Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Chok Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer Blood Generalities
Caricato da
api-3742802Descrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chok Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer Blood Generalities
Caricato da
api-3742802Copyright:
Formati disponibili
BLOOD
- circulating tissue that supplies nutrients, removes wastes, and coordinates metabolismunctions
- Functions: Metabolic – nutrition, excretion, respiration and hormone transport; Physical / Chemical – maintenance of acid-base, electrolyte and water balance; Body defense – WBC, coagulation
General Composition
- Blood = plasma (50-60%) + formed elements (40-50%) - 7-8% body weight - Specific gravity: 1.035 – 1.075
- Whole blood – formed elements = plasma – clotting factors = serum - 5-6L in male, 4-5 in female - Viscosity = 5-6x water
- Plasma = 90% water, 6-8% organic solutes, 2-4% inorganic solutes - Bright red arterial and darker red venous blood - pH: 7.35-7.45
Cellular Elements
Cell Subtype Description
Erythrocytes / RBC most abundant, 40-45% of blood, 5.2M in males, 4.6M in females, no organelles, 33% hemoglobin, biconcave, flat, no nucleus, strongly flexible (reversible deformation), 120 day life span
Nucleated – granulocytes (NEB) and agranulocytes (LM), phagocytosis, 4-10K in blood, shorter life span, active glycolysis, PPP, moderate oxidative phosphorylation, rich in lysosomes, has unique enzymes
(myeloperosidase & NADPH-oxidase), CD11, CD18
Neutrophil 58%, phagocytic, polymorphonuclears (PMN), infections
Leukocytes Eosinophil 2%, allergies, parasitism
Basophil 1%, heparin, histamine
Lymphocyte 33%, B lymphocyte for antibody production, T lymphocyte for cell-mediated immunity
Monocyte 4%, large phagocytes, clean up dead neutrophils
Thrombocytes / Platelet Irregularly shaped, colorless, 150-400K in blood, from megakaryocytes, no nucleus, platelet plug, glucose as energy, glycogen during coagulation
Reticulocyte Immature RBCs, active protein synthesis, has glycerol kinase
Plasma – Straw-colored, clear, 90% water, electrolytes, metabolites, nutrients, vitamins, hormones, proteins
Plasma Protein – 7.0-7.5g/dL, major part of solids in plasma, separation via (1) salting out – use of solvents fibrinogen, albumin, globulin; (2) Electrophoresis – albumin, α1, α2, β and γ fractions
Plasma Protein Description Abnormalities
Major plasma protein, 3.4-4.7g/dL, single polypep chain, 3 structural domains, 9 subdomains, ↓ = nephritic syndrome, hepatic cirrhosis
Albumin
osmotic effect, distribution and transport (FFAs, bilirubin, Ca, steroid hormones, W, sulfonamides, penicillin G, dicoumarol, aspirin)
Mostly conjugated, α1 or α2 based on electrophoretic mobility
α1-acid glycoprotein
High (42%) CHO content, intrchain disulfide bonds, unknown function
(orosomucoid)
α1-globulin
α1-fetoglobulin Fetal plasma and amniotic fluid, ↓ postnatally, homologous to albumin, elevate in hepatoma ↓ = hepatoma
Retinol-binding Transports retinol, equimolar complex with transthyretin (thyroxine)
protein
α-globulin
Inhibits leukocyte proteases, protects lung damage from inflammation, Emphysema (due to lack of countercheck of
α1-antitrypsin (α1
proteolytic damage), hepatic cirrhosis,
antiproteinase)
smokers
Heavenly blue, ↑ Cu, 8 Cu binding sites, ↓ = Wilson’s disease - ↑ Cu in brain and liver
Ceruloplasmin
α2-globulin
carries 90% of plasma Cu, ferroxidase (Fe2+ Fe3+), Cu+ homeostasis
¼ of α2-globulins, binds extracorpuscular Hgb noncovalently,
Haptoglobulin (Hp)
prevents Hgb loss in urine
Large, 4 identical subnits, internal cyclic thiol ester bond (Cys-Glu) = thio ester plasma CHON family,
α2 macroglobulin
Zn transport, panproteinase inhibitor, binds to cytokines and targets them
Transferrin Major component of plasma CHON (3%), transports iron, 2mol Fe / transferring, ↑ in pregnant and iron-deficients
β-globulin
Hemopexin Binds and prevents heme excretion, Fe reused in liver
C-reactive protein (CRP) Precipitates Group C polysacchs of Pneumococcus with Ca, promotes phagocytosis, <1mg/dL in adults, ↑ with acute infections Acute infections
β2-microglobulin Very small amounts, easily excreted, part of histocompatibility antigens
β-lipoprotein Fat transport, LDL has 50% total cholesterol Hypobetalipoproteinemia (↓ LDL)
γ-globulins Igs / antibodies, made by humoral immune system (B cells) with antigen stimulation ↑ = infections
