therapy. Side effects include: edema and anemia. Assess for hypoglycemia, monitor cbc, liver studies and cpk levels. May be taken with or without meals. Abdominal cramps, constipation, diarrhea, flatus, heartburn, rashes and rhabdomyolysis may occur. Ophthalmologic exams are recommended before and yearly during therapy. If patient develops muscle tenderness during therapy, monitor CPK levels. If CPK levels are markedly increased or myopathy occurs, therapy should be discontinued.
Side effects include nervousness restlessness tremor palpitations or tachycardia angina hypertension assess lung sounds, respiratory pattern and blood pressure before administration and during peak of medication Metered dose inhaler should be primed or tested before 1st use. Do not use spacer and discard after every use. Observe for bronchospasm. If condition occurs, withhold medication and notify physician immediately Anaphylaxis, Laryngeal edema, and reyes syndrome
Salsalate
Antipyretics
Produce analgesia and reduce inflammation and fever by
May increase the activity of
Nonopioid analgesics Salicylates
inhibiting the production of prostaglandins.
Saquinavir
Anti-retrovirals Protease inhibitors
Inhibits the action of HIV protease and prevents the cleavage viral polyproteins.
penicillins, phenytoin, methotrexate, valppoic acid, oral hypoglycemic agents and sulfonamides. Corticosteroids may decrease levels. May blunt the therapeutic response to diuretics, antihypertensives and NSAIDS. Concurrent use of Rifampin and rifabutin is contraindicated. Midazolam and triazolam increases CNS depression. Grapefruit juice increases serum levels. Garlic decreases levels.
(in children) may be fatal if they occur. Dyspepsia, epigastric distress, heartburn, and nausea are common. Patients who have asthma, allergies, and nasal polyps or who are allergic to tartrazine are at increased risk for developing hypersensitivity reactions. Administer after meals or with food or an antacid to minimize gastric irritation. Seizure and Steven Johnson Syndrome can be fatal if they occur. Abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, increased liver enzymes, jaundice, and nausea are common. Asses for change in severity of HIV symptoms or symptoms of opportunistic infections. Assess hematologic and hepatic tests. May cause anemia and thrombocytopenia. May cause hyperglycemia. Inform patient that this therapy does not cure HIV and the Importance of strict drug adherence. Administer within 2 hrs after full meal. Side effects include cramping and diarrhea. Assess patient for abdominal distention, presence of bowel sounds, and usual pattern of bowel function. Assess color, consistency, and amount of stool produced. Administer on an empty stomach for better results. Take with a full glass of water Side effects include: anxiety, drowsiness, sexual dysfunction, excessive sweating, pruritus, tremor, insomnia, diarrhea, nausea, hyponatremia, and increased appetite. Monitor mood changes, assess for suicidal tendencies, and monitor appetitie and nutritional intake. Administer as a single dose in the morning or evening without regard to
sennosides Senokot
Stimulant laxative
Active components of senna alter water and electrolyte transport in the large intestine resulting in an accumulation of water and Increased peristalsis.
May decrease absorption of other orally administered drugs because of decreased transit time.
Sertraline Zoloft
Antidepressant SSRI
Selectively inhibits the reuptake of serotonin in the CNS. Has little effect on norepinephrine or dopamine.
CI in hypersensitivity and MAOI use and concurrent use of citalopram. Wait at least 14 days after discontinuing MAOI use to begin using this drug.
Simvastatin (Zocor)
Lipid lowering agent HGM-CoA reductase inhibitor
Inhibits 3-hydroxy-3 methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, which is responsible for an early step in the synthesis of cholesterol. Lowers LDL, Increases HDL, decreases VLDL and triglycerides. Slows the progression of CAD with a decrease in MI and need for myocardial revascularization.
Additive cholesterol lowering effect or decreased effectiveness with bile acid sequestrants, May slightly increase digoxin levels, May increase effects of warfarin. Grapefruit juice increases blood levels and increases risk of toxicity. Use cautiously in geriatric patients thos with ng suctioning vomiting diarrhea CHF severe renal failure severe liver disease. May increase the activity of penicillins, phenytoin, methotrexate, valppoic acid, oral hypoglycemic agents and sulfonamides. Corticosteroids may decrease levels. May blunt the therapeutic response to diuretics, antihypertensives and NSAIDS.
meals. Abdominal cramps, constipation, diarrhea, flatus, heartburn, rashes and rhabdomyolysis may occur. Administer in the evening, no regard to food. Ophthalmologic exams are recommended before and yearly during therapy. If patient develops muscle tenderness during therapy, monitor CPK levels. If CPK levels are markedly increased or myopathy occurs, therapy should be discontinued.
