Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
II Parcial Cepreuni 2010-II
Caricato da
dyland_lennyCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
II Parcial Cepreuni 2010-II
Caricato da
dyland_lennyCopyright:
Formati disponibili
EUREKA, la mejor preparacin UNI
MAGDALENA: 694-4930, LOS OLIVOS: 521-5182, JESS MARA: 462-8880 Pgina 1
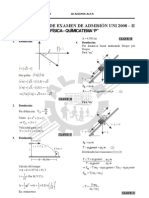
SOLUCIONARIO II PARCIAL
CEPREUNI 2010-II
FSICA
RESOLUCIN1
Nospidenxxt
Pordato ( ) y x, t 2sen x t 1
2
t | |
= t =
|
\ .
Paratodoxyt
i
1
sen x t
2 2
t | |
= t
|
\ .
x t
2 6
t t
t =
1 t
x
6 2
= +
CLAVE:A
RESOLUCIN2
Recordarque:
CUERPO SUM
LIQ TOTAL
V
V
esf total
liq total
40%V
V
glic
esf
glic esf
2
2, 5
5
= =
CLAVE:E
RESOLUCIN3
Como tienen la misma longitud inicial y el
latn
hierro
, el latn se dilata ms que el
hierro; por ello, el conjunto se curva hacia
abajo
q
Hierro
Latn
3
3mm 3 10 m
=
R
3
R 3 10
Senotaqueelngulocentraleselmismo
(f )Hierro (f )Latn
Hierro Latn 3
L L
R R 3 10
u = u =
+
( ) ( )
o Hierro o Latn
3
L 1 T L 1 T
R R 3.10
+ o A + o A
=
+
( )
5
5
3
1 1, 25 10 200
1 1,89 10 200
R R 3 10
+
+
=
+
R 2, 349 =
CLAVE:C
RESOLUCIN4
Pordatodelproblema: ( )
2
T V ........ 1 = o
delaecuacindeestado
( )
P V
P.V n RT T ....... 2
n R
= =
Reemplazando2en1
( )
2
PV
V P n R V
n R
= o = o
Paracalculareltrabajorealizadoporelgasen
el proceso de expansin desde
1
V hasta
2
V ,
construimoslagrficaPvsV.
Secumple: W
gas
REA
3mm
Latn
Hierro
L
o
aT
i
L
f
aT
i
200C
xm
ts
1/3
1/3
1/6
P
V
nRV
2
V
1
nRV
1
V
2
EUREKA, la mejor preparacin UNI
MAGDALENA: 694-4930, LOS OLIVOS: 521-5182, JESS MARA: 462-8880 Pgina 2
( )
1 2
2 1
nRV nRV
V V
2
o + o | |
=
|
\ .
( )
2 2
2 1
nR
V V
2
o
=
CLAVE:B
RESOLUCIN5
Observeque,dadoquelasramasverticalestie
nen la misma seccin transversal, el nivel que
desciende en la rama derecha es igual al que
asciendeenlaramaizquierda.
Porelteoremafundamentaldelahidrosttica.
A B
P P =
( ) ( )
2
o Hg o H O
P .g 2h P .g. 0, 85 + = +
( )( ) ( )( )
3 3
13, 6 10 g 2h 10 g 0, 85 =
h3,12cm
CLAVE:B
RESOLUCIN6
Porcondicin: ( ) ( )
C C
Joven Amiga
E E =
( )
2
2
Amiga Amiga
Joven Joven
m V
m V
....... 1
2 2
=
Adems,deldato
Joven Joven Amiga
V 25%V V + =
( )
Joven Amiga
5
V V .... 2
4
=
Reemplazando2en1
2
2 Amiga Joven
Joven Joven
5
m V
m V
4
2 2
| |
|
\ .
=
Joven Amiga
25
m m
16
=
Amiga Joven
16
m m
25
=
( )
Amiga
16
m 85 54, 4 kg
25
= =
CLAVE:C
RESOLUCIN7
Porlaconservacindelacantidaddemovimi
entoenelejeX:
31,5 i
0,254,0 i
3,25U
1,07 i
CLAVE:C
RESOLUCIN8
La energa total de un sistema masaresorte
estdadapor
( )
2 2 2
M
1 1
E K A m A
2 2
= = e
2
2
1 2
m A
2 T
(
t | |
=
(
|
\ .
