Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
STP Framework for Airtel's Marketing Segmentation, Targeting & Positioning
Caricato da
Akanksha GuptaDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
STP Framework for Airtel's Marketing Segmentation, Targeting & Positioning
Caricato da
Akanksha GuptaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
MARKETING MANAGEMENT Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning Submitted By:- Anand Rathi
MARKETING MANAGEMANT (Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning) PART 1 Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning: 1) Segmentation: Segmentation, targeti ng, and positioning together comprise a three stage process. We first, (1) Deter mine which kinds of customers exist, then (2) Select which ones we are best off trying to serve and, finally, (3) Implement our segmentation by optimizing our p roducts/services for that segment and communicating that we have made the choice to distinguish ourselves that way. Segmentation involves finding out what kinds of consumers with different needs e xist. In the auto market, for example, some consumers demand speed and performan ce, while others are much more concerned about roominess and safety.
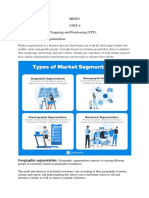
MARKETING MANAGEMANT (Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning) Types of Segmentation: 1) Geographic variables:a) Region of the world or country: East, West, South, No rth, Central, coastal, hilly, etc. b) Country size/country size: Metropolitan Ci ties, small cities, towns. c) Density of area: Urban, Semi-urban and Rural. d) C limate: Hot, Cold, Humid, Rainy. 2) Demographic variables:a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) i) j) k) Age Gender Family size Education Income Occupation Education Socioeconomic status Religion Nationality Language 3) Psychographic variables a) b) c) d) Personality Life style Value Attitude
MARKETING MANAGEMANT (Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning) 4) Behavioral variables a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) Benefit Sought. Product Usage Ra te. Brand Loyalty. Product end Use. Readiness-to-buy Stage. Decision Making Unit . Profitability. Income Status. In general, it holds true that You cant be all things to all people, and experience has demonstrated that firms that specialize in meeting the needs of one group o f consumers over another tend to be more profitable. Levels of Market Segmentati on:Mass Marketing Same product to all consumers (No segmentation) Segment Marketing Different products to one or more segments (some segmentation) Niche Marketing Different products to subgroups within segments (more segmentati on) Micromarketing Products to suit the tastes of individuals or locations (complete segmentation) Generically, there are three approaches to marketing. In the undifferentiated st rategy, all consumers are treated as the same, with firms not making any specifi c efforts to satisfy particular groups. This may work when the product is a stan dard one where one
MARKETING MANAGEMANT (Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning) Competitor really cant offer much that another one cant. Usually, this is the case only for commodities. In the concentrated strategy, one firm chooses to focus o n one of several segments that exist while leaving other segments to competitors . For example, Southwest Airlines focuses on price sensitive consumers who will forego meals and assigned seating for low prices. In contrast, most airlines fol low the differentiated strategy: They offer high priced tickets to those who are inflexible in that they cannot tell in advance when they need to fly and find i t impractical to stay over a Saturday. These travelersusually business travelerspa y high fares but can only fill the planes up partially. The same airlines then s ell some of the remaining seats to more price sensitive customers who can buy tw o weeks in advance and stay over. Note that segmentation calls for some tough ch oices. There may be a large number of variables that can be used to differentiat e consumers of a given product category; yet, in practice, it becomes impossibly cumbersome to work with more than a few at a time. Thus, we need to determine w hich variables will be most useful in distinguishing different groups of consume rs. 2) Targeting:A target market or target audience is a group of customers that the business has decided to aim its marketing efforts and ultimately its mercha ndise.[1] A well-defined target market is the first element to a marketing strat egy. The target market and the marketing mix variables of product, place(distrib ution), promotion and price are the two elements of a marketing mix strategy tha t determine the success of a product in the marketplace. A principal concept in target marketing is that those who are targeted show a strong affinity or brand loyalty to that particular brand. Research has shown that racial similarity, rol e congruence, labeling intensity of ethnic identification, shared knowledge and ethnic salience all promote positive effects on the target market. Research has generally shown that target marketing strategies are constructed from consumer i nferences of similarities between some aspects of the advertisement (e.g., sourc e pictured, language used, lifestyle represented) and characteristics of the con sumer (e.g. reality or desire of having the represented style. Consumers are per suaded by the characteristics in the advertisement and those of the consumer.
