Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
(P) Nursing Management
Caricato da
Kelvi DuranteDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
(P) Nursing Management
Caricato da
Kelvi DuranteCopyright:
Formati disponibili
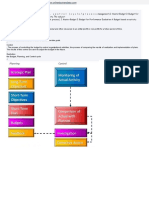
4 Major Steps of the Management Process
PLANNING Is deciding in advance what to do, how to do it, when to do it, and who is to do it Is the principal duty of all managers Involves determining objectives, strategies, programs, procedures, and rules to accomplish It is a cognitive proves for decision making. Decision making and planning are closely intertwined. However, a decision is not a plan but basically a resolution of alternative choices In general, planning is an intellectual process based on facts and information, not on emotion or wishes In nursing, planning helps to ensure that patients will receive the nursing services that they want and need and that these services are delivered by nursing workers Planning is such a primary and essential element of management that managers cannot be effective without it It has to be approached logically and calmly, it may threaten the insecure and may even threaten the administrator who must provide total support in terms of giving resources to accomplish divisional planning Planning is a continuous process, beginning with the setting of the goals and objective slaying out a plan of action to accomplish them, put them into play, review the process and the outcome, provide feedback and modify as needed
Planning organizing directing controlling Planning Controlling is also evaluating
4 Orientations to Planning Reactivism o o o o Looks to he past and considers technology an enemy Supports the old organizational forms of authoritarian, parternalistic hierarchy Planning is considered prerogative Prevents change by using crisis management which goal is to control discomfort without addressing its goal
Inactivism
Effective instrument is committee, to keep people busy until the work is outdated by insufficient resources
Preactivism o o Change is accelerated through technology Associated with science, technology, and future Future can be created an invented Technology is valued depending on how it is used, Experience reveals problems and experiment leads to their solutions
Interactivism o o
A Plan has 3 Characteristics It must involve the future It must involve action There is an organizational identification of the future course of action that will be taken by a particular planner or someone designated by him or for him in the organization Characteristics of a Good Plan Be precise with clearly-worded objectives including desired results and methods for evaluation Be guided by policies/procedures affecting the plan Indicate the priorities Develop actions that are flexible and realistic in terms of available personnel, equipment, facilities and time Develop a logical sequence of activities Include the most practical methods for achieving each objective Pervade the whole organization
Reasons for planning Planning leads to success & achievement of goals and objectives. Brings about behaviors that lead to desired action and outcomes. Employees can see the result of their labor Planning gives meaning to work, knowing that objectives help the employees relate what they are doing to Planning helps in coping with crisis. Plans anticipate emergencies, they allow the worker to function more calmly in efficiently when an actual crisis occurs Planning is cost effective. Some costs can be contained through planning of nurse. Example: projecting the number of nurses needed to care for a group of patients or ordering enough supplies for a unit Planning is based on the past and future helps reduce the element of change. Studying what has been successful or unsuccessful can give the manager a better idea of what to do in the future By planning, one discovers the need for change. Planning can point out opportunities or different services Planning is necessary for effective control. Mangers can evaluate the environment, resources and employees effectiveness
Resistance for planning
Planning is something that many managers avoid. Failure to plan may be attributed to the following factors: Managers may lack knowledge of the philosophy, goals and workings of the organization Managers may not understand the significance of planning, that success or failure of work activities relate to the quality of the plan Time spent on planning often seems distracted in relation to the day-to-day doings of ones job Some managers may lack confidence, fearing failure Some managers prefer to act on immediate problems because they generate immediate feedback Planning may bring unwanted change. Reluctant may exist because implementation of plans may require new activities that the individual is unwilling to engage in
