Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Glossary Chp7 Photosynthesis
Caricato da
kylevDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Glossary Chp7 Photosynthesis
Caricato da
kylevCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Glossary How Cells Acquire Energy
Chapter 7
absorption
Range of wavelengths that one or more specified pigments can absorb.
spectrum
anthocyanin Blue or red accessory pigment.
autotroph Any organism that makes its own food with an environmental energy source
(e.g., sunlight) and CO2 as its carbon source.
C3 plant Plant that uses three-carbon PGA as the first intermediate for carbon fixation.
C4 plant Plant that uses oxaloacetate (a four-carbon compound) as the first intermediate
for carbon fixation. CO2 is fixed twice, in two cell types; helps counter
photorespiration.
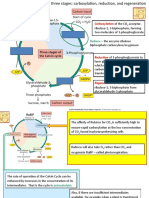
Calvin-Benson Light-independent cyclic reactions of photosynthesis that form sugars, using ATP
cycle energy, NADPH, and CO2.
CAM plant Type of plant that conserves water by opening stomata only at night, when it
fixes carbon dioxide by means of a C4 pathway.
carbon fixation First of the light-independent reactions. Rubisco, an enzyme, affixes carbon
(from CO2) to RuBP or to another compound for entry into the Calvin-Benson
cycle.
carotenoid An accessory pigment of photosynthesis; e.g., fucoxanthin.
chemoautotroph Any prokaryotic cell that synthesizes its own food using carbon dioxide as the
carbon source and an inorganic substance as the energy source.
chlorophyll Main photosynthetic pigment. Chlorophylls absorb all wavelengths of visible
light but not much of green and yellow ones.
chloroplast The organelle of photosynthesis in plants and many protistans.
electromagnetic All wavelengths from radiant energy less than 10-5 nm long to radio waves
spectrum more than 10 km long.
electron transfer Organized array of membrane-bound enzymes and cofactors that accept and
chain donate electrons in series. It sets up an electrochemical gradient that makes H+
flow across the membrane. The flow energy drives ATP formation at ATP
synthases.
fluorescence A destabilized molecule emits light when reverting to more stable form.
heterotroph Organism unable to make its own organic compounds; feeds on autotrophs,
other heterotrophs, organic wastes.
hydrothermal vent
A steaming fissure in the deep ocean floor; has unique ecosystems.
ecosystem
light-dependent The first stage of photosynthesis. Sunlight energy is trapped and converted to
reactions chemical energy of ATP, NADPH, or both, depending on the pathway.
light-independent Second stage of photosynthesis; sugar-building reactions that require
reactions phosphate-group transfers from ATP, electrons and H atoms from NADPH, and
carbon from CO2. The phosphorylated sugars from these reactions are then
converted to end products (e.g., sucrose, cellulose, starch).
PGA Important intermediate of glycolysis and of the Calvin-Benson cycle.
PGAL Intermediate of glycolysis and of the Calvin-Benson cycle.
photoautotroph Photosynthetic autotroph; any organism that synthesizes its own organic
compounds using CO2 for carbon atoms and sunlight for energy. Nearly all plants,
some protistans, and a few bacteria do this.
photolysis Reactions split water molecules using photon energy. The released electrons,
hydrogen used in noncyclic pathway of photosynthesis; oxygen is a by-product.
photon One unit of energy of visible light.
photosynthesis Sunlight energy trapped, converted to chemical energy (ATP, NADPH, or both);
then synthesis of sugar phosphates that are converted to sucrose, cellulose,
starch, and other end products. The main pathway by which energy and carbon
enter the web of life.
photosystem Cluster of many light-trapping pigments in a photosynthetic membrane.
phycobilin Type of accessory pigment; notably abundant in red algae and in cyanobacteria.
pigment Any light-absorbing molecule.
reaction center The only molecule (a special chlorophyll a) that can pass electrons out of a
photosystem to a nearby acceptor molecule.
rubisco An enzyme that catalyzes attachment of the carbon atom from CO2 to RuBP and so
starts the Calvin-Benson cycle of the light-independent reactions.
