Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Indian Leather Industry
Caricato da
Sandeep ChukkalaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Indian Leather Industry
Caricato da
Sandeep ChukkalaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Indian Leather Industry
The leather industry occupies a place of prominence in the Indian economy in view of its massive potential for employment, growth and exports. There has been an increasing emphasis on its planned development, aimed at optimum utilisation of available raw materials for maximising the returns, particularly from exports. The exports of leather and leather products gained momentum during the past two decades. There has been a phenomenal growth in exports from Rs.320 million in the year 1965-66 to Rs.69558 million in 1996-97. Indian leather industry today has attained well merited recognition in international markets besides occupying a prominent place among the top seven foreign exchange earners of the country. The leather industry has undergone a dramatic transformation from a mere exporter of raw materials in the sixties to that of value added finished products in the nineties. Policy initiatives taken by the Government of India since 1973 have been instrumental to such a transformation. In the wake of globalisation of Indian economy supported with liberalised economic and trade policies since 1991, the industry is poised for further growth to achieve greater share in the global trade. Apart from a significant foreign exchange earner, leather industry has tremendous potential for employment generation. Direct and indirect employment of the industry is around 2 million. The skilled and semi-skilled workers constitute nearly 50% of the total work force. The estimated employment in different sectors of leather industry is as follows: Sector Flaying, curing & Carcass Recovery Tanning & Finishing Full Shoe Shoe Uppers Chappals & Sandals Leather Goods & Garments Structure of the industry The leather industry is spread in different segments, namely, tanning & finishing, footwear & footwear components, leather garments, leather goods including saddlery & harness, etc. The estimated production capacity in different segments is as under Product Leather Hides Skins 64 million pieces 166 million pieces Capacity Total Employment 8,00,000 1,25,000 1,75,000 75,000 4,50,000 1,50,000
Footwear & Footwear Components a) Shoes b) Leather shoe uppers c) Non-leather shoes/chappals etc Leather Garments Leather Products Industrial Gloves Saddlery 100 million pairs 78 million pairs 125 million pairs 6 million pieces 70 million pieces 40 million pairs 6000 pieces
The major production centres for leather and leather products are located at Chennai, Ambur, Ranipet, Vaniyambadi, Trichi, Dindigul in Tamil Nadu, Calcutta in West Bengal, Kanpur in Uttar Pradesh, Jalandhar in Punjab, Bangalore in Karnataka, Delhi and Hyderabad in Andhra Pradesh. Raw material supplies There exists a large raw material base. This is on account of population of 194 million cattle, 70 million buffaloes, 95 million goats. According to the latest census, India ranks first among the major livestock holding countries in the world. In respect of sheep with 48 million sheeps, it claims the sixth position. These four species provide the basic raw material for the leather industry. The annual availability of 166 million pieces of hides and skins is the main strength of the industry. This is expected to go up to 218 million pieces by the end of year 2000. Some of the goat/calf/sheep skins available in India are regarded as speciality products commanding a good market. Abundance of traditional skills in training, finishing and manufacturing downstream products and relatively low wage rates are the two other factors of comparative advantage for India. Tanning and finishing capacity With tanning and finishing capacity for processing 1192 million pieces of hides and skins per annum spread over different parts of the country, most of which is organised along modern lives, the capability of India to sustain a much larger industry with its raw material resource is evident. In order to augment the domestic raw material availability, the Government of India has allowed duty free import of hides and skins from anywhere in the world. It is an attraction for any foreign manufacturer who intends to shift his production base from a high cost location to low cost base. Export Potential The leather industry, one of the major foreign exchange earners of the country recorded significant growth since the beginning of the decade. Today the share of the value added finished products in the total exports from leather sector are 80% as against 20% in 1970s.