(
2 2
2 2 2
M 2
2 m 2 (0, 5)
E A T (0,1) T
T 0, 25 5
t t t
= = =
CLAVE:A
ResueltoporLuisChvez
QUMICA
RESOLUCIN9
Enunadisolucinexotrmicalasolubilidadde
una sustancia tiene relacin inversa con la
temperatura.
h
h
0,85m
B
A
Agua
Mercurio
1,5 i
4 i
3kg
0,25kg
3,25kg
EUREKA, la mejor preparacin UNI
MAGDALENA: 694-4930, LOS OLIVOS: 521-5182, JESS MARA: 462-8880 Pgina 3
I. V Puede ser un gas o algn solido como
4
CeSO .
II. F Al aumentar la temperatura disminuye
lasolubilidad.
III. V Porque la solubilidad aumenta con la
disminucin de la temperatura en este tipo de
procesos.
CLAVE:C
RESOLUCIN10
I. V Los compuestos inicos son slidos a
temperaturaambiente,ydeacuerdoasucons
titucininternaseconsiderancristalinos.
II.VEnestosslidossuspartculasmsnti
mas no poseen un ordenamiento tridimensio
nal.
III.FDependedelaintensidaddelasinterac
cionesintermolecularespuentedehidrogeno,
dipolodipoloofuerzasdeLondon
CLAVE:B
RESOLUCIN11
Como el aire de la habitacin debe estar satu
rado, entonces la presin parcial del vapor en
ese ambiente debe ser la presin de vapor sa
turado a 20C. Usando la ecuacin universal y
elconceptodepresinparcial:
20C
V
V
V
P .V.M
m
R.T
=
( ) ( )( )
( )( )
4
V
18 3, 5.10 18
m 620, 2g
62, 4 293
= =
CLAVE:A
RESOLUCIN12
Balanceando la ecuacin y recordando que a
C.N. una mol de cualquier gas ideal ocupa un
volumende22,4litros
M 180 =
( ) g
C.N.
2
6 12 6 2 5
C H O 2C H OH 2CO +
180g
720g
2x22,4
V
l
C.N.
C.N.
V 179, 2 litros =
CLAVE:D
RESOLUCIN13
I.FSonsistemasmicroheterogneos
II. V Es una emulsin solida o gel, donde la
fasedispersalquidoylafasedispersante
slido.
III.VParaloscoloideseltamaodelaspart
culas de la fase dispersa estn comprendidas
entre 1 nm y 1000 nm, mientras que el tama
odemolculasoionesesmenorque1nm.
CLAVE:D
RESOLUCIN14
Oxidacin:
( ) 3 2 4 4 2
CrI 5Na 32OH 27e Na CrO 3NaIO 16H O 2
+
+ + + +
Reduccin
( )
2
Cl 2Na 2e 2NaCl 27
+
+ +
3 2 2 2 4
2CrI 27Cl 64Na OH 2Na CrO + +
4 2
6NaIO 54NaCl 32H O + + +
Agenteoxidante
2
A.O. : Cl
Agentereductor
3
A.R. : CrI
Relacinmolar
A.O 27
A.R 2
=
CLAVE:E
RESOLUCIN15
AFSulfato
2
4
SO
E.OS6
BV
( ) ( ) ( ) ac ac ac
HCN H CN
+
+
cido Cianuro
Cianhdrico
CF Clorito
2
ClO
( ) ( )
. . 3 E O Cl = +
DFCarbonato
2
3
CO
EF Cromato
2
4
CrO
CLAVE:B
RESOLUCIN16
I.VLasfuerzasdedispersindeLondontie
nenrelacindirectaconlamasamolecular.
II. V Las molculas de
( ) l
HCl se comportan
como dipolos permanentes ( )
R
0 = ; por lo
tanto las interacciones intermoleculares ms
importantes son las dipolodipolo y despus
las fuerzas de London que estn presentes en
todotipodemolculas.
III. F Las interacciones puente de hidrgeno
se dan entre molculas que presentan enlaces
OHoNHyenelflorurodehidrgenoHF.