Sodium Chloride
Mineral and electrolyte
Helps maintain water distribution, fluid and electrolyte balance Reduces Crneal edema by an osmotic effect
Side effects CHF, Pulmonary Edema, Edema, Hypernatremia and hypokalemia
Sodium salicylate
Antipyretics Nonopioid analgesics Salicylates
Produce analgesia and reduce inflammation and fever by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins.
Anaphylaxis, Laryngeal edema, and reyes syndrome (in children) may be fatal if they occur. Dyspepsia, epigastric distress, heartburn, and nausea are common. Patients who have asthma, allergies, and nasal polyps or who are allergic to tartrazine are at increased risk for developing hypersensitivity reactions. Administer after meals or with food or an antacid to minimize gastric irritation.
Sotalol Betapace
Antianginal Antihypertensive Antiarrhythmics Beta Blocker Non selective
Block stimulation of beta adrenergic and beta two adrenergic receptor sites Decreases heart rate and blood pressure, produces less bradycardia than other beta
Hypotension may occur with other antihypertensives NSAIDs may decrease antihypertensive
Side effects include fatigue, weakness, anxiety, blurred vision, arrhythmias, impotence, constipation, and diarrhea. May be administered with food.
blockers.
actions. CI in uncompensated CHF or pulmonary edema.
Patients receiving IV must have continuous ECG monitoring. Take apical pulse, if <50bpm withhold medication. Tell patient to change positions slowly to avoid orthostatic hypotension. Side effects include: dizziness, drowsiness, headache, insomnia, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea hypoglycemia and phlebitis at IV site. Assess patient for signs of infection, obtain culture before therapy is started, observe for signs of anaphylaxis. Pancreatitis and hepatitis may be deadly if they occur. Peripheral neuropathy is common. Asses for change in severity of HIV symptoms or symptoms of opportunistic infections. Assess for peripheral neuropathy and pancreatitis. Assess liver function tests. Inform patient that this therapy does not cure HIV and the Importance of strict drug adherence. Intacranial Hemorrhage, reperfusion arrythmias, anaphylaxis, Gi bleed, retroperitoneal bleeding, GU tract bleeding. Assess for bleeding every 15-30 min during the next 8 hr, and at least every 4 hr for the duration of therapy. Assess neuro status throughout therapy (changes may indicate Intracranial hemorrhage) Side effects include: ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity, muscle paralysis and hypersensitivity. Assess patient for signs of infection, obtain culture before admin. Evaluate hearing and balance before admin therapy. Seizure, insomnia, tremor, ascites, hypertension, peripheral edema, GI
Sparfloxacin Zagam
Anti infective Fluoroquinolone
Inhibit bacterial DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA gyrase.
CI in hypersensitivity and pregnancy, photosensitivity to other agents, unavoidable exposure to sun, bright natural light or uv rays. Use cautiously with drugs causing peripheral neuropathy.
Stavudine
Anti-retrovirals Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor
Converted intracellularly to stavudine triphosphate, which inhibits viral DNA synthesis and replication.
streptokinase
thrombolytic agents
Converts plasminogen to plasmin, which then degrades fibrin clots.
Asprin, NSAIDS, warfarin, heparin and heparin like agents.
streptomycin
Antiinfective Aminoglycoside
Inhibits protein synthesis in bacteria at level of 30s ribosome. Has a bactericidal action.
Tacrolimus
Immunosuppress ants
Inhibits T-lymphocyte activation.
CI in hypersensitivity. Inactivated by penicillins and cephalosporins when administered in renal insufficiency. Grapefruit juice increases absorption.
Potassium sparing diuretics or ACE inhibitors increases the risk of hyperkalemia. Risk of nephrotoxicity is increased by aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, cisplatin, or cyclosporine.
Telmisartan Micardis
Antihypertensive Angiotensin II receptor antagonist
Blocks vasoconstrictor and aldosterone-produing effects of angiotensin II at receptor sites, including vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal glands.
NSAIDS may decrease drug effects. Risk of hypotension when used with diuretics.
Temazepam
Sedative/ Hypnotic Benzodiazepine
Acts at many levels of the CNC to produce generalized CNS depression. Effects may be mediated by GABA.
Tenecteplase
thrombolytic agents
Converts plasminogen to plasmin, which then degrades fibrin clots.
