Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
About Clinical Performance of Nursing Students by Adah Chung
Caricato da
Nel Joshua MicayabasDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
About Clinical Performance of Nursing Students by Adah Chung
Caricato da
Nel Joshua MicayabasCopyright:
Formati disponibili
About Clinical Performance of Nursing Students By Adah Chung Although the study of medicine, anatomy, physiology, pharmacology and
clinical research is important for the practice of becoming a nurse, nursing students must also acquire the skills necessary to achieve competency. Nursing students must participate in clinical education, training and assessment in order to ensure that they can apply their knowledge in a competent manner for the care of their patients. Clinical performance of nursing students includes the accurate assessment and treatment of patients and the use of appropriate communication tools to be an effective caregiver. 1. Formal Education
o
Nursing students must participate in a formal education program, either at an associate's degree or bachelor's degree level. Formal education includes coursework in areas such as pathophysiology, chemistry, psychology, nutrition and anatomy. An appropriate background in clinical knowledge and theory will help prepare nursing students for competent clinical performance. Training/Clinical Rotations
All nursing education programs have a clinical component, in which students are supervised by clinicians in a clinical setting, such as a hospital, a clinic, home care or long-term care. Most education programs prescribe a number of hours of clinical work that nursing students are required to complete, with learning objectives specific to the nursing student's level of learning. A preceptor is responsible for ensuring that nursing students receive the clinical experiences necessary to meet the learning objectives and also for providing feedback to the nursing student. Simulation
Simulation labs are another way for nursing students to learn and practice clinical skills. In simulation labs, nursing students can practice skills such as monitoring heart rate, taking blood pressure, drawing blood, giving injections or inserting an IV on a mannequin designed to simulate a patient. These labs provide a safe environment for nursing students to practice their clinical performance skills. Areas of Clinical Performance
The areas of clinical performance required by nursing students include taking a history, physical assessment, medical procedures (such as inserting an IV or a catheter), interpersonal skills with patient, family and other professionals and the development of a treatment plan. Assessment of Clinical Performance
Clinical performance of nursing students is measured through observation and feedback during clinical rotations. They also are assessed using simulated clinical practice exams, in which nursing students complete simulated scenarios with patients in a fair and
objective way. Clinical performance of nursing students can be assessed and compared objectively through a clinical assessment using standardized patients.
Theories of Academic Performance Among Nursing Students By Siobhan Egan As nursing shortages threaten to create problems in the delivery of health care, nursing academic programs aim to encourage nursing candidates who will succeed. Studies have explored the predictive factors for success in university nursing programs. 1. Self-Regulated Learning
o
A study by the Graduate School of Education, University of Wollongong, Australia, suggested that students who engage in self-regulated learning are best prepared to meet the academic rigors of a nursing degree program. The study found that to be academically successful in a first-year bachelor of science nursing course, students need strong selfefficacy beliefs to employ a variety of learning strategies and to be convinced of the value and relevance of science to their nursing program. Intellectual Factors Better Predictors Than Non-Intellectual
A study in the Association of Black Nursing Faculty Journal hypothesized that certain non-intellectual factors, such as coping style, number of personal problems, age, marital status and employment status, would be more predictive of academic performance in the first year than would intellectual factors, such as high school grade point average and academic achievement test scores. However, the study found that intellective factors as a group were better predictors than the non-intellective factors. Support-Seeking Good Predictor
A Journal of Advanced Nursing study hypothesized that age and entry qualifications influence Northern England students' academic motivation and that this in turn affects their decisions to seek support, which subsequently influences their academic performance. The study found that support-seeking was indeed more predictive of student performance than entry qualifications.