The Planners Top Management (Chief Nurses and Assistants, Nursing Directors)
set the over-all goals and policies of the organization. Their responsibility covers the over-all management of the nursing service
Middle Management or Nursing Supervisors o o Direct the activities to actually implement the broad operating policies E.g., staffing and delivery of services to the units Formulation of policies, plans, rules and regulation, methods and procedures for activities and projects in coordinating
Lower of First-level Management o Do the daily and weekly plans for the administration of direct patient care in their respective units
Scope of Planning Forecast or Estimate of the Future It describes the ultimate condition or projections that provide the general incentive and direction to planning Should consider the: o o o plans Agency Community Goals of care
Forecast must be supported by facts, reasonable estimates, and accurate reflection of policies and
Set Objectives/Goals determine results desired Goals o Are statements of intent derived from the purposes of the organization and they are stated broadly and in general terms Objectives o Specific behavior or task set for accomplishment of a goal
Develop and schedule strategies * Programs o o Are series of activities that function together to facilitate attainment some desired goals Example: staff development programs, outreach programs, discharge teaching program
Strategic Planning Tactical Planning Unit planning Planning extents to the operational units of any healthcare agency Should be done on a daily basis * Is short term planning Converts objectives into actions and include activities, assignments, deadlines and provision for accountability It is considered as daily, weekly, and monthly planning Objectives for long term nursing activities of one to five years longer It has generally been understood that top administrators in nursing focus on strategic planning, whereas operational nurse managers focus on tactical planning.* Types of Plans (according to the * Long term plans: 3-5 years
IV. Prepare Budget Allocating resources Allocation of scarce resources on the bass of forecasted needs for proposed activities over a specific period of time A tool for planning, monitoring and controlling cost or a systemic plan for meeting expenses Budgeting and Planning o Is an ongoing activity in which revenues and expenses are managed to maintain *
Nurse manager has: Budgetary Planning in Nursing Expense Budgeting Is the process of forecasting, recording and monitoring the manpower, materials and supplies, and monetary needs of an organization in such a manner that operation of various components of the organization can be controlled Types of Expenses/Costs Fixed Costs o Remain constant as volume increases and decreases over a period of time Helps ensure that patients receive the nursing service they want Helps maintain needs from satisfied nursing workers Financial responsibility and accountability for managing the nursing budget Makes decision on adjusting the nursing budget to manage programs and costs e.g. adding and dropping programs, modifying revenues and expenses within the nursing unit
o o o o o
E.g., depreciation of equipment and buildings Do relate to volume and census like meals and linens Are fixed expenses that cannot be recovered even if program is cancelled E.g, advertising Direct cost Are the costs of providing the product or service directly related to patient care Personnel costs, variable cost of supplies
Variable Costs Sunk Costs
Other Costs
Indirect costs Are those incurred in the *
Systems/Approaches of Budgeting Centralized budgeting o o The budget are developed and imposed by the controller, administrator and the director or nursing with little or no consultation with lower level managers This top-down approach leaves the implementers of the bud without autonomy or the rights to appropriate or control ex* Decentralized Budgeting o Middle level manager becomes involved in the planning *
Components of Total Institution Budget
Manpower Budget o Includes wages and salaries paid to regular employees and fees paid to outside registries thru whom the institution contracts for temporary workers
Capital Expenditure Budget o Includes purchases of land, building, and major equipment of consideration expense and long life
Operating Budget o Includes the cost of supplies, minor equipment of considerable expenses
