Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Banlaw Sales Brochures FuelTrackTM System Overview
Caricato da
api-3752216Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Banlaw Sales Brochures FuelTrackTM System Overview
Caricato da
api-3752216Copyright:
Formati disponibili
1 FuelTrackTM System Overview
Banlaw Pipeline’s FuelTrackTM Fuel Management System is setting the standards in fuel monitoring and control.
FuelTrackTM Fuel Management System comprises of FuelTrackTM System Software application which is
Microsoft Windows compliant and a FuelTrackTM Depot unit which monitors and controls the fuel distribution.
1.1 FuelTrackTM System Software overview
The FuelTrackTM System Software provides a user friendly interface to configure and monitor the fuel
management system. Microsoft Access is used as the backend database providing ODBC and OLE connectivity
to other programmes such as Excel. This connectivity provides a method of extracting fuel transaction data for
reporting and interfacing to business systems such MIMS.
FuelTrackTM uses Crystal Reports for all its default reports:
• Fuel control report by day (litres/date/time/unit no/location dispensed)
• Fuel Control report by Unit No (litres/date/time/location dispensed)
• Total Volume dispensed report (by day)
• Total Volume dispensed report (by month)
• Total Volume dispensed by fleet (by day)
• Total Volume dispensed by fleet (by month)
• provide management reports by unit, group & class fuel & lube usages
• report to purchasing on stock levels & ordering,
Main FuelTrackTM System Screen
“Global Leaders in Hydrocarbon Management Systems” 1
1.2 FuelTrackTM Depot Unit overview
The FuelTrackTM Depot unit is a Microprocessor based system that is locally manufactured and supported by
Banlaw Pipeline. The Depot systems offer total flexibility in the control and monitoring of all different fuels,
lubes and oils.
• Robust and Industrially Designed
• Operation is Intuitive and user friendly
• Large character LCD user interface
• Provides automatic or manual entry vehicle identification
• Independently configurable
• Can monitor and control six (6) nozzles
• FuelTrackTM System can recognise up to 1,000 vehicles
• Individually retain in access of 10,000 transactions before the
last one if removed from the list
• Allows fuel transactions of up to 6.5 Million Litres to 2 decimal
places
• Four (4) digit User security access can be enabled with two (2)
levels of security, user and supervisor
• Ensure that fuel type matches vehicle requirements
• Can dispense by user entered batch levels
• Vehicles can placed into classes with 100 classes available.
Depots then control transaction to class limit.
• Transactions are recorded by type:
o T – Auto ID Transaction
o M – Manual Transaction FuelTrackTM Depot
o P – Pin Number Validated Transaction
o S – SMU Transaction
o E – SMU Transaction with manually entered engine hours
o O – SMU Transaction with manually entered odometer value
o D – Default entry (No identification detected)
• Configuration changes are locally logged and time stamped
• Engine hours can be automatically or manually entered
• Vehicle odometer can be automatically or manually entered
• Transactions can be logged by vehicle only or by user and vehicle
• Contractors can be provided with temporary pin numbers which automatically timeout after the preset
time.
• Depots can have water detection and or over fill protection implemented for automatic shutoff of fuel
lines.
• Depot nozzles can be configured to monitor lubricants and coolant and request user reason codes.
o Compartment – Engine, Hydraulic, Transmission, Coolant, Steering
o Service Type – Top Up, General Service, Mechanical failure
• System alarms with individual selection of email from and to addresses.
Enclosure: An IP67 rated cast aluminium enclosure Dimensions 90x260x160mm. Finish: Powder Coated Blue.
Power Supply: 250- 89 VAC or 12-24 VDC regulated power supply is installed inside the unit.
“Global Leaders in Hydrocarbon Management Systems” 2
1.3 Vehicle Recognition: Automatic ID
Each Depot Unit Console can monitor six issue points; two of the six nozzles have Automatic Identification
functionality. Once a fuel nozzle is connected, the Unique Serial Chip ID embedded into the fuel receiver is
sampled. The Serial Chip ID is a 12 Character Hex number. The Serial Chip is registered against the Vehicle
Unit Number and is stored in a memory buffer of the Depot Unit. This means that security is maximised as only
the vehicle that the nozzle is connected to can receive fuel - provided that it has been registered – thus preventing
unregistered receivers being issued fuel.