Additive CNS depression with alcohol, antihistamines, opoid analgesics. Decreased effectiveness with: levodopa, barbiturates, Rifampin or smoking Asprin, NSAIDS, warfarin, heparin and heparin like agents. Y site: Dextrosecontaining solutions. Do not admix
bleeding, pain, anorexia, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, nephrotoxicity, urinary tract infection, pruritus, rash, hyperglycemia, hyperkalemia, hypomagnesemia, anemia, lymphocytosis, thrombocytopenia, pareshesia, Anaphylaxis, and generalized pain may occur. Monitor B/P closely. Monitor CBC and platelet count. Inform patient of increased risk of lymphoma with this therapy. Side effects include: dizziness, fatigue, headache, hypotension, renal failure and hyperkalemia. Assess bp and pulse before administering. Assess patient for signs of angioedema (dyspnea and facial swelling), monitor I & O, auscultate lungs for rales or crackles, monitor labs. May be administered with or without meals. Hangover. Prolonged use may cause physical or psychological dependence. Administer with food to prevent GI irritation.
Terazosin Hytrin
Antihypertensive Peripherally acting
Dilates both arteries and veins by blocking postsynaptic alpha adrenergic receptors.
CI in hypersensitivity. Increased hypotension with
Intacranial Hemorrhage, reperfusion arrythmias, anaphylaxis, GI bleed, retroperitoneal bleeding, GU tract bleeding. Assess for bleeding every 15-30 min during the next 8 hr, and at least every 4 hr for the duration of therapy. Assess neuro status throughout therapy (changes may indicate Intracranial hemorrhage) Administer as IV bolus Over 5 sec. flush with Saline before and after. Side effects include: dizziness, headache, weakness, nasal conogestion, orthostatic hypotension,
antiadrenergics
other antihypertensives , alcohol, or nitrates.
Terbutaline
Bronchodilators Adrenergics
Result in the accumulation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate at beta adrenergic receptor. Produces bronchodiliation. Inhibits the release of mediators of immediate hypersensitivity reactions form mast cells.
Teriparatide
Hormone Parathyroid hormone
Regulates calcium and phosphate metabolism in bone and kidney by binding to specific cell receptors; stimulates osteoblastic activity. Increases calcium and decreases phosphorus.
Concurrent use with other adrenergic agents will cause increased adrenergic effects beta-blockers may decrease effects. Use with caffeine @ ephedra may increase stimulant effect. Transient hypercalcemia may increase the risk of dogoxin toxicity.
nausea and vomiting. Assess bp and pulse before administering. Syncope may occur 30-120 mi after administration, monitor I and O. administer initial dose at bedtime. Side effects include nervousness restlessness tremor palpitations or tachycardia angina hypertension assess lung sounds, respiratory pattern and blood pressure before administration and during peak of medication Observe for bronchospasm. Orthostatic hypotension may occur. Administer subcut into thigh or abdominal wall once daily. Solution should be clear and colorless. Store pen in refrigerator. Use immediately and return to refrigerator. Forteo pen can be used for up to 28 days. Discard after 28 days. Instruct patient to report signs of hypercalcemia (nausea, vomiting, constipation, lethargy, and muscle weakness). Side effects include: anxiety, tachycardia, nausea, vomiting. Assess bp, pulse, RR before therapy. Monitor I & O. monitor drug levels and observe for toxicity signs such as anorexia, vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, confusion, headache, flushing or seizures. Administer over 30 minutes. Advise patient to drink plenty of fluids, avoid otc cough, cold, or breathing preparations, minimize caffeine intake and to have serum levels tested periodically.
Theophylliine
Bronchodilators Phosphodiesterase inhibitors Xanthines
Inhibits phosphodiesterase, producing increased tissue concentrations of CAMP. Increased levels of Camp result in bronchodilation, cns stimulation, diuresis and gastric acid secretion.
Do not use in uncontrolled arrhythmias. Additive cv and cns side effects with adrenergic agents. Phenytoin and rifampin may decrease effectiveness. Y site incompatablility phenytoin.
Thiamine Vitamin B1
Vitamin supplement
Needed for pyruvate metabolism and carbohydrate metabolism.
No known interactions
Circulatory collapse and pulmonary edema can be deadly if they occur. Nausea and diarrhea are common. Patient needs to increase yeast, beef, liver, legumes, and whole grains in the diet.
Ticarcillin Ticarcillin/clavula nate
Anti-infective Extended spectrum penicillins
Binds to bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death. Clavulanate enhances resistance to beta lactamase, an enzyme that can inactiviate penicillins.
CI in hypersensitivity to penicillins. Probenecid increases blood levels. Diuretics and corticosteroids increase the risk of hypokalemia.
Ticlopidine Ticlid
Antiplatelet agents Platelet aggregation inhibitors
Inhibits platelet aggregation by altering the function of platelet membranes. Prolongs bleeding time.
Timolol Blocadren
Antianginal Antihypertensive Antiarrhythmics Beta Blocker Non selective
Block stimulation of beta adrenergic and beta two adrenergic receptor sites Decreases heart rate and blood pressure, produces less bradycardia than other beta blockers.