HCN H C N:
CLAVE:D
ResueltoporMichaelTvez
EUREKA, la mejor preparacin UNI
MAGDALENA: 694-4930, LOS OLIVOS: 521-5182, JESS MARA: 462-8880 Pgina 4
ARITMTICA
RESOLUCIN17
3
N a5bc5 K = = ab7
Seobservaque:
o
N 5 = ycomo
3
N K =
entonces
o
N 125 = Esdecir bc5puedeser:
125, 375, 625, 875
b b b b
a=6 a=4 a=1 a=-1
(No)
3
65125 5 521 (x) =
( )
3 2
45375 5 3 11 x =
6
15625 5 (si) a 1, b 6 = = =
( ) ( )
2 2
2 2
a 1 b 1 2 7 196 + + = =
CLAVE:B
RESOLUCIN18
( ) ( ) ( )
2 2 2
2
S n n 1 n 2 ....... n 10 = + + + + + + +
Porinduccin:
0
2 2 2
11 12 21
n 1 S 1 2 .... 11 11 2 21 11
6
= = + + + = =
Si:
2 2 2
n 2 S 2 3 .... 12 = = + + + =
0
2
12 13 25
1 649 11 59 11
6
= =
Si:
7 0
2 2 2
13 14 27
n 3 S 3 4 .... 13
6
= = + + + =
( )
0
2 2
1 2 814 11 2 37 11 + = =
Ssiempreesmltiplode11
CLAVE:D
RESOLUCIN19
( )
notas
(1er.ex.)
notas
(1er.ex.)
1er.ex.
S
Promedio 12, 4 S 12, 4n
n
= = =
( )
notas
(2do.ex.)
notas
(2do.ex.)
2do.ex.
S
Promedio 13,2 S 13,2n
n
= = =
( )
notas
(3er.ex.)
notas
(3er.ex.)
3er.ex.
S
Promedio 12,8 S 12,8n
n
= = =
Ordenando
12,4n; 12, 8n;13,2n
+24
+24
Demenoramayor:12,8n12,4n24
0,4n24 n 60 =
CLAVEC
RESOLUCIN20
Csar
70 3 70 3, 25 70 3, 30 70 3, 40 70 3, 50
Pr omedio
70 5
+ + + +
=
Cesar
16, 45
Pr omedio 3, 29
5
= =
Juan
1800 5
Pr omedio
1800 1800 1800 1800 1800
3 3, 25 3, 30 3, 40 3, 50
=
+ + + +
Juan
5
Pr omedio 3, 2814
1, 5237
= =
JuanS/3,28
CLAVE:D
RESOLUCIN21
Total12
Principales6,Asociados4,Auxiliares2
Seelige3miembros:
( )
12
3
12 11 10
n C 220
3 2 1
O = = =
Nospidenlaprobabilidaddequehayasolo
miembrosdelamismacategora
6
3
6 5 4
C 20
3 2 1
= =
4
3
4 3 2
C 4
3 2 1
= =
24
Slo3P:
Slo3A:
s
( )
24 6
P A
220 55
= =
CLAVE:C
ResueltoporJuanCastro
LGEBRA
RESOLUCIN22
( ) ( )( )
x 5 x 5
Ln x 1 2 .x 2 x 1 0 + <
| |( )( )
5 x
x 0 Lnx 1 x 1 2 1 0 > . + <
Pero
5 x
x 1 0 2 1 0 + > . > paratodox0
x 0 Lnx 1 0 > . <
x 0 Lnx Lne > . <
x 0 x e > . <
Portantox 0; e e CLAVE:B
EUREKA, la mejor preparacin UNI
MAGDALENA: 694-4930, LOS OLIVOS: 521-5182, JESS MARA: 462-8880 Pgina 5
RESOLUCIN23
Dato:
( ) 1
P 0 =
( ) ( ) 1 1
Q P 0
= =
( ) 1
P 1 a b c 0 = + + + =
( ) 1
P 1 a b c 0
= + + =
Igualando: a 0 b c 1 = . + =
2 2
b c 1 2bc + =
Reemplazando:
2 2
2 2 2 2
1 2bc b c
M 1
b c b c
+
= = =
+ +
CLAVE:D
RESOLUCIN24
Grficamenteunafuncintieneinversasitoda
recta horizontal corta a la grfica a lo ms en
unpunto.