Plant Equipment Dry-Break Receiver - Automatic Vehicle Recognition is carried out upon nozzle connection.
A FuelTrack Fuel Receiver (BMS23) replaces the existing fuel receiver, and performs the same “refuelling
function”. The BMS23 incorporates a unique ID chip, which remains passive until a fuel nozzle is connected.
Plant Equipment Dry-Break Nozzle - The Dry-Break nozzle (BMS800/BMS1000) is specially designed to
allow for automatic vehicle identification. Its functionality remains the same as the existing nozzle. A data wire
runs inside the fuel hose from within the nozzle and eventually “breaks out” to connect to the depot unit. The
Data wire is powered by a max of 5VDC, 5mA. The Depot Unit samples for Unit ID connection every ½ second.
If the nozzle is disconnected or if the vehicle drives away with the nozzle still connected, the Unit ID is lost and
the pump and control valves can be configured to promptly shut down.
Light Vehicles and Splash Filled Equipment - A Receiver adapter is fitted to each piece of equipment that also
houses a serial chip ID, which remains passive until a nozzle is connected.
Splash Fill Nozzle - A Splash fill nozzle is modified to accommodate for Automatic Vehicle Identification. This
consists of a “Snap” fitting collar that is fitted to the neck of the nozzle. The nozzle mates with the receiver
adapter and the Vehicle ID is sampled similar to the method that is used by the Dry-Break system.
Auto ID Nozzle
Auto ID receiver
“Global Leaders in Hydrocarbon Management Systems” 3
1.4 Vehicle Recognition
SMARTKeys - SMARTkeys are a cost effective method of identifying vehicles. Using a SMARTkey in order to
receive fuel requires the operator to touch the key - typically attached to say the key ring of the vehicle - against
a “reader” that is mounted on the face of the Depot Unit Console. The SMARTKey is recognised by the Depot
Unit and on validation the user is asked for to enter the nozzle required from the list of available nozzles.
Security may be enhanced by requesting User identification in the form of a manual user PIN number before
fuel/oil is issued.
KeyPad Manual Entry – If the SMARTKey is not available, vehicle recognition can be achieved using the
keypad on the depot unit console. Vehicle identification must be manually entered and if required user PIN
number as well.
Identification using
SMARTKey
1.5 SMU Hours and Odometer Capture
The monitoring of engine hours and or odometers can be automatically monitored by Banlaw Pipeline Service
Metered Units (SMUs). There are two types of SMU one for Heavy vehicles and one for Light Vehicles. An
SMU also has an onboard unique vehicle identification which ensures that engine hours and odometers are
recorded to the respective vehicle by the FuelTrackTM system.
The SMU is installed onboard the vehicle, for light vehicles typically inside the cabin, for heavy vehicle
externally normally near the fuel receiver. The SMU inputs are connected to the digital outputs on the engine
hour meter or engine oil pressure sensor and vehicle odometer. The SMU then logs engine hours and or
odometer pulses if connected. The procedure for obtaining fuel is that a Banlaw SMU SMARTKEY is used
instead of a standard SMARTKEY. The SMU SMARTKEY is placed on the SMU reader and the vehicle
identification, engine hours and odometer values are written to the SMU SMARTKey by the SMU. The SMU
SMARTKey is then pressed onto the FuelTrackTM Depot reader as per the standard SMARTKey. The
FuelTrackTM Depot automatically identifies that it’s a SMU SMARTKey that is used and transfers the vehicle
identification, engine hours and odometer values if enabled for the nozzle selected. Refuelling is then as normal.
