Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Fungi
Caricato da
Jocelyn SarcaogaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Fungi
Caricato da
Jocelyn SarcaogaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
JmJ Marist Brothers Notre Dame of Dadiangas University
Name: Claire Joy L. Sarcaoga Schedule: T-TH 12:00- 3:00 Fungi Activity 6 Introduction:
Date: July, 26 2011 Course: BsBiology 2
Fungi are heterotrophs, meaning they cant produce their own food. They are closest to animals because of its ability to absorb nutrients and not able to perform photosynthesis. Fungi are known as decomposers and most of the time they get nutrients from other organisms. They like places which are moist and warm. Fungi may grow very vast due to their mycelium and hyphae. Statement of the Problem: 1. What are the characteristics and representative species of Zygomycetes, Ascomycetes, Basidiomycetes and Deuteromycetes? 2. How do fungi appear under the microscope? 3. What is the life cycle of a typical fungus? Materials: 1-Compound Microscope 1-Slide and Slip Yeast suspension (Saccharomyces cereveseae) Prepared Slides: Corn Rust Methods: 1. Request for the materials needed. 2. Observe the different specimen under the microscope using the different objectives. 3. Draw the observed specimen fill in the figure 6. 4. Fill in the table 6.1. 5. Draw the life cycle of zygomycete and basidiomycete on the figure 6.2 and 6.3.
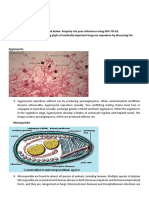
Results and Discussions: Table 6 Classification and Characteristics of Fungi. Group Characteristics Zygomycete - Vegetative mycelium that lack septa -Zygote is produce. -May reproduce sexual or asexual.
Representative Species Black bread mold
Ascomycete -Microscopic spores inside special, elongated cells or sacs. -Produces Ascospores. -May reproduce sexual or asexual.
Yeast
Basidiomycete -Produce spores that are formed outside a pedestallike structure, the basidium. -Produces Basidiospores. -May reproduce sexual or asexual.
Corn Rust
Deuteromycete -Imperfect fungi. -Unknown way of reproduction.
Molds
Kingdom fungi are a kingdom closest to plants and animals. Unlike plants they do not produce their own food; they arent capable of ingestion like animals do. They have their own way of getting their food. Fungi are using its hyphae to absorb the nutrients on its surrounding. There are different types of phylum under the kingdom fungi; they have differences from each other. Zygomycetes are fungi that are capable of producing
zygospores to reproduce. Ascomycetes are fungi that have asci where the spores reside. The basidiomycetes are fungi which are composed of basidium all over its body. Deuteromycetes are imperfect fungi, they have an unknown reproduction and most of them are causing diseases that are harmful. Some fungi are deadly and some are used for medicinal purposes. These fungi are able to live and grow as vast as a whole forest. They are known to be the biggest organism in the whole world.
Figure 6.1 S. cereveseae and corn rust under different objectives. These are the specimens that represent kingdom fungi. Fungi are known to get nutrients by absorption. They are non-photosynthetic organisms and they are not classified as animals either. These two specimens are examples of fungi. S. cereveseae is yeast also known as bakers yeast use for baking and other food related uses. It is responsible for the brewing of beer or any alcoholic drinks. It is able to multiply in a very short time, it is easily cultured. It is the most known yeast because of its usefulness for us. Corn rust can be easily recognized by the development of dark, reddish-brown pustules scattered over both the upper and lower surface of the corn leaves. It is a fungi causing disease to corns that damages the yields that may be harvest. Spores capable of infecting corn are blown northward during the growing season and become established on the corn crop. There are fungi that are helpful and useful to us and there are also some that may harm us.
Figure 6.2 Life Cycle of Black Bread mold (Rhizopus stolonifer), zygomycetes. Biology Seventh edition By: Solomon et al. 2006 This figure represents a zygomycete life cycle. A fungi may reproduce sexually or asexual. Sexual reproduction takes place only between mating different mating types. After their hyphae meet and form gametangia. ` Gametangia unite and the nuclei fuse. A single zygospore develops within a thick walled, black zygoporangium. Meiosis occurs then the zygospore germinates. The merging hypha develops sporangium. Spores are released and may germinates, giving rise to new hyphae. In asexual reproduction, certain hyphae form sporangium. When released they give rise to new hyphae. The haploid generation is dominant than the diploid generation on its life cycle.