RuBP An enzyme that catalyzes attachment of the carbon atom from CO2 to RuBP and so
starts the Calvin-Benson cycle of the light-independent reactions.
stoma A gap between two guard cells in leaf or stem epidermis. Opens or closes to control
(stomata) CO2 movement into a plant and H2O and O2 out of it. Stomata help plants conserve
water.
stroma A semifluid matrix between the thylakoid membrane system and two outer
membranes of a chloroplast; a zone where sucrose, starch, cellulose, and other
end products of photosynthesis are assembled.
thylakoid Inner chloroplast membrane often folded as interconnected flattened sacs; forms a
single compartment for hydrogen ions. Light-trapping pigments, and enzymes used
to form ATP, NADPH, or both, are embedded in it.
wavelength A wavelike form of energy in motion. The horizontal distance between the crests of
every two successive waves
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- CHAPTER 04 Some Types of Chemical ReactionsDocumento149 pagineCHAPTER 04 Some Types of Chemical Reactionssuper3boy100% (9)
- AC Example Problems Unit 1 Chemical Equations and Reaction SDocumento5 pagineAC Example Problems Unit 1 Chemical Equations and Reaction Ssuper3boyNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 03 Equations and Reaction StoichiometryDocumento100 pagineCHAPTER 03 Equations and Reaction Stoichiometrysuper3boy100% (1)
- Nuts and Bolts LabNameDocumento4 pagineNuts and Bolts LabNamekylevNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Pop. Inter. (A)Documento10 pagineTest Pop. Inter. (A)kylevNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 7 Ecology Study GuideDocumento21 pagineUnit 7 Ecology Study Guidekylev0% (1)
- Final Exam 2009 SPRDocumento1 paginaFinal Exam 2009 SPRkylevNessuna valutazione finora
- Viruses, Protists Part III)Documento49 pagineViruses, Protists Part III)kylevNessuna valutazione finora
- Invertebrates SPR 2009Documento201 pagineInvertebrates SPR 2009kylevNessuna valutazione finora
- SW Chapter 22 Protistans KeyDocumento13 pagineSW Chapter 22 Protistans Keykylev100% (3)
- Ch25 Inverts) Part 2Documento86 pagineCh25 Inverts) Part 2kylev100% (1)
- Ch25 Inverts) Part 1Documento85 pagineCh25 Inverts) Part 1kylev100% (1)
- Chapter 21 Prokaryotes KeyDocumento10 pagineChapter 21 Prokaryotes Keykylev100% (3)
- SW Chapter 21 KeyDocumento9 pagineSW Chapter 21 KeykylevNessuna valutazione finora
- Viruses, Protists) Part IIDocumento46 pagineViruses, Protists) Part IIkylevNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Questions CHP 13 (KEY) 2Documento6 pagineReview Questions CHP 13 (KEY) 2kylevNessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft PowerPoint - ch14 Lecture (Protein Synthesis)Documento31 pagineMicrosoft PowerPoint - ch14 Lecture (Protein Synthesis)kylev100% (4)
- Review Questions CHP 12 (KEY)Documento3 pagineReview Questions CHP 12 (KEY)kylevNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 Genetics) LabsDocumento31 pagineUnit 4 Genetics) Labskylev100% (2)
- Unit 4 Genetics) Study GuideDocumento1 paginaUnit 4 Genetics) Study GuidekylevNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 Genetics) Lecture OutlinesDocumento13 pagineUnit 4 Genetics) Lecture Outlineskylev100% (3)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - Shobhit NirwanDocumento21 paginePhotosynthesis in Higher Plants - Shobhit NirwanVraj M Barot100% (1)
- Phytosynthesis: Pharmaceutical Botany With TaxonomyDocumento2 paginePhytosynthesis: Pharmaceutical Botany With TaxonomyVanessa RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- A2 Edexcel Biology Session 4 1 PhotosyntDocumento22 pagineA2 Edexcel Biology Session 4 1 PhotosyntRick WuNessuna valutazione finora