Category Finished Leather Leather Footwear Footwear Components Leather Garments Leather Goods Saddlery and Harness Total
(Value in million US$) 1998-99 265.2 290.2 243.7 368.6 429.0 33.4 1630.1
Export of Leather and Leather Products from India
140000 120000
Rs. Million
117223.4 110343.2 101143 81520.38 61570.61 69557.8
100000 80000 60000 40000 20000 0 1993-94
1994-95
1995-96
1996-97
1997-98
1998-99
Country Germany USA Italy UK France Spain Russia Portugal Australia Denmark Netherlands Hong Kong Others Total
1998-99 15462 10826 8317 9744 3240 3103 1009 1240 1465 808 2127 258 9958 69558
(Value in million Rs.) Share in total exports in 1998-99 22.23 % 15.56 % 11.96 % 14.00 % 4.6 % 4.46 % 1.445 % 1.78 % 2.10 % 1.16 % 3.06 % 3.25 % 14.32 % 100 %
Top ten Indian leather exporters Tata International Ltd. Florind Shoes Ltd. Punihani International Farida Shoes Ltd. Mirza Tanners Ltd. T. Abdul Wahid & Company Hindustan Lever Ltd. Super House Leather Ltd. RSL Industries Ltd. Presidency Kid Leather Ltd. Indian Leather Footwear Industry India is the world's second largest producer of footwear; its production estimated over 700 million pairs per annum. At about US $ 300 million per year, footwear accounts for 18 percent share of total exports of leather exports. Various types of shoes produced and exported from India include dress shoes, casuals, moccasins, sports shoes, horacchis, sandals, ballerinas, and booties. Major production centres are Chennai (Madras), Delhi, Agra, Kanpur, Mumbai (Bombay), Calcutta and Jalandhar. Most of the modern footwear manufacturers in India are already supplying to well established brands in Europe and USA. The large domestic market and the opportunity to cater to world markets makes India an attractive destination for technology and investments. Equally relevant is it for the footwear components industry, at this juncture, it is posed for real growth and diversification. Indian Leather Goods Industry Items produced by this sector include, in addition to bags, handbags, handgloves and industrial gloves, wallets, ruck sacks, folios, brief cases, travelware, belts, sports goods, upholstery and saddlery goods. A surfeit of modern units in Chennai, Kanpur and Calcutta employing skilled human resources and equipped with modern and sophisticated machinery account for a diversified range of superlative small leather goods including bags, purses, wallets, industrial gloves etc. made of quality leathers of cows, sheep, goats and buffaloes. The products meet the requirement of bulk buyers and consumers in Europe, USA and Australia. The major market for Indian leather goods is Germany, with an offtake of about 25 per cent of the leather goods produced in India followed by USA, UK, France and Italy. With products ranging from designer collections to personal leather accessories, this sector has a share of 20.53 per cent in the leather industry, while maintaining an average growth rate of 11 per cent recorded in the last five years.
Indian Saddlery Industry India is one of the largest producers of saddlery and harness goods in the world. The saddlery industry was established in the 19th century primarily to cater to the needs of military and police. From then on initiatives were taken to develop, the industry and today there are over 150 units in the organised sector, out of which approximately 105 are 100% export oriented units. Kanpur, in the state of Uttar Pradesh, is a major production centre for saddlery goods in India accounting for more than 95% of the total exports of saddlery items from India. Kanpur, because of its specialisation in tanning and finishing of buffalo hides is the only centre in the country where harness leather, which is major input for saddlery industry, is manufactured. The export of saddlery and harn'ess items have showed an annual growth rate of about 40% reaching DM 64 million during 1998-99. The major importers of Indian saddlery are Germany, USA, UK, France, Scandinavia, Netherlands, Japan, Australia and New Zealand. Indian Leather Garments Industry The Leather Garment Industry occupies a place of prominence in the Indian leather sector. The product classification of leather garments comprise of jackets, long coats, waist coats, shirts, pant/short, children garments, motorbike jackets, aprons and industrial leather garments. Indian leather garments, which entered the world market only in the mid-eighties with exports of Rs. 15 crores in 1997-98, account for about Rs. 1530 crore in 1997-98. The major export destination of leather garments from India is Germany. In 1997, German imports of leather garments aggregated DM 1786 million of which DM 304 million worth of imports went from India. India, China and Turkey were the major suppliers of leather garments for the German market, as they accounted for about 78% of the market share. Among the three major exporting nations of leather garments, India maintains a similar level of market share of about 20%, in both German and EU markets. Other markets for India include Italy, U.K., U.S.A. France, Spain and Netherlands. Recently, successful attempt had been made for exports to Denmark, Switzerland and Canada. Indian leather industry - Investment & Sales The ratio of investment : sales value is 1: 2.25, which is very low when compared to other industries. This is mainly due to low capacity utilization of the units. The capacity utilisation of units in respect of hides converting raw into unfinished leathers is estimated at 49%, raw to finished 60% and unfinished to finished 70%. In the case of skin based tanneries, the respective percentages are 64, 67 and