MARKETING MANAGEMANT (Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning) 3) Positioning:In marketing, positioning has come to mean the process by which m arketers try to create an image or identity in the minds of their target market for its product, brand, or organization. Although there are different definition s of Positioning, probably the most common is: identifying a market niche for a brand, product or service utilizing traditional marketing placement strategies ( i.e. price, promotion, distribution, packaging, and competition). Product positi oning process Generally, the product positioning process involves: 1) Defining t he market in which the product or brand will compete (who the relevant buyers ar e) 2) Identifying the attributes (also called dimensions) that define the produc t 'space' 3) Collecting information from a sample of customers about their perce ptions of each product on the relevant attributes 4) Determine each product's sh are of mind 5) Determine each product's current location in the product space 6) Determine the target market's preferred combination of attributes (referred to as an ideal vector) 7) Examine the fit between: 8) The position of your product 9) The position of the ideal vector 10) Position.
MARKETING MANAGEMANT (Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning) PART 2
MARKETING MANAGEMANT (Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning) SEGMENTATION OF AIRTEL Segmentation is very important because of the better pred ictability of the target consumer group and to design the proper marketing mix s trategy. On the basis of Geographic variables: Region wise: East Region (West Ben gal, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh etc) West Region (Gujarat, Rajasthan, Maharashtra etc) South Region (Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala etc) North Region (Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh etc) Central Region (Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jha rkhand etc) Density of area: Urban (Cities Such As Mumbai, Delhi, Pune, Jaipur e tc) Semi-urban (Nasik, Aurangabad, Ahemadnagar etc) Rural (Baramati, Khed, Saswa d etc) On the basis Demographic variables: Age : 1) From age group 18 to 35: As m ost of the people start using a mobile from the age of 18 so we may make a segme nt of a age group 18 to 35 as most of the will be students and remaining will be freshers working in the industry. So they need SMS plans for chatting and they also need cheap calling rates. We may provide the FRINDZ card to them.
MARKETING MANAGEMANT (Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning) 2) 35 and above: As most of these group will be working and dont use mobile for S MS and chatting. So this group needs only the calling facility at a reasonable r ate. This Group may continue using the general plan. Income PREPAID & POSTPAID : Generally the mobile service providers plan their ma rketing strategies according to the prepaid market and postpaid market. So it is basically depends upon the income of the consumer that whether he selects the p repaid or postpaid. Generally the consumers with low income choose prepaid and c onsumers with high income choose postpaid. On the basis of Behavioral variables Brand Loyalty: We can also segment it on the basis of the loyal customers and no n loyal customers of the brand. We can provide various schemes and offers to the loyal customers to retain him with our product.