CLAVE:D
RESOLUCIN25
PuestoquePyQsonidnticossecumple:
*ad54e
ac3 a3c33ee
b1e10 be9
cd1 dc12e
ce2c3 c3e
Luego,en*
e2e54e e7;a7;
b2;c10;d9
Adems
( )
4 3 17
x, y
P 3x 3x y 10y = + +
Portanto
adbcbe
( ) ( ) 1;1 1; 1
P Q 15
+ =
CLAVE:E
RESOLUCIN26
i ( ) ( )
2
1
3
f x a x b 2; 0 x
2
= + s s
delgrficodado:
1;2eselvrtice b1
0;1 ( )
2
1
f 1 a 1 2 a 1 e = + =
ii ( )
2
3
f x c x 2 2; x d
2
= + s s
( )
2
d;1 f 1 c d 2 2 e = + , pero d 2 del gr
fico
1 c(d 2) 2 = +
1 c(d 2) =
Adems
1 2
3 3
f f
2 2
| | | |
=
| |
\ . \ .
7 c
2
4 2
= +
1
c
2
= ;d4 portanto
7
c d
2
+ =
CLAVEC
ResueltoporRubnQuispe
GEOMETRA
RESOLUCIN27
S
P
D
M
H A
1
2/3
T
1 C B
45
1/2
1/2
1
1/3
1
3 53 /2
Delafigura:
sector APD
S S S
A
=
( ) ( )
2 1 1 1
S 1 1
2 4 2 3
t | | | |
=
| |
\ . \ .
1 3 4
S
8 6 24
t t
= =
CLAVEB
RESOLUCIN28
Piden:APx
Datos:PE4 .
AE2
Como ABesdimetro:
m AEB 90 =
Porteoremadelastres
Perpendiculares:
90 m AEP =
Finalmenteenel
AAEP:
x 2 5 =
CLAVE:A
x
2
A
E
B
P
4
EUREKA, la mejor preparacin UNI
MAGDALENA: 694-4930, LOS OLIVOS: 521-5182, JESS MARA: 462-8880 Pgina 6
RESOLUCIN29
X-6
6 C
A
N
m
M
B
f
f
x
Dato: .m16
MBCN:inscriptible
Teoremadelassecantes
( )
x x 6 m =
2
x 6x 16 =
x 8 =
CLAVE:B
RESOLUCIN30
Sepide:
a
x
b
=
Considerando que AB a es el lado del cua
drado Recuerde que las diagonales de un
pentgono regular son paralelas a sus lados
opuestos, por eso al trazar FP IH se deduce
que FP EG , Luego la diagonal EG del pen
tgono mide a ver figura. Por ltimo, sabe
mos que en el pentgono regular su lado es la
seccinureadesudiagonal,esdecir:
5 1
b a
2
| |
=
|
|
\ .
a
x 1, 6
b
= =
CLAVE:C
Nota:
En el pentgono regular las diagonales son
congruentes,entoncessededuce:
( ) EG FI PF FPI = > A
Peroenelgrfico:EGAByPFAD
Entonces: AB AD, lo que nos indica que
ABCDnoesuncuadrado.
RESOLUCIN31
135
45
B
M
A
L
N C
r
O
r
r
P
R 2
( )
4 2 1 +
Delafigura:
( )
r 2 r 4 2 1 + = + r 4 =
Luego: L r = u
( )
3
L 4
4
t | |
=
|
\ .
L 3 = t
CLAVE:D
ResueltoporManuelTrujillo
yAnbalTrucios
TRIGONOMETRA
RESOLUCIN32
Delosdatos
3
CD BC
2
= ,
7
DE BC
2
= y
m ACE = u
x
y
D B
A E
7k
3k 2k C
q
Notamos x y + = u
Ademspiden ( ) tg tg x y u = +
A B
C
D
I P H
F
E G
b
b
b
b
b
EUREKA, la mejor preparacin UNI
MAGDALENA: 694-4930, LOS OLIVOS: 521-5182, JESS MARA: 462-8880 Pgina 7
tgx tgy
tg
1 tgx.tgy
+
u =
Reemplazamosconvenientemente
2 3
35
7 7
tg
2 3
43
1
7 7
+
u = =
CLAVE:E
RESOLUCIN33
De:
2
2
1 cos 2 2cos
P
2sen 1 cos 2
u u
= +
u + u
1 sen2
Q
sen cos
+ u
=
u+ u
Tenemos o;
4
t
ue ,y 2u eIQ.
Luegodelaspropiedadesdedegradacin.