Fibrinogen Becomes fibrin for hemostasis, ↑ during menstruation, pregnancy, inflammation, infection
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- USTNotesGroup2010 Brainstem AnatomyDocumento3 pagineUSTNotesGroup2010 Brainstem Anatomyapi-3742802100% (1)
- USTNG2010 Brain ModelDocumento13 pagineUSTNG2010 Brain Modelapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- His To Notes FinalDocumento17 pagineHis To Notes Finalapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer LectinsDocumento2 pagineChok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer Lectinsapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Water Soluble 2Documento1 paginaWater Soluble 2api-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer Vit MinDocumento3 pagineChok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer Vit Minapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer Structural CTDocumento3 pagineChok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer Structural CTapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer Nutritional AspectDocumento3 pagineChok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer Nutritional Aspectapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer OlfactionDocumento3 pagineChok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer Olfactionapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer Nutritional DisordersDocumento2 pagineChok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer Nutritional Disordersapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer AgingDocumento3 pagineChok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer Agingapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer EyeDocumento2 pagineChok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer Eyeapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer BrainDocumento3 pagineChok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer Brainapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Trace Elements 1Documento1 paginaTrace Elements 1api-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Water Soluble 1Documento1 paginaWater Soluble 1api-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chok Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer Nucleic AcidDocumento1 paginaChok Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer Nucleic Acidapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Trace Elements 2Documento1 paginaTrace Elements 2api-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fat SolubleDocumento1 paginaFat Solubleapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chok Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer O2 Co2 Transport StorageDocumento3 pagineChok Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer O2 Co2 Transport Storageapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer MuscleDocumento2 pagineChok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer Muscleapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer BoneDocumento2 pagineChok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer Boneapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Eric Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer RBC Iron HemeDocumento2 pagineEric Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer RBC Iron Hemeapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chok Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer XenoDocumento2 pagineChok Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer Xenoapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chok Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer Nucleotide MetabDocumento3 pagineChok Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer Nucleotide Metabapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chok Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer OncoDocumento2 pagineChok Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer Oncoapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chok Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer Igs MHC ComplementDocumento3 pagineChok Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer Igs MHC Complementapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chok Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer O2 Metab ToxicDocumento3 pagineChok Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer O2 Metab Toxicapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chok Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer Blood CoagulationDocumento2 pagineChok Biochem 3rd Shift Reviewer Blood Coagulationapi-3742802100% (1)