Types of Institutional Budget depending upon Management Philosophy Open-ended o Is a financial plan in which each operating manager presents a sing cost estimate for what he considers the optimal activity level for each program in his unit, without indicating how * Flexible Budget o o Consists of several financial plans, each of a different level of activity or for different operating conditions Top management can select the budget ot can shift the spending level up or down to permit higher or lower levels of productivity Performance Budget o o o Is based on functions such as direct nursing care supervision, quality control, etc. One in which cost are computed for an entire program Example: Home care program, outreach program, etc. Program Budget
Zero based Budget o Requires managers to justify in detail the cost of all programs, both old and new, with every annual budget preparation
Sunset Budget o Is designed to self-destruct within a prescribed period to ensure cessation of the funded program by a predetermined date
V. Establish Policies, Procedures/Standard Policies Procedures Provide a more specific guide to action than a policy. It is a step by step guide Indicate the minimal level of achievement acceptable to meet objective A technique for allocating ones time through the setting of goals, assigning priorities, identifying and eliminating wasted time and using managerial technique to reach goals efficiently Ones personality, education and culture influence how he or she manages time Standards Time Management Are referred to as standing plans and are used repeatedly Are guides or basic rules that govern action at all levels in the organization. It seems for the goals of the agency
Symptoms of Time Management Time Management Principles: Planning anticipates the problems that arise from actions without thought. It anticipates the crises* Rushing, fatgue, and listlessness with hours of non-productivity Constan*
Setting deadlines in ones work, adhering to them and excellent exercise in self-discipline Prevent procrastination deferring, postponing, or putting off actions and decision that cause lost opportunities and productivity
Time-saving techniques, Devices & Methods to Better Use of Time: Conduct an inventory of your activities o o o o o Log activities for 1 day Identify time problems Examine old habits of not using time well & understand why you are doing so Set priorities Plan on making things happen rather than reacting to crises
Set goals and objectives and write them down
Use calendars, executive planners, logs or journals, write what you expect to accomplish yearly, monthly, wekly or daily Breakdown * Devote a few minutes at the beginning of each day for planning o o At the end of the day, account for the tasks you have accomplished Prepare a list of what are to be done the following day
Organize you work space Close you door when you need to concentrate o o Agree on a period of quiet office time Avoid having an open door policy
10/08/2009 03:38:00
10/08/2009 03:38:00
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Unit-3: Planning: Dr. Belay KDocumento39 pagineUnit-3: Planning: Dr. Belay Kዘንገና ቲዩብNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning Key to Management SuccessDocumento75 paginePlanning Key to Management SuccessjintuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ncm119: Nursing Leadership and Management Study Guide 6: The Nursing Management Process: Planning Topic OutlineDocumento9 pagineNcm119: Nursing Leadership and Management Study Guide 6: The Nursing Management Process: Planning Topic OutlineElizabeth DaligdigNessuna valutazione finora
- Reaching Goals and ObjectivesDocumento58 pagineReaching Goals and ObjectivesKesalan TerasaNessuna valutazione finora
- PlanningDocumento45 paginePlanningrocky mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Behavioural Aspects of BudgetingDocumento13 pagineBehavioural Aspects of BudgetingKanumuri MouliNessuna valutazione finora
- Functions of ManagementDocumento27 pagineFunctions of ManagementOmar MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2: Planning and Organizing at Supervisory Level: Presented by Er - Shital BhalgatDocumento50 pagineUnit 2: Planning and Organizing at Supervisory Level: Presented by Er - Shital BhalgatRushikesh Shinde100% (1)
- PMDocumento76 paginePMShwetaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM107 PlanningDocumento59 pagineNCM107 Planningebtg_f100% (1)
- Planning Involves Selecting Mission and Objectives As Well As The Actions To Achieve ThemDocumento5 paginePlanning Involves Selecting Mission and Objectives As Well As The Actions To Achieve ThemBhagyashreeNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning & Types of PlansDocumento23 paginePlanning & Types of PlansKarish_J89Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Management Process PlanningDocumento19 pagineThe Management Process PlanningHowardNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning OrganizingDocumento63 paginePlanning Organizingprincessangela12345678Nessuna valutazione finora
