Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Bluetooth
Caricato da
Tejashree NipaneDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Bluetooth
Caricato da
Tejashree NipaneCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Bluetooth is an open specification for a radio system that provides the network infrastructure to enable short range wireless
communication of data and voice. It comprises of a hardware component and a software component. The specification also describes usage models and user profi les for these models. Bluetooth is named after the Danish King Harald Blaatand. This article give s you an overview of the Protocol architecture. WHAT IS BLUETOOTH? luetooth is an open specification for a radio system that provides the network infrastructure to enable short range wireless communication of data and voice. It comprises of a hardware component and a software component. The specification also describes usage models and user profiles for these models. Bluetooth is named after the Danish King Harald Blaatand "Bluetooth", who successfully united Denmark and Norway during his rule from 940 to 985 AD. B Bluetooth unleashes the concept of "hidden computing" by providing radio devices "unconscious" connectivity without the user's proactive intervention. It provides a bearer service for wireless (WAP) applications. BLUETOOTH CHARACTERISTICS Bluetooth radios operate in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 Gigahertz using 79 channels between 2.402 GHz to 2.480 GHz (23 channels in some countries). The range for bluetooth communication is 0-30 feet (10 meters) with a power consumption of 0dBm (1mW). This distance can be increased to 100 meters by amplifying the power to 20dBm. The bluetooth radio system is optimized for mobility. Bluetooth supports two kinds of links: Asynchronous Connectionless (ACL) links for data transmission and Synchronous Connection oriented (SCO) links for audio/voice transmission. The gross bluetooth data rate is 1 Mbps while the maximum effective rate on an asymmetric ACL link is 721 Kbps in either direction and 57.6 Kbps in the return direction. A symmetric ACL link allows data rates of 432.6 Kbps. Bluetooth also supports up to three 64Kbps SCO channels per device. These channels are guaranteed bandwidth for transmission. BLUETOOTH ARCHITECTURE Bluetooth communication occurs between a master radio and a slave radio. Bluetooth radios are symmetric in that the same device may operate as a master and also the slave. Each radio has a 48 bit unique device address (BD_ADDR) that is fixed.
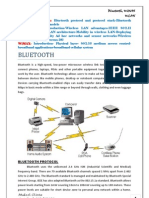
Two or more radio devices together form ad-hoc networks called piconets. All units within a piconet share the same channel. Each piconet has one master device and one or more slaves. There may be up to seven active slaves at a time within a piconet. Thus each active device within a piconet is identifiable by a 3 bit active device add ress. Inactive slaves in unconnected modes may continue to reside within the piconet. A master is the only one that may initiate a bluetooth communication link. However, once a link is established, the slave may request a master/slave switch to become the master. Slaves are not allowed to talk to each other directly. All communication occurs within the slave and the master. Slaves within a piconet must also synchronize their internal clocks and frequency hops with that of the master. Each piconet uses a different frequency hopping sequence. Radio devices used Time Division Multiplexing (TDM). A master device in a piconet transmits on even numbered slots and the slaves may transmit on odd numbered slots. Multiple piconets with overlapping coverage areas form a scatternet. Each piconet may have only one master, but slaves may participate in different piconets on a time-division mult iplex basis. A device may be a master in one piconet and a slave in another or a slave in more than one piconet.
THE PROTOCOL STACK The protocols of the bluetooth stack can be divided into four different categories: BLUETOOTH CORE PROTOCOLS BaseBand The baseband and the Link control layers enable the physical RF link between bluetooth devices to form a piconet. Both circuit and packet switching is used. They provide two kinds of physical links using the baseband packets. Synchronous connection oriented (SCO) and Asynchronous connectionless (ACL). ACL packets are used for data only, while the SCO packets may contain audio only or a combination of audio and data. The Link Manager Protocol The link manager protocol is responsible for the link setup between bluetooth units. This protocol layer caters to issues of security like authentication, encryption by generating, exchanging and checking the link and encryption keys. It also deals with control and negotiation of baseband pack et sizes.
