Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Redox Lab
Caricato da
Katelyn SinclairDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Redox Lab
Caricato da
Katelyn SinclairCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Oxidation and Reduction
By: Katie Sinclair Introduction: When two reactants are combined, it is common for one reactant to attract electrons of another atom, possibly causing the atoms to stabilize or become charged. A redox reaction occurs when there is a shift in electron density between atoms. Reduction is when an atom gains electron density, while oxidation is when an atom loses electron density. The reducing agent is the reactant that gains electrons during the reaction, effectively causing another reactant to become reduced. Similarly, the oxidizing agent is the reactant which loses electrons during a reaction, causing another reactant to become oxidized. Some atoms are more easily reduced and oxidized than others, which can be observed through experimental observation. Purpose: To test and observe the reaction of metals and halogens combined with different metallic and halide ions in order to estimate the ease with which each can be reduced. Materials / Procedure: See handout titled An Introduction to Oxidation Reduction. Observations: See attached observation sheets. Analysis: 1) The copper ions were reduced by two metals, zinc and lead. The lead ions were reduced by one metal, zinc. The zinc ions were not reduced by any of the metals. 2) Ag Cu Pb Zn 3) Pb Cu Cu + + + + + + + 1e 2e 2e 2e Zn Zn Pb Ag Cu Pb Zn Pb Cu Cu + + + Zn Zn Pb
4) The aqueous chlorine was reduced by two of the halide ions, bromide and iodide. The aqueous bromine was reduced by one of the halide ions, iodide. The aqueous iodine was not reduced by any of the halide ions. 5) Cl Br I 6) Cl Cl Br 7) Cl Br Ag I Cu Pb Zn + + + + + + + + + + + + + 2e 2e 2e 2Br 2I 2I 2e 2e e 2e 2e 2e 2e 2Cl 2Br 2I 2Cl 2Cl 2Br 2Cl 2Br Ag 2I Cu Pb Zn + + + Br I I
8) a) It would not be feasible to store a solution of copper sulfate in a container made of metallic zinc. This is because the copper ions in the copper sulfate are stronger oxidizing agents than zinc metal, meaning that they will donate ions to the zinc metal in order to stabilize. This will spontaneously react to form copper metal and zinc ions, meaning that storing copper sulfate in a metallic zinc container would not work. b) It would be feasible to store a solution of copper sulfate in a container made of metallic silver. This is because the copper ions in the copper sulfate are not strong enough oxidizing agents to pull electrons away from the stable silver metal. There will be no spontaneous reaction meaning that it is possible to store copper sulfate solution in a metallic silver container. c)It would be expected that jewelery made from an alloy of silver and copper would tarnish when bromine fumes are present. This is because bromine is a stronger oxidizing agent than both copper and silver, meaning that bromine atoms are capable of taking electrons from both metals, effectively oxidizing them, in order to stabilize.
Conclusion: It can be concluded that some metals and halogens, as well as their metallic and halide ion counterparts, are all oxidized and reduced with a certain amount of ease relative to each other. With the empirical data gained from this experiment, a table was formed displaying the order of strongest oxidizing agents to weakest oxidizing agents. When observing the other side of the table, the weakest reducing agents to strongest reducing agents are shown. Using this table, it is possible to predict which reactants will react during an experiment, as well as which atoms or ions will be oxidized or reduced based on the strength of the oxidizing and reducing agents used. This is useful because it can be determined what will happen in a reaction before actually trying it, reducing the risk of a potentially dangerous reaction, or eliminating the need to experiment with reactants that will not have a chemical reaction.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Self Healing MaterialsDocumento418 pagineSelf Healing Materialsmaged_abdnagho100% (1)
