Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
The Main Circuit Board of A Microcomputer
Caricato da
amandeep123Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
The Main Circuit Board of A Microcomputer
Caricato da
amandeep123Copyright:
Formati disponibili
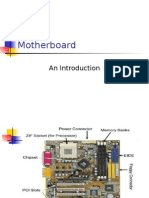
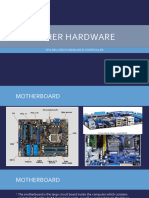
What is mother board:The main circuit board of a microcomputer.
The motherboard contains the connectors for attaching additional boards. Typically, the motherboard contains the CPU, BIOS, memory, mass storage interfaces, serial and parallel ports, expansion slots, and all the controllers required to control standard peripheral devices, such as the display screen, keyboard, and disk drive. Collectively, all these chips that reside on the motherboard are known as the motherboard's chipset.
On most PCs, it is possible to add memory chips directly to the motherboard. You may also be able to upgrade to a faster PC by replacing the CPU chip. To add additional core features, you may need to replace the motherboard entirely. (1)
PCI slots:-
PCI (part of the PCI Local Bus standard and often shortened to PCI) is a computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer. These devices can take either the form of an integrated circuit fitted onto the motherboard itself, called a planar device in the PCI specification, or an expansion card that fits into a slot. PCI cards used in PCs include: network cards, sound cards, modems, extra ports such as USB or serial, TV tuner cards and disk controllers. Historically video cards were typically PCI devices, but growing bandwidth requirements soon outgrew the capabilities of PCI. PCI video cards remain available for supporting extra monitors and upgrading PCs that do not have any AGP or PCI Express slots.
BIOS chip:-
The BIOS of PC software is built into the PC, and is the first code run by a PC when powered on ('boot firmware'). The primary function of the BIOS is to load and start an operating system. When the PC starts up, the first job for the BIOS is to initialize and identify system devices such as the video display card, keyboard and mouse, hard disk, CD/DVD drive and other hardware. The BIOS then locates software held on a peripheral device (designated as a 'boot device'), such as a hard disk or a CD, and loads and executes that software, giving it control of the PC.This process is known as booting, or booting up.
SERIAL PORT:-
a serial port is a serial communication physical interface through which information transfers in or out one bit at a time (contrast parallel port).Throughout most of the history of personal computers, data transfer through serial ports connected the computer to devices such as terminals and various peripherals.
PARALLEL PORT:A parallel port is a type of interface found on computers (personal and otherwise) for connecting various peripherals. In computing, a parallel port is a parallel communication physical interface. It is also known as a printer port or Centronics port. The IEEE 1284 standard defines the bidirectional version of the port, which transmits data bits at the same time
(in "parallel"). This is the opposite of serial transmission where one bit is transmitted at a time.
USB PORT:-
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a specification to establish communication between devices and a host controller (usually personal computers), developed and invented by Ajay Bhatt while working for Intel.USB is intended to replace many varieties of serial and parallel ports. USB can connect computer peripherals such as mice, keyboards, digital cameras, printers, personal media players, flash drives, and external hard drives. For many of those devices, USB has become the standard connection method. USB was designed for personal computers, but it has become commonplace on other devices such as smart phones, PDAs and
video game consoles, and as a power cord between a device and an AC adapter plugged into a wall plug for charging. As of 2008, there are about 2 billion USB devices sold per year, and approximately 6 billion totals sold to date.
CPU socket or CPU slot:-
A CPU socket or CPU slot is an electrical component that attaches to a printed circuit board (PCB) and is designed to house a microprocessor. It is a special type of integrated circuit socket designed for very high pin counts. A CPU socket provides many functions, including providing a physical structure to support the CPU, providing support for a heat sink, facilitating replacement (as well as reducing cost) and most importantly forming an electrical interface both with the CPU and the PCB. CPU sockets can most often be found in most desktop and server computers (laptops typically use surface mount CPUs), particularly those based on the Intel x86 architecture on the motherboard.