Logical Link Control and Adaptation Layer (L2CAP) The bluetooth logical link control and adaptation layer supports higher level multiplexing, segmentation and reassembly of packets, and Quality of Service (QoS) communication and Groups. This layer does not provide any reliability and uses the baseband ARQ to ensure reliability. Channel identifiers are used to label each connection end point. Service Discovery Protocol (SDP) SDP is the basis for discovery of services on all bluetooth devices. This is essential for all bluetooth models. Using the SDP device information, services and the characteristics of the services can be queried and after that a connection between two or more bluetooth devices may be established. Other service discovery protocols such as Jini, UpnP etc. maybe used in conjunction with the bluetooth SDP protocol. RFCOMM The RFCOMM protocol is the basis for the cable replacement usage of bluetooth. It is a simple transport protocol with additional provisions for emulating the 9 circuits of RS-232 serial ports over L2CAP part of the bluetooth protocol stack. This is based in the ETSI standard TS 07.10 and supports a large base of legacy applications that use serial communication. It provides a reliable data stream, multiple concurrent connections, flow control and serial cable line settings. Telephony Control Protocol Specification (TCS Binary) The TCS binary protocol defines the call control signaling for the establishment of speech and data calls between bluetooth devices. It is based on the ITU-T Q.931 recommendation. It is a bit oriented protocol and also provides group management. The Host Controller Interface (HCI) The HCI provides a command interface to the base-band controller, link manager a nd access to the hardware status and control registers. The interface provides a uniform method of accessing the bluetooth baseband capabilities. The Host control transport layer abstracts away transport dependencies and provides a common device driver interface to various interfaces. Three interfaces are defined in the core specification: USB, RS-232, and UART.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- MEMORY MANAGEMENT Mac Os XDocumento15 pagineMEMORY MANAGEMENT Mac Os Xapi-370045660% (10)
- Bluetooth IntroductionDocumento4 pagineBluetooth IntroductiongowdamandaviNessuna valutazione finora
- A Survey On Bluetooth TechnologyDocumento22 pagineA Survey On Bluetooth TechnologytarasmartinNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth Protocol StackDocumento3 pagineBluetooth Protocol Stackkayal_eceNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth Technology: Submitted ByDocumento12 pagineBluetooth Technology: Submitted Bynational777Nessuna valutazione finora
- BluetoothDocumento8 pagineBluetoothGouse111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Modern WierlessDocumento17 pagineModern Wierlesspolandpasa23Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth: Class Maximum Permitted Power MW (DBM) Range (Approximate) Class 1 Class 2 Class 3Documento3 pagineBluetooth: Class Maximum Permitted Power MW (DBM) Range (Approximate) Class 1 Class 2 Class 3sathiendranrkNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth, IEEE 802.11, WIMAXDocumento30 pagineBluetooth, IEEE 802.11, WIMAXMukesh71% (7)
- Authenticated Data Scrambler and Descrambler For Advanced Bluetooth DevicesDocumento4 pagineAuthenticated Data Scrambler and Descrambler For Advanced Bluetooth DevicesijaertNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Phones, Etc. A Bluetooth Chip Is Designed To Replace Cables by Taking The InformationDocumento5 pagineMobile Phones, Etc. A Bluetooth Chip Is Designed To Replace Cables by Taking The InformationSahilNessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless PANDocumento26 pagineWireless PANkkpandyaji2013100% (2)
- The Bluetooth SystemDocumento16 pagineThe Bluetooth Systemy.priyankareddy7661Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth ArchitectureDocumento9 pagineBluetooth ArchitectureLilambuj KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Bluetooth Protocols - WikipediaDocumento1 paginaList of Bluetooth Protocols - WikipediathhNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth Protocol StackDocumento3 pagineBluetooth Protocol StackVishal SathawaneNessuna valutazione finora
- WC 12Documento1 paginaWC 12api-3761679Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth TechnologyDocumento13 pagineBluetooth TechnologyK.Rohit GoudNessuna valutazione finora
- BluetoothDocumento13 pagineBluetoothNimmi KNessuna valutazione finora
