Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Endo Disorders
Caricato da
Jelai DDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Endo Disorders
Caricato da
Jelai DCopyright:
Formati disponibili
GLAND
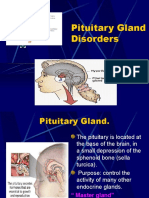
I. PITUITARY GLAND a. Anterior Lobe (Adenohypophysis)
HORMONE
Growth hormone (GH)
FUNCTION
- growth of cells, bones and tissues
TARGET ORGAN/ REGULATION
- TARGET ORGAN: whole body - controlled by GHRH/GHIH - increases after eating and after onset of deep sleep - TARGET ORGAN: breasts, gonads - controlled by PRH - secretions occurs during later hours of sleep - TARGET ORGAN: Thyroid gland - controlled by TRH and negative feedback from plasma T4 levels - TARGET ORGAN: adrenal cortex - controlled by CRH and negative feedback by cortisol levels
DISORDERS
Gigantism increase of GH in adulthood Acromegaly increase of GH in adults Dwarfism decrease of GH in adulthood
Prolactin (PRL)
- breast development and lactation - regulates reproductive function - necessary for growth and function of the thyroid gland - necessary for growth and and maintenance of size of the adrenal cortex - controls release of glucocorticoids (cortisol), mineralocoricoids (aldosterone) - growth, maturity and function of primary and secondary sex organs
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Adenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
Hyperthyroidism (Graves Disease 2 to increase of TSH) Cushings Disease increase of ACTH
GONADOTROPINS (FSH , LH, MSH)
b. Posterior Lobe (Neurohypophysis)
Anti-Diuretic Hormone (ADH/Vasopressin )
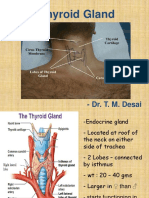
Oxytocin II. THYROID GLAND -TH -T3 and T4 - Calcitonin
- regulates osmolality and body water volume - increases permeability of collecting ducts (kidneys) results to increase water reabsorption - stimulates milk 'let down' and uterine contraction - Regulates metabolic rate of all cells and growth and devt of all tissues - Maintains/lowers serum calcium levels Controls circulation of calcium & inorganic phosphorous in blood - Influences electrolyte concentration & fluid volume.
- TARGET ORGANS: gonads - secretion controlled by GnRH - Males - secreted if there is a decreased male sex hormones - Females - normal menstrual cycle - TARGET ORGAN: kidneys - secretion is stimulated if there is increased serum osmolality, modest hypotension (vise versa) -TARGET ORGAN: breast tissue and uterus - Secreted in response to TSH - secreted-elevated serum calcium - calcium-rich foods - Ca+ - suppresses release of calcitonin
Diabetes Insipidus decrease of ADH
III. PARATHYROID GLAND IV. ADRENAL GLANDS a. Adrenal Cortex
Parathormone (PTH)
Adrenocorticoids (corticosteroids,
Hypothyroidism: Cretinism in children Myxedema in adults Goiter Hyperthyroidism, Thyroid Storm, Thyroiditis, Carcinoma, Hypoparathyroidism, Hyperparathyroidism Addisons disease (hypofunction of cortices) Cushings disease (hyperfunction of
b. Adrenal Medulla
corticoids) 1. Mineralocorticoids, aldosterone 2. Glucocorticoids, cortisol (hydrocortisone) 3. Sex hormones (androgen, estrogen, progesterone) Catecholamines (epinephrine / norepinephrine)
- Influences metabolism of glucose, protein & fat - Concerned with bodys responses to physical & mental stress
aldosterone)
V. PANCREAS
Insulin- controls metabolism bet. Meals Glucagon- increases blood glucose
- Stimulate heart - Constrict blood vessels - Dilate bronchioles - RR - Hyperglycemia -Stimulated by intake of glucose and amino Acids -stimulated by dec. blood glucose level and inc. amino acid levels.