3.5 DATA ANALYSIS PLAN Upon completion of data collection, data were coded, captured on Excel and theni m p o r t e d i n t o t h e s t a t i s t i c a l P a c k a g e f o r S o c i a l S c i e n c e s ( S P S S ) v e r s i o n 1 4 . 0 f o r analysis. Descriptive statistics were used mainly to summarize the data and provideanswers to the first three research objectives, whereas, the independent sample t-tests and one-way ANOVA tests and post hoc Tukeys HSD test were used to identifysignificant differences for the last research objective. These analyses included thecomparisons of final year nursing students knowledge, attitudes and practices bydemographic characteristics
http://www.lawphil.net/statutes/presdecs/pd1976/pd_996_1976.html
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Effects of Blended Learning On Knowledge, Skills, and Satisfaction Innursing Students A Meta-AnalysisDocumento7 pagineThe Effects of Blended Learning On Knowledge, Skills, and Satisfaction Innursing Students A Meta-AnalysisZilbran BerontaxNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Perceptions of The Role of Emotional Intelligence in College Success: A Phenomenological StudyDocumento21 pagineStudent Perceptions of The Role of Emotional Intelligence in College Success: A Phenomenological StudyInternational Journal of Business Marketing and ManagementNessuna valutazione finora
- Review of Related LiteratureDocumento5 pagineReview of Related LiteratureMelissa Agarrado ReputanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Piagets Cognitive Devt TheoryDocumento8 paginePiagets Cognitive Devt TheoryMartin AlvinNessuna valutazione finora
- Time To Learn. Understanding Patient Centered CareDocumento7 pagineTime To Learn. Understanding Patient Centered CareAden DhenNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication Skills Doctors PDFDocumento2 pagineCommunication Skills Doctors PDFKendraNessuna valutazione finora
- Field Observation NotesDocumento14 pagineField Observation Notesapi-271122505100% (1)
- An Exploration of School Nurse Role in Secondary Girls Schools in BahrainDocumento6 pagineAn Exploration of School Nurse Role in Secondary Girls Schools in BahrainGlobal Research and Development ServicesNessuna valutazione finora
- Motivating Students in The 21st Century: Peer ReviewDocumento9 pagineMotivating Students in The 21st Century: Peer ReviewreemmajzoubNessuna valutazione finora
- 2005 Idsa Ats Hospital Acquired Pneumonia GuidelinesDocumento8 pagine2005 Idsa Ats Hospital Acquired Pneumonia GuidelinesAlejandro CasillasNessuna valutazione finora
- Advantages and Disadvantages of The Objective Structured Clinical Examination OSCE in Nursing Education A Literature ReviewDocumento5 pagineAdvantages and Disadvantages of The Objective Structured Clinical Examination OSCE in Nursing Education A Literature ReviewEditor IJTSRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Qualitative Analysis of Functional Groups AssignmentDocumento6 pagineQualitative Analysis of Functional Groups AssignmentChristyNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines For Observation of Online TeachingDocumento16 pagineGuidelines For Observation of Online TeachingIriskathleen AbayNessuna valutazione finora
- Hospital Aquired Pneumonia - FullDocumento26 pagineHospital Aquired Pneumonia - FullSuvad Dedic100% (1)
- Critical Review of Simulation-Based Medical Education Research, 2003-2009Documento14 pagineCritical Review of Simulation-Based Medical Education Research, 2003-2009cegarcia100% (1)
- Higher Education Research and InnovationDocumento242 pagineHigher Education Research and Innovationjrufino5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Service Learning Case StudyDocumento7 pagineService Learning Case StudyRussellAivazianNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessing Work Readiness Using Reflective PracticeDocumento11 pagineAssessing Work Readiness Using Reflective PracticeTina ZubovicNessuna valutazione finora
- The Power and Importance of Formative AssessmentDocumento4 pagineThe Power and Importance of Formative AssessmentRefi SativaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Educational Program in NursingDocumento2 pagineBasic Educational Program in NursingSj EclipseNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching StrategiesDocumento13 pagineTeaching StrategiesNoreen Q. SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Evidence Based PracticeDocumento3 pagineEvidence Based PracticeTyler HemsworthNessuna valutazione finora
- The Roles Parents Play in Online LearningDocumento2 pagineThe Roles Parents Play in Online LearningJhoanna Pauline MamansagNessuna valutazione finora
- Competency Based Education....... AmritaDocumento3 pagineCompetency Based Education....... AmritaGurinder GillNessuna valutazione finora