ATX:ATX (Advanced Technology Extended) is a computer form factor specification developed by Intel in 1995 to improve on previous de-facto standards like the AT form factor. It was the first big change in computer case, motherboard, and power supply design in many years, improving standardization and interchangeability of parts. The specification defines
the key mechanical dimensions, mounting point, I/O panel, power and connector interfaces between a computer case, a motherboard, and a power supply. With the improvements it offered, including lower costs, ATX overtook AT completely as the default form factor for new systems within a few years.
ATX addressed many of the AT form factor's annoyances that had frustrated system builders. Other standards for smaller boards (including microATX, FlexATX and mini-ITX) usually keep the basic rear layout but reduce the size of the board and the number of expansion slot positions. In 2003, Intel announced the BTX standard, intended as a replacement for ATX. As of 2009, the ATX form factor remains a standard for do-ityourselfers; BTX has however made inroads into pre-made systems.
DIMM SOCKETS:-
DIMM sockets are where the computer's RAM, (or Random Access Memory), is installed. DIMM stands for Dual Inline Memory Module. The reason it is called "Dual" is because both sides of the memory module have completely separate connections from the other side of the module.
CHIPSET:-
The term chipset is commonly used to refer to a set of specialized chips on a computer's motherboard or an expansion card. In personal computers the first chipset for the IBM PC AT was the NEAT chipset by Chips and Technologies for the Intel 80286 CPU. A chipset is usually designed to work with a specific family of microprocessors. Because it controls communications between the processor and external devices, the chipset plays a crucial role in determining system performance.
ISA SLOT:-
Industry Standard Architecture (in practice almost always shortened to ISA) was a computer bus standard for IBM compatible computers. It is designed to connect peripheral cards to the motherboard, ISA allows for bus mastering although only the first 16 MB of main memory are available for direct access. The 8-bit bus ran at 4.77 MHz (the clock speed of the IBM PC and IBM PC/XT's 8088 CPU), while the 16-bit bus operated at 6 or 8 MHz (because the 80286 CPUs in IBM PC/AT computers ran at 6 MHz in early models and 8 MHz in later models.) IBM RT/PC also used the 16-bit bus.
CPU:The simplest of terms, its your computers brain. The processor tells your computer what to do and when to do it, it decides which tasks are more important and prioritizes them to your computers needs.
There is and have been many processors on the market, running at many different speeds. The speed is measured in Megahertz or MHz A single MHz is a calculation of 1 million cycles per second (or computer instructions), so if you have a processor running at 2000 MHz, then your computer is running at 2000,000,000 cycles per second, which in more basic terms is the amount of instructions your computer can carry out. Another important abbreviation is Gigahertz or GHz. A single GHz or 1 GHz is the same as 1000 MHz. Sounds a bit confusing, so here is a simple conversion: 1000 MHz (Megahertz) = 1GHz (Gigahertz) = 1000,000,000 Cycles per second (or computer instructions). Now you can see why they abbreviate it, could you imagine going to a PC store and asking for a one thousand million cycle PC please. A bit of a mouth full isnt it?
So when buying a new computer always looks for fastest you can afford. The fastest on the market at the time of writing this article is 3.8 GHz (3800 MHz). Remember though that it is not necessary to purchase such a fast processor, balance your needs, do you really need top of the range? Especially when the difference says between a 3.5 GHz (3500 MHz) and a 3.8 GHz (3800 MHz) processor will be barely noticed (if noticed at all) by you, while the price difference is around 100. With the money you save you could get a nice printer and scanner package. Now that we have covered the speeds, there is one more important subject to cover. Which processor? There are 3 competitors at present, the AMD Athlon, Intel Pentium and the Intel Celeron. They come in many guises, but basically the more cores they have and the higher the speed means better and faster. Processors now come as dual core, triple core and quad core. These processors are the equivalent of running two CPUs (Dual core), three CPU's (Triple core) or four (Quad core).
In the past Intel Pentium the best and most expensive of them all, and remains today one of the most popular on the market. In laymans terms it is/was the designer processor, although AMD have some superb if not better releases and equally highly priced and advanced products. It would be hard to say which is best as they are direct competitors. Lastly there is the Intel Celeron; this processor is a budget version of the Intel Pentium 4, the processor you find in most budget computers. If the purse is tight, and you need a computer, then this is your port of call. You will find many sub 400 computers fitted with this processor.