MARKETING MANAGEMANT (Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning) Targeting of Airtel Airtel has targeted the premium and upper middle class. The motto behind this this only those segments should be targeted who value time and have the paying capacity. During the introduction stage there was a huge pressu re to get consumers across to hook up with their brand, because getting them to Airtel by their earlier brand and switching their brand loyalty was too tough. A irtel marketers have been concentrating totally on the business executive class but now that the basic viable volumes has been built up and prices have declined to a certain extent they are planning to venture further field. TARGETING AREAS : Professionals by giving free calls in postpaid connections. Entrepreneur by gi ving various plan in which they may get internal calling free. Youth with the FRI ENDZ Scheme. Targeting Students by introducing postpaid connection only for stude nts and with zero rentals. Positioning: The product is supposed to be a business efficiency tool. A lifesty le revolution and a status symbol The emphasis is to remove misconception that t he cell phone is an expensive means of communication Its a day to day use commodi ty and is no more a symbol of status.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Marketing Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning PF AirTelDocumento10 pagineMarketing Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning PF AirTelAnand Rathi75% (12)
- Segmentation, Targeting and PositioningDocumento8 pagineSegmentation, Targeting and PositioningNilesh SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning Process for Service Sector ManagementDocumento11 pagineSegmentation, Targeting and Positioning Process for Service Sector ManagementghaswalainshaNessuna valutazione finora
- ALM 4103 Strategic Management Course OutlineDocumento36 pagineALM 4103 Strategic Management Course OutlineReichelle Anne BereberNessuna valutazione finora
- Segmenting and TargetingDocumento22 pagineSegmenting and TargetingMalik MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Identify Attractive Market Segments and Choose A Target Marketing StrategyDocumento9 pagineIdentify Attractive Market Segments and Choose A Target Marketing StrategyUmmu Umairah100% (1)
- Quick Overview SummaryDocumento13 pagineQuick Overview SummaryPepijn SchaffersNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 C's STP 4 P'sDocumento6 pagine5 C's STP 4 P'sAda Araña DiocenaNessuna valutazione finora
- How brands are positioned in consumers' mindsDocumento4 pagineHow brands are positioned in consumers' mindsAnonymous rWn3ZVARLgNessuna valutazione finora
- Market Segmentation ChapterDocumento17 pagineMarket Segmentation Chapterswarnima singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Targeted marketing strategies through market segmentationDocumento69 pagineTargeted marketing strategies through market segmentationRisky Rider NaWazNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8: Identifying Market Segments and TargetsDocumento12 pagineChapter 8: Identifying Market Segments and TargetsJewellrie Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Market Analysis and Planning and SegmentationDocumento59 pagineMarket Analysis and Planning and SegmentationShailendra ChaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- PGD Marketing Management Assignment on Market SegmentationDocumento24 paginePGD Marketing Management Assignment on Market SegmentationPAUL TIMMYNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7Documento6 pagineChapter 7singhashish5444Nessuna valutazione finora
- Market Segmentation: Its Role in Sales Performance in Nigeria Business EnvironmentDocumento5 pagineMarket Segmentation: Its Role in Sales Performance in Nigeria Business Environmentsteven timotyNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.4 MKTG SegmentationDocumento2 pagine3.4 MKTG SegmentationdatrikamadhusudanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7Documento4 pagineChapter 7Nedzma HrvatNessuna valutazione finora
- SegmentationDocumento9 pagineSegmentationMinatoNessuna valutazione finora
- MB203 UNIT-4 Market Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning (STP) : Concepts of Market SegmentationDocumento7 pagineMB203 UNIT-4 Market Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning (STP) : Concepts of Market SegmentationARVIND YADAVNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Market SegmentationDocumento15 pagine2 Market Segmentationmboyajustine6Nessuna valutazione finora