2
2sen 1 cos 2 u = u
2
2cos 1 cos 2 u = + u
Operamos: P2
Adems ( )
2
1 sen2 sen cos + u = u+ u
Entonces: Q1
Finalmente:PQ
CLAVE:C
RESOLUCIN34
Delaecuacin
2tgxcsc x 2csc x tgx 1 0 + =
Factorizamosconvenientemente
tgx12cscx10
Dondecadafactoresunposiblecero.
tgx 1 0 tgx 1 = =
x k , k z
4
t
= t + e
1
2csc x 1 0 csc x
2
+ = =
Nocontempladoenlavariacindela
cosecante.
Finalmentevemoslosvaloresquepuede
tomark,paraquelassolucionesseencuentren
enelintervalode
| | 2 ; 2 t t
x k
4
t
= t +
k 2 x 2
4
t
= = t+
k 1 x
4
t
= = t+
k 0 x
4
t
= =
k 1 x
4
t
= = t+
Luego
sol
= t
CLAVEB
RESOLUCIN35.
Sea: sen cos 1 u u =
Donde: sen cos 2sen
4
t | |
u u = u
|
\ .
Luego: 2sen 1 2sen 1
4 4
t t | | | |
u = v u =
| |
\ . \ .
Deaqu:
( ) 2k 1
4 4
t t
u = +
k
, k z
2
t
u = e
Entonces:
3
0, , , , 2
2 2
t t
u = t t
`
)
soluciones
5 = t
CLAVEC
RESOLUCIN36
Si: tanxarccotx1
Donde: x arc cotx k , k z
4
t
= t + e
Despejando: arc cotx x k
4
t
= t
Luego: x cot x k
4
t | |
= t
|
\ .
1 cotx
x
1 cotx
+
=
tan x 1
x
tan x 1
+
=
Proporcionamosobteniendo
x 1
tan x
x 1
+
=
CLAVED
ResueltoporRalAlejo
37.A 38.A 39.B 40.D
41.C 42.D 43.C 44.C
45.C 46.C 47.D 48.E
49.A 50.C 51.A
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Problemas resueltos de Hidráulica de CanalesDa EverandProblemas resueltos de Hidráulica de CanalesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (7)
- La Guía Definitiva en Matemáticas para el Ingreso a la UniversidadDa EverandLa Guía Definitiva en Matemáticas para el Ingreso a la UniversidadValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (11)
- Métodos Matriciales para ingenieros con MATLABDa EverandMétodos Matriciales para ingenieros con MATLABValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Algebra Preuniversitario (600 Ejercicios Resueltos)Documento148 pagineAlgebra Preuniversitario (600 Ejercicios Resueltos)Jean Hernandez79% (61)
- La guía definitiva en Matemáticas para el Ingreso al BachilleratoDa EverandLa guía definitiva en Matemáticas para el Ingreso al BachilleratoValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (9)
- Ingeniería química. Soluciones a los problemas del tomo IDa EverandIngeniería química. Soluciones a los problemas del tomo INessuna valutazione finora
- Logaritmos XavierDocumento4 pagineLogaritmos XavierXavier Huamani C.86% (7)
- Aritmetica 9Documento7 pagineAritmetica 9vegacarlos89Nessuna valutazione finora
- Problemas Capitulo 3 Leven Spiel CompletoDocumento54 pagineProblemas Capitulo 3 Leven Spiel CompletoJosep LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Resolucion Examen de Admision UNA PUNO - CEPREUNA 15 Junio 2014Documento5 pagineResolucion Examen de Admision UNA PUNO - CEPREUNA 15 Junio 2014Gustavo Antonio Alca Arpasi0% (1)
- Diseno de Estructura Melalicas Seccion Compuesta PDFDocumento313 pagineDiseno de Estructura Melalicas Seccion Compuesta PDFCesar Lopez100% (2)
- Curvas en Coordenadas PolaresDocumento7 pagineCurvas en Coordenadas PolaresEmmanuel Alvarez TeloxaNessuna valutazione finora
- Derivada MaterialDocumento2 pagineDerivada MaterialCarlos Montúfar100% (1)
- Practica 4 Mecanica Clásica UpiicsaDocumento23 paginePractica 4 Mecanica Clásica Upiicsarequiem100% (1)
- La ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesDa EverandLa ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesNessuna valutazione finora
- CpuuDocumento75 pagineCpuuSilverTelloFernadez0% (1)
- Geometric modeling in computer: Aided geometric designDa EverandGeometric modeling in computer: Aided geometric designNessuna valutazione finora
- Solucionario - Guía de Ciencias QuímicaDocumento31 pagineSolucionario - Guía de Ciencias QuímicaWalter Raul CulquiNessuna valutazione finora
- Solucionario UniDocumento9 pagineSolucionario UniDiego ÁlvarezNessuna valutazione finora
- FisicaiDocumento11 pagineFisicaiAllan ScottNessuna valutazione finora
