Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Convenience Foods
Caricato da
Prashant DhapateDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Convenience Foods
Caricato da
Prashant DhapateCopyright:
Formati disponibili
The Need of Convenience Foods in Present Scenario.
Appanna T Changappa, Prashant V Dhapate 2010-12 Batch AGRICULTURE AND FOOD MANAGEMENT INSTITUTE, MYSORE.
Abstract:
Rapid urbanization and changes in social and cultural practices have modified the food habits of the community. Industrial development in Indian cities has compelled labour from villages to migrate to cities in search of employment. It is estimated that within the next ten years, half of worlds population will be living and working in urban areas. Increase in buying power and long hours spent away from home commuting to work places, make convenience foods a necessity in every home.
Convenience Food:
Convenience food is commercially prepared food designed for ease of consumption. Products designated as convenience foods are often prepared food stuffs that can be sold as hot, ready-toeat dishes, as room-temperature, shelf-stable products or as refrigerated or frozen products that require minimal preparation (typically just heating). These products are often sold in portion controlled, single serve packaging designed for portability for "on-the-go" eating. Convenience food can include products such as candy beverages, soft drinks , juices, milk, fast food, nuts, fruits and vegetables in fresh or preserved states, processed meats and cheeses, and canned products such as soups and pasta dishes are also included.
Need:
Most food consumed in developed countries is in the form of convenience foods. Convenience foods are foods that require little labour and time to prepare. A packet green pea is a convenience food since it requires no shelling. A packet of whole wheat flour is also convenience food as it has been already been milled. A packet instant idli mix is mare of convenience food, and ready to eat or heat and eat foods like chicken keema matar or canned palak paneer are mast convenient since they need to further cooking.
Many different types of convenience foods are available in market today. The speed and efficiency of cooking and service increases dramatically with the use of convenience foods, giving the caterer, homemaker, or working professional more time to develop other activities. The convenience food revolution is possible because of wide variety of chemicals which are added to food not only to preserve it but to enhance its overall quality. These numerous chemicals, tested and permitted by law to be added to food are called food additives. Convenience foods generally contain some level of preservatives to prevent spoilage and thus last longer on the shelf" and thus have the advantage of a longer shelf life, and thereby contains its costs further. There are also significant economies of scale with convenience foods, since the value proportion is that they can be prepared with minimal effort often only by simple re-heating, thus translating into the further benefit that a bulk quantity can often be stocked. Many convenience foods are available in cans or other special plastic packaging, allowing them to be frozen or chilled. Today convenience foods are being specially packed for caterers and are available in large catering packs. Manufacturers of specialized food supplies pack foods that it fits into standard catering equipment, e.g., catering packs that fit in to vending machines. The caterer can choose between smaller packs and larger packs that are economical. Convenience foods vary widely in their palatability, nutrient content and cost. The consumer can choose from a bewildering display of snacks, soups, sauces, fruit chunks and juices, desserts, meat and vegetable preparations gravies in the ready to eat and ready to cook form. They need to be warmed up in a microwave before they are served. The preservation, or canning, of fruits and vegetable in the early 1900s was the predecessor to the convenience food market. Large quantities of food could be stocked in cans and used only as required and the convenience food market emerged as a major industry by the early 1960's. There is now available a broad range of convenience foods including breakfast, lunch and dinner offerings as well as snacks. Additional social trends accelerated the expansion of convenience foods. The rise of the two-earner family in the latter part of the 20th century as well as the move to the city and suburb has contributed to the acceptance of convenience foods. Advances in both foods processing and packaging have also shaped further growth. Acceptance by high population emerging markets such as India and China will also help drive the convenience food market.