RAM:Random Access Memory (RAM) provides space for your computer to read and write data to be accessed by the CPU (central processing unit). When people refer to a computer's memory, they usually mean its If you add more RAM to your computer, you reduce the number of times your CPU must read data from your hard disk. This usually allows your computer to work considerably faster, as RAM is many times faster than a hard disk. RAM is volatile, so data stored in RAM stays there only as long as your computer is running. As soon as you turn the computer off, the data stored in RAM disappears. When you turn your computer on again, your computer's boot firmware (called BIOS on a PC) uses instructions stored semi-permanently in ROM chips to read your operating system and related files from the disk and load them back into RAM.
SDR, DDR, DDR2, and DDR3 RAM
Several types of RAM are used in modern computers. Before 2002, most computers used single data rate (SDR) RAM. Most computers made since then use either double data rate (DDR),
DDR2, or DDR3 RAM. DDR2 is able to achieve faster transfer rates to prevent limitation of your CPU's performance, and DDR3 technology takes these advancements even further.
Note that these RAM technologies are not interchangeable. One type of RAM will not function if installed with another type, and physical differences in the RAM modules prevent them from even being inserted in the same computer.
HARD DISK DRIVE (HDD):A hard disk drive (hard disk, hard drive, HDD) is a non-volatile storage device for digital data. It features one or more rotating rigid platters on a motor-driven spindle within a metal case. Data is encoded magnetically by read/write heads that float on a cushion of air above the platters, with modern storage capacity measured in gigabytes and terabytes. Hard disk manufacturers quote disk capacity in SI-standard powers of 1000, wherein a terabyte is 1000 gigabytes and a gigabyte is 1000 megabytes. With file systems that measure capacity in powers of 1024, available space appears somewhat less than advertised capacity. The first HDD was invented by IBM in 1956. They have fallen in size and cost over the years, displacing floppy disks in the late 1980s as the preferred long-term storage mechanism for personal computers. Most desktop systems today have standardized on the 3.5" form factor, and though mobile systems most often use 2.5" drives, both sizes operate on similar high-speed serial interfaces.
Raw unformatted capacity of a hard disk drive is usually quoted with SI prefixes (metric system prefixes), incrementing by powers of 1000; today that usually means gigabytes (GB) and terabytes (TB). This is conventional for data speeds and memory sizes which are not inherently manufactured in power of two sizes, as RAM and Flash memory are. Hard disks by contrast have no inherent binary size as capacity is determined by number of heads, tracks and sectors. This can cause some confusion because some operating systems may report the formatted capacity of a hard drive using binary prefix units which increment by powers of 1024. A one terabyte (1 TB) disk drive would be expected to hold around 1 trillion bytes (1,000,000,000,000) or 1000 GB; and indeed most 1 TB hard drives will contain slightly more than this number. However some operating system utilities would report this as around 931 GB or 953,674 MB. (The actual number for a formatted capacity will be somewhat smaller still, depending on the file system). Following are the several ways of reporting
SI prefixes (hard drive) 1 TB (Terabyte) 1000 GB (Gigabyte)
equivalent 1 * 10004 B 1000 * 10003 B
Binary prefixes (OS)
equivalent
0.9095 TB (Terabyte) 0.9095 * 10244 B 931.3 GB (Gigabyte) 931.3 * 10243 B 953,674.3 MB 953,674.3 * 10242 1,000,000 MB (Megabyte) 1,000,000 * 10002 B (Megabyte) B 1,000,000,000 KB 1,000,000,000 * 1000 976,562,500 KB 976,562,500 * 1024 (Kilobyte) B (Kilobyte) B 1,000,000,000,000 B (byte)
