Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Semester 1 Chapter 2 Communicating Over The Network V 4.0
Caricato da
Elvedin SalihovicDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Semester 1 Chapter 2 Communicating Over The Network V 4.0
Caricato da
Elvedin SalihovicCopyright:
Formati disponibili
SEMESTER 1 CHAPTER 2 Communicating over the Network V 4.0 2.0.
1
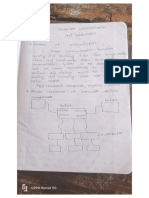
What are the five aspects of the information network we will focus on in this course? Devices that make up the network Media that connect the devices Messages that are carried across the network Rules and processes that govern network communications Tools and commands for constructing and maintaining networks Message source, destination or receiver, channel. Data or information networks capable of carrying many different types of communications, including traditional computer data, interactive voice, video, and entertainment products. It would cause delays.
2.1.1
What are the three elements of communication? What is the definition of the term network for this course? What would happen to the network if a message was sent as one massive continuous stream of bits? Define segmentation of messages What are the 2 advantages of segmentation?
2.1.2
Breaks communication into pieces. Increase the reliability of network communications. By sending smaller individual pieces from source to destination, many different conversations can be interleaved on the network. A process where multiple data streams are combined into one signal. Visible components on a network platform such as laptops, pc, switches. These devices form the interface between the human network and the underlying communication network, Referred to end device, device that communicates over network. Servers are hosts that have software installed that enables them to provide information and services, like email or web pages, to other hosts on the network. Clients are hosts that have software installed that enables them to request and display the information obtained from the server. Hubs, Switches, Routers, Communication servers and modems, security devices. Regenerate and retransmit data signals Maintain information about what pathways exist through the network and internetwork Notify other devices of errors and communication failures Direct data along alternate pathways when there is a link failure Classify and direct messages according to QoS priorities Permit or deny the flow of data, based on security settings Copper, fiber optic, and wireless. The distance the media can successfully carry a signal. The environment in which the media is to be installed.
What is multiplexing?
2.1.3 2.1.4
What is hardware on a network? What are end devices on a network? What is the definition of a host? What is the definition of a server? What is the definition of a client?
2.1.5
List examples of intermediary devices. List examples of process that intermediary devices perform.
2.1.6
What are the 3 primary types of media used in modern networks? What criteria should be used to select network media?
2.2.1
What are the ways in which network infrastructure can vary? What is the definition of a LAN?
2.2.2 2.2.3
What is the definition of a WAN? What is an internetwork? What is an intranetwork?
2.2.4. 1
Define a NIC Define a physical port Define an interface
2.3.2
What process do networking layer protocol suites describe?
What is proprietary?
2.3.3
What does the use of standards and protocols provide? What is an application protocol? What is a Transport Protocol? What is the Internetwork Protocol
2.3.4
What is the Network Access Protocol?
2.3.5 2.4.1
What do networking protocols describe? What are the benefits of using a layered model to describe networking?
The amount of data and the speed at which it must be transmitted. The cost of the media and installation The size of the area covered The number of users connected The number and types of services available An individual network usually spans a single geographical area, providing services and applications to people within a common organizational structure, such as a single business, campus or region Networks that connect LANs in geographically separated locations The interconnection of two or more network connections. Private connection of LANs and WANs that belongs to an organization, and is designed to be accessible only by the organization's members, employees, or others with authorization. Network Interface Card - A NIC, or LAN adapter, provides the physical connection to the network at the PC or other host device A connector or outlet on a networking device where the media is connected to a host or other networking device. Specialized ports on an internetworking device that connect to individual networks The format or structure of the message The method by which networking devices share information about pathways with other networks How and when error and system messages are passed between devices The setup and termination of data transfer sessions One company or vendor controls the definition of the protocol and how it functions. The use of standards in developing and implementing protocols ensures that products from different manufacturers can work together for efficient communications. Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is a common protocol that governs the way that a web server and a web client interact Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is the transport protocol that manages the individual conversations between web servers and web clients The most common internetwork protocol is Internet Protocol (IP). IP is responsible for taking the formatted segments from TCP, encapsulating them into packets, assigning the appropriate addresses, and selecting the best path to the destination host. Network access protocols describe two primary functions, data link management and the physical transmission of data on the media Functions that occur during network communications Assists in protocol design Fosters competition because products from different vendors can work together. Prevents technology or capability changes in one layer from affecting other layers above and below. Provides a common language to describe networking
2.4.2
2.4.3
2.4.4
What are the two basic types of networking models? What are the two primary models used when describing networking? What is done at the Application Layer? What is done at the Transport Layer? What is done at the Internet Layer? What is done at the Network Access Layer? What are the seven steps in a complete communication process?