- CEPREUNI - SolucionarioPC0607I PDFDocumento10 pagineCEPREUNI - SolucionarioPC0607I PDFmayracadena1100% (2)
- ProblemasResueltos PolimerosDocumento13 pagineProblemasResueltos PolimerosMattDoCarmoNessuna valutazione finora
- SOLPRE4PCDocumento13 pagineSOLPRE4PCCesar ColoradoNessuna valutazione finora
- Problema de Metodos Numericos 12Documento17 pagineProblema de Metodos Numericos 12FabioRangel0% (1)
- Solucionario Del Examen Parcial - Meza Cahuana MaryDocumento8 pagineSolucionario Del Examen Parcial - Meza Cahuana MaryMary Cruz Meza CahuanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Clase 10-Equilibrio de ComplejosDocumento34 pagineClase 10-Equilibrio de ComplejosEduardoLalo MamaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Solucionario 12Documento3 pagineSolucionario 12Erik TrujilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Trignometria 13 TRANSFORMACIONESDocumento9 pagineTrignometria 13 TRANSFORMACIONESelio50% (2)
- Solucionario C - DDocumento4 pagineSolucionario C - DRichard Callo CNessuna valutazione finora
- Solucionario N1 PDFDocumento4 pagineSolucionario N1 PDFunionsustiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Solucionario 1pc PreDocumento11 pagineSolucionario 1pc PreJulio Campos ValenzuelaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4toano SolucionarioDocumento15 pagine4toano SolucionarioPeter Bobadilla Puma100% (1)
- Solucionario Eti N 08Documento15 pagineSolucionario Eti N 08Jafet Mayon100% (3)
- Ejercicios Resueltos 2 2013BDocumento9 pagineEjercicios Resueltos 2 2013Bdemer22Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ejemplo 1Documento5 pagineEjemplo 1Franz Erick Cruz TapiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Solucionario San Marcos 2010Documento15 pagineSolucionario San Marcos 2010juancarlosteeducaNessuna valutazione finora
- Solu SDocumento10 pagineSolu Sjuan carlosNessuna valutazione finora
- Saco Oliveros Uni2014 I Sol MDocumento12 pagineSaco Oliveros Uni2014 I Sol MCristian Bustamante CarrascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Problemas U2Documento7 pagineProblemas U2Alma Sosa Flores100% (1)
- Certamen 1 - 2005 PDFDocumento2 pagineCertamen 1 - 2005 PDFeduardo_avendañoNessuna valutazione finora
- Certamen 1 Pauta de CorreccionDocumento2 pagineCertamen 1 Pauta de CorreccionAlexis DanielNessuna valutazione finora
- Equilibrio Quimico DeberDocumento8 pagineEquilibrio Quimico DeberNarky_12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Solve A. 3 478Documento3 pagineSolve A. 3 478JuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Parcial ResistenciaDocumento15 pagineParcial ResistenciaomarNessuna valutazione finora
- Purcell-Calculo Diferencial e IntegralDocumento6 paginePurcell-Calculo Diferencial e IntegralDavid RinconNessuna valutazione finora
- Sucesiones y Series (ER) PDFDocumento59 pagineSucesiones y Series (ER) PDFGerardo CossNessuna valutazione finora
- Trabajo 1 - Problemas de TermodinamicaDocumento5 pagineTrabajo 1 - Problemas de TermodinamicaJheyson AlvarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Sol2 - 2009Documento14 pagineSol2 - 2009Miller López GuerreroNessuna valutazione finora
- Separata ELECTROQUIMICADocumento14 pagineSeparata ELECTROQUIMICAalejj19100% (1)
- Trabajo 02 Cruz Caja Jesus AngelDocumento12 pagineTrabajo 02 Cruz Caja Jesus AngelJESUS ANGEL CRUZ CAJANessuna valutazione finora
- Universidad de CartagenaDocumento14 pagineUniversidad de CartagenaRalph MarrugoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ex Jul 11 QFIIDocumento4 pagineEx Jul 11 QFIIAitor PastorNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecuaciones TrigonometricasDocumento4 pagineEcuaciones Trigonometricascarlos_kard0322688Nessuna valutazione finora
