Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
HKCEE1
Caricato da
api-3739994Descrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
HKCEE1
Caricato da
api-3739994Copyright:
Formati disponibili
HKCEE PAST PAPER 87-94/SECTION 1/LQ/PAGE 1
Section 1 Fundamentals of Matter
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1987 Q.4(b)
The table below lists some physical data for sodium chloride and tetrachloromethane:
Sodium chloride Tetrachloromethane
Melting point (°C) 808 -23
Solubility in water at 25 °C (g/100 cm3) 32 insoluble
(i) Explain the difference in melting point between sodium chloride and tetrachloromethane in
terms of the nature of forces between particles.
(ii) Draw the electronic structures of sodium chloride and tetrachloromethane, indicating the
arrangement of electrons in the outermost shells only.
(iii) Draw a three-dimensional diagram of
(1) the lattice structure of solid sodium chloride.
(2) The shape of a tetrachloromethane molecule. [out of syllabus]
(iv) 32 g of sodium chloride, 32 g of tetrachloromethane and 50 cm3 of water are shaken together
in a stoppered bottle and then allowed to settle. After a few minutes, what would be
observed.
(7/8 marks)
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1988 Q.1(a)
X, Y and Z are three elements with atomic numbers less than twenty. The following table provides
some information about these elements:
Element X Element Y Element Z
No. of outermost shell electrons 2 4 6
Appearance at room temperature Grey solid Black solid with a Yellow solid
bright lustre
Conduction of electricity Good Good Poor
Nature of oxide The oxide (XO) The oxide (YO2) The oxide (ZO2)
is basic. is acidic. is acidic.
(i) In which group of the Periodic Table should Z be placed?
(ii) Classify X, Y and Z as metal or non-metal, and explain your classification.
(iii) X and Z can form a compound A, while Y and Z can form a compound B.
(1) Draw the electronic structures of A and B, showing the outermost electrons only.
(2) Explain whether A or B would have the higher melting point.
(3) Explain whether X acts as an oxidizing or a reducing agent in the formation of A.
(iv) Under what condition would X react with the oxide YO2? Write an equation for this reaction.
(12 marks)
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1989 Q.1(c)
P, Q, R and S represent four elements of atomic numbers 10, 14, 17 and 19 respectively.
(i) Which TWO of these elements would form
(1) an ionic compound?
(2) a covalent compound?
(ii) For the compounds in (i) above,
(1) Draw their electronic structures, showing electrons in the outermost shell only.
(2) Explain which compound is more volatile in terms of the forces between particles.
HKCEE PAST PAPER 87-94/SECTION 1/LQ/PAGE 2
(5 marks)
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
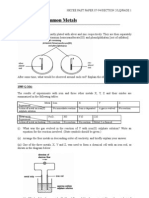
1990 Q.1(b)
The TWO diagrams above represent part of the structures of an allotrope of carbon, and sodium
chloride at room temperature.
(i) What type of bonding exists in each of the substances shown above?
(ii) State a condition under which each substance can conduct electricity. Explain your answers.
(iii) Name an allotrope of carbon other than that shown above. [out of syllabus]
(iv) Which allotrope of carbon is used to
(1) make pencil lead? [out of syllabus]
(2) cut glass?
Explain your answers with reference to the different arrangements of atoms in these two
allotropes.
(v) Do you agree with the statement “sodium chloride cannot easily be changed into sodium and
chlorine”? Explain your answer.
(9/12 marks)
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1991 Q.1(a)
The following is a part of the Periodic Table:
Group
III IV VI VII
Second period
Third period
Referring to the letters indicated in the above table, answer the following questions:
(i) (1) What is the name for the family of elements of which b and f are members?
(2) In what way are the electronic arrangements of the atoms of element b and f
(I) similar to each other?
(II) different from each other?
(ii) Element d has a higher melting point than element c. Explain.
(iii) The oxide of element d is insoluble in water and amphoteric (this term is out of syllabus
now).
(1) Give the formula for this oxide.
(2) Suggest suitable chemical tests to show that the oxide is amphoteric. [out of syllabus]
(iv) Two elements in the above table have allotropes.
(1) Explain the meaning of ‘allotropes’. [out of syllabus]
(2) Suggest what the two elements are. [out of syllabus]
(v) Element e can form compound with element a and c separately.