- Escape Room EDU Teacher InstructionsDocumento41 pagineEscape Room EDU Teacher InstructionsNina Romero Ricci100% (1)
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocumento11 paginePhotosynthesis and Cellular RespirationNikki RØA0% (1)
- IB Biology Topic 08 - Metabolism, Respitaion & Photosynthesis HL Revision SheetDocumento1 paginaIB Biology Topic 08 - Metabolism, Respitaion & Photosynthesis HL Revision SheetMarwan PharaonNessuna valutazione finora
- Bspil-574-S-Bio Photosynthesis-DarkDocumento1 paginaBspil-574-S-Bio Photosynthesis-DarkJagdish RajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Science: Quarter 1, WK 6 - Module 1Documento31 pagineScience: Quarter 1, WK 6 - Module 1Elisha Kate AmitNessuna valutazione finora
- L8 9 PhotosynthesisDocumento30 pagineL8 9 PhotosynthesisCheng FuNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Photosynthesis PogilDocumento10 pagine11 Photosynthesis PogilEmmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Biology 9th Edition Peter Raven Full DownloadDocumento26 pagineTest Bank For Biology 9th Edition Peter Raven Full Downloadtimothybarberkscbxipoam100% (37)
- Stomata and Chlorophyll'S Influence On The Resistance of Several Maize Varieties Against Downy MildewDocumento6 pagineStomata and Chlorophyll'S Influence On The Resistance of Several Maize Varieties Against Downy Mildewmuhammad fikriNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Guide - Exercise 3Documento3 pagineLaboratory Guide - Exercise 3Alaniss Viveca AgnoNessuna valutazione finora
- Redox and Photosynthesis: Redox Reactions Electron Transport Chains Light ReactionsDocumento34 pagineRedox and Photosynthesis: Redox Reactions Electron Transport Chains Light ReactionsshiyiNessuna valutazione finora
- SSGBIO1 - CM Week 7Documento61 pagineSSGBIO1 - CM Week 7christine ManuelNessuna valutazione finora
- HL PhotosynthesisDocumento10 pagineHL PhotosynthesisMerima AzNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes On Light Reaction of PhotosynthesisDocumento5 pagineNotes On Light Reaction of Photosynthesisxdobby260Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chloroplast and PhotosynthesisDocumento19 pagineChloroplast and PhotosynthesisFizul HelmiNessuna valutazione finora
- RespirationDocumento26 pagineRespirationSarang2426Nessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis NotesDocumento6 paginePhotosynthesis NotesLavanya TheviNessuna valutazione finora
- Calvin CycleDocumento14 pagineCalvin CycleWahyu ArifNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions Electron Transport Chain A Rollercoaster Ride That Produces EnergyDocumento3 pagineQuestions Electron Transport Chain A Rollercoaster Ride That Produces Energyqwerty masterNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis - Part 1Documento90 paginePhotosynthesis - Part 1Antonio WilloughbyNessuna valutazione finora
- C4 Carbon Fixation - WikipediaDocumento55 pagineC4 Carbon Fixation - WikipediaBashiir NuurNessuna valutazione finora
- Algal Pigments PDFDocumento5 pagineAlgal Pigments PDFmanoj_rkl_07Nessuna valutazione finora
- BIO 9.3 - HomeworkDocumento4 pagineBIO 9.3 - HomeworkalradilaylaNessuna valutazione finora
- General Biology 1 Module 3Documento18 pagineGeneral Biology 1 Module 3BarachielNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbohydrate Biosynthesis in Plants: 20.3 Biosynthesis of Starch and Sucrose 20.4 Synthesis of Cell Wall PolysaccharidesDocumento27 pagineCarbohydrate Biosynthesis in Plants: 20.3 Biosynthesis of Starch and Sucrose 20.4 Synthesis of Cell Wall PolysaccharidesOsman AbhimataNessuna valutazione finora
- Why Women Wash The DishesDocumento7 pagineWhy Women Wash The DishesOLehj Santos80% (5)
- Photosynthesis Literature ReviewDocumento8 paginePhotosynthesis Literature Reviewaflsbdfoj100% (1)