Increased risk of bleeding with warfarin, heparins, tirofiban, epifibatide, clopidogrel, or thrombolytic agents. Absorption is increased with food. Hypotension may occur with other antihypertensives NSAIDs may decrease antihypertensive actions. CI in uncompensated CHF or pulmonary edema.
Side effects include: diarrhea, hypokalemia, rashes, phlebitis and anaphylaxis. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before starting therapy. observe for signs of anaphylaxis, evaluate renal and hepatic function, cbc, k levels, and bleeding times. Change IV sites every 48 hrs to prevent phlebitis, inject ticarcillin only deep into a well muscled mass to minimize discomfort and massage well. Ticarcillin/clavulanate administer over 30 min via Y site or direct IV. Agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, intracranial bleeding, and neutropenia may be deadly if they occur. Diarrhea and rashes are common. Monitor bleeding time during therapy. Administer with food with food or immediately after eating to minimize GI discomfort and increase absorption. Side effects include fatigue, weakness, anxiety, blurred vision, arrhythmias, impotence, constipation, and diarrhea. May be administered with food. Patients receiving IV must have continuous ECG monitoring. Take apical pulse, if <50bpm withhold medication. Tell patient to change positions slowly to avoid orthostatic hypotension.
Tizanidine HCL
Antispasiticity agents
Acts as an agonist at central alpha adrenergic receptor sites. Reduces spasticity by
Use cautiously in renal impairment, concurrent
Side effects include:anxiety, depression, dizziness, sedation, weakness,
Adrenergics
increasing presynaptic inhibition of motor neurons.
antihypertensive therapy, geriatric patients and impaired hepatic function.
CI in hypersensitivity. Inactivated by penicillins and cephalosporins when administered in renal insufficiency. CI in hypersensitivity.
hypotension, abd pain, diarrhea, dyspepsia and fever. Monitor BP and pulse. May be taken without regard to meals.
Side effects include: ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity, muscle paralysis and hypersensitivity. Assess patient for signs of infection, obtain culture before admin. Evaluate hearing and balance before admin therapy. IV infuse over 30-60 min. Side effects include: dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, abnormal vision, nausea, ataxia and paresthesia. Assess for seizure activity and chronic pain. May be administered without regard to meals. Should be discontinued gradually. Side effects include dizziness hypotension constipation diarrhea dehydration and increased BUN levels. Monitor daily weight and intake and output. Monitor blood pressure and pulse before and during administration. Monitor electrolyte levels. Give undiluted. Administer slowly over two minutes.
tobramycin
Antiinfective Aminoglycoside
Inhibits protein synthesis in bacteria at level of 30s ribosome. Has a bactericidal action.
Topiramate Topamax
Anticonvulsant
Action may be a result of blockade of na channels in neurons. Enhancement of GABA, and inhibitory neurotransmitter. Prevention of activation of excitatory receptors.
Torsemide
Loop diuretic
Inhibit the reabsorption of sodium and chloride from the loop of Henle and distal renal tubule.
Demadex
Increased hypotension with antihypertensives May increase the effects of warfarin. Increased risk of hypokalemia when used with other diuretics. Torsemide: Y site incompatibilities: Do not mix with other drugs or solutions. Excessive hypotension may occur with use of other antihypertensive. Y site incompatibility amphotericin b, cefepime, phenytoin.
Trandolapril mavik
Antihypertensive ace inhibitor
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors block the conversion of angiotensin one to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin two.
Side effects include cough hypotension taste disturbances proteinuria monitor blood pressure and pulse frequently during dose adjustments and periodically during therapy. Monitor weight and assess for fluid overload, monitor cbc, wbc and urine protein prior and during therapy. Teach patient to change positions slowly to reduce orthostatic hypotension and avoid excessive salt intake.
Trazodone
Antidepressant
Alters the effects of serotonin in the CNS.
Triamcinolone
Antiasthmatics Corticosteroids
Potent, locally acting anti inflammatory and immune modifier.
CI in hypersensitivity, recovery period after MI, concurrent electroconvulsive therapy. May increase digoxin or phenytoin levels. Use cautiously in diabetes and glaucoma, underlying immunosuppressi on.
Side effects include: Drowsiness, hypotension, dry mouth, and tremor. Monitor mood changes, suicidal tendencies, bp and pulse before and during therapy,
Triazolam
Sedative/ Hypnotic Benzodiazepine
Acts at many levels of the CNC to produce generalized CNS depression. Effects may be mediated by GABA.
Trimethoprim/sulf amethoxazole
Anti infective Antiprotozoal Folate antagonist Sulfonamides
Combination inhibits the metabolism of folic acid in bacteria at two different points.
Trovafloxacin trovan
Anti infective Fluoroquinolone
Inhibit bacterial DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA gyrase.