Light Vehicle
SMU
Heavy Vehicle
SMU
“Global Leaders in Hydrocarbon Management Systems” 4
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Data Acquisition from HD Vehicles Using J1939 CAN BusDa EverandData Acquisition from HD Vehicles Using J1939 CAN BusNessuna valutazione finora
- "Gps Off-Line" MonitoringDocumento36 pagine"Gps Off-Line" MonitoringRakesh PonnojuNessuna valutazione finora
- Cen-Tech (Harbor Freight) Scan Tool - 60794Documento84 pagineCen-Tech (Harbor Freight) Scan Tool - 60794marks007577850% (6)
- Automatic Number Plate Recognition: Fundamentals and ApplicationsDa EverandAutomatic Number Plate Recognition: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Fuel Theft Using GSM and GpsDocumento62 pagineFuel Theft Using GSM and GpsbazeeshaikngmNessuna valutazione finora
- OTI EasyFuelPlus Brochure EnglishDocumento2 pagineOTI EasyFuelPlus Brochure EnglishHarshal KulkarniNessuna valutazione finora
- Fuel Tank Monitoring SystemDocumento3 pagineFuel Tank Monitoring SystemCALLCOMM FUEL LEVEL SENSOR AND SOLUTIONNessuna valutazione finora
- G LocatorDocumento8 pagineG LocatorHimanshu VarshneyNessuna valutazione finora
- Novedades Jaltest CV 221 enDocumento13 pagineNovedades Jaltest CV 221 enqusayNessuna valutazione finora
- C-PAC Control Philosophy OverviewDocumento4 pagineC-PAC Control Philosophy OverviewYan LuzhanskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Computador de Bordo - Autool-X50-Plus-Car-Obd-Hud-Smart-Digital-Meter-User-ManualDocumento13 pagineComputador de Bordo - Autool-X50-Plus-Car-Obd-Hud-Smart-Digital-Meter-User-ManualIvanorTrentinNessuna valutazione finora
- Tachosoft Kilometraje Calculator ManualDocumento22 pagineTachosoft Kilometraje Calculator ManualAcosta Manuel100% (3)
- User Guide: Tachosoft Online Mileage CalculatorDocumento22 pagineUser Guide: Tachosoft Online Mileage CalculatorMarcelo DecimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation 18may - PlatformDocumento23 paginePresentation 18may - PlatformleoboppNessuna valutazione finora
- Vehicle Tracking System & Fleet Management Purchase Proposal For Mr.Documento10 pagineVehicle Tracking System & Fleet Management Purchase Proposal For Mr.Matthew Franklin60% (5)
- Final Year Mechanical Projects at Chennai and BangaloreDocumento3 pagineFinal Year Mechanical Projects at Chennai and BangaloreAshokkumarKrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2014 ACCESSORIES AND EQUIPMENT Electronic Control Modules - Service Information - Compass & Pa..Documento53 pagine2014 ACCESSORIES AND EQUIPMENT Electronic Control Modules - Service Information - Compass & Pa..JizzbagNessuna valutazione finora
- MS300 Manual - 1.01Documento39 pagineMS300 Manual - 1.01xuzebin100% (1)
- Trekntell - User Guide - Activation ProcessDocumento32 pagineTrekntell - User Guide - Activation ProcessHarun VijayakumaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Automatic Fuel Tank Monitoring Tracking Theft DeteDocumento4 pagineAutomatic Fuel Tank Monitoring Tracking Theft DetecafubodoNessuna valutazione finora
- Asset Tracking and Fleet TelematicsDocumento32 pagineAsset Tracking and Fleet TelematicsMusasizi MusaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fuel Log 2Documento2 pagineFuel Log 2wangdid khatiNessuna valutazione finora
- T24 Fleet GPS Tracker SystemDocumento4 pagineT24 Fleet GPS Tracker SystemNnanna ChidiebereNessuna valutazione finora
- Freightliner BC M2 Driver Manual PDFDocumento197 pagineFreightliner BC M2 Driver Manual PDFRubén GonzàlezNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Bulletin: SECTION: 307-00Documento2 pagineTechnical Bulletin: SECTION: 307-00GPS MPWTNessuna valutazione finora
- Mhub 855Documento2 pagineMhub 855ucb51525354Nessuna valutazione finora
- Manual-Motor de Gasolina Cm11 MkiiDocumento4 pagineManual-Motor de Gasolina Cm11 MkiiNallely MassoNessuna valutazione finora