Figure 6.3 Life Cycle of typical Basidiomycete. Biology Seventh edition By: Solomon et al. 2006 This figure shows the life cycle of a typical basidiomycete. Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of two haploid hyphae. It has different mating types to form a secondary mycelium composed of dikaryotic hyphae. Basidiomycetes develop microscopic club-shaped called basidia. Fruiting bodies periodically develop from secondary mycelium. Basidia form along the gills of the basidiocarps. In each basidium the n+n nuclei fuse. Meiosis occurs, producing four basidiospores. The basidiospores are released and they germinate to form primary mycelia. The process continues to flow. Hyphae of mycelium consist of monokaryotic cells. Unlike most other group asexual reproduction is less common in basidiomycetes. These kind of fungus are needing source of Nitrogen for them to multiply.
Conclusions: After performing the said activity the following conclusions were drawn: 1. That each of the clade of fungi has their own distinct characteristics from each other, such as biological importance and their ways of reproduction. 2. That the fungi appear under the microscope having different structures. 3. That a typical fungus produces sexually and asexually.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Little Facts of Life: 350 Mini Readings in BiologyDa EverandLittle Facts of Life: 350 Mini Readings in BiologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 5-Bio320 (Fungi)Documento49 pagineChap 5-Bio320 (Fungi)Radius JuliusNessuna valutazione finora
- Classifications of Fungi - Biology For Majors IIDocumento12 pagineClassifications of Fungi - Biology For Majors IISaviru SandivNessuna valutazione finora
- BSECSCI 14 (Fungi) Patinga, Christine Mae V.Documento4 pagineBSECSCI 14 (Fungi) Patinga, Christine Mae V.Christian PatingaNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of FungiDocumento5 pagineClassification of FungiSoumit PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- BIO 102 by DR Keshinro OMDocumento32 pagineBIO 102 by DR Keshinro OMfaborodeharyomideNessuna valutazione finora
- YeastDocumento17 pagineYeastvyoma agarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Snake ToxinsDocumento11 pagineSnake ToxinsEesha NoorNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Mycology-Chapter-OneDocumento70 pagine1 - Mycology-Chapter-OneMimo HemadNessuna valutazione finora
- FungiDocumento15 pagineFungisukikiwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro Fungi AssignDocumento15 pagineMicro Fungi Assignashhar khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Kingdom Fungi NotesDocumento4 pagineKingdom Fungi NotesAmi GNessuna valutazione finora
- Kingdom Fungi Group 3 Post LabDocumento64 pagineKingdom Fungi Group 3 Post LabClemence Marie FuentesNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Kingdom FungiDocumento26 pagineBiology Kingdom FungiFrance SaavedraNessuna valutazione finora
- DeutromycetesDocumento10 pagineDeutromyceteshendra_s_backNessuna valutazione finora
- Post Lab QuestionsDocumento2 paginePost Lab QuestionsSyafiqah AzirahNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproduction of FungiDocumento12 pagineReproduction of FungiIDSP Uttarakhand100% (1)
- MBC 305 Pat 1and 2Documento19 pagineMBC 305 Pat 1and 2Usman SurajNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap21worksheet FungiDocumento3 pagineChap21worksheet FungiJashayla GillespieNessuna valutazione finora
- Molds YeastDocumento8 pagineMolds YeastAnandNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio English Fungi Made Ayu Malina Dewi 1913041005Documento7 pagineBio English Fungi Made Ayu Malina Dewi 1913041005Ayu MalinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module On FungiDocumento10 pagineModule On FungiIsha GishNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer To Question #1Documento18 pagineAnswer To Question #1JAp BlancoNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer To Question #1Documento18 pagineAnswer To Question #1JAp BlancoNessuna valutazione finora
- C11 16-Aug-2016 Bit1007 EthDocumento12 pagineC11 16-Aug-2016 Bit1007 EthsantoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Barracas MycologyDocumento3 pagineBarracas MycologyAlleinad BarracasNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Medical Mycology: by Prof Ashraf MOGAHEDDocumento61 pagineIntroduction To Medical Mycology: by Prof Ashraf MOGAHEDlianazulak100% (2)
