Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
PG 5&6 Part 1
Caricato da
Abrielle TactayDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
PG 5&6 Part 1
Caricato da
Abrielle TactayCopyright:
Formati disponibili
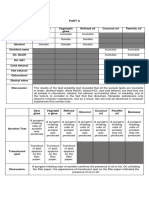
Disorder
Causative factor / Cause/ Contributing factor *Catheterization *Systemic disease
S/S
Medical TX
Surgical TX
Other TX
Nursing Consideration
Acute Cystitis/ UTI -inflammation of the urinary bladder - urethra ( most common route) - most common in women
-Frequency -Dysuria
-Antibiotics or sulfanamides - mild analgesics
N/A
N/A
- Encourage fluids /3-4 L if in atibiotic therapy ( prevent urinary stasis & crystals) - avoid tight fitting underwear - avoid irritants ( soaps, bubble baths - low sugar ( sugar promotes infection) - avoid sexual activity as much as possible ( risk for UTI) - Void immediately before & after sexual activity - warm packs alleviate pain - Vit C ( Acidify urine = prevent bacteria)
* changes in vaginal pH -Hematuria & other in women abnormal components of urine ( pus, WBC, + urine culture - heavy feeling in the abdomen or the perineumn
- phenazopyridine hydrochloride (pyridium)= orange red urine
Chronic Cystitis - recurrent UTI
- Frequency - Nocturia - incontinence LABS - High bacterial counts
Long term antibiotic therapy ( 3-6 mos)
N/A
Lubricant for vaginal irritation
- NC Acute UTI - Encourage shower ( avoid pushing bacteria up the urinary tract ) - monitor s/s yeast infections r/t antibiotic therapy - clean catch midstream spec. or intermittent straight catheterization
( accurate urine culture N/A Acute pyelonephritis -inflammation of the renal pelvis and the medulla - most common kidney disease - E.coli - ascending infection from Lower Urinary Tract or indwelling catheter - Rapid onset fever + chills - flank pain - pyuria -n/v - Headache frequency+ dysuria ( if infection reaches bladder) LABS: - Bacteuria - WBC - Casts Chronic Pyelonephritis - recurrent infections - urinary tract obstruction Interstitial cystitis - autoimmune, - inflammatory - infection Long term antimicrobial therapy N/A N/A NC Acute pyelonephritis - antimicrobial therapy ( 10 -14 days) - antibiotic - sulfanamides - urinary antiseptics - IV fluids ( dehydration r/t n/v) N/A - Med attention STAT for plank pain, fever & n/v -bed rest - encourage fluids - oral care - skin care - nourishment - pain management - reposition at least every 2 hrs
- lining of the bladder becomes leaky & allows irritants from the onset assoc. w/ UTI or urine to contact the instrumentation of the muscular wall causing Bladder irritability - common in women (20 -50 yrs old) - men w/ abacterial prostitis
- urge to void every 5 to Elmiron ( rebuilds 30 mins ( many days, protective layer of the no relief) bladder lining) - pelvic pain - dyspareunia - penile tip pain + perineal pain ( for men) LABS - Free of bacteria weekly for 6 wks - DMSO - Hydrocortisone - heparin - lidocaine
Hydrodistention ( ^ symptoms 1st few wks) PT - Stress reduction Techniques
- remove bladder irritants from diet - encourage fluids - little manipulation of the pelvic area as possible - stress management - social support, counselling
Glumerulonephritis - group of diseases in which kidneys are damaged and partly destroyed by the inflammation of the gallbladder
Acute infection ( poststreptococcal glumerulonephritis)
leads to Nephrotic syndrome aeb proteinuria + edema - 2 to 3 wks post URI - scarlet fever - streptococcus -Pale, puffy face - edema - nocturia family notices 1st -Antibiotics ( penicillin) - dietary management -bed rest - Daily I&O -Daily wt. - skin care -oral care - passive / active exercises - bed rest - law salt & fluid intake - low protein diet ( to reduce ammonia) -transfusion - pt in orthopneic position to facilitate breathing -
Acute Glumerulonephritis - common in children
Chronic Glumerulonephritis - may develop immediately after an acute episode - damages the kidney by destroying the nephrons and thereby disrupting the function - may lead to: ESRD Pulmonary edema ^ BP Cerebral hemorrhage CHF Renal Failure