- Alcohol, Phenol and Ethers Digital Notes by Bharat PanchalDocumento24 pagineAlcohol, Phenol and Ethers Digital Notes by Bharat Panchalzaid ansari86% (7)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Die Casting DieDocumento156 pagineDie Casting DieHeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Engineering MCQs: Thermodynamics and PropertiesDocumento180 pagineChemical Engineering MCQs: Thermodynamics and PropertiesEngr Javeed Nawaz QaisraniNessuna valutazione finora
- Robinair Bombas de Vacío 15401 601Documento32 pagineRobinair Bombas de Vacío 15401 601MarcWorld100% (1)
- Discharge Plasma and Ion - Surface InteractionsDocumento50 pagineDischarge Plasma and Ion - Surface InteractionsIriantoNessuna valutazione finora
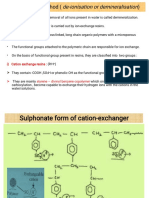
- Ion Exchange ProcessDocumento10 pagineIon Exchange Process056 Jatin GavelNessuna valutazione finora
- FINAL EDIT - Jurnal Bang Wahyu16 - TEKNOSIA FT UNIBDocumento14 pagineFINAL EDIT - Jurnal Bang Wahyu16 - TEKNOSIA FT UNIBLeonardo EmyusNessuna valutazione finora
- The Effect of Strain Rate On Mechanical PropertiesDocumento11 pagineThe Effect of Strain Rate On Mechanical Propertiesmechanicaltestinglab.acmsNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiences in Designing and Operating The Latest 1,050-MW Coal-Fired BoilerDocumento5 pagineExperiences in Designing and Operating The Latest 1,050-MW Coal-Fired BoilerswatkoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem Depth Study - Mod 8Documento6 pagineChem Depth Study - Mod 8Charlotte JaisonNessuna valutazione finora
- Ayush Walke Micro Project - NON-DESTRUCTIVE TESTDocumento23 pagineAyush Walke Micro Project - NON-DESTRUCTIVE TESTYash ChahandeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - Ii Principles of PhotocatalysisDocumento10 pagineChapter - Ii Principles of PhotocatalysisAbbas aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Llautó M38 CuZn37Documento2 pagineLlautó M38 CuZn37Josep TanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Bioplastic: Sustainable Green Plastic: December 2015Documento3 pagineBioplastic: Sustainable Green Plastic: December 2015Lakshmipriya GopinathNessuna valutazione finora
- Palruf PVC BrochureDocumento19 paginePalruf PVC BrochureSerguei DobrinNessuna valutazione finora
- Nitofill EPLV : Constructive SolutionsDocumento4 pagineNitofill EPLV : Constructive SolutionsmilanbrasinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Depithers For Efficient Preparation of Sugar Cane Bagasse Fibers in Pulp and Paper IndustryDocumento8 pagineDepithers For Efficient Preparation of Sugar Cane Bagasse Fibers in Pulp and Paper IndustryAlphonse SambranoNessuna valutazione finora
- Rust Protection by Metal Preservatives in The Humidity CabinetDocumento9 pagineRust Protection by Metal Preservatives in The Humidity CabinettoanvmpetrologxNessuna valutazione finora
- Lateral-Torsional Buckling of Orthotropic Rectangular Section BeamsDocumento8 pagineLateral-Torsional Buckling of Orthotropic Rectangular Section BeamsMina AdlyNessuna valutazione finora
- Bodan: Highway-Rail Level Grade Crossing SystemDocumento26 pagineBodan: Highway-Rail Level Grade Crossing SystemprincevidduNessuna valutazione finora
- Certificate of Conformity: No. CLSAN 080567 0058 Rev. 00Documento2 pagineCertificate of Conformity: No. CLSAN 080567 0058 Rev. 00annamalaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Masterseal 380 TDSDocumento2 pagineMasterseal 380 TDSArasu DonNessuna valutazione finora
- SymbolDocumento48 pagineSymbolmomoitachiNessuna valutazione finora
- CF31 Sort110 EU Data Sheetchainflex CF31Documento6 pagineCF31 Sort110 EU Data Sheetchainflex CF31Luiz Felipe OliveiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Flash Point by Abel's ApparatusDocumento3 pagineFlash Point by Abel's ApparatusAbhishek JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Molecular Liquids: Chandrabhan Verma, Eno E. Ebenso, Indra Bahadur, M.A. QuraishiDocumento14 pagineJournal of Molecular Liquids: Chandrabhan Verma, Eno E. Ebenso, Indra Bahadur, M.A. QuraishiterNessuna valutazione finora
- Load CalculationsDocumento3 pagineLoad CalculationsWilkenn TuazonNessuna valutazione finora
- Aluminium Cookware To MinimizeDocumento7 pagineAluminium Cookware To MinimizeKeep CalmNessuna valutazione finora
- Machined Seals: Product RangeDocumento43 pagineMachined Seals: Product RangeAnonymous r3MoX2ZMTNessuna valutazione finora