Types of convenience foods: Category
Category 1: Basic product The product needs some preparation before cooking Ready to cook product The product needs no further Preparation before cooking
Examples
Shelled green peas
Category 2:
Frozen green peas
Category 3:
Category 4:
Category 5:
Ready to use product The product must be prepared an heated Precooked product This is prepared dish which needs to be heated before consumption Table ready product The packet can be opened and consumed as it is
Instant tomato soup powder
Paneer tikka masala
Potato chips
Consumer behavior and trend:
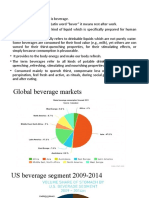
Urban is where the action is, 1 billion population i.e., 30% of population live in Urban areas. India is urbanizing in a rapid rate of 2.5% per annum, the number of cities over 10 lakhs population is expected to be double in next 20 years (35 to 70 cities), In India professionals are increasing (growing service sector), Increasing number of working women (15% in Urban India). Due to increasing working women in cities traditional cooking is difficult so people prefer ready to eat kind of food which can be prepared and served in a short period of time. Most of convenience foods are consumed for breakfast in the form of noodles, pasta, oat meal etc.
Market Structure:
The market for convenience food is continually being extended with new companies and solutions entering the field many small firms adding niche brands and products. At the same time, large food corporations are constantly expanding their own product lines and packaging. In terms of packaging, the range is very broad. A convenience food snack item could be sold as a single item, packaged as a dozen or more or even sold in bulk form in big-box stores. Large supermarket and hypermarket chains also continue to add new products and focus continually on testing for new trends. The recent move toward green, natural or environmentally friendly foods has greatly advanced the advent of the organic food marketplace or at least those with essentially organic ingredients. Conversely, these products may likely also have a reduced shelf life. Again, though the market contains many large corporations, there are also thousands of niche providers. Total market for food products is Rs. 2,500 Billion of this; processed food is Rs.1,400 Billion. New products are continually introduced.
The following estimate was made for new product introductions recently:
Product Type
Sweeteners/sugars Weight control products Breakfast cereals Beverages Confectionery Desserts & ice cream Dairy Snacks Processed meat/seafood Soup Spreads Condiments/seasonings Meals & entrees Bakery Side dishes Fruits & vegetables Baby food
New Product Introductions
83 48 114 1576 1273 450 544 710 646 254 295 1298 543 1126 421 254 21
543
Major players:
Hindustan Lever, MTR, Parle, Pepsi, Coco Cola, Nestle, ITC, Cadbury and Dabur.
Demand Dynamics:
The general factors driving the growth of the food sector are increase in urban population, increase in disposable income in rural areas and companies aggressive promotion of product awareness.
Rise in Disposable Income:
With increasing disposable income and subsequent rise in quality of living and hygiene concerns, the average Indians spending on grocery and personal care products will likely increase. Currently, the average Indian spends about 48%, also the majority, of his total income on groceries (~40%) and personal care products (~8%).
Rise in Disposable Income (In USD Thousands):
Convenience Food Business Investments: Company
Nestle
Investment
Nestle plans to capitalize on the health and convenience food consumption trend by expanding its brand portfolio through new launches in dairy products (probiotic and low fat dahi, milkshake and fruit yoghurt), prepared foods (Maggi Healthy Soups, Rice Noodles) and beverages (Nescafe Mild and an expanding chain of vending machines). In 2008, Kellogg positioned its Special K cereal as a health management alternative for urban women ITC Foods, who entered into the health food category in early 2007 with Sun feast Sachin Fit Kit range, today earns more than 50% of its revenue from health-related products Pepsi and Coca Cola will grow focus on noncarbonated drinks. Pepsi has acquired Tropicana and now is considering launching milk-based drinks. Coca Cola is planning to introduce energy and sports drinks In 2007, Dabur offered the 'Real Active' juices portfolio with the introduction of first packaged vegetable juice. Dabur is now
Kellogg
ITC .