- Secreted in response to stress
Pheochromocytoma (increase of production of both hormones)
Secreted in response to low blood glucose level
Diabetes Mellitus
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Endocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsDa EverandEndocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocumento25 pagineEndocrine Systemangel_maui100% (13)
- 40.43.function of Endocrine - Pptx?targetDocumento28 pagine40.43.function of Endocrine - Pptx?targetAnnemerline RavixNessuna valutazione finora
- Anterior Pituitary GlandDocumento29 pagineAnterior Pituitary GlandSyed Mohammad Osama AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine DisordersDocumento91 pagineAssessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine DisordersAirme Raz AlejandroNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine SystemDocumento30 pagineEndocrine SystemYary MayorNessuna valutazione finora
- Pituitary Gland DisordersDocumento80 paginePituitary Gland DisordersNang KhamNessuna valutazione finora
- CC Endo GuideDocumento2 pagineCC Endo GuideManelli Faten BuenaventuraNessuna valutazione finora
- Kuliah PituitariDocumento48 pagineKuliah PituitariLona Veronika HutajuluNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System - LectureDocumento213 pagineEndocrine System - LectureRosita Antiquina Elopre100% (1)
- Endocrine System Part 2Documento31 pagineEndocrine System Part 2Lmashley GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Hormonas HipofisariasDocumento58 pagineHormonas Hipofisariasitaliaman100% (1)
- Hormone Regulation & Endocrine StructuresDocumento28 pagineHormone Regulation & Endocrine StructuresFujoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pituitary DisordersDocumento42 paginePituitary DisordersDudy HumaediNessuna valutazione finora
- The Endocrine System (Notes)Documento4 pagineThe Endocrine System (Notes)Wasim HakimNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Pitutary GlandDocumento44 pagine2 Pitutary GlandHanen ZedanNessuna valutazione finora
- ENDOCRINE SYSTEM and Disorders LectureDocumento153 pagineENDOCRINE SYSTEM and Disorders LectureAnthony Riggs100% (1)
- Week 16 Endocrine SystemDocumento16 pagineWeek 16 Endocrine Systemrichard respetoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pituitary DisordersDocumento38 paginePituitary DisordersJaspreet KangNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine New EditionDocumento150 pagineEndocrine New Editiondigracia manatigaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hormones: Resmia A. MaulanaDocumento42 pagineHormones: Resmia A. MaulanaCanny CańasNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine Test 8 NotesDocumento9 pagineEndocrine Test 8 NotesHayden ShulerNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases: Qian Xing, MD, PHDDocumento49 pagineEndocrinology and Metabolic Diseases: Qian Xing, MD, PHDFathimathNessuna valutazione finora
- ArainDocumento71 pagineArainAllah Bux KhosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hormones Are Chemical Substances Synthesized From Amino Acids and Cholesterol That Act OnDocumento19 pagineHormones Are Chemical Substances Synthesized From Amino Acids and Cholesterol That Act OnJasminKate SutacioNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine SystemDocumento3 pagineEndocrine SystemAnne Jillian83% (6)
- Pharmacology: EndocrineDocumento210 paginePharmacology: EndocrineSharifa Darayan100% (1)
- Gland Location Hormone Chemical Nature Target Structure Function Hypersecretion HyposecretionDocumento6 pagineGland Location Hormone Chemical Nature Target Structure Function Hypersecretion Hyposecretiondave_1128Nessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine: Mo GbessayDocumento88 pagineEndocrine: Mo GbessayVivian KamaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine DrugsDocumento172 pagineEndocrine DrugsAlvim Tiel FactorNessuna valutazione finora
- Hormone Regulation of Elasmobranch Physiology: Chris Bedore and Shannon LongDocumento74 pagineHormone Regulation of Elasmobranch Physiology: Chris Bedore and Shannon LongFeblin VersiliantinaNessuna valutazione finora