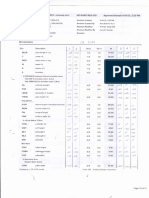
70. The main reasons reported for under utilisation of capacity are raw material shortage, high price of raw materials, lack of modernisation, financial constraints, power constraints and stringent environmental regulations. Investment details of Indian leather industry Sector Tanning SSI Large / medium Foot Wear SSI Large / medium Leather goods SSI Large / medium Leather Garments SSI Large / medium No. of Units Average Investment per unit * (in Rs. Crores) 2.25 5.00 Sub Total (I) 0.80 3.78 Sub Total (II) 0.50 1.68 Sub Total (III) 1.00 4.00 Sub Total (IV) Total Cost (in Rs. Crores) 2423.25 400.00 2823.25 440.00 189.00 629.00 195.00 16.80 211.80 390.00 40.00 430.00 4094.05 1228.21 5322.26
1077 80 550 50 390 10 390 10 Total (I+II+III+IV)
Unorganised sector (@30% of total amount) Total Amount
Composition of Indian leather exports to Germany (1998-99)
3% 31% 15% 30% Leather Leather Garments Leather Footwear Leather Goods Footwear Component Saddlery and Harness 8% 13%
Export of leather and leather products to Germany (1998-99)
120 109.5 113.2
Million US $
100 80 60 40 20 0
Leather Leather Footw ear Footw ear Component Leather Garments Leather Goods
48.86 28.25
56.03
8.51
Saddleryand Harness
Marketing of leather and leather products in Germany & the EU
The leather sector offers a good potential which Indian entrepreneurs can exploit in Germany and other EU markets characterised by ever growing competitiveness in terms of price and quality, on one hand, and the environmental considerations, on the other. With a strong foothold that the Indian leather industry has had for long in these markets, and its advantage of raw material and labour resources, Indian leather exporters can, and should, mount a concerted marketing campaign to wrest a share consistent with their inherent strength and potential. This has to be done against the background of the wellknown salient features of the German market: The world's second largest import and export market A difficult buyers' market with hyper competition and high expectations A dynamic multi-faceted market with rapid technological development and innovations A market where a considerable amount of buying power is devoted to satisfying individual needs A market influenced by the rising average age of the population and low birth rate A market where environment awareness and eco-friendly production becomes more and more a pre-requisite for successful marketing of products Recipe for market intelligence Market information through journals and magazines Schuhmarkt Schuhkurier Lederwaren Report
Quick Market Assessment Window shopping Backward calculation of price Catalogues/ leaflets Trade Fairs GDS Dusseldorf Expo-Riva Schuh - Italy Leipzig Fashion Fair Lederwarenmesse - Offenbach Agents Marketing channels The emerging trend in Germany has been towards direct imports. The other noteworthy feature is the integration of retailing and manufacturing, particularly for the footwear sector. This has led to increased emphasis on distribution aspects of business. Other distributors, like departmental stores, mail order houses, super markets and non-leather shops have also gained importance. Many outlets get direct supplies either from the manufacturers and importers or from wholesalers and buying associations (Einkaufs- Verband, e.V.). These developments necessitate the marketing strategies to be attuned to the specifics of the different channels, keeping in sharp focus the changes taking place in the distribution pattern of chain stores, retailers, discounters, etc. The strategy should focus on a structural approach to the promotion of export of leather products from India. This must include market information for exploring new markets, participation in different international trade fairs, organising trade delegations, organising buyer-seller meets, liaisoning with the representatives of the buying houses, etc. For the successful marketing of their products, the Indian exporters should aim for long lasting trade relations based on stable partnerships. In such a context, the German importer needs to be viewed as much more than only a buyer and distributor. He would normally take care of the timely development of the samples and collections through fashion and design information and also by employing pattern makers and designers. In addition, he would organise advertising and PR activities, besides holding sufficient stocks. Environmental aspects for leather products Manufacturers who produce environmentally sound products will enjoy a competitive advantage in all business relations with EU in general and Germany in particular. The pitch has to be to successfully emphasise the environmental