Initial stage: - few symptoms other than: >mild general malaise > pale & dilute urine > slight anemia > hypertension > marked edema ( anasarca) Course of Disease - 10 -30 yrs > s/s renal insufficiency Advance stage > blurred vision >blindness Terminal Stage: > epistaxis > gastrointestinal bleeding
Antihypertensives ( for -Dialysis edema -kidney transplant
Restricted salt and water intake
Hydronephrosis
Obstruction blocking
Depending at the site of Removal of the cause
-is distension and dil the outflow of urine,
ation of the renal pelvis calyces
obstruction
of obstruction complete obstruction
- reversible if acute
pain,pressure, causing the waste products accumulate in s/s of UTI or kidney the kidney and back up stones if present in the blood leading to ESRD Primary : pain at the site colic - excruciating pain, in waves as the ureter to force the obstructing stone onward - gross hematuria( trauma in ureter) - asymptomatic or - mild hematuria - urgency - urge incontinence bladder stones s/s
medical emergency
Calculi Unknown - formed in the kidneys & descend to the maybe : infections urinary tract dehydration - lithiasis urinary stasis - common in men urine : uric acid calcium oxylate stones ^ uric acid = gouty arthritis risk for pt. W/: - MS - Diabetes - UTI
-Analgesics -antispasmodics -
- cystoscope Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy - stab wound @flank, catheter inserted, ultrasound waves crushes the stones ESWL ( extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy) - stones in the kidney or upper ureters are blasted to smaller pieces Urethroscopic Calculi removal- stone removal without crushing - using stone basket. ( tong like instrumentation used to grab stone from ureter) - bleeding risk Lithotripsy use of soundwaves to crush stones obstructing the bladder, gallbladder or ureter
N/A
- Strain urine for calculi - Care pt. Stone removal (ESWL) PRE OP >Explain the procedure > in tx table, H2O cushion or tub > mild sedative + gen anesthesia POST OP > urine must be slightly bloody or rose > observe 1-2 days > fluids > strain urine >monitor s/s infections > report hematuria > warm packs (comfort)
* stent post UCR & lithotripsy Surgical Removal a) ureterolithotomysurgical removal of the cslculi in the ureter b) nephrolithotomy incision into the kidney and removal Stricture - narrowing of the urinary tract -common in men Fibrous bands - Frequency - dysuria - burning - stretching via sounds and bougies -Urethrotomy - incision of a urethral stricture Emotional Support Maybe genetics Asymptomatic or pain, decreased kidney function May not be necessary if no kidney disruption involved other wise , removal of the cysts Polycytric kidney disease -multiple cyst in the kidneys Cancer of the kidney/Nephroma/ hypernephroma - characterized by malignant kidney tumors - mostly men Malignant kidney tumor usually invades aorta & vena cava -Painless hematuria - fever -wt. Loss -malaise -palpable flank mass (painful later) chemotherapy Nephrectomy (early stage) curative radiation - bleeding risk - monitoring urine output ( risk UTI)
Benign Renal cyst * Monocystic kidney disease - single cyst in the kidneys
Bladder tumor -most common site of urinary cancer -mostly malignant -in bladder wall or small warts
-Chemicals -smoking -lung cancer - correlated to: caffeine artificial sweeteners
Painless hematuria
Chemotherapy (+tumor removal)
Transurethral resection of the bladder ( TUBRT) - Superficial tumor removal via: a) endoscopic resection (cutting out) b) fulguration ( destruction by electricity) - Resectoscope (tube, bladder to urethra) -Laser therapy -cystotomy -cutaneous cysthotomy -suprapubic cystocath -cystectomy ( stent bet. Ureter + ileum used post surg)
Radiation (+ tumor removal) complication: radiation cystitis -lead to loss of bladder compliance - appearance rough + red - tx for urge incontinence applicable
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- It Complaint Management SystemDocumento26 pagineIt Complaint Management SystemKapil GargNessuna valutazione finora