CD-ROM:CD-ROM (an acronym of "compact disc read-only memory") is a pre-pressed compact disc that contains data accessible to, but not writable by, a computer for data storage and music playback, the 1985 Yellow Book standard developed by Sony and Philips adapted the format to hold any form of binary data. CD-ROMs are popularly used to distribute computer software, including games and multimedia applications, though any data can be stored (up to the capacity limit of a disc). Some CDs hold both computer data and audio with the latter capable of being played on a CD player, while data (such as software or digital video) is only usable on a computer (such as ISO 9660 format PC CD-ROMs). These are called enhanced CDs . Although many people use lowercase letters in this acronym, proper presentation is in all capital letters with a hyphen between CD and ROM. It was also suggested by some, especially soon after the technology was first released, that CD-ROM was an acronym for "Compact Disc read-only-media", or that it was a more "correct" definition. This was not the intention of the original team who developed the CD-ROM, and common acceptance of the "memory" definition is now almost universal. This is probably in no small part due to the widespread use of other "ROM" acronyms such as Flash-ROMs and EEPROMs where "memory" is usually the correr
At the time of the technology's introduction it had more capacity than computer hard drives common at the time. The reverse is now true, with hard drives far exceeding CDs, DVDs and Blue-ray, though some experimental descendants of it such as HVDs may have more space and faster data rates than today's biggest hard drive
CD-ROM drives
CD-ROM discs are read using CD-ROM drives. A CD-ROM drive may be connected to the computer via an IDE (ATA), SCSI, S-ATA, Firewire, or USB interface or a proprietary interface, such as the Panasonic CD interface. Virtually all modern CD-ROM drives can also play audio CDs as well as Video CDs and other data standards when used in conjunction with the right software. CD-ROM drive can sometimes be a misnomer for newer drives that are capable for reading and burning DVDs, the CD's successor which is now the standard optical disc drive.
**************** END****************
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Components of A MotherboardDocumento14 pagineComponents of A MotherboardvcinfotechNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer System, HardwareDocumento201 pagineComputer System, Hardwareapi-3833170Nessuna valutazione finora
- MotherboardDocumento27 pagineMotherboardமகான் சிறோன்Nessuna valutazione finora
- Identifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionDocumento14 pagineIdentifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionBrenda Macanlalay Asuncion80% (5)
- Familiarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and PeripheralsDocumento98 pagineFamiliarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and Peripheralsjuliet brusola100% (1)
- Motherboard Components... CSEDocumento28 pagineMotherboard Components... CSEAtulay Mahajan100% (1)
- BIOS or Basic Input Output SystemDocumento13 pagineBIOS or Basic Input Output SystemSaymon Casilang SarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- Motherboard PresentationDocumento20 pagineMotherboard PresentationAMIT SINGH100% (1)
- Hardware BibleDocumento123 pagineHardware BibleMitko JosifoskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Otherhardware Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3Documento54 pagineOtherhardware Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3somerandomhedgehog100% (1)
- CHN EXPDocumento32 pagineCHN EXPAnanduNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Systems Servicing NC Ii: Core Competency # 1Documento54 pagineComputer Systems Servicing NC Ii: Core Competency # 1Jeremi CorpinNessuna valutazione finora
- PlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6Da EverandPlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A Motherboard ?Documento13 pagineWhat Is A Motherboard ?Ian OffemariaNessuna valutazione finora
- IL NT MRS 1.5 Reference Guide 2Documento105 pagineIL NT MRS 1.5 Reference Guide 2JuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Motherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryDocumento8 pagineMotherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryJhay Consolacion WalkerNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.0 Motherboard DEFINITION: Is The Central Printed Circuit Board (PCB) in SomeDocumento20 pagine1.0 Motherboard DEFINITION: Is The Central Printed Circuit Board (PCB) in Somekadilobari100% (3)
- Assignment CS by ABRARDocumento9 pagineAssignment CS by ABRARThe King studioNessuna valutazione finora
- Class NotesDocumento12 pagineClass NotesHeart WeyganNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary Report in TRDocumento9 pagineSummary Report in TREllie KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer MotherboardDocumento15 pagineComputer MotherboardElsabet KindeNessuna valutazione finora