functions and capabilities. Protocol models and reference models. OSI and TCP/IP Represents data to the user plus encoding and dialong control. Supports communication between diverse devices across diverse networks. Determines the best path through the network. Controls the hardware devices and media that make up the network. 1. Creation of data at the Application layer of the originating source end device 2. Segmentation and encapsulation of data as it passes down the protocol stack in the source end device 3. Generation of the data onto the media at the Network Access layer of the stack 4. Transportation of the data through the internetwork, which consists of media and any intermediary devices 5. Reception of the data at the Network Access layer of the destination end device 6. Decapsulation and reassembly of the data as it passes up the stack in the destination device 7. Passing this data to the destination application at the Application layer of the destination end device Data - The general term for the PDU used at the Application layer Segments Packet Frame Bits From top to bottom This process is reversed at the receiving host. The data is decapsulated as it moves up the stack toward the end user application. Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link, Physical. Transport Timing and Synchronization Bits Destination and Source Physical Addresses Destination and source Logical Network Addresses Destination and Source Process Number Encoded Application Data. Frame
2.4.5
2.4.6. 1 2.4.6. 2 2.4.7 2.4.8 2.5.1
What is the PDU for the application layer? What is the Transport Layer PDU? What is the PDU for the Internet Layer? What is the PDU for the Network Access Layer? What PDU is used when physically transporting the information over the medium? How is the protocol stack processed when sending information? What is the process use at the receiving end called? What are the seven layers of the OSI Model? Which Layers of the OSI Model parallel with the TCP/IP Model? What does the physical layer do? What addresses does the data link layer use? What address does the network layer use? What does the transport layer use? What do the upper layers use? What is the PDU for Layer 2 called
2.5.2
2.5.3
What is the layer 2 address called? What happens after the frame has reached its destination? What are layer 3 devices primarily designed for? What address is used at Layer 3? What is the PDU of the Layer 3 information? Which device decapsulates the frame at the edge of a network? What does a router do? What happens when the frame reaches the end device? What does the information in the frame provide at Layer 4? How is each application or service represented at Layer 4?