- Freightliner 108SD 114SD Truck Driver's Manual PDFDocumento192 pagineFreightliner 108SD 114SD Truck Driver's Manual PDFmucusseteNessuna valutazione finora
- Owner's Manual & Safety InstructionsDocumento84 pagineOwner's Manual & Safety InstructionsLuis LópezNessuna valutazione finora
- Chime/Buzzer Warning SystemsDocumento6 pagineChime/Buzzer Warning Systemsthomas rulduNessuna valutazione finora
- Fuelomat Gold Brochure Soft VersionDocumento4 pagineFuelomat Gold Brochure Soft VersionYuttanaNessuna valutazione finora
- EMD Mi 1746Documento22 pagineEMD Mi 1746Kim PedersenNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluidscan Handheld Lubricant Condition MonitorDocumento11 pagineFluidscan Handheld Lubricant Condition MonitormancjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Freightliner Coronado 122SD and 132SD Driver's Manual PDFDocumento183 pagineFreightliner Coronado 122SD and 132SD Driver's Manual PDFAram MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Fuel Management SystemDocumento9 pagineFuel Management Systemsudhirbane17Nessuna valutazione finora
- Issued: November, 2020Documento4 pagineIssued: November, 2020sohail nasirNessuna valutazione finora
- RashidJLR SCRIPT Tool IntroductionDocumento6 pagineRashidJLR SCRIPT Tool IntroductionCabrio SpecNessuna valutazione finora
- A4 - Intro To Automatic Transmissions July 2008Documento67 pagineA4 - Intro To Automatic Transmissions July 2008Jhay Dela Cruz CoteloNessuna valutazione finora
- New Cascadia Driver's Manual2 PDFDocumento203 pagineNew Cascadia Driver's Manual2 PDFjesus silvaNessuna valutazione finora
- New Cascadia Driver's Manual2 PDFDocumento203 pagineNew Cascadia Driver's Manual2 PDFjesus silvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lamborghini Gallardo 5 0 MT 530 L S 4x4 Kupe 2d 2007 2014Documento125 pagineLamborghini Gallardo 5 0 MT 530 L S 4x4 Kupe 2d 2007 2014hd01787876756Nessuna valutazione finora
- New Cascadia 2016Documento207 pagineNew Cascadia 2016taurino Delgado100% (1)
- Autel MaxScan GS500 Scan Tool User ManualDocumento50 pagineAutel MaxScan GS500 Scan Tool User ManualQuliar Lucy100% (1)
- DasDocumento96 pagineDasHari BaskarNessuna valutazione finora
- DiagnosticLink 808 FeaturesDocumento30 pagineDiagnosticLink 808 FeaturesArtemio100% (1)
- Safety Precautions in An Automotive Workshop by SamiiDocumento76 pagineSafety Precautions in An Automotive Workshop by Samiijocasam2000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Aviation - Market B094 GB Rev0Documento12 pagineAviation - Market B094 GB Rev0Cak LontongNessuna valutazione finora
- Adm Is003Documento7 pagineAdm Is003EloyNessuna valutazione finora
- Terminal Automation SystemDocumento18 pagineTerminal Automation SystemVenkatesan N100% (2)
- Autoplug Fuel ProbesDocumento2 pagineAutoplug Fuel ProbesTINANessuna valutazione finora
- Data System: Limited The TheDocumento3 pagineData System: Limited The Themohana_raoYNessuna valutazione finora
- Atc2672 X12 ECM Calibration ATC For Grove and TadanoDocumento2 pagineAtc2672 X12 ECM Calibration ATC For Grove and TadanoJhon De la CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Cascadia Driver's ManualDocumento253 pagineCascadia Driver's Manualzap2mNessuna valutazione finora
- 2009 Ddec ReferenceDocumento32 pagine2009 Ddec ReferenceCarlos RiffoNessuna valutazione finora
- Maint RecommendDocumento76 pagineMaint RecommendToufik BenamroucheNessuna valutazione finora
- Fleet Management Proposal: Technocrat Consult and IT Systems LimitedDocumento9 pagineFleet Management Proposal: Technocrat Consult and IT Systems LimitedFemi Ayo-yusufNessuna valutazione finora
- OBDII Readyness Failure Fact SheetDocumento4 pagineOBDII Readyness Failure Fact SheetAlexander HeimNessuna valutazione finora