Herren Mode Woche - Munich Igedo Fashion Fair - Dsseldorf SPOGA - Cologne
soundness of the product in the information to the buyers since major attention is being paid to the increasing role of the environmental regulations. Therefore, the manufacturers have to view their products and production processes not just by looking at traditional aspects like price, quality, customer demands, etc. but also at the environment. Environmentally sound production, consequently, opens new market opportunities. The regulations concerning the ban on the use of Azo Dyes and PCP need to be specially taken care of. Use of both these inputs has been banned due to their carcinogenic nature. Likewise, for compliance with the German packing regulations, Indian suppliers have to stick to the basic principle that packaging material be reusable and recyclable. Consumers may have a tendency to choose products, which are easily recognisable as such and are labeled according to legal stipulations. The hallmark for these environment-friendly products is normally referred to as ECO-LABEL. This indicates that the product is manufactured in consonance with the environmental regulations. Global Scenario : The global trade in leather and leather products has been increasing over the years from mere US$ 4 billion in 1972 to US$ 70 billion in 1997. Although the exports of Indian leather and leather products have grown manifold during the past decades, our country's share in global trade is around 3% among world imports of leather products. Whereas India's share in world imports of leather footwear is 1%. Major exporting countries of leather footwear are China (14% share), Portugal (6% share), Brazil (5% share) and Indonesia (4% share). India's share in world imports of leather garments is 6%. Major exporting countries of leather garments are China (36% share), Germany (9% share), Italy (7% share), Turkey (5% share) and Pakistan (4% share) India's share in world imports of leather goods is 7%. Major exporting countries are China (22% share), Italy (22 % share), France (7% share) and Greece (5% share), India's share in world imports of harness and saddlery is 8%. Major exporting countries of harness & saddlery are Germany (14 % share), U.K. (14 % share), China (12% share). Overall, India is facing fierce competition in international market from countries like China, Vietnam, Thailand, Indonesia, etc., which are emerging as major manufacturing countries. East European countries like Poland, Romania, Czech and Slovak Republics have re-emerged as major production centres particularly for footwear sector. These countries pose major challenge to Indian exporters as they enjoy geographical advantage.
SWOT Analysis of the Indian leather industry
Strengths
High Growth Ready availability of highly skilled and cheap manpower Large raw material base Policy initiatives taken by the Government Threats
Opportunities
Rising potential in the domestic market Growing fashion consciousness globally Use of information technology and decision support software to help eliminate the length of the production cycle for different products
Capability to assimilate new Major part of the industry is technologies and handle large unorganised projects Limited scope for mobilising funds private placements public and issues through development design upgradation and
Continuous emphasis on product
(many businesses are family-owned) Difficulty in obtaining bank loans resulting in high Stricter Weaknesses
Use of e-commerce in direct marketing
cost
of
private borrowing international standards High competition from East European countries other countries Lack of communication facilities and skills and Asian
Lack of warehousing support from the government International price fluctuation Huge labour force resulting in high labour charges Lack of strong presence in the global fashion market Unawareness of international standards by many players
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Assignment LeatherDocumento6 pagineAssignment LeatherAhmed MastanNessuna valutazione finora
- LeatherDocumento15 pagineLeatherSingh Nitin80% (5)
- Leather Industry Report 1transparentDocumento18 pagineLeather Industry Report 1transparentvikramullalNessuna valutazione finora
- Leather Goods FinalDocumento15 pagineLeather Goods FinalImran1978Nessuna valutazione finora
- Summer Internship ReportDocumento69 pagineSummer Internship ReportShobhitShankhalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Leather Products Export To Germany (EXIM)Documento29 pagineLeather Products Export To Germany (EXIM)Thomas KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Industry Analysis Report Indian Leather IndustryDocumento31 pagineIndustry Analysis Report Indian Leather Industrybalaji bysani100% (1)