MAC Address Information is removed as the data is decapsulated and moved up the protocol stack to Layer 3. To move data from one local network to another local network within an internetwork must include identifiers that enable intermediary network devices to locate hosts on different networks Header of the packet. Router Use the network identifier portion of this address to determine which path to use to reach the destination host The frame and packet headers are removed and the data moved up to Layer 4. Specific process or service running on the destination host device that will act on the data being delivered By Port Number
2.5.4
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Hacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisDa EverandHacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Data CommunicationDocumento36 pagineIntroduction To Data CommunicationAbdikarim AbdullahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networking Refers To Connected Computing Devices 222Documento13 pagineComputer Networking Refers To Connected Computing Devices 222RAY COOLNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento22 pagineChapter 2Abdullah KhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- CN 1Documento7 pagineCN 1T024KOUSTAV CHATTERJEENessuna valutazione finora
- 201980090184+computer Network Final AssignmentDocumento10 pagine201980090184+computer Network Final AssignmentMd. Ziaul Haque ShiponNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Communications and NetworkingDocumento55 pagineData Communications and NetworkingnadritzyNessuna valutazione finora
- C2Documento32 pagineC2getagetagetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment System: Take Assessment - Enetwork Chapter 2 - Ccna Exploration: Network Fundamentals (Version 4.0)Documento4 pagineAssessment System: Take Assessment - Enetwork Chapter 2 - Ccna Exploration: Network Fundamentals (Version 4.0)Mohamed AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE541 Data Network 1: Communicating Over The NetworkDocumento37 pagineECE541 Data Network 1: Communicating Over The NetworkAzri AzsrNessuna valutazione finora
- Modul CCNA Cyber Ops Day5eDocumento54 pagineModul CCNA Cyber Ops Day5eFerdy JuliyantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 - Protocol Architecture - Computer NetworksDocumento12 pagineChapter 8 - Protocol Architecture - Computer Networkschandushar1604100% (3)
- Handout CS407 - Routing and SwitchingDocumento186 pagineHandout CS407 - Routing and SwitchingThe Muslim LadyNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking - Chapter Two-1Documento25 pagineNetworking - Chapter Two-1minichelNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Fundamentals - Chapter 2Documento43 pagineNetwork Fundamentals - Chapter 2Henrry ClavijoNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Models: Ambo University Woliso Campus Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceDocumento73 pagineNetwork Models: Ambo University Woliso Campus Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceNoel GirmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rooman Technologies: Vocational Training Project Report OnDocumento25 pagineRooman Technologies: Vocational Training Project Report OnCatherine NippsNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA 1 Chapter 7 NotesDocumento7 pagineCCNA 1 Chapter 7 Notesdercole69Nessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA Exploration - Network Fundamentals 7 Data Link Layer 7.0 Chapter Introduction 7.0.1 Chapter IntroductionDocumento35 pagineCCNA Exploration - Network Fundamentals 7 Data Link Layer 7.0 Chapter Introduction 7.0.1 Chapter IntroductiongetagetagetaNessuna valutazione finora
- PART (1) : Assignment Brief and Guidance: (Scenario)Documento15 paginePART (1) : Assignment Brief and Guidance: (Scenario)Minh Tuấn NgôNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter7 Data Link LayerDocumento91 pagineChapter7 Data Link LayerGladys EliverNessuna valutazione finora
- CSE25NFE - Chapter 2 - Week 2and 3Documento62 pagineCSE25NFE - Chapter 2 - Week 2and 3mashfiq islamNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networks HandbookDocumento189 pagineComputer Networks HandbookDhirenkumar RathodNessuna valutazione finora
- E-Commerce Chapter 2: E-Mail and Internet 2.1 Computer Communication SystemDocumento10 pagineE-Commerce Chapter 2: E-Mail and Internet 2.1 Computer Communication Systemshravan1108Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networks:: OSI Reference ModelDocumento11 pagineComputer Networks:: OSI Reference ModelMasterNessuna valutazione finora