Additive CNS depression with alcohol, antihistamines, opoid analgesics. Decreased effectiveness with: levodopa. Avoid grapefruit juice. CI in hypersensitivity to sulfonamides or trimethoprim. Y site imcomp. Fluconazole, midazolam, vinorelbine. Manufacturer rec. that no other medication or solution be admixed with trimethoprim/sulf amethoxazole. CI in hypersensitivity and pregnancy.
Side effects include: headache, dysphonia, hoarseness, oropharyngeal fungal infections, and flu like syndrome. Monitor RR and lung sounds. Assess for adrenal insufficiency such as anorexia, nausea, weakness, fatigue, hypotension and hypoglycemia. May cause increase in serum glucose levels. Teach that this should not be used to treat an attack. Assess for signs and symptoms of infection. Dizziness, excessive sedation, hangover, headache.
Side effects include: nausea, vomiting, rashes, phlebitis at IV site, erythema multiforme and fever. Assess patient for infection. Obtain culture before starting therapy. Assess IV site for phlebitis. Do not administer IM. Administer around the clock with a full glass of water. Infuse over 60-90 min, do not administer rapidly or by bolus injection. Side effects include: dizziness, drowsiness, headache, insomnia, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea hypoglycemia and phlebitis at IV site. Assess patient for signs of infection, obtain culture before therapy
Urokinase
thrombolytic agents
Converts plasminogen to plasmin, which then degrades fibrin clots.
Asprin, NSAIDS, warfarin, heparin and heparin like agents.
Valacyclovir Valtrex
Antiviral
Interferes with the viral DNA synthesis.
Probenecid and Cimetine increases blodd levels
Valsartan diovan
Antihypertensive Angiotensin II receptor antagonist
Blocks vasoconstrictor and aldosterone-produing effects of angiotensin II at receptor sites, including vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal glands.
NSAIDS may decrease drug effects. Risk of hypotension when used with diuretics.
Vancomycin
Anti infective
Binds to bacterial cell wall, resulting in cell death.
CI in hypersensitivity. May cause additive ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity with other ototoxic and nephrotoxic
is started, observe for signs of anaphylaxis. May be taken without regard to meals. Intacranial Hemorrhage, reperfusion arrythmias, anaphylaxis, GI bleed, retroperitoneal bleeding, GU tract bleeding. Assess for bleeding every 15-30 min during the next 8 hr, and at least every 4 hr for the duration of therapy. Assess neuro status throughout therapy (changes may indicate Intracranial hemorrhage) Administer via infusion pump Headache and nausea may occur. Thrombocytopenic prpura/ hemolytic uremic syndrome is fatal if occurs. Inform the patient that Valacyclovir does not prevent the spread of infection. Until all lesions have crusted, precautions should be taken around others who have never had chicken pox or varicella vaccine or peole who are immunosuppressed. Advise patient that this therapy is not a cure. Avoid sexual contact while lesions are present. Use condoms in the absence of lesions. Side effects include: dizziness, fatigue, headache, hypotension, renal failure and hyperkalemia. Assess bp and pulse before administering. Assess patient for signs of angioedema (dyspnea and facial swelling), monitor I & O, auscultate lungs for rales or crackles, monitor labs. May be administered with or without meals. Side effects include nephrotoxicity, phlebitis, anaphylaxis, fever and chills. Assess for infection, monitor IV site closely. Vancomycin is irritating to tissues and causes necrosis and pain. Monitor bp during iv infusion. Assess bowel status.
Venlafaxine Effexor
Antidepressant Antianxiety
Inhibits serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake in the CNS.
drugs. Increased risk of histamine flush when used with general anesthetics in children. CI in hypersensitivity, MAOI use and active liver disease.
Administer over 60 min. do not administer rapidly.
Verapamil
Antianginal Antihypertensive Antiarrhythmics Calcium channel blocker
Inhibits the transport of calcium into myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cells resulting in inhibition of excitation-contraction coupling and subsequent contraction. Decrease SA and AV conduction and prolong AV node refractory period in conduction tissue.
Additive hypotension may occur when used with other antihypertensives. bradycardia may result when used with beta-blockers. Concurrent ingestion of grapefruit juice increases blood levels and effects.
Voriconazole
Antifungal
Inhibits fungal ergosterol synthesis leading to production of abnormal fungal cell wall.
Warfarin Coumadin
Anticoagulants Coumarins
Interferes with hepatic synthesis of vitamin k dependent clotting factors 2,7,9,10.