- Konnwei Kw310 Can Obdii+Eobd Code Reader: SpecificationsDocumento16 pagineKonnwei Kw310 Can Obdii+Eobd Code Reader: SpecificationsSean CanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Bulletins TB - Multi Compartment Tanks 0300Documento4 pagineTechnical Bulletins TB - Multi Compartment Tanks 0300api-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- PhoneList (FirstName)Documento35 paginePhoneList (FirstName)api-3752216100% (3)
- Technical Bulletins TB - Quick-Fill Tank VentsDocumento13 pagineTechnical Bulletins TB - Quick-Fill Tank Ventsapi-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Bulletins TB - Quick-Fill Tank VentsDocumento13 pagineTechnical Bulletins TB - Quick-Fill Tank Ventsapi-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Bulletins TB - Nozzle Shut-Off MechanismDocumento4 pagineTechnical Bulletins TB - Nozzle Shut-Off Mechanismapi-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wiggins Vents Info Wiggins VentsDocumento2 pagineWiggins Vents Info Wiggins Ventsapi-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bam 800 T001 - Air TestDocumento2 pagineBam 800 T001 - Air Testapi-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Bulletins TB - 800LPM Installation AdviceDocumento4 pagineTechnical Bulletins TB - 800LPM Installation Adviceapi-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Bulletins TB - Fluid Theory 0400Documento8 pagineTechnical Bulletins TB - Fluid Theory 0400api-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Bulletins TB - 1000LPM Installation Advice 0601 - 1Documento5 pagineTechnical Bulletins TB - 1000LPM Installation Advice 0601 - 1api-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Bulletins TB - 800LPM Installation Advice 0601Documento5 pagineTechnical Bulletins TB - 800LPM Installation Advice 0601api-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Scully Systems - Scully Systems Electronic Tank Truck Equipment - Files Banlaw FillSafeTM Electronic Overfill Protection SystemDocumento3 pagineScully Systems - Scully Systems Electronic Tank Truck Equipment - Files Banlaw FillSafeTM Electronic Overfill Protection Systemapi-3752216100% (1)
- Technical Bulletins TB - Dual Tanks 0300Documento4 pagineTechnical Bulletins TB - Dual Tanks 0300api-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bam 800 T004 - Nozzle Flow Testing GuidelinesDocumento11 pagineBam 800 T004 - Nozzle Flow Testing Guidelinesapi-3752216100% (1)
- Filtered Vents FilteredVentDocumento2 pagineFiltered Vents FilteredVentapi-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Scully Systems - Scully Systems Electronic Tank Truck Equipment - Files Banlaw FillSafeTM Electronic Overfill Protection SystemDocumento3 pagineScully Systems - Scully Systems Electronic Tank Truck Equipment - Files Banlaw FillSafeTM Electronic Overfill Protection Systemapi-3752216100% (1)
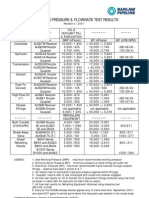
- Technical Bulletins Hydrostatic Pressure & Flow Test Results Rev3Documento1 paginaTechnical Bulletins Hydrostatic Pressure & Flow Test Results Rev3api-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Installation Guidelines Installation and Inspection Guidlines For The AUS 25A Quick Fill VentsDocumento1 paginaInstallation Guidelines Installation and Inspection Guidlines For The AUS 25A Quick Fill Ventsapi-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Installation Guidelines Installation Guidlines On The Installation of 800LPM Refueling SystemDocumento1 paginaInstallation Guidelines Installation Guidlines On The Installation of 800LPM Refueling Systemapi-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Oil Sampling Valve Oil Sampling Valve0001Documento1 paginaOil Sampling Valve Oil Sampling Valve0001api-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Banlaw Sales Brochures Filtered VentDocumento2 pagineBanlaw Sales Brochures Filtered Ventapi-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fill Safe General Operating Instructions 08-05Documento1 paginaFill Safe General Operating Instructions 08-05api-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Banlaw Sales Brochures FillSafeDocumento2 pagineBanlaw Sales Brochures FillSafeapi-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Risk Analysis Refueling Nozzles RA Refuelling Nozzles - Generic Rev3Documento39 pagineRisk Analysis Refueling Nozzles RA Refuelling Nozzles - Generic Rev3api-3752216100% (1)