HKCEE PAST PAPER 87-94/SECTION 1/LQ/PAGE 3
(1) Draw the electronic structures of these compounds, showing the outermost electrons
ONLY.
(2) Which of these two compounds has a higher melting point? Explain your answer.
(9/13 marks)
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1992 Q.3(b)
Neon, a monatomic gas, occurs naturally as a mixture of three isotopes. The relative abundance of
these isotopes is tabulated below:
Isotope 20
10Ne 21
10Ne 22
Ne
10
Abundance (%) 90.52 0.31 9.17
(i) State the number of electrons in the outermost shell of a neon atom.
(ii) Explain why neon gas is monatomic.
(iii) What is meant by the term 'isotope’?
(iv) Calculate
(1) the relative atomic mass of neon.
(2) the density (in g dm-3) of neon gas at room temperature and pressure.
(Molar volume of gas at room temperature and pressure = 24.0 dm3)
(7 marks)
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1993 Q.2(b)
Physical properties of substances depend mainly on the types of binding force between their
constituent particles.
(i) The melting points of diamond and tetrachloromethane are 3750 °C and -23 °C respectively.
Draw 3-dimensional diagrams for the structure of diamond and for a tetrachloromethane
molecule [out of syllabus]. Hence explain the difference in their melting points.
(ii) In their solid states, sodium conducts electricity but sodium chloride does not. Explain.
(iii) Explain why tetrachloromethane does not conduct electricity in liquid state.
(6/7 marks)
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1993 Q.4(a)
The following table given some information about W, X, Y and Z which represent particles of
some elements. These particles are either atoms or ions.
Mass number Atomic number No. of protons No. of electrons No. of neutrons
W 12 12 12
12 10 12
35 17 17
17 17 20
(i) In which group of the Periodic Table should W be placed? Explain your answer.
(ii) (1) What is the relationship between W and X?
(2) Suggest a chemical reaction which can change W into X.
(iii) Molecules of Y and of Z are both diatomic.
(1) Draw the electronic structure of a molecule of Y, showing electrons in the outermost
shells only.
(2) Do molecules of Y and of Z have the same chemical properties? Explain your answer.
HKCEE PAST PAPER 87-94/SECTION 1/LQ/PAGE 4
(iv) W can form a compound with Z. Calculate the formula mass of the compound formed.
(7 marks)
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1994 Q.7(b)
The table below lists some physical properties of lead, bromine and lead(II) bromide.
Lead Bromine Lead(II) bromide
Melting point 328 °C -7 °C 370 °C
Electrical conductivity in the solid state conducting non-conducting non-conducting
Electricity conductivity in the liquid state conducting non-conducting ---
(i) Explain the difference in melting points between bromine and lead(II) bromide.
(ii) Explain the difference in electrical conductivity between lead and lead(II) bromide in the solid
state.
(iii) Will lead(II) bromide conduct electricity in the liquid state? Explain your answer.
(5 marks)
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
<END OF SECTION 1>
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Study of Mangrove HabitatDocumento14 pagineA Study of Mangrove Habitatapi-3739994100% (1)
- MC Ques Eng H2SO4 SO2Documento31 pagineMC Ques Eng H2SO4 SO2api-3739994Nessuna valutazione finora
- MC Ques Eng Redox Rxns AnsDocumento8 pagineMC Ques Eng Redox Rxns Ansapi-3826629Nessuna valutazione finora
- MC Ques Eng DetergentsDocumento10 pagineMC Ques Eng Detergentsapi-3739994100% (1)
- MC Ques Eng ElectrolysisDocumento3 pagineMC Ques Eng Electrolysisapi-3739994Nessuna valutazione finora
- HKCEE (CHDocumento6 pagineHKCEE (CHapi-3739994Nessuna valutazione finora
- MC Chlorine HypochloriteDocumento14 pagineMC Chlorine Hypochloriteapi-3826629100% (1)
- HKCEE2Documento4 pagineHKCEE2api-3739994Nessuna valutazione finora
- HKCEE7Documento4 pagineHKCEE7api-3739994Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ce MC AssertionDocumento3 pagineCe MC Assertionapi-3739994Nessuna valutazione finora
- Past Paper - Planet EarthDocumento2 paginePast Paper - Planet Earthapi-3739994Nessuna valutazione finora