- Embryo Reviewer Repro SysDocumento2 pagineEmbryo Reviewer Repro Sysapi-3742802Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
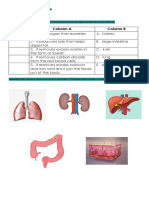
- Long Test 2 - Science 6: Match The Excretory Organs in COLUMN B With Its Description in COLUMN ADocumento3 pagineLong Test 2 - Science 6: Match The Excretory Organs in COLUMN B With Its Description in COLUMN Akatherine corveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardio Book PDFDocumento34 pagineCardio Book PDFDwi PascawitasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Causes of AneurysmsDocumento11 pagineCauses of AneurysmsMathew Ace M. OmilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Download Transport Phenomena in Biological Systems 2nd Edition Free PDFDocumento4 pagineDownload Transport Phenomena in Biological Systems 2nd Edition Free PDFhamzaNessuna valutazione finora
- BED BATHING HandoutDocumento7 pagineBED BATHING HandoutDharylle CariñoNessuna valutazione finora
- Investigation Report: Flowcytometry. Carried Out by Sysmex XN-2000 SeriesDocumento1 paginaInvestigation Report: Flowcytometry. Carried Out by Sysmex XN-2000 SeriesNafis ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Plasma SubstitutesDocumento40 paginePlasma Substitutesneha_dand1591Nessuna valutazione finora
- Acupuncture For Disorders of BloodDocumento26 pagineAcupuncture For Disorders of BloodGordana Petrovic100% (1)
- What Is Septic ShockDocumento6 pagineWhat Is Septic Shocksalome carpioNessuna valutazione finora
- Combined Science Notes Form 3 Biology Section Cells and NutritionDocumento190 pagineCombined Science Notes Form 3 Biology Section Cells and NutritionTakunda Tatiwa0% (1)
- 1 Hematology TestDocumento48 pagine1 Hematology TestAhmed YassinNessuna valutazione finora
- Umbilical Cord Blood Bank, Future Child Health InsuranceDocumento2 pagineUmbilical Cord Blood Bank, Future Child Health Insurancenvtaa rnaNessuna valutazione finora
- DVTDocumento4 pagineDVTMàŗwā TāhāNessuna valutazione finora
- B KochharDocumento12 pagineB KochharJitendraBhartiNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 7 SOF National Science Olympiad Sample Paper TitleDocumento2 pagineClass 7 SOF National Science Olympiad Sample Paper TitlepawanNessuna valutazione finora
- ABG Poster A3Documento1 paginaABG Poster A3Araceli Ecot Calunod100% (2)
- PHBIO lecture on DVT and PEDocumento5 paginePHBIO lecture on DVT and PEJamie Angelo PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Hematology FinalDocumento103 pagineHematology Finalallanrnmanaloto100% (1)
- Destined For DominionDocumento167 pagineDestined For DominionDr. A.L. and Joyce Gill100% (3)
- Biochemistry 3070 - Myoglobin and Hemoglobin: Oxygen Transport ProteinsDocumento44 pagineBiochemistry 3070 - Myoglobin and Hemoglobin: Oxygen Transport ProteinsNiveditha ChalukyaNessuna valutazione finora
- HB 0329 004 1102728 HB QIAamp DNA Mini Blood Mini 0516 WWDocumento72 pagineHB 0329 004 1102728 HB QIAamp DNA Mini Blood Mini 0516 WWJuçara SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood NursingDocumento34 pagineBlood NursingManikanta GupthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aqua Water Purification - Aqua Soft NaturalDocumento5 pagineAqua Water Purification - Aqua Soft NaturalIsrael ExporterNessuna valutazione finora
- B Blab 7 Panel Spring 2012Documento16 pagineB Blab 7 Panel Spring 2012pzaballero7063Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transportation in Animals and Plants Worksheet 10 PDFDocumento2 pagineTransportation in Animals and Plants Worksheet 10 PDFParul ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- 16th International Mathematics and Science Olympiad Science Test QuestionsDocumento21 pagine16th International Mathematics and Science Olympiad Science Test QuestionsThanh Dinh100% (2)
- Crystal Vibrations Ailments PDFDocumento161 pagineCrystal Vibrations Ailments PDFIonela Solcanu100% (3)
- Blood Pressure Automatic: Intelli SenseDocumento2 pagineBlood Pressure Automatic: Intelli SenseDnGNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood: Muhammad Iqbal Lecturer KMUDocumento40 pagineBlood: Muhammad Iqbal Lecturer KMUKomal NayabNessuna valutazione finora
- NOTES LIFE PROCESSES (Respiration, ExcretionDocumento3 pagineNOTES LIFE PROCESSES (Respiration, ExcretionGokulVijayGopal G10Nessuna valutazione finora