- Indian Leather Industry Is The Core Strength of The Indian Footwear IndustryDocumento3 pagineIndian Leather Industry Is The Core Strength of The Indian Footwear IndustrySubhro SarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Deloitte Report Leather and FootwearDocumento84 pagineDeloitte Report Leather and Footwearpgpm710Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Quick Review of Emerging Leather Sector of BangladeshDocumento10 pagineA Quick Review of Emerging Leather Sector of BangladeshAtabur RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Internship Report of Leather CoordinatorsDocumento19 pagineInternship Report of Leather Coordinatorswaleed ahmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Human resource and skill gaps in India's leather industry until 2022Documento48 pagineHuman resource and skill gaps in India's leather industry until 2022anix12100% (1)
- Leather Industry PresentationDocumento18 pagineLeather Industry PresentationSara Pervez100% (1)
- Leather Exporting PDFDocumento20 pagineLeather Exporting PDFAyman BrohiNessuna valutazione finora
- Testing in The Leather Industry - Standardization of Leather TestingDocumento8 pagineTesting in The Leather Industry - Standardization of Leather Testingzeqs9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Leather Industry and The Export Market of India..Sanjay YadavDocumento50 pagineLeather Industry and The Export Market of India..Sanjay Yadavsanjayyadav007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Business - Plan - of - Leather - Products - GlemKore International (Opc) PVT LTD, SBIDocumento21 pagineBusiness - Plan - of - Leather - Products - GlemKore International (Opc) PVT LTD, SBIUjjwal SenNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Footwear IndustryDocumento29 pagineIndian Footwear IndustryRita ChatterjiNessuna valutazione finora
- Export & ImportDocumento29 pagineExport & ImportKhan ZiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pakistan's Leather Industry: An OverviewDocumento22 paginePakistan's Leather Industry: An Overviewminnie908Nessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study Leather Industrial Parks PDocumento144 pagineCase Study Leather Industrial Parks PGayatri G.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Leather and FootwearDocumento10 pagineLeather and FootwearArun SudarshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Export-Import Procedure and Documentation: Topic: Exporting Leather Products To Germany Hussain Chunawala Roll No. 07Documento29 pagineExport-Import Procedure and Documentation: Topic: Exporting Leather Products To Germany Hussain Chunawala Roll No. 07Thomas KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Leather Goods Manufacturing Unit (Wallets)Documento18 pagineLeather Goods Manufacturing Unit (Wallets)Brandon RichardsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Low Polution Leather TanningDocumento8 pagineLow Polution Leather TanningFarhad HossainNessuna valutazione finora
- Pakistan's Leather Shoe Exports ProjectDocumento16 paginePakistan's Leather Shoe Exports ProjectFaizan Ahmad AfzalNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Profile-Leather IndustryDocumento15 pagineIndustrial Profile-Leather IndustryPratistha BhargavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Value Chain AnalysisDocumento76 pagineValue Chain AnalysisA B M Rafiqul Hasan Khan67% (3)
- Bangladeshi Leather IndustryDocumento8 pagineBangladeshi Leather IndustrySyed Nayem100% (1)
- A Blueprint of African Leather IndustryDocumento86 pagineA Blueprint of African Leather IndustryZaib KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- CBI Market Survey: Leather Garments in SwedenDocumento7 pagineCBI Market Survey: Leather Garments in SwedensirdlugorekiNessuna valutazione finora
- Leather Goods Manufacturing Unit (Wallets) PDFDocumento18 pagineLeather Goods Manufacturing Unit (Wallets) PDFSyed Zeeshan AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Study of Indian Leather Industry-2003 VersionDocumento194 pagineStudy of Indian Leather Industry-2003 VersionUzma EhteshamNessuna valutazione finora
- FootwearDocumento18 pagineFootweargehanun100% (1)
- How To Start Leather Industry: Click HereDocumento5 pagineHow To Start Leather Industry: Click HereYasir Rafiq0% (1)
- Feasibility Report-LeatherDocumento48 pagineFeasibility Report-Leathermadihashkh75% (4)
- Footwear Machinery Part IIDocumento13 pagineFootwear Machinery Part IIsanjana sadhukhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing PlanDocumento16 pagineMarketing Plannayima jannatNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of Pakistani Leather Industry PDFDocumento7 pagineOverview of Pakistani Leather Industry PDFMuhammad Shahid RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Project PPT LeatherDocumento12 pagineProject PPT Leathernitinsachdeva21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pollution of Leather IndustryDocumento70 paginePollution of Leather IndustryBalaji GajendranNessuna valutazione finora