- Motherboard and Its Component (11813705)Documento10 pagineMotherboard and Its Component (11813705)DeePäk YädävNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 - Reading3 - MotherboardDocumento8 pagineModule 2 - Reading3 - MotherboardChristopher AdvinculaNessuna valutazione finora
- CPH Microproject PDFDocumento12 pagineCPH Microproject PDFRohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Motherboard: Board or Logic BoardDocumento9 pagineMotherboard: Board or Logic BoardappatujuNessuna valutazione finora
- Motherboard - Wikipedia PDFDocumento41 pagineMotherboard - Wikipedia PDFDance plus 3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Parts of MotherboardDocumento86 pagineParts of MotherboardKurt BalaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Motherboard Study NotesDocumento2 pagineMotherboard Study NotesaniketiluNessuna valutazione finora
- Motherboard: Personal Computers Printed Circuit Board Computers Apple Logic BoardDocumento7 pagineMotherboard: Personal Computers Printed Circuit Board Computers Apple Logic BoardMustafa MuhammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Amarpreet Singh Bhawanpreet Singh Kulwinder Singh Manjeet SinghDocumento10 pagineAmarpreet Singh Bhawanpreet Singh Kulwinder Singh Manjeet Singhmanjeetsinghnavab100% (1)
- Motherboard: The CPUDocumento10 pagineMotherboard: The CPU000pssNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-II: Accessory BoardDocumento39 pagineUnit-II: Accessory BoardNavi KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 02 - Main Parts of ComputerDocumento22 pagineLesson 02 - Main Parts of ComputerDummy AccountNessuna valutazione finora
- The Parts of A Computer MotherboardDocumento5 pagineThe Parts of A Computer MotherboardSlashDhan143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Parts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10Documento4 pagineParts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10DeathNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Notes of Second Yr 2022Documento269 pagineFinal Notes of Second Yr 2022RAM KrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- MOTHERBOARDDocumento70 pagineMOTHERBOARDCha DechavezNessuna valutazione finora
- Parts of MotherboardDocumento63 pagineParts of MotherboardMarivic Omosura ItongNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.assemble Computer HardwareDocumento18 pagine1.assemble Computer HardwareallyzamoiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Hardware&Networking Manual 231124 165519Documento46 pagineHardware&Networking Manual 231124 165519crecbhoomi21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Motherboard and Computer PeripheralsDocumento51 pagineBasics of Motherboard and Computer PeripheralsPratik JadhavNessuna valutazione finora
- To Make Comparative Study On MotherboardsDocumento13 pagineTo Make Comparative Study On MotherboardsPankaj GillNessuna valutazione finora
- MotherboardDocumento15 pagineMotherboardFredrick MugoNessuna valutazione finora
- ChipsetDocumento10 pagineChipsetCesar Rodriguez Espinoza0% (1)
- Familiarization of Computer) Fcpit Prac No. 1 PDFDocumento32 pagineFamiliarization of Computer) Fcpit Prac No. 1 PDFSantpreet Singh Kalra83% (6)
- Components of HardwareDocumento9 pagineComponents of HardwareNUTS GAMINGNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1-Mastering Lan and Trouble ShootingDocumento17 pagineUnit 1-Mastering Lan and Trouble Shootingbala smileyNessuna valutazione finora
- Comfiguração Da BIOS-SETUPDocumento44 pagineComfiguração Da BIOS-SETUPEliasNessuna valutazione finora
- Motherboard - Wikipedia PDFDocumento46 pagineMotherboard - Wikipedia PDFLorien Lolong LamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mother BoardDocumento29 pagineMother BoardSwayamprakash PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Report About Motherboard and CpuDocumento15 pagineReport About Motherboard and CpuLournie ErodistanNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of ComputerDocumento33 pagineAnatomy of ComputerPrateek GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Repair and Maintenance PC System ComponentsDocumento14 pagineRepair and Maintenance PC System ComponentsMuvubuka KatimaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Hardware Servicing Safety and PrecautionsDocumento70 pagineComputer Hardware Servicing Safety and PrecautionsMary MillareNessuna valutazione finora