- SMB3103Documento147 pagineSMB3103xasantalan3Nessuna valutazione finora
- BasidiomycotaDocumento22 pagineBasidiomycotaRuchika PokhriyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Eukaryotic Microorganism SDocumento30 pagineEukaryotic Microorganism Smarvin candorNessuna valutazione finora
- Fungi Lab: Michael Ngim Biosc 145 Dr. DixonDocumento6 pagineFungi Lab: Michael Ngim Biosc 145 Dr. DixonSelella NgimNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil ScienceDocumento4 pagineSoil ScienceBheeyahh Marie AvilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acfrogchloixrhjnyk8y9iuao8lzkia Ybvszstmw7o05 Sva54tizhioflk96q018t Qihg5nva0szd9elh4yckd4bwdz0edogqipe 8fdnumu4f83qwrpqkdjeqtwry Bvbb506dhhjfkad7hjDocumento15 pagineAcfrogchloixrhjnyk8y9iuao8lzkia Ybvszstmw7o05 Sva54tizhioflk96q018t Qihg5nva0szd9elh4yckd4bwdz0edogqipe 8fdnumu4f83qwrpqkdjeqtwry Bvbb506dhhjfkad7hjParibesh BhujelNessuna valutazione finora
- General Structure and Classification of Fungus: Sakshi SinghDocumento12 pagineGeneral Structure and Classification of Fungus: Sakshi SinghShiksha singh Shiksha singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Deuteromycota EnglishDocumento6 pagineDeuteromycota EnglishMuhammad Nur50% (2)
- Characteristics of FungiDocumento3 pagineCharacteristics of Fungihely shahNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab ReportDocumento15 pagineLab ReportValentinoDullSatinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 9 - MicroorganismsDocumento20 pagineChap 9 - Microorganismsdiamehta1512Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2011 087 Microbiology Intro To Mycology FinalDocumento7 pagine2011 087 Microbiology Intro To Mycology FinalCristinaConcepcionNessuna valutazione finora
- FUNGIDocumento3 pagineFUNGIDevanand DongreNessuna valutazione finora
- General Features of AlgaeDocumento6 pagineGeneral Features of AlgaeSreeja RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Fungus-Like ProtistsDocumento21 pagineFungus-Like ProtistsMia IbayNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology (Unity & Diversity of Life) Living World: 2.2.5 ProtozoansDocumento4 pagineBiology (Unity & Diversity of Life) Living World: 2.2.5 ProtozoansIqbal A MirNessuna valutazione finora
- CLASS 11 Biological Classification Part 2 Kingdom Fungi To Lichens.Documento11 pagineCLASS 11 Biological Classification Part 2 Kingdom Fungi To Lichens.Rozita PraveenNessuna valutazione finora
- Fungal Classification, Structure, and ReplicationDocumento23 pagineFungal Classification, Structure, and ReplicationDoc RomeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Fungi (Definition Paragraph-Classification)Documento6 pagineFungi (Definition Paragraph-Classification)jefriNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 5 Part 1 FungiDocumento5 pagineChap 5 Part 1 FungiclrssNessuna valutazione finora
- Fungi Types, Morphology & Structure, Uses and Disadvantages: AscomycotaDocumento7 pagineFungi Types, Morphology & Structure, Uses and Disadvantages: Ascomycotacasey lynNessuna valutazione finora
- L4 FungiDocumento54 pagineL4 Fungif22b0054Nessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of FungiDocumento12 pagineClassification of FungiPrabhavati Ghotgalkar100% (1)
- Basidiomicetos UstigaloDocumento17 pagineBasidiomicetos UstigaloDayane ValencioNessuna valutazione finora
- DocumentDocumento9 pagineDocumentAshutosh KashyapNessuna valutazione finora
- Biodiversity of Micro-OrganismsDocumento58 pagineBiodiversity of Micro-Organismsowethugwama09Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ebook - Mushrooms - The Mushroom CultivatorDocumento374 pagineEbook - Mushrooms - The Mushroom CultivatorSunny ChosaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Mushroom CultivatorDocumento374 pagineThe Mushroom CultivatorClaude-MichelNessuna valutazione finora
- The Little Book of Mushrooms: An Illustrated Guide to the Extraordinary Power of MushroomsDa EverandThe Little Book of Mushrooms: An Illustrated Guide to the Extraordinary Power of MushroomsNessuna valutazione finora
- Mushroom Spotter's Deck: A Field Guide to Fungi & Their Age-Old WisdomDa EverandMushroom Spotter's Deck: A Field Guide to Fungi & Their Age-Old WisdomNessuna valutazione finora