- PituartaryDocumento3 paginePituartarynancy dasNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Diagnosis of Endocrine Diseases and HypersensitivityDocumento60 pagineLaboratory Diagnosis of Endocrine Diseases and HypersensitivityFolahanmi AyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Disorders of The Anterior Pituitary - ESWDocumento78 pagineDisorders of The Anterior Pituitary - ESWpakdejackNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 HZ Hypothalamic and Pituitary Hormones HZDocumento20 pagine2 HZ Hypothalamic and Pituitary Hormones HZAmirabbas SaffariNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Endocrine SystemDocumento12 pagineHuman Endocrine SystemTabada NickyNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 6 Endocrine SystemDocumento39 pagineScience 6 Endocrine Systemcharmaine_olivia_1100% (1)
- A&PII Test 1Documento14 pagineA&PII Test 1Alyssa BattcockNessuna valutazione finora
- Endo EndoDocumento45 pagineEndo EndomaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Raghu Prasada M S MBBS, MD Assistant Professor Dept. of Pharmacology Ssims & RCDocumento27 pagineDr. Raghu Prasada M S MBBS, MD Assistant Professor Dept. of Pharmacology Ssims & RCNastase Daniela EcaterinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To EndocrinologyDocumento53 pagineIntroduction To EndocrinologyAli ArainNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocumento26 pagineEndocrine Physiologysam bossaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Pituitary Gland Phamela Joy S. Alvarez Anatomic and Physiologic OverviewDocumento27 pagineThe Pituitary Gland Phamela Joy S. Alvarez Anatomic and Physiologic OverviewEdelrose LapitanNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenal Steroids, GH, ProlactinDocumento34 pagineAdrenal Steroids, GH, ProlactinMohammad Hazamyn Hazrul HamzahNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Endocrine Disorders FINALDocumento166 pagineReview Endocrine Disorders FINALmeranith100% (10)
- Disorders of The Endocrine SystemDocumento26 pagineDisorders of The Endocrine SystemBader ZawahrehNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine Disorders Worksheetanskey2012-1Documento5 pagineEndocrine Disorders Worksheetanskey2012-1mezuniga1100% (1)
- Lect.2-Thyroid GlandDocumento20 pagineLect.2-Thyroid GlandParthvi ParmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine ChartDocumento7 pagineEndocrine Chartwjg2882Nessuna valutazione finora
- NM 24 Endohypothapituit 2007Documento71 pagineNM 24 Endohypothapituit 2007api-26938624Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anterior Pituitary (Autosaved)Documento33 pagineAnterior Pituitary (Autosaved)BABLU GAMINGNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine DisordersDocumento3 pagineEndocrine DisordersIrish OrleansNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusDocumento9 pagineEndocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusRohan Sahu0% (1)
- The Endocrine System Lesson 1Documento44 pagineThe Endocrine System Lesson 1Heaven Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- 7sistem EndokrinDocumento72 pagine7sistem EndokrinAlfianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pituitary Gland: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocumento14 paginePituitary Gland: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleSuresh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, Ph.D.Research ScholarDocumento32 pagineM.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, Ph.D.Research ScholarM.PRASAD NAIDUNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine and SecretionsDocumento25 pagineEndocrine and SecretionsNelson Louie III RicerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Hormones: Prof. Dr. V P SoniDocumento21 pagineHormones: Prof. Dr. V P SoniPadma VishwanathNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture EndoDocumento3 pagineLecture EndoRycris Mae Dela PeñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Glucose MonitoringDocumento1 paginaBlood Glucose MonitoringJelai DNessuna valutazione finora
- Food Exchange ListDocumento4 pagineFood Exchange ListJelai D50% (2)
- Nursing Assessment According To GordonDocumento3 pagineNursing Assessment According To GordonJelai DNessuna valutazione finora
- Gordon's Functional Health PatternsDocumento2 pagineGordon's Functional Health PatternsJelai D0% (1)
- Gordon's QuestionnaireDocumento2 pagineGordon's QuestionnaireJelai DNessuna valutazione finora