CI in current use of rifampin, Phenobarbital, mephobarbital and lactose intolerance. Do not infuse with other drugs including parenteral nurtrition, blood or other medications. CI in pregnancy, uncontrolled bleeding, open wounds, active ulcer disease, recent brain, eye, or spinal cord injury or surgery, uncontrolled htn. Antidote is vitamin k is case
Side effects include: abnormal dreams, anxiety, dizziness, headache, insomnia, nervousness, weakness, rhinitis, abdominal pain, ecchymoses, paresthesia and chills. . Monitor mood changes, suicidal tendencies, bp and pulse before and during therapy, monitor liver function. Side effects include anxiety confusion peripheral edema diarrhea nausea vomiting hyperglycemia arrhythmias nocturia. Monitor blood pressure and pulse before administration. Monitor I & O and for peripheral edema. Patient should remain recumbent for at least 1 hr after iv admin. In order to minimize hypotensive effects. Admin. Undiluted over 2 min for each single dose. Side effects include: visual disturbances, allegic reactions, tachycardia photosensitivity and dizziness. Monitor visual function, allergic reactions during infusion, monitor lft and renal function. Administer 1 hr before or 1 hr after meals. Infuse over 1-2 hr at a rate not to exceed 3mg/kg/hr. Side effects include:cramps, nausea, dermal necrosis, bleeding and fever. Assess patient for signs of bleeding and hemorrhage and thrombosis. Monitor pt and other clotting factors. Inr needs to be 2-3 times the control value. Monitor stool and urine for blood. Med required 3-5 days to reach
of overdose.
Zidovudine
Anti-retrovirals Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor
After intracellular conversion to its active form, inhibits viral RNA synthesis by inhibiting the enzyme DNA polymerase. Prevents viral replication.
Increased bone marrow suppression with other drugs that have bone marrow suppressing agents. Increased neurotoxicity with acyclovir.
effective levels. Administer as low bolus injection over 12 min into a peripheral vein. Avoid IM injections. Seizures may be fatal if they occur. Headache, weakness, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, anemia, and granulocytopenia are common. Asses for change in severity of HIV symptoms or symptoms of opportunistic infections. Monitor CBC q 2wks during first 8 wks of therapy, decrease to q 4 wks after the first 2 mo. Inform patient that this therapy does not cure HIV and the Importance of strict drug adherence.
Zolpidem
Sedative/ Hypnotic
Produces CNS depression by binding to GABA receptors.
Ambien
CNS depression with sedative hypnotics, opioid analgesics and antihistamines. Food decreases and delays absorption.
Side effects include: amnesia, dizziness, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. Assess mental status and sleep patterns. Provide comfort measures. Tablets should be swallowed whole with a full glass of water.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Albuterol sulfate for asthma reliefDocumento19 pagineAlbuterol sulfate for asthma reliefCamille PinedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Piperacillin-Tazobactam AntibioticDocumento9 paginePiperacillin-Tazobactam Antibiotic배기숭Nessuna valutazione finora
- FINAL Drug StudyDocumento9 pagineFINAL Drug StudyKristen Leigh MarianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento22 pagineDrug StudyColleen Fretzie Laguardia NavarroNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineDocumento8 pagineDrug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineAiryn CanonNessuna valutazione finora
- CVA Drug StudyDocumento51 pagineCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- Atropine Sulfate InjectionDocumento4 pagineAtropine Sulfate InjectionIrawanMarlyNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug AnalysisDocumento3 pagineDrug AnalysisAnn Aquino100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocumento70 pagineDrug Studyjahmaicao50% (2)
- Drug StudyDocumento3 pagineDrug StudyGail SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento28 pagineDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Complete Drugs StudyDocumento13 pagineComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Drug CardsDocumento32 pagineNursing Drug CardsJenna Rasmussen100% (3)
- Drug StudyDocumento9 pagineDrug StudyEzshkha OngueNessuna valutazione finora
- Propanolol and Spironolactone Drug StudyDocumento2 paginePropanolol and Spironolactone Drug StudyLisette Castillo91% (11)
- Drug StudyDocumento6 pagineDrug StudyMaurence John Feliciano LuluquisenNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDocumento12 pagineCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- Drug StudiesDocumento16 pagineDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- Drug 25Documento17 pagineDrug 25carol_gigliotti24100% (1)