- Market Segmentation: 1. Demographic Segmentation: The WhoDocumento12 pagineMarket Segmentation: 1. Demographic Segmentation: The WhoAtanu MojumderNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Behaviour AssignmentDocumento7 pagineConsumer Behaviour AssignmentGeorge AddaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Market Segmentation: Naveen Kumar PGFB0925Documento18 pagineMarket Segmentation: Naveen Kumar PGFB0925summernaveenNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5Documento4 pagineChapter 5PRECIOUS JOY PATIGDASNessuna valutazione finora
- 1Documento60 pagine1Shiven RahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Market SegmentationDocumento3 pagineMarket SegmentationijaertNessuna valutazione finora
- Segmentation, Targett, PositioningDocumento6 pagineSegmentation, Targett, PositioningkavitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes 3Documento3 pagineNotes 3Ankit SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- B. Steps in Target Marketing:: Market Segmentation Market Targeting Market PositioningDocumento9 pagineB. Steps in Target Marketing:: Market Segmentation Market Targeting Market PositioningSameel Ur RehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- SegmentationDocumento6 pagineSegmentationAda Araña Diocena0% (1)
- Demographic SegmentationDocumento20 pagineDemographic Segmentationbhaven9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module - 2 (HM322)Documento24 pagineModule - 2 (HM322)rfgvgfNessuna valutazione finora
- Market Segmentation ChapterDocumento17 pagineMarket Segmentation Chapterjaspal singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Classifying Customers to Develop Targeted Marketing StrategiesDocumento13 pagineClassifying Customers to Develop Targeted Marketing StrategiesOmkar Reddy PunuruNessuna valutazione finora
- Theme 7 Customer Driven Marketing StrategyDocumento9 pagineTheme 7 Customer Driven Marketing StrategyUrwa RiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Market Segmentation Targeting PositioningDocumento9 pagineMarket Segmentation Targeting PositioningAlemayehu gabisaNessuna valutazione finora
- MM Unit-2Documento20 pagineMM Unit-2ak980272Nessuna valutazione finora
- Meaning / What Is Marketing Segmentation?Documento36 pagineMeaning / What Is Marketing Segmentation?jaynishshahNessuna valutazione finora
- Market Segmentation: Submitted To: Submitted byDocumento24 pagineMarket Segmentation: Submitted To: Submitted byRuchi BansalNessuna valutazione finora
- PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING - Unit 2 STPDocumento78 paginePRINCIPLES OF MARKETING - Unit 2 STPaddityarajNessuna valutazione finora
- STPDDocumento37 pagineSTPDGaurav NavaleNessuna valutazione finora
- SegmentationDocumento50 pagineSegmentationFRABATO7Nessuna valutazione finora
- STP Marketing Framework Breaks Down Segmentation, Targeting and PositioningDocumento19 pagineSTP Marketing Framework Breaks Down Segmentation, Targeting and Positioningalankrita saikiaNessuna valutazione finora
- From-Bus. Adm. DepartmentDocumento56 pagineFrom-Bus. Adm. DepartmentgajendradoodiNessuna valutazione finora
- Segmentation, Targetting and Positioning DefinitionDocumento13 pagineSegmentation, Targetting and Positioning Definitionsumittiwary1may1988Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmaceutical PromotionDocumento25 paginePharmaceutical PromotionZisan Ahmed ZikoNessuna valutazione finora
- Market SegmentationDocumento3 pagineMarket SegmentationFaith GuballaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6Documento5 pagineChapter 6Ali RaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 5 Learning MaterialDocumento6 pagineWeek 5 Learning MaterialFatema ZehraNessuna valutazione finora
- Im Unit 3Documento10 pagineIm Unit 3Ankush TyagiNessuna valutazione finora
- Page - 1Documento17 paginePage - 1Taohid KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pom q1 Module7 Week7Documento9 paginePom q1 Module7 Week7Max Montefalco100% (1)
- Social Marketing MangementDocumento70 pagineSocial Marketing MangementVenugopal VenugopalNessuna valutazione finora
- Targeting Tourist Markets with SegmentationDocumento5 pagineTargeting Tourist Markets with SegmentationDjared James MinasNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Segmentation 1Documento3 pagineMarketing Segmentation 1Adefisayo BoluwatifeNessuna valutazione finora