- Clase Práctica de Balance de Energía Con Reacción Química.Documento7 pagineClase Práctica de Balance de Energía Con Reacción Química.Victor GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicios de ApuntalamientoDocumento12 pagineEjercicios de ApuntalamientoJesús Fernández SernaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Plan Semana 25 2024 TumejormaestroDocumento6 pagine6 Plan Semana 25 2024 TumejormaestroVianeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller de Semana 10Documento4 pagineTaller de Semana 10Giancarlo Diosdado Castro MendizabalNessuna valutazione finora
- S01 Lab Virtual 1 INTROD ELECTROSTATICADocumento2 pagineS01 Lab Virtual 1 INTROD ELECTROSTATICACLAUDIA RUIZNessuna valutazione finora
- LINO PRESENTACION Proyecto SocioproductivoDocumento36 pagineLINO PRESENTACION Proyecto SocioproductivoLino Bello RezamanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ciencias AuxiliaresDocumento1 paginaCiencias AuxiliaresPastoquemadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Teoría 1 Magnetismo PDFDocumento13 pagineTeoría 1 Magnetismo PDFcynthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Clase 6 Capacitores e InductoresDocumento11 pagineClase 6 Capacitores e InductoresYeison Cifuentes BaqueroNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 TGN 2014 Introducción PDFDocumento61 pagine1 TGN 2014 Introducción PDFnairdanipso123Nessuna valutazione finora
- RetrocausalidadDocumento18 pagineRetrocausalidadrangdroll dzogchenrimeNessuna valutazione finora
- Diseño Del Sistema ElectricoDocumento10 pagineDiseño Del Sistema ElectricoJorge CabreraNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual FM 71 Climat 2017Documento35 pagineManual FM 71 Climat 2017yennNessuna valutazione finora
- Estabilidad de Taludes y Empuje de TierrasDocumento86 pagineEstabilidad de Taludes y Empuje de TierrasMartin CasasNessuna valutazione finora
- VNMHDocumento20 pagineVNMHErnestina Ruiz VillamarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicios Resueltos y PropuestosDocumento17 pagineEjercicios Resueltos y PropuestosAndy Thu PekeNessuna valutazione finora
- Informe Fluidos (Viscosidad)Documento13 pagineInforme Fluidos (Viscosidad)A.PcNessuna valutazione finora
- Solucionario Examen Parcial Fisica 2Documento5 pagineSolucionario Examen Parcial Fisica 2Luis Enrique Torres LauraNessuna valutazione finora
- Que Se Puede Hacer Con El CacaoDocumento3 pagineQue Se Puede Hacer Con El CacaoGenesis J SantillanNessuna valutazione finora
- Los Fundamentos de La Teoría de La Gravitación de Einstein - Notas - Wikisource PDFDocumento106 pagineLos Fundamentos de La Teoría de La Gravitación de Einstein - Notas - Wikisource PDFpasc86Nessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratorio de Ecuaciones Diferenciales Segundo Corte.1.Documento11 pagineLaboratorio de Ecuaciones Diferenciales Segundo Corte.1.Alfredo Rodriguez MatuteNessuna valutazione finora
- La Cultura de La CrueldadDocumento6 pagineLa Cultura de La CrueldadAnita SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- El Absurdo Creador - de El Mundo Como Un Supermercado - Michel HouellebecqDocumento5 pagineEl Absurdo Creador - de El Mundo Como Un Supermercado - Michel Houellebecqgabo245100% (1)
- Ciencia Con Consciencia Capitulo Por La Ci - Edgar MorinDocumento38 pagineCiencia Con Consciencia Capitulo Por La Ci - Edgar MorinGRISSELLA IPARRAGUIRRENessuna valutazione finora
- Principios de Electromagnetismo y Maquinas de C.C.Documento11 paginePrincipios de Electromagnetismo y Maquinas de C.C.Fernando Mazas Hernandez100% (1)
- Cartas Materiales Mendez 2018Documento27 pagineCartas Materiales Mendez 2018Mario JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Trabajo de InvestigacionDocumento7 pagineTrabajo de InvestigacionJosue ButronNessuna valutazione finora
- Todo Sobre Incertidumbre ProspectivaDocumento6 pagineTodo Sobre Incertidumbre ProspectivaErikaCastilloNessuna valutazione finora