- MedSurg Medication Study Guide Test 1Documento12 pagineMedSurg Medication Study Guide Test 1Sarah PlunkettNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study 68-75Documento8 pagineDrug Study 68-75joshua_santiago_5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study Classification and Effects of Piperacillin Sodium and TazobactamDocumento6 pagineDrug Study Classification and Effects of Piperacillin Sodium and TazobactamArvin BeltranNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug and NCPDocumento15 pagineDrug and NCPgeelawlietNessuna valutazione finora
- Coronary Heart Disease With AsthmaDocumento31 pagineCoronary Heart Disease With AsthmaEf LablaNessuna valutazione finora
- Felodipine Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento22 pagineFelodipine Nursing ResponsibilitiesPaula Xavier AlfalahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study HydralazineDocumento10 pagineDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Antenatal Glucocorticoid Therapy and Fetal Lung MaturationDocumento32 pagineAntenatal Glucocorticoid Therapy and Fetal Lung Maturationcclaire197% (37)
- Drug StudyDocumento10 pagineDrug StudyFranco ObedozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Labs Drug Study 1Documento17 pagineLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide for NLN RN Pharmacology Exam Drugs and Their UsesDocumento64 pagineStudy Guide for NLN RN Pharmacology Exam Drugs and Their UsesRichard BakerNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral meds: Drug dosages, mechanisms, effectsDocumento15 pagineOral meds: Drug dosages, mechanisms, effectsitsmechachaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento10 pagineDrug StudyRye IbarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Nicardipine (: ClassificationDocumento14 pagineNicardipine (: ClassificationWilliam CiferNessuna valutazione finora
- Name of Drug Route/Dose Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects/Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento9 pagineName of Drug Route/Dose Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects/Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiespauchanmnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study GuideDocumento9 pagineDrug Study GuideSh3meeNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti-inflammatory corticosteroid hydrocortisone generic and brand names, dosage, classification, actions, indications, contraindications and side effectsDocumento6 pagineAnti-inflammatory corticosteroid hydrocortisone generic and brand names, dosage, classification, actions, indications, contraindications and side effectstrinaLCNessuna valutazione finora
- CHN Drug StudyDocumento10 pagineCHN Drug StudyJoshua Cyryll ComiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento8 pagineDrug Studysarah1217Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mefenamic Acid Drug ProfileDocumento3 pagineMefenamic Acid Drug ProfileAhmad WaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Icu Drug StudyDocumento7 pagineIcu Drug StudyHazel Palomares100% (1)
- Captopril Drug Study for Congestive Heart FailureDocumento8 pagineCaptopril Drug Study for Congestive Heart FailureMae Therese B. MAGNONessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento10 pagineDrug StudyHelen ReonalNessuna valutazione finora
- Generic Name Captopril Brand NamesDocumento18 pagineGeneric Name Captopril Brand NamesAiko Villacortes100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocumento3 pagineDrug Studyanon_11638632Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento6 pagineDrug StudyChickz HunterNessuna valutazione finora
- Paracetamol and Levofloxacin Drug StudyDocumento9 pagineParacetamol and Levofloxacin Drug StudyKevin Sam AguirreNessuna valutazione finora
- Pedia Ward Drug Study...Documento12 paginePedia Ward Drug Study...Sheena Arnoco ToraynoNessuna valutazione finora
- Emergency DrugsDocumento5 pagineEmergency DrugsArra PlacidesNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrolithiasis - Drug StudyDocumento5 pagineNephrolithiasis - Drug StudyAia JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento8 pagineDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Name of The Drug Drug Classes Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityDocumento4 pagineName of The Drug Drug Classes Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityKirstele Nicole QuijanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Paracetamol Antipyretic and Analgesic GuideDocumento7 pagineParacetamol Antipyretic and Analgesic GuideAnne Monique Moran OngjocoNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study: OmeprazoleDocumento5 pagineDrug Study: Omeprazoleclau_latojaNessuna valutazione finora
- Name of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing ManagementDocumento3 pagineName of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing Managementjhappo31Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento11 pagineDrug StudyNedemar OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Amlodipine BesylateDocumento7 pagineAmlodipine BesylatebabuagoodboyNessuna valutazione finora
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesDa EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Urinary Tract Nursing Care GuideDocumento38 pagineUrinary Tract Nursing Care GuideIke Agbor97% (33)
- HAAD ReviewerDocumento35 pagineHAAD ReviewerSydRey92% (24)