- Fuel Trial Results Fuel TrialsDocumento2 pagineFuel Trial Results Fuel Trialsapi-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fast Fill Couplers LubeCentralhfcouplingsDocumento2 pagineFast Fill Couplers LubeCentralhfcouplingsapi-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fast Fill Couplers NEW FJ Broch PG 12Documento1 paginaFast Fill Couplers NEW FJ Broch PG 12api-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fast Fill Couplers FF Coupling Price List-06Documento1 paginaFast Fill Couplers FF Coupling Price List-06api-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fast Fill Couplers LC Hi-Flow FlyerDocumento3 pagineFast Fill Couplers LC Hi-Flow Flyerapi-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fast Fill Couplers Flush Face Flyer - PDDocumento2 pagineFast Fill Couplers Flush Face Flyer - PDapi-3752216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Review Problems Chapter 4 Solutions PDFDocumento4 pagineReview Problems Chapter 4 Solutions PDFAntoninoNessuna valutazione finora
- ST7201-Finite Element MethodDocumento14 pagineST7201-Finite Element MethodVishal RanganathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Georgi Lecture Notes On Weak Interactions Physics Harvard Web Draft 1998Documento167 pagineGeorgi Lecture Notes On Weak Interactions Physics Harvard Web Draft 1998manosmagicas7340Nessuna valutazione finora
- L4 Subdivision of PlotsDocumento20 pagineL4 Subdivision of PlotsKenny BoatNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.project FullDocumento75 pagine1.project FullKolliparaDeepakNessuna valutazione finora
- RomerDocumento20 pagineRomerAkistaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Oculus SDK OverviewDocumento47 pagineOculus SDK OverviewparaqueimaNessuna valutazione finora
- BASF Snap Fit Design GuideDocumento24 pagineBASF Snap Fit Design Guideomerscheen100% (6)
- BSIT Nov Dec 2012 2nd CycleDocumento59 pagineBSIT Nov Dec 2012 2nd CyclePiyush PriyankNessuna valutazione finora
- ADA Practical File: Kartik KatariaDocumento34 pagineADA Practical File: Kartik KatariaKilari TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- TOEC8431120DDocumento522 pagineTOEC8431120Dvuitinhnhd9817Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocumento49 pagineChapter 1 IntroductionGemex4fshNessuna valutazione finora
- Implant TrainingDocumento5 pagineImplant Trainingrsrinath91Nessuna valutazione finora
- EXP.2 Enzyme Extraction From BacteriaDocumento3 pagineEXP.2 Enzyme Extraction From BacteriaLinhNguyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 17 Exp 3 RDR Chemical KineticsDocumento4 pagineChem 17 Exp 3 RDR Chemical KineticscrazypatrishNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial Week 5 AnswersDocumento8 pagineTutorial Week 5 Answerspotato moon berryNessuna valutazione finora
- Engine Performance Data at 1500 RPM: QSK 1 Cummins IncDocumento4 pagineEngine Performance Data at 1500 RPM: QSK 1 Cummins IncBalariniRetífica100% (1)
- MoazzamMaqsood Transcript PDFDocumento3 pagineMoazzamMaqsood Transcript PDFmoazzam maqsoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 12 Differentiation CHPT 7 & 8Documento60 pagineGrade 12 Differentiation CHPT 7 & 8Sri Devi NagarjunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiber SyllabusDocumento1 paginaFiber SyllabusPaurav NayakNessuna valutazione finora