- Zimmerman 2004Documento14 pagineZimmerman 2004Oscar MuñozNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 Assessment Briefing and Planning 2223Documento21 pagineModule 2 Assessment Briefing and Planning 2223Mohamed AbdelhadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Instructional Design ProjectDocumento34 pagineInstructional Design Projectchill83301Nessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching StrategiesDocumento14 pagineTeaching Strategieseden barredaNessuna valutazione finora
- Interprofessional Collaboration Three Best Practice Models of Interprofessional EducationDocumento11 pagineInterprofessional Collaboration Three Best Practice Models of Interprofessional Educationanzila widyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Research ParadigmDocumento1 paginaResearch ParadigmJohnny WalkerNessuna valutazione finora
- Project-Based Learning Model Practicality On Local Network Devices Installation SubjectDocumento13 pagineProject-Based Learning Model Practicality On Local Network Devices Installation SubjectNovi Eko WahyudiNessuna valutazione finora
- Effective Use of Learning ObjectivesDocumento6 pagineEffective Use of Learning ObjectivesIamKish Tipono ValenciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Ed - Chapter 3Documento33 pagineHealth Ed - Chapter 3Kevin CamilozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Research ProposalDocumento5 pagineResearch ProposalPIR AIZAZ ALI SHAHNessuna valutazione finora
- Genomics and Nursing PracticeDocumento7 pagineGenomics and Nursing Practicebernadette_olaveNessuna valutazione finora
- ICEEE 2017 LearningStyles PDFDocumento8 pagineICEEE 2017 LearningStyles PDFWolfmystery OfficialNessuna valutazione finora
- Adaptive LearningDocumento10 pagineAdaptive Learningapi-341841292Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mastery LearningDocumento162 pagineMastery LearningCidney100% (1)
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: (Nsaids)Documento38 pagineNon-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: (Nsaids)Mylyn LagartejaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Human Needs Approach, A Basic Handbook For Nursing StudentsDocumento23 pagineThe Human Needs Approach, A Basic Handbook For Nursing StudentsEcaroh Hew SmailliwNessuna valutazione finora
- Ebp Formative Synthesis PaperDocumento9 pagineEbp Formative Synthesis Paperapi-404415990Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Academic Stress of Final-Year Students in Covid-19 Pandemic EraDocumento10 pagineThe Academic Stress of Final-Year Students in Covid-19 Pandemic EraYuliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategies For Disseminating ResearchDocumento12 pagineStrategies For Disseminating Researchafiani qonitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Three Pedagogies in Higher EducationDocumento15 pagineChapter Three Pedagogies in Higher EducationNurhalimah FebriantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chicago Notes and Bibliography StyleDocumento6 pagineChicago Notes and Bibliography StyleJuan C. MartínezNessuna valutazione finora
- Bone Marrow Donation: By:Angela Bush Alexa PomanteDocumento18 pagineBone Marrow Donation: By:Angela Bush Alexa Pomantesueiannacci100% (1)
- Nursing As A PhilosophyDocumento28 pagineNursing As A PhilosophyErik Karcher100% (1)
- FHEA Guidance Notes For ApplicantsDocumento9 pagineFHEA Guidance Notes For ApplicantsZubair JatoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Theoretical Foundations of NursingDocumento3 pagineTheoretical Foundations of NursingThereseNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Proposal Assignment 08Documento3 pagineResearch Proposal Assignment 08sahhhhhhhNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam 1 Review BotanyDocumento16 pagineExam 1 Review BotanyLolaNessuna valutazione finora
- AIINEDUCATIONDocumento9 pagineAIINEDUCATIONOlavario Jennel PeloNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.psychosocial Aspects of Health and DiseaseDocumento30 pagine5.psychosocial Aspects of Health and DiseaseFaisal MehboobNessuna valutazione finora
- HIV TestDocumento5 pagineHIV TestMahesa NaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of Attitude of Nursing Mothers Towards Childhood Immunization in Some Selected Communities in Bali, LGA of Taraba StateDocumento56 pagineAssessment of Attitude of Nursing Mothers Towards Childhood Immunization in Some Selected Communities in Bali, LGA of Taraba StateJoshua Bature SamboNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching and Learning at The BedsideDocumento23 pagineTeaching and Learning at The BedsideJohn SummertonNessuna valutazione finora
- g7 Research Proposal FinalDocumento36 pagineg7 Research Proposal FinalChristian Leo Venzon MoringNessuna valutazione finora
- Research - ScriptDocumento8 pagineResearch - ScriptRheizhelle Anne LaguraNessuna valutazione finora
- Effectiveness of Related Learning Experience in Nursing Students Biostat1Documento12 pagineEffectiveness of Related Learning Experience in Nursing Students Biostat1Rose Ann67% (3)