- Past Paper - Microscopic WorldDocumento7 paginePast Paper - Microscopic Worldapi-3739994100% (1)
- Past Paper - Acids and Alkalis - LQDocumento10 paginePast Paper - Acids and Alkalis - LQapi-3739994100% (2)
- Past Paper Electrochemistry LQDocumento15 paginePast Paper Electrochemistry LQapi-3739994100% (1)
- Past Paper - Important Products From Petroleum - LQDocumento3 paginePast Paper - Important Products From Petroleum - LQapi-3739994Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Sub Zero Operations ManualDocumento57 pagineSub Zero Operations Manualpascal rosasNessuna valutazione finora
- C20R Optimized Start Technique For C20 and C20RDocumento4 pagineC20R Optimized Start Technique For C20 and C20REstevamNessuna valutazione finora
- PETSOC-09-07-18 Gas Condensate Reservoir Performance PDFDocumento7 paginePETSOC-09-07-18 Gas Condensate Reservoir Performance PDFMiguel Angel GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Practica Gases PrefaDocumento1 paginaPractica Gases PrefaAlejandro Poma VillarrealNessuna valutazione finora
- CSEC 2021 June Workshop SolutionsDocumento16 pagineCSEC 2021 June Workshop Solutionspoet100% (1)
- Pogil Boyles LawDocumento4 paginePogil Boyles LawRussel OtillaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Boiler Mechanical Design GroupDocumento170 pagine2 Boiler Mechanical Design GroupFraser LamontNessuna valutazione finora
- Conduction and Breakdown in Gases - SVDocumento85 pagineConduction and Breakdown in Gases - SVtawanda daniel dengu67% (3)
- Reservoir Engineering Exercise Set 1Documento9 pagineReservoir Engineering Exercise Set 1Mohammad HaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Specification of Gas Supply To Tecjet 110Documento4 pagineSpecification of Gas Supply To Tecjet 110siyavash seifNessuna valutazione finora
- Annual Boiler Tuneup Checklist: Fading FiberglassDocumento1 paginaAnnual Boiler Tuneup Checklist: Fading FiberglasssamsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Portable Percent Oxygen Analyzer With USB Data LoggingDocumento1 paginaPortable Percent Oxygen Analyzer With USB Data LoggingAbduol llyNessuna valutazione finora
- Adv PT1Documento23 pagineAdv PT1AdvaithNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Thermodynamics MCQDocumento50 pagineEngineering Thermodynamics MCQShriram Pandian100% (2)
- Annex Lesson 1Documento9 pagineAnnex Lesson 1Crystal DavisNessuna valutazione finora
- 12th Passed-NEET-AIATS - 0Documento6 pagine12th Passed-NEET-AIATS - 0SANTOSH KUMAR100% (1)
- Written IN General Chemistry: Maharlika Highway, Brgy. Campetic, Palo, LeyteDocumento54 pagineWritten IN General Chemistry: Maharlika Highway, Brgy. Campetic, Palo, LeyteJireh Mae CorderoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pseg Bill Mohamed DaboDocumento6 paginePseg Bill Mohamed Daboyusuf FajarNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy Mid Year ExamDocumento13 paginePhy Mid Year ExamKendrickNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Indoor Air Quality MonitoringDocumento4 pagineDesign of Indoor Air Quality MonitoringKadek ArisudamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Soot Deposits and Fires in Exhaust Gas BoilersDocumento21 pagineSoot Deposits and Fires in Exhaust Gas BoilersJose G. CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 1Documento20 pagineExperiment 1Shelvin NaiduNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Factors On The Hydrogen Composition in The Carburizing ProcessDocumento7 pagineEffect of Factors On The Hydrogen Composition in The Carburizing ProcessAndi PrayogaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 2 KeytermsDocumento2 pagine3 2 Keytermsapi-291995478Nessuna valutazione finora
- @unacademyplusdiscounts Arihant BITSAT Prep Guide 2020Documento1.367 pagine@unacademyplusdiscounts Arihant BITSAT Prep Guide 2020Ritviz AggarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Rocket Activities 1Documento3 pagineRocket Activities 1badmintNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento151 pagineUntitledSANDEEP GautamNessuna valutazione finora
- Tourbe Sci Hub 1Documento4 pagineTourbe Sci Hub 1Samir BenkiraneNessuna valutazione finora