- LeatherDocumento2 pagineLeatherAlim MaheraliNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Bangladesh Leather Industry ReportDocumento42 pagineAnalysis of Bangladesh Leather Industry ReportJahir HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Fddi Prospectus 2021Documento59 pagineFddi Prospectus 2021Indronil BhowalNessuna valutazione finora
- INSPIRED - Leather Sector Report - Jan 13Documento54 pagineINSPIRED - Leather Sector Report - Jan 13idlpar010% (1)
- Types of LeatherDocumento3 pagineTypes of LeatherEnrico S. RosalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Costing GuideDocumento58 pagineShoe Costing GuidePrafful MehraNessuna valutazione finora
- Catwalk Case StudyDocumento4 pagineCatwalk Case StudyPritam PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Major Footwear's Industry Visit ReportDocumento17 pagineMajor Footwear's Industry Visit ReportRadhaChaturvediNessuna valutazione finora
- Pak Leather Crafts Limited PakistanDocumento24 paginePak Leather Crafts Limited Pakistansherazhasan22Nessuna valutazione finora
- Leather Compendium2013Documento193 pagineLeather Compendium2013Satyadev RajuNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Profitable Leather and Leather Products Manufacturing Projects. Business Ideas in Leather Finishing and Leather Tanning Industry.-720748 PDFDocumento48 pagineList of Profitable Leather and Leather Products Manufacturing Projects. Business Ideas in Leather Finishing and Leather Tanning Industry.-720748 PDFMd WasimNessuna valutazione finora
- Leather: From the Raw Material to the Finished ProductDa EverandLeather: From the Raw Material to the Finished ProductNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Leather Industry Exports GrowthDocumento10 pagineIndian Leather Industry Exports Growthrajanikanthreddy_mNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Leather Industry OverviewDocumento30 pagineIndian Leather Industry OverviewPrithvi DhanukaNessuna valutazione finora
- Leather IndustryDocumento7 pagineLeather IndustrySumit ChandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Leather IndustryDocumento23 pagineLeather IndustryChhaya SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- BATA INDIA LIMITED Final OneDocumento65 pagineBATA INDIA LIMITED Final OneGaurav MudgalNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Strategies For Domestic Sale of Laether Products.: Project ReportDocumento27 pagineMarketing Strategies For Domestic Sale of Laether Products.: Project ReportAdwait VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Footwear IndustryDocumento23 pagineIndian Footwear IndustryEshuGupta2208Nessuna valutazione finora
- MBA Warehouse Mangement Project PDFDocumento82 pagineMBA Warehouse Mangement Project PDFImran KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- M.A Sociology II YearDocumento5 pagineM.A Sociology II YearMohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- Project On Work Environment in Hero HondaDocumento82 pagineProject On Work Environment in Hero HondaMohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- 302EL2Documento4 pagine302EL2abcdef1985Nessuna valutazione finora
- 302EL2Documento15 pagine302EL2Mohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- Pattern For Personality EnrichmentDocumento1 paginaPattern For Personality EnrichmentMohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of MisDocumento5 pagineStructure of MisMohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- Recommendation LetterDocumento1 paginaRecommendation LetterMohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- Trend Analysis of Income StatementDocumento1 paginaTrend Analysis of Income StatementMohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- MANF Guidelines for Minority StudentsDocumento16 pagineMANF Guidelines for Minority StudentsHarpreet SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- GowebviewDocumento2 pagineGowebviewMohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- AnalysisDocumento1 paginaAnalysisMohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- ASUS AuthorizedDocumento1 paginaASUS AuthorizedMohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- International Business: Subject Code: Credit: L+P: 4+0 Teaching Hours: 60 HrsDocumento1 paginaInternational Business: Subject Code: Credit: L+P: 4+0 Teaching Hours: 60 HrsMohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis 2Documento1 paginaAnalysis 2Mohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- Emerging Trends in HRMDocumento5 pagineEmerging Trends in HRMhardeepcharmingNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis IDocumento1 paginaAnalysis IMohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- Od HDocumento1 paginaOd HMohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- HR TopicsDocumento2 pagineHR TopicsDHINNAHHNessuna valutazione finora