- History of MotherboardDocumento2 pagineHistory of MotherboardPro KodigoNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Computer Hardware and TroubleshootingDocumento39 pagineBasic Computer Hardware and TroubleshootingR. BorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Motherboard Major Parts and FunctionDocumento3 pagineMotherboard Major Parts and FunctionVic Picar0% (1)
- Computer Hardware: Intel AMD Dual CoreDocumento6 pagineComputer Hardware: Intel AMD Dual CoreanishklNessuna valutazione finora
- TESDA Assestment Review (Motherboard) 2015Documento77 pagineTESDA Assestment Review (Motherboard) 2015Sharalyn P. SiaNessuna valutazione finora
- A+ Computing ConceptsDocumento8 pagineA+ Computing ConceptsMafiozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Prashanti Institute of Technology & ScienceDocumento18 paginePrashanti Institute of Technology & Sciencezalanipulkit0% (1)
- Motherboard EnglishDocumento9 pagineMotherboard EnglishallamNessuna valutazione finora
- DELL PowerEdge T610Documento206 pagineDELL PowerEdge T610salam78auNessuna valutazione finora
- MB Manual Z390-Gaming-X 1001 e PDFDocumento48 pagineMB Manual Z390-Gaming-X 1001 e PDFJoakoPrudenzaNessuna valutazione finora
- 775i65GV multiQIGDocumento84 pagine775i65GV multiQIGMaria Gabriela Herrera CuaurmaNessuna valutazione finora
- List Detailed Step by Step Procedure in Assembling A System UnitDocumento11 pagineList Detailed Step by Step Procedure in Assembling A System UnitlailaNessuna valutazione finora
- Crown Notes 2017Documento28 pagineCrown Notes 2017Adil MushtaqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Hi-Fi A85S3/Hi-Fi A75S3/Hi-Fi A55S3 Setup Manua: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDocumento55 pagineHi-Fi A85S3/Hi-Fi A75S3/Hi-Fi A55S3 Setup Manua: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineRachmad PascalNessuna valutazione finora
- Manuale Scheda Madre MSIDocumento99 pagineManuale Scheda Madre MSIMauro NdunditeNessuna valutazione finora
- Marshaling Cabinet Purpose PDFDocumento5 pagineMarshaling Cabinet Purpose PDFMohammed MustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- M7C09v1 0Documento149 pagineM7C09v1 0dikuanNessuna valutazione finora
- B550 Pro4Documento91 pagineB550 Pro4이호원Nessuna valutazione finora
- Part NamegDocumento3 paginePart Namegapi-256724840100% (1)
- The Motherboard Reference TermsDocumento6 pagineThe Motherboard Reference TermsMax PowerNessuna valutazione finora
- It Workshop Lab ManualDocumento85 pagineIt Workshop Lab Manualbalajiyadav0456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ig31g-M7s 081022Documento47 pagineIg31g-M7s 081022PeTru MocanNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.3.2.7 Lab - Exploring Router Physical CharacteristicsDocumento14 pagine6.3.2.7 Lab - Exploring Router Physical CharacteristicsParthPatel100% (5)
- Sierra Wireless FX30S: User GuideDocumento74 pagineSierra Wireless FX30S: User Guidehamdi galipNessuna valutazione finora
- H61M VG3Documento69 pagineH61M VG3Adina BubulinaNessuna valutazione finora
- XPDADocumento2 pagineXPDAFuad Khairul MuttaqinNessuna valutazione finora
- BIT 2102 Computer Systems and OrganizationDocumento21 pagineBIT 2102 Computer Systems and Organizationwillyman3009Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Micro-Project Report On ": MotherbordDocumento29 pagineA Micro-Project Report On ": MotherbordPratik GadilkarNessuna valutazione finora
- K8Upgrade-VM800: User ManualDocumento38 pagineK8Upgrade-VM800: User ManualSyed Irfan BashaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ga-970a-D3 V.1.2.e User ManualDocumento96 pagineGa-970a-D3 V.1.2.e User Manualzxcv1ingrNessuna valutazione finora
- BCM 6345Documento3 pagineBCM 6345Hoang LeNessuna valutazione finora
- Motherboard Manual Ga-8i945gmf-Rh e Socket 775 PDFDocumento80 pagineMotherboard Manual Ga-8i945gmf-Rh e Socket 775 PDFjavi.martinNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Comptia A Guide To It Technical Support 10th Edition Jean Andrews Joy Dark Jill West 2Documento14 pagineTest Bank For Comptia A Guide To It Technical Support 10th Edition Jean Andrews Joy Dark Jill West 2Guadalupe Price100% (35)
- Motherboard HandoutDocumento5 pagineMotherboard HandoutJudea SantiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- PC Maintenance Lab ReportDocumento21 paginePC Maintenance Lab ReportSoma SahaNessuna valutazione finora