- Examenes de CiscoDocumento37 pagineExamenes de CiscoClevemanNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 Exam Answers: Physical Data LinkDocumento35 pagineModule 2 Exam Answers: Physical Data LinkLukáš MračekNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking Basics: Dept. of Computer Science Faculty of Science and TechnologyDocumento33 pagineNetworking Basics: Dept. of Computer Science Faculty of Science and TechnologyMahmud Ridwan JoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes-Lec 1 - Introductory LectureDocumento75 pagineNotes-Lec 1 - Introductory LectureWaseem FarooqNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Data Link LayerDocumento35 pagine7 Data Link LayerRashed ZamanNessuna valutazione finora
- CCN Note First Module - CompressedDocumento21 pagineCCN Note First Module - CompressedsbaleemaNessuna valutazione finora
- Considerations in Planning A Network Infrastructur1Documento4 pagineConsiderations in Planning A Network Infrastructur1humbuNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of Comp NWsDocumento42 pagineOverview of Comp NWsfahana abdul vahabNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1: Networking Theory & Java Overview: Prepared By: Siti Nur Ain FTK 2016Documento38 pagine1.1: Networking Theory & Java Overview: Prepared By: Siti Nur Ain FTK 2016ainnNessuna valutazione finora
- 17BCS2998 Assignment1Documento7 pagine17BCS2998 Assignment1samswag2898Nessuna valutazione finora
- CN - Question BankDocumento45 pagineCN - Question BankJAYA DHARSHINI GNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Device Configuration PDFDocumento24 pagineChapter 1 Device Configuration PDFShambel WorkuNessuna valutazione finora
- CS2302-Computer Networks - Anna University Engineering Question Bank 4 UDocumento49 pagineCS2302-Computer Networks - Anna University Engineering Question Bank 4 UsamlawNessuna valutazione finora
- CISCO-7 Data Link LayerDocumento27 pagineCISCO-7 Data Link LayerPraveen KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- BSNLDocumento14 pagineBSNLRavi SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3: Network Protocols and Communications: ObjectivesDocumento8 pagineChapter 3: Network Protocols and Communications: Objectivesovidiu0702Nessuna valutazione finora
- Define Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationDocumento5 pagineDefine Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationAbu SayedNessuna valutazione finora
- Name - Prajwal Ghale Roll On - NP000477 Section - B: Question No.1Documento4 pagineName - Prajwal Ghale Roll On - NP000477 Section - B: Question No.1Prajwal GhalezNessuna valutazione finora
- Define Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationDocumento4 pagineDefine Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationAbu SayedNessuna valutazione finora
- Define Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationDocumento4 pagineDefine Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationAbu SayedNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud NetworkingDocumento26 pagineCloud NetworkingHeliosNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking NotesDocumento10 pagineNetworking NotesADITYA RAJNessuna valutazione finora
- Internetworking Models: Model Was Created by The International Organization ForDocumento45 pagineInternetworking Models: Model Was Created by The International Organization Forkerya ibrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA Final Exam ReviewerDocumento50 pagineCCNA Final Exam ReviewerBdick CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento24 pagineChapter 2Sue BrandrethNessuna valutazione finora
- CN Module-IDocumento24 pagineCN Module-Imbucse a9Nessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA Network Fundamentals Chapter 2 Exam AnswersDocumento27 pagineCCNA Network Fundamentals Chapter 2 Exam AnswersSelvir KamberovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter One (Net Admin 2021)Documento55 pagineChapter One (Net Admin 2021)Mirko MekonenNessuna valutazione finora
- Layer OSIDocumento3 pagineLayer OSIClarence Joy BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- IS 103 Chapter 4Documento20 pagineIS 103 Chapter 4Batang PasawaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers 1Documento2 pagineAnswers 1Carl Siga100% (1)