- Business PlanningDocumento31 pagineBusiness PlanningAnonymous XybLZfNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - 2 Planning and MBODocumento29 pagineUnit - 2 Planning and MBOhardeepcharmingNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Monitoring and Evaluation GuideDocumento50 pagineProject Monitoring and Evaluation GuideYonas BEZUNessuna valutazione finora
- PB301 BUSINESS PLANNING CONCEPTSDocumento29 paginePB301 BUSINESS PLANNING CONCEPTSEunice TzpNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning ProcessDocumento25 paginePlanning ProcessArthiKalisamy100% (3)
- ManagementDocumento12 pagineManagementFatima Batool0% (1)
- Planning: Cecille O. Martinez RN, RM, Man, Edd (C)Documento90 paginePlanning: Cecille O. Martinez RN, RM, Man, Edd (C)Nicole Marin-ChingNessuna valutazione finora
- Indicative Planning: 2. Planning Is Looking AheadDocumento5 pagineIndicative Planning: 2. Planning Is Looking AheadPrasann RoyNessuna valutazione finora
- PIMR (FOM) Unit II 0IIIDocumento64 paginePIMR (FOM) Unit II 0IIIshivam gangradeNessuna valutazione finora
- MIS - 423 Planning Process-1BDocumento48 pagineMIS - 423 Planning Process-1BTomiwaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Management Process PlanningDocumento22 pagineThe Management Process PlanningAisa Ordonez Galo-CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- PlanningDocumento7 paginePlanningCherry Savannah AbenojarNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning & Types of PlansDocumento25 paginePlanning & Types of PlansPuni SubramaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning Theory 1 UNIT 5 NotesDocumento12 paginePlanning Theory 1 UNIT 5 NotesSanjay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Foundation of PlanningDocumento25 pagineChapter 3 Foundation of PlanningNabin GautamNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning PPT 2Documento19 paginePlanning PPT 2Jay RNNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2Documento58 pagineUnit 2niyati dixitNessuna valutazione finora
- Project M & E, CH-1Documento56 pagineProject M & E, CH-1sadorNessuna valutazione finora
- PoM Module1 PlanningDocumento33 paginePoM Module1 Planningdeveloperamit4uNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning - EMBADocumento3 paginePlanning - EMBApawanshrestha1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pom Unit 2Documento49 paginePom Unit 2AkshayKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- IT107 HandOut 009Documento4 pagineIT107 HandOut 009jin_adrianNessuna valutazione finora
- POM Chapter 4+Documento21 paginePOM Chapter 4+Garrv JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Budgeting: An Important Management ToolDocumento37 pagineBudgeting: An Important Management ToolMahfuzulNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento91 pagineChapter 2brhanegebrewahd414Nessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Mangement 4Documento45 pagineStrategic Mangement 4kritikachhapolia100% (1)
- MGMT Theory & Prac - Chap-4Documento5 pagineMGMT Theory & Prac - Chap-4Kashi MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept of PlanningDocumento29 pagineConcept of PlanningJotinWahengbamNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4. Planning and Decision MakingDocumento46 pagineUnit 4. Planning and Decision MakingJenny ShresthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ems11es Unit 2Documento32 pagineEms11es Unit 2Ndiphiwe MaliwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sem1 202324 Unit4Documento29 pagineSem1 202324 Unit4brandon bernardNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning: Organization and ManagementDocumento25 paginePlanning: Organization and ManagementYan Art GencianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning and Decision Making GuideDocumento38 paginePlanning and Decision Making GuideAayush ShresthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Essentials of Planning & MBODocumento24 pagineEssentials of Planning & MBOSubhendu JanaNessuna valutazione finora
- What is Planning? - Understanding the Planning Process in 40 CharactersDocumento10 pagineWhat is Planning? - Understanding the Planning Process in 40 CharactersReymart CasupananNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is MonitoringDocumento14 pagineWhat Is MonitoringKipyegon ErickNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning: Glenda Casundo Joanne Bernadette AguilarDocumento23 paginePlanning: Glenda Casundo Joanne Bernadette AguilarJoanne Bernadette AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Management Process - PlanningDocumento52 pagineManagement Process - PlanningAnroe CariasoNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Functions of Management - PlanningDocumento36 pagine5 Functions of Management - PlanningYASH SANJAY.INGLE100% (1)