- Research PresentationDocumento14 pagineResearch PresentationCeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic OsteomyelitisDocumento4 pagineChronic OsteomyelitisNel Joshua MicayabasNessuna valutazione finora
- Xandra ENDODocumento3 pagineXandra ENDONel Joshua MicayabasNessuna valutazione finora
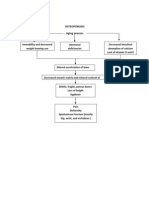
- Osteoporosis Pa Tho PhysiologyDocumento1 paginaOsteoporosis Pa Tho PhysiologyNel Joshua MicayabasNessuna valutazione finora
- Gentamycin Dopamine HCL, Oxacillin NaDocumento2 pagineGentamycin Dopamine HCL, Oxacillin NaNel Joshua MicayabasNessuna valutazione finora
- Diazepam and FurosemideDocumento3 pagineDiazepam and FurosemideNel Joshua MicayabasNessuna valutazione finora
- Esa Appeals FactsheetDocumento36 pagineEsa Appeals FactsheetClaire TNessuna valutazione finora
- FNCP - Problem 3 HTNDocumento3 pagineFNCP - Problem 3 HTNteuuuuNessuna valutazione finora
- Asa PSC System PDFDocumento2 pagineAsa PSC System PDFKen WonNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Key Ielts 2Documento16 pagineAnswer Key Ielts 2Sovannak OnNessuna valutazione finora
- Acupuncture LectureDocumento10 pagineAcupuncture Lectureapi-5481010020% (1)
- GCC Human Drugs Subv2.1Documento103 pagineGCC Human Drugs Subv2.1AmrNessuna valutazione finora
- Tipos de Diabetes - Diabetes MonogenicaDocumento27 pagineTipos de Diabetes - Diabetes MonogenicaSara AmorimNessuna valutazione finora
- Antiinflammatorydrugs: Beatriz Monteiro,, Paulo V. SteagallDocumento19 pagineAntiinflammatorydrugs: Beatriz Monteiro,, Paulo V. SteagallYohan Oropeza VergaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Occupational Therapy in Mental Health A Vision For Participation 2nd Edition Catana Brown Virginia C Stoffel Jaime MunozDocumento3 pagineTest Bank For Occupational Therapy in Mental Health A Vision For Participation 2nd Edition Catana Brown Virginia C Stoffel Jaime MunozDavid Ortiz97% (36)
- The Influence of Music in Horror Games (Final Draft)Documento7 pagineThe Influence of Music in Horror Games (Final Draft)Panther LenoXNessuna valutazione finora
- Target Heart Rate Lesson PlanDocumento4 pagineTarget Heart Rate Lesson PlanEryn YeskeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Report 15438869 20231127064225Documento1 paginaLab Report 15438869 20231127064225carilloabhe21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Food SafetyDocumento2 pagineFood SafetymacmanueNessuna valutazione finora
- Nurses Progress NotesDocumento2 pagineNurses Progress Notesvan100% (1)
- Sarah J. (Englert) Dunham RN, BSN, MS, FNPDocumento3 pagineSarah J. (Englert) Dunham RN, BSN, MS, FNPapi-309264509Nessuna valutazione finora
- Knowledgeand Beliefson Mental Illnessamong Church Leaders Basisfor Trainingand DevelopmentDocumento15 pagineKnowledgeand Beliefson Mental Illnessamong Church Leaders Basisfor Trainingand DevelopmentG Asilo, Jynelle A.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Week 2 SolutionsDocumento4 pagineWeek 2 Solutionsannavarapuanand100% (2)
- ReferencesDocumento2 pagineReferencesapi-451063936Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hauber 2019Documento10 pagineHauber 2019Laura HdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Consequences of Adverse Childhood Experiences: A Systematic ReviewDocumento9 pagineHealth Consequences of Adverse Childhood Experiences: A Systematic ReviewCocia Podina Ioana RoxanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture in Geriatrics Physical Therapy 1Documento27 pagineLecture in Geriatrics Physical Therapy 1S.ANessuna valutazione finora
- Peran Perawat KomDocumento27 paginePeran Perawat Komwahyu febriantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Azibact MMDocumento37 pagineAzibact MMરહીમ હુદ્દાNessuna valutazione finora
- Philippine Saviours: Narratives of Filipino Intensive Care Nurses and Their Ways On Handling Chronically Ill PatientsDocumento38 paginePhilippine Saviours: Narratives of Filipino Intensive Care Nurses and Their Ways On Handling Chronically Ill PatientsHannah SampianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Medieval BodiesDocumento2 pagineMedieval BodiesKoh Yen SinNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 4abcDocumento11 paginePart 4abcMatthew Guevarra100% (1)
- Disorder and Diseases of Digestive SystemDocumento8 pagineDisorder and Diseases of Digestive SystemCristina AnganganNessuna valutazione finora
- 2018 MUSE Inspire Conference - Show and Tell SessionsDocumento13 pagine2018 MUSE Inspire Conference - Show and Tell SessionsMichele LambertNessuna valutazione finora
- Curriculum Vitae Professor Ngai Ngan-pun (魏雁滨教授)Documento22 pagineCurriculum Vitae Professor Ngai Ngan-pun (魏雁滨教授)api-26075761Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pappas Bikhazi 2023 Babe Ruth S Anaplastic Epidermoid Carcinoma of The NasopharynxDocumento5 paginePappas Bikhazi 2023 Babe Ruth S Anaplastic Epidermoid Carcinoma of The NasopharynxVinoster ProductionNessuna valutazione finora