- CHED Memorandum Order No. 14 Series of 2009Documento129 pagineCHED Memorandum Order No. 14 Series of 2009PhilippineNursingDirectory.com81% (27)
- Gordon's Functional Health PatternsDocumento2 pagineGordon's Functional Health PatternsJelai D0% (1)
- AP1 Lab16 Endocrine System FA2021Documento11 pagineAP1 Lab16 Endocrine System FA2021daleng subNessuna valutazione finora
- Vetocept® (Buserelin Acetate) : Drug Form: Chemistry: Composition: ActionDocumento1 paginaVetocept® (Buserelin Acetate) : Drug Form: Chemistry: Composition: ActionImran KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- CortisoneDocumento3 pagineCortisonedb100067Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2013 ENDOCRINE PHARMACOLOGY Word Notes PDFDocumento52 pagine2013 ENDOCRINE PHARMACOLOGY Word Notes PDFNicole Opao100% (4)
- Acusera 2111EC 2112EC 2113C Mindray CL Series - Update 09 2022Documento3 pagineAcusera 2111EC 2112EC 2113C Mindray CL Series - Update 09 2022Ulises Saldias RoaNessuna valutazione finora
- MR NITIN PDFDocumento2 pagineMR NITIN PDFVenkat Nitin GuttaNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine SystemDocumento6 pagineEndocrine SystemCaviles, Jasmin S.Nessuna valutazione finora
- List of Human HormonesDocumento7 pagineList of Human HormonesKeerthana BathojuNessuna valutazione finora
- EndocrinologyDocumento12 pagineEndocrinologyNathaniel Derige AndesNessuna valutazione finora
- Hormones:: Signaling MoleculesDocumento20 pagineHormones:: Signaling MoleculesSangeeta DwivediNessuna valutazione finora
- Somatostain: Growth Hormone - Inhibiting Hormone (GHIH)Documento9 pagineSomatostain: Growth Hormone - Inhibiting Hormone (GHIH)Daniel AtiehNessuna valutazione finora
- مذكرة فارماكولوجي روعةDocumento56 pagineمذكرة فارماكولوجي روعةKomang Gede Suwija Negara100% (1)
- Oxytocin, ADH Lecture For 2nd Year MBBS by DR Waeem KausarDocumento28 pagineOxytocin, ADH Lecture For 2nd Year MBBS by DR Waeem KausarIMDCBiochemNessuna valutazione finora
- Omnitrope 10mg1.5ml Uses, Side Effects, InteraDocumento1 paginaOmnitrope 10mg1.5ml Uses, Side Effects, InteraAliNessuna valutazione finora
- Which OCP Is Best HandoutDocumento4 pagineWhich OCP Is Best HandoutMarianna LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lyphochek Immunoassay Plus Control Levels 1, 2 and 3Documento1 paginaLyphochek Immunoassay Plus Control Levels 1, 2 and 3aa shuvoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sap MonopousDocumento14 pagineSap MonopousLaksmi Sri WardanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction - Functions of Aldosterone and GlucocorticoidsDocumento19 pagineIntroduction - Functions of Aldosterone and GlucocorticoidssabaNessuna valutazione finora
- UT Progestin PDFDocumento10 pagineUT Progestin PDFLidyaNessuna valutazione finora
- CSE Grade 10 Science Lesson PlanDocumento6 pagineCSE Grade 10 Science Lesson PlanJelly Marie Baya FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanism of Hormone ActionDocumento27 pagineMechanism of Hormone Actiondaffa fatihNessuna valutazione finora
- Price List of Sensetech S300 Immunoflorescence Analyzer Uk: Valid Till Dec 31, 2021Documento2 paginePrice List of Sensetech S300 Immunoflorescence Analyzer Uk: Valid Till Dec 31, 2021muhammad israeel100% (1)
- PDFDocumento9 paginePDFCésar CuadraNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacological Control of Reproduction in The Dog and BitchDocumento22 paginePharmacological Control of Reproduction in The Dog and BitchVeterinary TirupathiNessuna valutazione finora
- CC 2 Lec-CompreDocumento105 pagineCC 2 Lec-CompreLyra Dennise Llido100% (2)
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocumento3 pagineCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationNANDAKUMAR BABUNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 10 A2.2 Pituitary and Hypothalamus The Bodys Control CentersDocumento40 pagineScience 10 A2.2 Pituitary and Hypothalamus The Bodys Control CentersKhobie PabilicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 9 Endocrine HormonesDocumento18 pagineLecture 9 Endocrine HormonesKC PalattaoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Endocrine Glands & Their HormonesDocumento35 pagineThe Endocrine Glands & Their HormonesEtta Sagita Leonora100% (1)
- Manual Motor Om 457la - Mercedes BenzDocumento310 pagineManual Motor Om 457la - Mercedes BenzCamila RodriguesNessuna valutazione finora