- EConsole1 Quick Start Guide ENGDocumento21 pagineEConsole1 Quick Start Guide ENGManuel Casais TajesNessuna valutazione finora
- C191HM Powermeter and Harmonic Manager CommunicationsDocumento30 pagineC191HM Powermeter and Harmonic Manager CommunicationsRoberto GarridoNessuna valutazione finora
- Fisher Paykel SmartLoad Dryer DEGX1, DGGX1 Service ManualDocumento70 pagineFisher Paykel SmartLoad Dryer DEGX1, DGGX1 Service Manualjandre61100% (2)
- PRD Doc Pro 3201-00001 Sen Ain V31Documento10 paginePRD Doc Pro 3201-00001 Sen Ain V31rudybestyjNessuna valutazione finora
- Specializations MTech Software SystemsDocumento5 pagineSpecializations MTech Software SystemsAkanksha SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Chapter - Oil and Gas Well Drilling Technology PDFDocumento19 pagineSample Chapter - Oil and Gas Well Drilling Technology PDFDavid John100% (1)
- Quarter 4 Summative Test No. 1 Mga Layunin Code Bahagda N Bilang NG Aytem Kinalalagyan NG BilangDocumento4 pagineQuarter 4 Summative Test No. 1 Mga Layunin Code Bahagda N Bilang NG Aytem Kinalalagyan NG Bilangmichelle milleondagaNessuna valutazione finora
- PDC NitDocumento6 paginePDC NitrpshvjuNessuna valutazione finora
- GS (2006) Vol 2 Rev20 S15 Steel ReinforcementDocumento14 pagineGS (2006) Vol 2 Rev20 S15 Steel ReinforcementLap Chun TUNGNessuna valutazione finora
- TrimLite™ UT20706 HomeliteDocumento7 pagineTrimLite™ UT20706 HomeliteBKVNessuna valutazione finora
- SketchUp Success for Woodworkers: Four Simple Rules to Create 3D Drawings Quickly and AccuratelyDa EverandSketchUp Success for Woodworkers: Four Simple Rules to Create 3D Drawings Quickly and AccuratelyValutazione: 1.5 su 5 stelle1.5/5 (2)
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataDa EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (22)
- Gas-Liquid And Liquid-Liquid SeparatorsDa EverandGas-Liquid And Liquid-Liquid SeparatorsValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (3)
- Certified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationDa EverandCertified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Practical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationDa EverandPractical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- FreeCAD | Step by Step: Learn how to easily create 3D objects, assemblies, and technical drawingsDa EverandFreeCAD | Step by Step: Learn how to easily create 3D objects, assemblies, and technical drawingsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsDa EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (10)
- CATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchDa EverandCATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (10)
- Beginning AutoCAD® 2022 Exercise Workbook: For Windows®Da EverandBeginning AutoCAD® 2022 Exercise Workbook: For Windows®Nessuna valutazione finora
- Enhanced Oil Recovery Handout: A Focus on WaterfloodingDa EverandEnhanced Oil Recovery Handout: A Focus on WaterfloodingNessuna valutazione finora
- Beginning AutoCAD® 2020 Exercise WorkbookDa EverandBeginning AutoCAD® 2020 Exercise WorkbookValutazione: 2.5 su 5 stelle2.5/5 (3)
- Autodesk Fusion 360: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users (3rd Edition)Da EverandAutodesk Fusion 360: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users (3rd Edition)Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Autodesk Inventor 2020: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate UsersDa EverandAutodesk Inventor 2020: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate UsersNessuna valutazione finora
- AutoCAD 2023 : Beginners And Intermediate user GuideDa EverandAutoCAD 2023 : Beginners And Intermediate user GuideNessuna valutazione finora