- 1.1 Networking: General Network Techniques - When Computers Communicate On A Network, They SendDocumento66 pagine1.1 Networking: General Network Techniques - When Computers Communicate On A Network, They SendSanthosh SomaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Brief Summary On TCP/IPDocumento30 pagineA Brief Summary On TCP/IPShubham VishwakarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- CCDN NotesDocumento35 pagineCCDN NotesYeekshu ChouhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Asiignment With SolutionDocumento56 pagineAsiignment With SolutionmaulikNessuna valutazione finora
- What's New in VENUE 5.1 Software For S6LDocumento12 pagineWhat's New in VENUE 5.1 Software For S6LJulian BuitragoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sybase IQ Installation and ConfigurationDocumento112 pagineSybase IQ Installation and ConfigurationVijaya ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Scanner Premium v248 Latest PDFDocumento2 pagineNetwork Scanner Premium v248 Latest PDFGregoryNessuna valutazione finora
- St-55 Data Communication (Compatibility Mode)Documento28 pagineSt-55 Data Communication (Compatibility Mode)Ranjeet SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- X12DPT B6Documento154 pagineX12DPT B6RavivarNessuna valutazione finora
- T5000 ManualDocumento394 pagineT5000 ManualMike MooreNessuna valutazione finora
- Iq Solutions Appliances Tech Specs - April 6, 2020Documento86 pagineIq Solutions Appliances Tech Specs - April 6, 2020Lucho OrtegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs PDFDocumento5 paginePacket Tracer - Configuring VLANs PDFNaufal Saidhus SyuhurNessuna valutazione finora
- Elastix 2.3 HA ClusterDocumento12 pagineElastix 2.3 HA Clusterleossj2Nessuna valutazione finora
- E2 PTAct 2 9 1 DirectionsDocumento2 pagineE2 PTAct 2 9 1 DirectionsAsad RiazNessuna valutazione finora
- AVCOM Master GUI User GuideDocumento23 pagineAVCOM Master GUI User GuideatitomaximNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 1 - Introduction To WWWDocumento27 pagineChapter - 1 - Introduction To WWWsagarmethaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gigavue Cloud Suite For Azure - Data SheetDocumento8 pagineGigavue Cloud Suite For Azure - Data Sheetjianhao weeNessuna valutazione finora
- Control Units System - Ul Product Iq 4100esDocumento13 pagineControl Units System - Ul Product Iq 4100escnreyes3Nessuna valutazione finora
- 500 Mbps Mini Powerline Ethernet Adapter: Edition 1, 03/2012Documento52 pagine500 Mbps Mini Powerline Ethernet Adapter: Edition 1, 03/2012UlrikAndréTuemandNessuna valutazione finora
- Technicolor TC7300E PDFDocumento34 pagineTechnicolor TC7300E PDFJuan GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- User's Guide: Smartpack2 Master ControllerDocumento32 pagineUser's Guide: Smartpack2 Master ControllerNeacsu Florin-MariusNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1Documento25 pagineLecture 1Mei ÀsísNessuna valutazione finora
- NI SMD-7613/7614/7615/7616: User ManualDocumento50 pagineNI SMD-7613/7614/7615/7616: User ManualManunoghiNessuna valutazione finora
- aBA2128 PDFDocumento82 pagineaBA2128 PDFblade520Nessuna valutazione finora
- Network Components-3Documento2 pagineNetwork Components-3Ahmed SayedNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT-1 Part-A: 1. Define E-CommerceDocumento52 pagineUNIT-1 Part-A: 1. Define E-CommerceAbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- WCR G54 ManualDocumento41 pagineWCR G54 ManualChristian Loyola100% (1)
- New Products and Solutions Directory: 2018 Automation Fair® EventDocumento75 pagineNew Products and Solutions Directory: 2018 Automation Fair® EventJuan Esteban Benjumea BenjumeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethernet Storage Guy Multimode VIF - 1597495433Documento42 pagineEthernet Storage Guy Multimode VIF - 1597495433George ZavalisNessuna valutazione finora
- LOYTEC Function Descriptions 2020 ENDocumento16 pagineLOYTEC Function Descriptions 2020 ENEbuzer GÜLHANNessuna valutazione finora
- 1050 Series Product Brochure - EnglishDocumento8 pagine1050 Series Product Brochure - EnglishRyan WilliamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Learner Guide Troubleshooting HP Networks 1041 No WatermarkDocumento108 pagineLearner Guide Troubleshooting HP Networks 1041 No WatermarkИбрагим Озден ДуманNessuna valutazione finora
- Administrate Network and Hardware PeripheralsDocumento14 pagineAdministrate Network and Hardware PeripheralsGizaw TadesseNessuna valutazione finora
- AKM Server Management GuideDocumento155 pagineAKM Server Management GuidekevindanthonyNessuna valutazione finora