- Forms Day CareDocumento15 pagineForms Day CareAira ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- DR Bob Jantzen's Differential GeometryDocumento485 pagineDR Bob Jantzen's Differential GeometryBGMoney5134Nessuna valutazione finora
- Results and Discussion of Lipid Solubility, Identification, and AnalysisDocumento5 pagineResults and Discussion of Lipid Solubility, Identification, and AnalysisStarrrNessuna valutazione finora
- Critical Success FactorsDocumento12 pagineCritical Success Factorsmoon1377Nessuna valutazione finora
- IILM Institute For Higher EducationDocumento8 pagineIILM Institute For Higher EducationPuneet MarwahNessuna valutazione finora
- 3D MapsDocumento1.128 pagine3D MapsjoangopanNessuna valutazione finora
- An Evaluation of The Performance Contracting On Organisation Performance A Case of Kenyatta University, Kenya PDFDocumento15 pagineAn Evaluation of The Performance Contracting On Organisation Performance A Case of Kenyatta University, Kenya PDFAlexander DeckerNessuna valutazione finora
- TCS Case StudyDocumento21 pagineTCS Case StudyJahnvi Manek0% (1)
- Power Window System OverviewDocumento2 paginePower Window System OverviewMaxi SardiNessuna valutazione finora
- Dsu Teach Camp Schedule 2023Documento11 pagineDsu Teach Camp Schedule 2023api-674280680Nessuna valutazione finora
- DuPont Shift Schedule ExplainedDocumento3 pagineDuPont Shift Schedule ExplainedHanzNessuna valutazione finora
- Ala CalculationDocumento4 pagineAla CalculationAgus SupriadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Oracle Hyperion Financial Management: Lightstream Analytics Pte LTDDocumento63 pagineOracle Hyperion Financial Management: Lightstream Analytics Pte LTDJunnei LiuspitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dabhol Power Plant: Case Analysis Report OnDocumento11 pagineDabhol Power Plant: Case Analysis Report OnDhruv ThakkarNessuna valutazione finora
- 978 0 387 95864 4Documento2 pagine978 0 387 95864 4toneiamNessuna valutazione finora
- Infobasic - 3Documento64 pagineInfobasic - 3Kishore KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Annex 2.1: Contingency Plan Template For SchoolDocumento21 pagineAnnex 2.1: Contingency Plan Template For SchoolJapeth PurisimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Product Note - CIMA Advanced Diploma in Management Accounting - Web ILT v1Documento3 pagineProduct Note - CIMA Advanced Diploma in Management Accounting - Web ILT v1equinoxNessuna valutazione finora
- Linux File System OverviewDocumento64 pagineLinux File System OverviewMayur IngleNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Ratio AnalysisDocumento8 pagineFinancial Ratio AnalysisrapsisonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 26 STAINING OF MUSCLE AND BONE - Group3Documento6 pagineChapter 26 STAINING OF MUSCLE AND BONE - Group3Krizelle Vine RosalNessuna valutazione finora
- LSP1 circuit board component layout and schematicDocumento1 paginaLSP1 circuit board component layout and schematicEvely BlenggoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pengaruh Penerapan Pendekatan Pembelajaran Pada Mata Pelajaran Ekonomi Di Sma Negeri 15 PalembangDocumento15 paginePengaruh Penerapan Pendekatan Pembelajaran Pada Mata Pelajaran Ekonomi Di Sma Negeri 15 PalembangDharma AdjieNessuna valutazione finora
- Starch and Cereals RecipeDocumento20 pagineStarch and Cereals RecipeWinsher Pitogo100% (1)
- Hydraulic CaculationDocumento66 pagineHydraulic CaculationgagajainNessuna valutazione finora
- Jindal Power's Coal Handling Plant OverviewDocumento29 pagineJindal Power's Coal Handling Plant Overviewsexyakshay26230% (1)
- Dialog+ 2016 - BrochureDocumento6 pagineDialog+ 2016 - BrochureirmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Educ 210Documento2 pagineEduc 210Julie Ann CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Javascript Lesson For Vii and ViiiDocumento90 pagineJavascript Lesson For Vii and ViiiAKSHAJ BAJAJNessuna valutazione finora