Pepsi, Coca Cola
Dabur
focusing on low-fruit concentrate drinks and low calorie baked goods
All India Mean Per Capita Consumption:
Food Items 1987/88 Processed Food(kgs/month) Beverages (litres/month) 0.41 2.34 Rural 1999/2000 1.60 2.30 1987/88 0.80 5.84 Urban 1999/2000 2.20 6.40
All India Mean Consumption and Expenditure Shares (%):
Food Items 1987/88 Processed Food Beverages 8.28 2.83 Rural 1999/2000 9.4 3.9 1987/88 13.59 5.38 Urban 1999/2000 16.7 6.5
Nutritive value of one precooked serving: Paneer tikka masala (100 g): Nutrient
Calories (kCal/kj) Calories from fat Total fat (g) Saturated fat (g) Cholesterol (mg) Sodium (mg)
Amount
191/802 139 15 9 10 310
% daily value
23 45 3 13
Total carbohydrate (g) Fibre (g) Sugar (g) Protein (g) Vitamin A Vitamin C Calcium Iron
8 2 5 5
3 8 10 24 5 4 11
Criticisms:
Critics have derided the increasing trend of convenience foods because of numerous issues. Several groups have cited the environmental harm of single serve packaging due to the increased usage of plastics that contributes to solid waste in landfills.
Conclusion:
The ever increasing market for convenience foods is it tinned, canned, chilled, frozen or preserved, presents a whole array of complex operations in food processing. This weaning away from the traditional fare of yesteryears provides a tremendous and challenge to food industry. Serving safe, attractive and nutritious food that is wholesome and bacteriological safe and conforms to quality standards. The urban workforce does not have the time or inclination to follow the traditional recipes and would rather pick up packed, clean and reasonably priced meals rather than return home from work and do domestic chores.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Chapter - 3 Convenience FoodsDocumento5 pagineChapter - 3 Convenience FoodsKrishna Chaudhary100% (1)
- Objectives of Menu PlanningDocumento2 pagineObjectives of Menu PlanningRakesh SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Asian Cuisine ExamDocumento2 pagineAsian Cuisine ExamRaimound MarcuzNessuna valutazione finora
- Recipe Standardization ProcessDocumento5 pagineRecipe Standardization ProcessReggie Ann Perez50% (2)
- Menu MerchandisingDocumento73 pagineMenu MerchandisingChandan Srivastava80% (5)
- HACCP in Soy Milk PDFDocumento18 pagineHACCP in Soy Milk PDFFairuza Arofah Izdiharina100% (2)
- New PPT of SeafoodDocumento44 pagineNew PPT of SeafoodPraveen NegiNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Food ProcessingDocumento4 pagineHistory of Food ProcessingGayatri Tallapragada100% (1)
- Methods of Food PurchasingDocumento10 pagineMethods of Food Purchasingrizzwan khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Food and Beverage ManagementDocumento22 pagineFood and Beverage ManagementChandan Singh75% (4)
- 01 - Introduction To Quantity and Institutional Food ProductionDocumento12 pagine01 - Introduction To Quantity and Institutional Food ProductionMarvin Louie Tan Valeros50% (2)
- Menu AnalysisDocumento27 pagineMenu Analysismtki150% (2)
- Beverage Classification and TypesDocumento40 pagineBeverage Classification and TypesMuhammad Awais100% (1)
- Feasibility Study of Soya ProductDocumento18 pagineFeasibility Study of Soya ProductSorabh Dung0% (1)
- 3.3 PFPP-Lab ManualDocumento28 pagine3.3 PFPP-Lab ManualSB TEKNessuna valutazione finora
- FeasibilityDocumento7 pagineFeasibilitylaura89% (9)
- Standardize RecipeDocumento19 pagineStandardize RecipeThessalonica Manguiat SinohinNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.1.1.introduction Food PreservationDocumento39 pagine3.1.1.introduction Food PreservationFefin IriantiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Food Service System (Autosaved)Documento19 pagineThe Food Service System (Autosaved)Antonia Guiriba100% (1)
- Enzymatic and Non-Enzymatic BrowningDocumento2 pagineEnzymatic and Non-Enzymatic BrowningChristian Ramos NievesNessuna valutazione finora
- Cocos Nucifera Automatic Jam MakerDocumento13 pagineCocos Nucifera Automatic Jam MakerErick AguadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Food DispersionDocumento92 pagineFood DispersionGuadalupe Gutierrez100% (2)