- Outlines of Dairy Bacteriology, 8th edition A Concise Manual for the Use of Students in DairyingDa EverandOutlines of Dairy Bacteriology, 8th edition A Concise Manual for the Use of Students in DairyingNessuna valutazione finora
- Acog Practice Bulletin TiroidesDocumento10 pagineAcog Practice Bulletin TiroidesMerpi Alvarez Goris100% (1)
- Organs and Organ Systems P1Documento8 pagineOrgans and Organ Systems P1Arniel CatubigNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydatidiform MoleDocumento2 pagineHydatidiform MolePaola AgustinNessuna valutazione finora
- Gynae KEMU Toacs StationsDocumento8 pagineGynae KEMU Toacs StationsMuhammad Aacem Khan100% (1)
- Task 4 On BirminghamDocumento9 pagineTask 4 On BirminghamdesbestNessuna valutazione finora
- Testicular SelfexamDocumento2 pagineTesticular Selfexambenya23100% (2)
- Chapter 008Documento11 pagineChapter 008api-281340024Nessuna valutazione finora
- Protozoa and PoriferaDocumento2 pagineProtozoa and Poriferatezpur123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Placenta Umbilical CordDocumento39 paginePlacenta Umbilical Cordbel4ronaldoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Gynecology & Obstetrics Medical Conferences-The Ovary UnraveledDocumento12 pagineGynecology & Obstetrics Medical Conferences-The Ovary Unraveledovary2009Nessuna valutazione finora
- Discharge PlanDocumento5 pagineDischarge PlanYoshimi Salazar Sasaki100% (1)
- BFISDocumento1 paginaBFISEverestNessuna valutazione finora
- Theories of Labor OnsetDocumento4 pagineTheories of Labor OnsetCzarina PorciunculaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study of Menstrual Distress Questionnaire in First Year Medical StudentsDocumento4 pagineA Study of Menstrual Distress Questionnaire in First Year Medical StudentswidyaersafitriNessuna valutazione finora
- GROWTH CHARTS, Continued: Weight-For-Length PercentilesDocumento2 pagineGROWTH CHARTS, Continued: Weight-For-Length PercentilesSolom SlmNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper 2 Biology 1996 Paper 2+ansDocumento19 paginePaper 2 Biology 1996 Paper 2+ansapi-3812894100% (1)
- Effect of Antidepressant Medications On Semen Parameters and Male FertilityDocumento8 pagineEffect of Antidepressant Medications On Semen Parameters and Male FertilitySueNessuna valutazione finora
- Gender IdentityDocumento5 pagineGender IdentityMiss_M90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Palisade Mesophyll Cells in LeaveDocumento2 paginePalisade Mesophyll Cells in LeaveAisha ShahidNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Reproduction WJECDocumento12 pagineHuman Reproduction WJECTharanga HewabuhageNessuna valutazione finora
- Prenatal Diagnosis - Morphology Scan and Invasive MethodsDocumento220 paginePrenatal Diagnosis - Morphology Scan and Invasive MethodsIndera VyasNessuna valutazione finora
- Individual Activity Reproductive SystemDocumento3 pagineIndividual Activity Reproductive Systemshiela100% (1)
- Format For Listing Empaneled Providers For Uploading in State/UT WebsiteDocumento17 pagineFormat For Listing Empaneled Providers For Uploading in State/UT WebsiteSpace HR100% (1)
- Survey of Family in Kathmandu FinalDocumento90 pagineSurvey of Family in Kathmandu FinalIrada Parajuli GautamNessuna valutazione finora
- Giant Omphalocele With OEIS Complex - A Case ReportDocumento3 pagineGiant Omphalocele With OEIS Complex - A Case ReportIOSRjournalNessuna valutazione finora
- A Level Biology CAIE Topic 14 Control and CoordinationDocumento75 pagineA Level Biology CAIE Topic 14 Control and CoordinationADEEL AHMAD100% (1)
- Chronic Kidney Disease and The Involvement of Estrogen Hormones in Its Pathogenesis and ProgressionDocumento10 pagineChronic Kidney Disease and The Involvement of Estrogen Hormones in Its Pathogenesis and Progressionshe-docNessuna valutazione finora
- Production of Hybrid CatfishDocumento6 pagineProduction of Hybrid Catfishaji mustofaNessuna valutazione finora
- Simone de Beauvoir: Is Impossible For A Bird To Fly On Only One Wing." - Swami VivekanandaDocumento5 pagineSimone de Beauvoir: Is Impossible For A Bird To Fly On Only One Wing." - Swami VivekanandapramitNessuna valutazione finora
- Uwise HYDocumento3 pagineUwise HYJack GuccioneNessuna valutazione finora