- 04 Planning Process, Strategic Planning and Operational Planning.Documento22 pagine04 Planning Process, Strategic Planning and Operational Planning.ravi anandNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nature and Purpose of PlanningDocumento50 pagineThe Nature and Purpose of Planningbabu41652107Nessuna valutazione finora
- PlanningDocumento36 paginePlanningEsperanza DisepedaNessuna valutazione finora
- BudgetDocumento4 pagineBudgetAschenaki MebreNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Managing ResoursceDocumento45 pagine6 Managing Resourscesisay SolomonNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical and Mathematical Skills BookletDocumento30 paginePractical and Mathematical Skills BookletZarqaYasminNessuna valutazione finora
- Awareness Training On Filipino Sign Language (FSL) PDFDocumento3 pagineAwareness Training On Filipino Sign Language (FSL) PDFEmerito PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Us Aers Roadmap Noncontrolling Interest 2019 PDFDocumento194 pagineUs Aers Roadmap Noncontrolling Interest 2019 PDFUlii PntNessuna valutazione finora
- A Case Study On Implementing ITIL in Bus PDFDocumento7 pagineA Case Study On Implementing ITIL in Bus PDFsayeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Audience AnalysisDocumento7 pagineAudience AnalysisSHAHKOT GRIDNessuna valutazione finora
- DNS Mapping and Name ResolutionDocumento5 pagineDNS Mapping and Name ResolutionAmit Rashmi SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 1 RDL2Documento101 pagineGroup 1 RDL2ChristelNessuna valutazione finora
- Med 07Documento5 pagineMed 07ainee dazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hem Tiwari Vs Nidhi Tiwari Mutual Divorce - Revised VersionDocumento33 pagineHem Tiwari Vs Nidhi Tiwari Mutual Divorce - Revised VersionKesar Singh SawhneyNessuna valutazione finora
- Leibniz Integral Rule - WikipediaDocumento70 pagineLeibniz Integral Rule - WikipediaMannu Bhattacharya100% (1)
- BS 476-7-1997Documento24 pagineBS 476-7-1997Ivan ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Larry Dossey - HealingBeyondtheBodyDocumento2 pagineLarry Dossey - HealingBeyondtheBodypaulxeNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Musicianship ChecklistDocumento1 paginaBasic Musicianship ChecklistStefanie MeijerNessuna valutazione finora
- Tangina Tapos NadenDocumento7 pagineTangina Tapos NadenJamesCubeNessuna valutazione finora
- Absolute TowersDocumento11 pagineAbsolute TowersSandi Harlan100% (1)
- Novel anti-tuberculosis strategies and nanotechnology-based therapies exploredDocumento16 pagineNovel anti-tuberculosis strategies and nanotechnology-based therapies exploredArshia NazirNessuna valutazione finora
- Global Trustworthiness 2022 ReportDocumento32 pagineGlobal Trustworthiness 2022 ReportCaroline PimentelNessuna valutazione finora
- Advantages and Disadvantages of A MonopolyDocumento7 pagineAdvantages and Disadvantages of A MonopolyRosalyn RayosNessuna valutazione finora
- 056 Set 1 C ChemistryDocumento16 pagine056 Set 1 C ChemistryEepen JohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost-Benefit Analysis of The ATM Automatic DepositDocumento14 pagineCost-Benefit Analysis of The ATM Automatic DepositBhanupriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Completing-Your-Copy-With-Captions-And-Headlines Lesson-1Documento24 pagineCompleting-Your-Copy-With-Captions-And-Headlines Lesson-1api-294176103Nessuna valutazione finora
- UTS - Comparative Literature - Indah Savitri - S1 Sastra Inggris - 101201001Documento6 pagineUTS - Comparative Literature - Indah Savitri - S1 Sastra Inggris - 101201001indahcantik1904Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vietnamese Grammar Questions and Answers DocumentDocumento1 paginaVietnamese Grammar Questions and Answers DocumentMinJenNessuna valutazione finora
- Portal ScienceDocumento5 paginePortal ScienceiuhalsdjvauhNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Action and Core Values and Principles of Community-Action InitiativesDocumento5 pagineCommunity Action and Core Values and Principles of Community-Action Initiativeskimberson alacyangNessuna valutazione finora
- Cartha Worth SharingDocumento27 pagineCartha Worth SharingtereAC85Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ardipithecus Ramidus Is A Hominin Species Dating To Between 4.5 and 4.2 Million Years AgoDocumento5 pagineArdipithecus Ramidus Is A Hominin Species Dating To Between 4.5 and 4.2 Million Years AgoBianca IrimieNessuna valutazione finora
- Social Media Marketing - AssignmentDocumento8 pagineSocial Media Marketing - AssignmentAllen RodaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 Ba Core 11 LessonsDocumento37 pagineModule 1 Ba Core 11 LessonsLolita AlbaNessuna valutazione finora
- GNED 500 Social AnalysisDocumento2 pagineGNED 500 Social AnalysisEshita SinhaNessuna valutazione finora