- Messaging Bluetooth For Your Future .Documento14 pagineMessaging Bluetooth For Your Future .vkylovekumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth: Name and LogoDocumento7 pagineBluetooth: Name and LogoRey HeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth FinalDocumento9 pagineBluetooth Finaldhruba88Nessuna valutazione finora
- BluetoothDocumento8 pagineBluetoothVignesh SbNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is BluetoothDocumento32 pagineWhat Is BluetoothHeni Jayanti SutadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Bluetooth Technology: Why It's Name Is Bluetooth?Documento8 pagineIntroduction To Bluetooth Technology: Why It's Name Is Bluetooth?Mishthi ErNessuna valutazione finora
- Module IV: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 4.1 To Understand Bluetooth TechnologyDocumento13 pagineModule IV: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 4.1 To Understand Bluetooth TechnologyAbhirami SNessuna valutazione finora
- Report On Bluetooth® NetworkingDocumento15 pagineReport On Bluetooth® NetworkingSubash PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetoothtechnology 1Documento26 pagineBluetoothtechnology 1Rahul NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth TechDocumento23 pagineBluetooth Techapi-3746880100% (1)
- Bluetooth: ObjectiveDocumento8 pagineBluetooth: ObjectivePradeepCoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of Award of Degree of Bachelor of Technology in Computer Science and EngineeringDocumento22 pagineSubmitted in Partial Fulfillment of Award of Degree of Bachelor of Technology in Computer Science and EngineeringAmol ChaudhariNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth CiaDocumento4 pagineBluetooth CiaMegha LakhawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth TechnologyDocumento19 pagineBluetooth TechnologyToaster97Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth Technology: Mary Grace C. Raborar Eteeap - BseceDocumento19 pagineBluetooth Technology: Mary Grace C. Raborar Eteeap - Bseceust_eteeapNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment-2: CO-415 WMC BluetoothDocumento6 pagineAssignment-2: CO-415 WMC Bluetooth2K18/IT/080 PALAK MEENANessuna valutazione finora
- BluetoothDocumento4 pagineBluetoothSunil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- BluetoothDocumento27 pagineBluetoothshanty85Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth TechnologyDocumento13 pagineBluetooth TechnologysneharachNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth Technology Seminar ReportDocumento23 pagineBluetooth Technology Seminar ReportAbhinav KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth: LMP (Link Management Protocol)Documento3 pagineBluetooth: LMP (Link Management Protocol)Harish ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Welcome To Bluetooth Technology: Presented by M.L.Nikhil (09MD1A0438), III E.C.E G.J.S.Pavan Kumar (09MD1A0417), III E.C.EDocumento24 pagineWelcome To Bluetooth Technology: Presented by M.L.Nikhil (09MD1A0438), III E.C.E G.J.S.Pavan Kumar (09MD1A0417), III E.C.Eplanetshacker100% (2)
- Bluetooth TechnologyDocumento17 pagineBluetooth TechnologyAbhinay GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- BluetoothDocumento3 pagineBluetoothliyomNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth: Seminar Report ForDocumento16 pagineBluetooth: Seminar Report FortravelnagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth Technology: EE 737 Digital Spread Spectrum Techniques Instructor: Dr. James Stephens Date: 24 May, 2004Documento15 pagineBluetooth Technology: EE 737 Digital Spread Spectrum Techniques Instructor: Dr. James Stephens Date: 24 May, 2004Rajesh LenkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth Technology in Wireless CommunicationsDocumento12 pagineBluetooth Technology in Wireless CommunicationsLiliana AmpNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Bluetooth ProtocolsDocumento4 pagineList of Bluetooth ProtocolsPratyush0% (1)
- Bluetooth Basics Mod 1Documento5 pagineBluetooth Basics Mod 1kaustav banerjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 4Documento41 pagineChap 4Bikila DessalegnNessuna valutazione finora