- Od GDocumento1 paginaOd GMohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- Definition of Consumer BehaviorDocumento67 pagineDefinition of Consumer BehaviorSuman PoudelNessuna valutazione finora
- Managerial Communnication NotesDocumento4 pagineManagerial Communnication NotesMohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- Staff Recommended BY Name of The Applicant Appl. NO. MAR KS RemarksDocumento22 pagineStaff Recommended BY Name of The Applicant Appl. NO. MAR KS RemarksMohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- Business CommunicationDocumento70 pagineBusiness CommunicationJericho PedragosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Brand loyalty: What influences consumer adherenceDocumento65 pagineBrand loyalty: What influences consumer adherenceMohammed Bilal0% (1)
- BBA II and III Year Updated Syllabus 2015Documento35 pagineBBA II and III Year Updated Syllabus 2015Mohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- 000101224868Documento3 pagine000101224868Mohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- Mashook Curriculam VitaeDocumento2 pagineMashook Curriculam VitaeMohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- HR TopicsDocumento2 pagineHR TopicsDHINNAHHNessuna valutazione finora
- Assalaaamu AlaikkummmmDocumento2 pagineAssalaaamu AlaikkummmmMohammed BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- LA Canvas Newspaper Issue 3Documento12 pagineLA Canvas Newspaper Issue 3Kev371Nessuna valutazione finora
- Carpet Languages PeoplesDocumento1.557 pagineCarpet Languages PeoplespronaturaalNessuna valutazione finora
- Instyle UK October 2014Documento252 pagineInstyle UK October 2014Viktoria Hosszu100% (1)
- Revista Autumn 2013Documento132 pagineRevista Autumn 2013Gabby Funes de Schaw100% (12)
- ByHer Crochet BTSDocumento44 pagineByHer Crochet BTSlizbeth vasquez100% (3)
- (Essay) Fashion Defines A Person CharacterDocumento1 pagina(Essay) Fashion Defines A Person Characterno nameNessuna valutazione finora
- 2013 Beretta SpA Accessories WorkbookDocumento736 pagine2013 Beretta SpA Accessories WorkbookAris TaxydromosNessuna valutazione finora
- Interview Scoring RubricDocumento12 pagineInterview Scoring RubricVitorito MejiaNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF 118 Poses For PhotographyDocumento104 paginePDF 118 Poses For PhotographySaymon100% (2)
- Kenmore 385.17026 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualDocumento128 pagineKenmore 385.17026 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualiliiexpugnansNessuna valutazione finora
- Finding the Perfect Outfit for Your Body ShapeDocumento4 pagineFinding the Perfect Outfit for Your Body Shapedraping pattern sloperNessuna valutazione finora
- Socks Soar On Two Circular Needles: A Manual of Elegant Knitting Techniques and PatternsDocumento50 pagineSocks Soar On Two Circular Needles: A Manual of Elegant Knitting Techniques and PatternsMarcs100% (11)
- Faster Funnier Quick Start GuideDocumento32 pagineFaster Funnier Quick Start GuidesagarNessuna valutazione finora
- The Garment and Apparel HandbookDocumento3 pagineThe Garment and Apparel HandbookCharles Baidoo MameyNessuna valutazione finora
- Function and Symbolism of KenteDocumento24 pagineFunction and Symbolism of KenteIsaac Johnson Appiah100% (1)
- Fav CC For Males 2022Documento13 pagineFav CC For Males 2022ᴄ ᴀ ɴ ᴅ ɪ ᴇNessuna valutazione finora
- I-Mt - LRF: DimensionsDocumento4 pagineI-Mt - LRF: DimensionsIbranesa NissreyasaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ancient Mesopotamia-1Documento20 pagineAncient Mesopotamia-1api-250958195Nessuna valutazione finora
- Store Visit Report at Superdry, MidvalleyDocumento17 pagineStore Visit Report at Superdry, MidvalleygslSuetLinNessuna valutazione finora
- Philae Elsa PatternDocumento5 paginePhilae Elsa PatternanitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Basic WardrobeDocumento51 pagineChapter 3 Basic WardrobeSherry Avena100% (4)
- My Sails 3 New Prirocnik Za Ucitelje TestiDocumento12 pagineMy Sails 3 New Prirocnik Za Ucitelje TestiTjaša KrajncNessuna valutazione finora
- The Karen Cardigan OriginalDocumento9 pagineThe Karen Cardigan Originalliz-lo100% (1)
- Janetscott Resume-3Documento1 paginaJanetscott Resume-3api-247847769Nessuna valutazione finora
- Harley Davidson Fall Core MotorClothes CatalogDocumento27 pagineHarley Davidson Fall Core MotorClothes CatalogChok ThawornmatNessuna valutazione finora
- Heer Ranjha: Name: Iffra Khan Roll Num: 103Documento7 pagineHeer Ranjha: Name: Iffra Khan Roll Num: 103amna khanNessuna valutazione finora
- TR - Tailoring (Casual) NC IIDocumento58 pagineTR - Tailoring (Casual) NC IIJMiguel Abueg100% (4)
- Material SelfDocumento20 pagineMaterial SelfRaphaella XylianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lulu Tulipe & TutuDocumento8 pagineLulu Tulipe & TutuNatasha Tripathi100% (3)
- Himstedt CatalogDocumento114 pagineHimstedt CatalogKatarína Schmiesterová67% (3)