- Internship Report in Food ServicesDocumento36 pagineInternship Report in Food ServicesMuhammad Sohaib33% (3)
- Beverage ControlDocumento41 pagineBeverage ControlOm Singh89% (9)
- Ice Cream ManufacturingDocumento19 pagineIce Cream ManufacturingMostafa Abd El AlemNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Asian CuisineDocumento97 pagineIntroduction To Asian CuisineJeffrey TuballaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Week Menu CycleDocumento3 pagine3 Week Menu CycleEstong TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pineapple ProcessingDocumento6 paginePineapple Processingveguruprasad100% (2)
- Menu ManagementDocumento15 pagineMenu ManagementAdarsh ShrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tiesa PolvoronDocumento10 pagineTiesa PolvoronSaireen Rose Peritos AumanNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Food Science Edited 15. 09.2019Documento37 pagineIntroduction To Food Science Edited 15. 09.2019Jessica chi100% (1)
- Food Safety and SanitationDocumento17 pagineFood Safety and SanitationBetel Abe50% (4)
- Marketing Plan Lechon 1Documento23 pagineMarketing Plan Lechon 1Mariah SoternoNessuna valutazione finora
- F&B Pro M2. Unit 1. Designing Foodservice FacilityDocumento28 pagineF&B Pro M2. Unit 1. Designing Foodservice Facilitygene roy hernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Food Service IndustryDocumento15 pagineIntroduction To Food Service IndustryClaire GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Plan: A. Product DescriptionDocumento24 pagineMarketing Plan: A. Product DescriptionGrahsie Abella Paño-GuertaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6th Sem. Food Production Notes PDFDocumento83 pagine6th Sem. Food Production Notes PDFPanigrahi Abha100% (3)
- Recipe Development and StandardizationDocumento9 pagineRecipe Development and StandardizationJohn Rodrique Galindez100% (2)
- Catering Module 1 (Word)Documento11 pagineCatering Module 1 (Word)Princess Rolene Mamaradlo100% (1)
- PR2 Group Chapter 1 &2Documento20 paginePR2 Group Chapter 1 &2Le Claire SanglayNessuna valutazione finora
- Setting Up of Proper Waste Management in Ihm GwaliorDocumento69 pagineSetting Up of Proper Waste Management in Ihm GwaliorAmitKumarYadav100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Food Purchasing and Receiving ControlDocumento22 pagineChapter 4 Food Purchasing and Receiving ControlArifin Fu50% (2)
- Lab Report Experiment 3Documento3 pagineLab Report Experiment 3Argel LargadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Section A F&B Service 5th SemDocumento14 pagineSection A F&B Service 5th Semvmarkan93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - The Food and Beverage IndustryDocumento19 pagineChapter 1 - The Food and Beverage IndustryPaola QuintosNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of CateringDocumento4 pagineTypes of CateringFlashlight StudioNessuna valutazione finora
- Fermentation in Food Processing Typically Is The Conversion of Carbohydrates To Alcohols and Carbon Dioxide or Organic Acids Using YeastsDocumento7 pagineFermentation in Food Processing Typically Is The Conversion of Carbohydrates To Alcohols and Carbon Dioxide or Organic Acids Using YeastsHuzzain PangcogaNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Status and Future Trends of Beverage IndustryDocumento31 pagineCurrent Status and Future Trends of Beverage IndustryGaurav Srivastava100% (3)
- Fast Food IndustryDocumento9 pagineFast Food IndustrykevinpetersonNessuna valutazione finora
- Fast FoodDocumento6 pagineFast FoodGel-An Pet I. MadalogdogNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Catering ManagementDocumento18 pagineIntroduction To Catering ManagementOlive Factoriza25% (4)
- Cereal Products FixDocumento20 pagineCereal Products Fixhelsha afifah anggrainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Food Jam ProcessingDocumento11 pagineFood Jam ProcessingVienna Chan100% (1)
- Fats in BakingDocumento34 pagineFats in BakingLuqman Hakim100% (1)
- Materials Requirement PlanningDocumento89 pagineMaterials Requirement PlanningVatsal PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Commissary FoodserviceDocumento15 pagineCommissary FoodserviceJowee Tigas100% (1)