- Segementatiion Targeting PositiongDocumento41 pagineSegementatiion Targeting PositiongVishal MalhotraNessuna valutazione finora
- How to Sell (eCommerce) - Marketing and Internet Marketing StrategiesDa EverandHow to Sell (eCommerce) - Marketing and Internet Marketing StrategiesNessuna valutazione finora
- Learn About Intensifiers and How to Use Them Effectively in WritingDocumento3 pagineLearn About Intensifiers and How to Use Them Effectively in WritingCheryl CheowNessuna valutazione finora
- CLS1Documento3 pagineCLS1Shaina Kaye De GuzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Market and Portfolio Management Assignment 2Documento6 pagineFinancial Market and Portfolio Management Assignment 2leeroy mekiNessuna valutazione finora
- Permit Part-2 Process-Oriented Permit in SAPDocumento13 paginePermit Part-2 Process-Oriented Permit in SAPsachinWebDNessuna valutazione finora
- WWII Engineer Amphibian TroopsDocumento162 pagineWWII Engineer Amphibian TroopsCAP History Library67% (3)
- Đề Số 1 - Đề Phát Triển Đề Minh Họa 2023Documento20 pagineĐề Số 1 - Đề Phát Triển Đề Minh Họa 2023Maru KoNessuna valutazione finora
- Life Insurance Exam Questions and Answers PDFDocumento13 pagineLife Insurance Exam Questions and Answers PDFDairo GaniyatNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study ON: The Spark Batteries LTDDocumento8 pagineCase Study ON: The Spark Batteries LTDRitam chaturvediNessuna valutazione finora
- Efectele Crizei Economice Asupra Politicilor Pietei Muncii Din RomaniaDocumento24 pagineEfectele Crizei Economice Asupra Politicilor Pietei Muncii Din Romaniacristian_incaltarauNessuna valutazione finora
- Research On Ignorance of The Law Excuses No One From ComplianceDocumento12 pagineResearch On Ignorance of The Law Excuses No One From ComplianceAnonymous iOYkz0wNessuna valutazione finora
- EIA GuidelineDocumento224 pagineEIA GuidelineAjlaa RahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Norlys 2016Documento124 pagineNorlys 2016elektrospecNessuna valutazione finora
- Elegant Tranquil Blue Agency by SlidesgoDocumento41 pagineElegant Tranquil Blue Agency by SlidesgoJoana TavaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines For Planning Conjunctive Use of SUR Face and Ground Waters in Irrigation ProjectsDocumento34 pagineGuidelines For Planning Conjunctive Use of SUR Face and Ground Waters in Irrigation Projectshram_phdNessuna valutazione finora
- Company BackgroundDocumento17 pagineCompany Backgroundzayna faizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 (Social Innovation)Documento7 pagineModule 1 (Social Innovation)Marinette Medrano50% (2)
- Frito LaysDocumento6 pagineFrito LaysElcamino Torrez50% (2)
- D882 - Pruebas A Películas.Documento11 pagineD882 - Pruebas A Películas.CamiloSilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Paper About Cebu PacificDocumento8 pagineResearch Paper About Cebu Pacificwqbdxbvkg100% (1)
- Macroeconomics Canadian 8th Edition Sayre Solutions Manual 1Documento9 pagineMacroeconomics Canadian 8th Edition Sayre Solutions Manual 1tyrone100% (52)
- The Judicial Affidavit RuleDocumento20 pagineThe Judicial Affidavit RuleMhay ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Priceliost Ecatalog 2021 Div. DiagnosticDocumento2 paginePriceliost Ecatalog 2021 Div. Diagnosticwawan1010Nessuna valutazione finora
- TROOP - of - District 2013 Scouting's Journey To ExcellenceDocumento2 pagineTROOP - of - District 2013 Scouting's Journey To ExcellenceAReliableSourceNessuna valutazione finora
- Elasticity of DemandDocumento64 pagineElasticity of DemandWadOod KhAn100% (1)
- HTTP://WWW - Authorstream.com/presentation/kunalcmehta 1123128 Exim PolicyDocumento2 pagineHTTP://WWW - Authorstream.com/presentation/kunalcmehta 1123128 Exim PolicyPranesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Office of The Controller of Examinations Anna University:: Chennai - 600 025Documento4 pagineOffice of The Controller of Examinations Anna University:: Chennai - 600 025M.KARTHIKEYANNessuna valutazione finora
- Mid Semester ExaminationDocumento2 pagineMid Semester ExaminationMOHAMMED RIHANNessuna valutazione finora
- Fuel Pumps Left in Off PositionDocumento7 pagineFuel Pumps Left in Off PositionherbuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry1207 Lab 4Documento2 pagineChemistry1207 Lab 4Kayseri PersaudNessuna valutazione finora