- Urinary Tract Nursing Care GuideDocumento38 pagineUrinary Tract Nursing Care GuideIke Agbor97% (33)
- Urinary Tract Nursing Care GuideDocumento38 pagineUrinary Tract Nursing Care GuideIke Agbor97% (33)
- Random FactsDocumento338 pagineRandom Factscyram81100% (1)
- All Objectives HematologyDocumento45 pagineAll Objectives HematologyNursing200980% (5)
- Urinary Tract Nursing Care GuideDocumento38 pagineUrinary Tract Nursing Care GuideIke Agbor97% (33)
- Urinary Tract Nursing Care GuideDocumento38 pagineUrinary Tract Nursing Care GuideIke Agbor97% (33)
- NCLEX Lab Values GuideDocumento5 pagineNCLEX Lab Values GuideYolanda Williams100% (1)
- HAAD ReviewerDocumento35 pagineHAAD ReviewerSydRey92% (24)
- Hesi HintsDocumento16 pagineHesi HintsYolanda Williams100% (1)
- HAAD ReviewerDocumento35 pagineHAAD ReviewerSydRey92% (24)
- Lec 12 - Drugs Used in PTDocumento14 pagineLec 12 - Drugs Used in PTAiqa QaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation of Efficacy and Tolerability of Acetaminophen Paracetamol and Mefenamic Acid As Antipyretic in Pediatric Pati PDFDocumento7 pagineEvaluation of Efficacy and Tolerability of Acetaminophen Paracetamol and Mefenamic Acid As Antipyretic in Pediatric Pati PDFrasdiantiNessuna valutazione finora
- AcetaminophenDocumento3 pagineAcetaminophenShaira Tan100% (1)
- Combiflam Tablets PI - 08072019Documento13 pagineCombiflam Tablets PI - 08072019ArunNessuna valutazione finora
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Know Your OptionsDocumento11 pagineRheumatoid Arthritis: Know Your OptionsMartin UllielNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Pain Questions - LathaDocumento5 pagineAcute Pain Questions - LathaNishanth yedavalliNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbuncle, Incision, Drainage, DebridementDocumento11 pagineCarbuncle, Incision, Drainage, DebridementAlvin Germo PasuquinNessuna valutazione finora
- Leaflet 50mg/75mg Tablets Prevent Stomach UlcersDocumento1 paginaLeaflet 50mg/75mg Tablets Prevent Stomach UlcersM AyyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. John Camm Curso Anticoagulacion Charla #1 PDFDocumento68 pagineDr. John Camm Curso Anticoagulacion Charla #1 PDFCarlosVillarrealNessuna valutazione finora
- Non-Opioid Drugs: A.M.Takdir MusbaDocumento38 pagineNon-Opioid Drugs: A.M.Takdir MusbaRey AlwiwikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Pain Management: Lecture Note Powerpoint PresentationDocumento48 paginePain Management: Lecture Note Powerpoint PresentationTobiDaNessuna valutazione finora
- CASE PRESENTATION ON PUD: PEPTIC ULCER DISEASEDocumento28 pagineCASE PRESENTATION ON PUD: PEPTIC ULCER DISEASEAntoNessuna valutazione finora
- Treatment of Acute Low Back Pain - UpToDateDocumento19 pagineTreatment of Acute Low Back Pain - UpToDateJeissonPargaSalasNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento6 pagineDrug StudyDsquared100% (1)
- Herniated Nucleus Pulposus (Report) - 2Documento27 pagineHerniated Nucleus Pulposus (Report) - 2Angelu Gabrielle CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Ketorolac drug info: dosage, mechanism, indications, contraindications, adverse effectsDocumento2 pagineKetorolac drug info: dosage, mechanism, indications, contraindications, adverse effectsRona PieNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology MnemonicsDocumento91 paginePharmacology MnemonicsKnizhonki Knizhonki96% (72)
- Otc Template Pi IbuprofenDocumento3 pagineOtc Template Pi IbuprofenAnindaNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulationandin vitroEvaluationofBuccalTabletsofPiroxicam PDFDocumento11 pagineFormulationandin vitroEvaluationofBuccalTabletsofPiroxicam PDFFransisca Cornelia PutriNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Medical Abbreviations With MeaningsDocumento16 pagineCommon Medical Abbreviations With MeaningsWilliam Franz SyNessuna valutazione finora
- IV PCDocumento27 pagineIV PCNusrat Jahan MuniaNessuna valutazione finora
- InflammatoryDocumento20 pagineInflammatoryAS RifathNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study TramadolDocumento2 pagineDrug Study TramadolKersey Adricula RicaldeNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate, Tramadol, AmlodipineDocumento10 pagineDrug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate, Tramadol, AmlodipineFlauros Ryu Jabien100% (1)
- Drug Study HydrocodoneDocumento1 paginaDrug Study HydrocodoneYlrenne DyNessuna valutazione finora
- Vancouver 2010 Paralympic Pharmacy GuideDocumento146 pagineVancouver 2010 Paralympic Pharmacy GuideVsevolod BentsianovNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs Post PartumDocumento3 pagineDrugs Post PartumanreilegardeNessuna valutazione finora
- NSAIDs Ketorolac Parenteral Form Drug Test QuestionsDocumento18 pagineNSAIDs Ketorolac Parenteral Form Drug Test QuestionsKhidir BabikirNessuna valutazione finora
- Barrientos Case StudyDocumento6 pagineBarrientos Case StudyCalvin Dante BarrientosNessuna valutazione finora
- pharamcology unit 10 answersDocumento13 paginepharamcology unit 10 answersLovren YoungNessuna valutazione finora