- Good Food Manufacturing Practices: See Discussions, Stats, and Author Profiles For This Publication atDocumento17 pagineGood Food Manufacturing Practices: See Discussions, Stats, and Author Profiles For This Publication atVadhila RefiNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Report On F&BDocumento45 pagineProject Report On F&BManisha Gupta80% (5)
- MRP Project Report On Food&Dairy Industry New UpdateDocumento107 pagineMRP Project Report On Food&Dairy Industry New UpdateVishal PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Food and BeverageDocumento38 pagineFood and BeveragesagarramakaNessuna valutazione finora
- ATFTI PackEx-2016 Issue-3Documento36 pagineATFTI PackEx-2016 Issue-3djalmaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Abington Journal 03-20-2013Documento24 pagineThe Abington Journal 03-20-2013The Times Leader100% (1)
- SIRIMDocumento1 paginaSIRIMdandiar1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Additional QuestionsDocumento3 pagineAdditional Questionskarthikdora_007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Graeters PresentationDocumento24 pagineGraeters Presentationapi-3840676790% (1)
- Marketing Strategy of CocaDocumento95 pagineMarketing Strategy of CocaSurabhi GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading TOEFLDocumento4 pagineReading TOEFLPo Andri0% (1)
- EMF TelanganaDocumento163 pagineEMF TelanganaDiya Finding New WaysNessuna valutazione finora
- ReportDocumento15 pagineReportJaylord AgpuldoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicios 6,7,8Documento274 pagineEjercicios 6,7,8Lía YndiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Analysis Report On Crispy CrunchDocumento10 pagineCase Analysis Report On Crispy CrunchLime RoadNessuna valutazione finora
- Training Restaurant EmployeesDocumento13 pagineTraining Restaurant Employeessamsharif100% (2)
- Business Proposal: Gdb3023: Engineering Economic and EntreprenuershipDocumento3 pagineBusiness Proposal: Gdb3023: Engineering Economic and EntreprenuershipMirrovshan SagdullaevNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Plan: Zaffy'S CuisineDocumento13 pagineBusiness Plan: Zaffy'S CuisineZafar IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Fast Food IndustryDocumento17 pagineFast Food IndustryJosh SimmonsNessuna valutazione finora
- Late Night TV Comedy PacketDocumento21 pagineLate Night TV Comedy PacketLos SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 - Assignment 1 Practice Case Examination BackgrounderDocumento16 pagineModule 3 - Assignment 1 Practice Case Examination BackgrounderAsif NanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Namkeen Manufacturing Unit DPR by NiftemDocumento26 pagineNamkeen Manufacturing Unit DPR by NiftemSiddhartha ModakNessuna valutazione finora
- SankalpDocumento4 pagineSankalpSupriya Gunthey RanadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Mcdo HistoryDocumento2 pagineMcdo HistoryPaulin Joy ArceNessuna valutazione finora
- Wawa PortfolioDocumento17 pagineWawa Portfoliojaime_hutkinNessuna valutazione finora
- SPAR International Annual Report 2018 PDFDocumento56 pagineSPAR International Annual Report 2018 PDFCristian Cucos CucosNessuna valutazione finora
- McdonaldsDocumento77 pagineMcdonaldsaster5262100% (1)
- Kitchen and Restaurant BrigadeDocumento26 pagineKitchen and Restaurant BrigadeCarlos Baul DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Colloquial AzerbaijaniDocumento30 pagineColloquial Azerbaijaninotwinner100% (4)
- Budget of Works-TleDocumento12 pagineBudget of Works-TleJOEL ESPENIDANessuna valutazione finora
- EUIPO McDonalds RevocationDocumento7 pagineEUIPO McDonalds RevocationOlivera MedenicaNessuna valutazione finora
- CV & PortfolioDocumento22 pagineCV & PortfolioshelmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Model Canvas - Ipe PDFDocumento1 paginaBusiness Model Canvas - Ipe PDFRonald IpeNessuna valutazione finora
- Pas Mantap Soal Pemecahan DewaDocumento6 paginePas Mantap Soal Pemecahan DewaAlkaml TheaNessuna valutazione finora