- Video Streaming Over Bluetooth A Survey 2457Documento8 pagineVideo Streaming Over Bluetooth A Survey 2457charmaineNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth Technology Seminar Report PDFDocumento21 pagineBluetooth Technology Seminar Report PDFSuvankar DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth PiconetDocumento25 pagineBluetooth PiconetAbhishek SkNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth TechnologyDocumento13 pagineBluetooth TechnologyParthasarathi AnbalaganNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth: M. Habibullah Pagarkar & Chinmay ShahDocumento16 pagineBluetooth: M. Habibullah Pagarkar & Chinmay ShahAishwaryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abstract:: The Bluetooth TechnologyDocumento8 pagineAbstract:: The Bluetooth Technologymohd shafeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth TechnologyDocumento11 pagineBluetooth TechnologyRam Kumar Bhandari100% (1)
- Versatile Routing and Services with BGP: Understanding and Implementing BGP in SR-OSDa EverandVersatile Routing and Services with BGP: Understanding and Implementing BGP in SR-OSNessuna valutazione finora
- Advances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsDa EverandAdvances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsGabriele ManganaroValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- Open System LANs and Their Global Interconnection: Electronics and Communications Reference SeriesDa EverandOpen System LANs and Their Global Interconnection: Electronics and Communications Reference SeriesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Oracle Developer A Tutorial On Oracle Forms, Reports and GraphicsDocumento119 pagineOracle Developer A Tutorial On Oracle Forms, Reports and GraphicsAbhishekNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyper Threading and Hyper TransportDocumento3 pagineHyper Threading and Hyper TransportrubinschNessuna valutazione finora
- CGNV2-datasheet Modem Caracteristicas PDFDocumento2 pagineCGNV2-datasheet Modem Caracteristicas PDFFreddy Cortes0% (1)
- Annexure-II (6TH SEM UG ECE)Documento21 pagineAnnexure-II (6TH SEM UG ECE)Venkatesh ghNessuna valutazione finora
- CDMA RF Performance Analysis & Troubleshooting Guide R28.0 - FinalDocumento191 pagineCDMA RF Performance Analysis & Troubleshooting Guide R28.0 - FinalSarathy ParthaNessuna valutazione finora
- ThinkCentre M72e DatasheetDocumento4 pagineThinkCentre M72e DatasheetrogromNessuna valutazione finora
- LoRa Remote I - O DatasheetDocumento3 pagineLoRa Remote I - O DatasheetsusiloharjoNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Access Control Quiz3 PDFDocumento2 pagineNetwork Access Control Quiz3 PDFDaljeet SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- HistoryDocumento1 paginaHistorykodiakq3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Safety Relay 3SK1 en-USDocumento226 pagineManual Safety Relay 3SK1 en-USAENessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1 OsDocumento16 pagineAssignment 1 OsVisnu Maran100% (1)
- F5 BIG-IP LTM Essentials WBT Lab Guide v11Documento105 pagineF5 BIG-IP LTM Essentials WBT Lab Guide v11edwardwaithaka40% (5)
- Configuring SSHDocumento4 pagineConfiguring SSHMario BilićNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction of Pic16f877a MicrocontrollerDocumento16 pagineIntroduction of Pic16f877a MicrocontrollerMohd Amirul Mukminin Bin Mohd DaliNessuna valutazione finora
- VSAT Security OverviewDocumento13 pagineVSAT Security OverviewMahmoud Ben RahalNessuna valutazione finora
- 1756 Um001 - en P PDFDocumento210 pagine1756 Um001 - en P PDFAlafael AraújoNessuna valutazione finora
- 3GPP Fault ManagementDocumento21 pagine3GPP Fault ManagementyelcynNessuna valutazione finora
- DX DiagDocumento30 pagineDX DiagRida Firda SolehaNessuna valutazione finora
- DHCP Sequence DiagramDocumento1 paginaDHCP Sequence DiagramManojNessuna valutazione finora
- CMSV6 Operation Manual V1.1 PDFDocumento25 pagineCMSV6 Operation Manual V1.1 PDFIsmaelNessuna valutazione finora
- IoT Based Water Level Monitoring System With An Android ApplicationDocumento4 pagineIoT Based Water Level Monitoring System With An Android ApplicationEditor IJRITCCNessuna valutazione finora
- Edt GDDocumento364 pagineEdt GDAre VijayNessuna valutazione finora
- Imanual 84Documento11 pagineImanual 84Beny AbdouNessuna valutazione finora
- DTR SHDSL Efm r4112h App M 20100119Documento20 pagineDTR SHDSL Efm r4112h App M 20100119IsmetNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar On Google Chrome OS: Submitted To: Submitted byDocumento16 pagineSeminar On Google Chrome OS: Submitted To: Submitted bySaurabh SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- TDU 107 Touch Display Unit: Compatible With AGC-4Documento25 pagineTDU 107 Touch Display Unit: Compatible With AGC-4edwinNessuna valutazione finora
- Mastering Citrix® XenDesktop® - Sample ChapterDocumento63 pagineMastering Citrix® XenDesktop® - Sample ChapterPackt PublishingNessuna valutazione finora
- Rajib Mall Lecture NotesDocumento74 pagineRajib Mall Lecture NotesAnuj NagpalNessuna valutazione finora