Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Muscles of Facial Expression: Muscle List by Region
Caricato da
Sara ScatesDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Muscles of Facial Expression: Muscle List by Region
Caricato da
Sara ScatesCopyright:
Formati disponibili
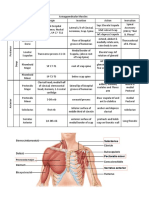
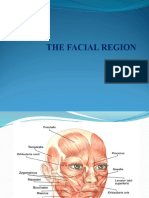
Muscle List by region
Muscles of facial expression
Occiptofrontalis Frontal belly FrontalisElevates Eyebrows in glancing upward and expressions of surprise or fright, draws scalp forward wrinkles skin of forehead. O: Galea aponeurotica. I: Supcutaneous tissue of eyebrows. N: Facial Retracts scalp; fixes galea aponeurotica so frontalis can act on eyebrows. O: superior nuchal line and temporal bone, I: galea aponeurotica. Orbicularis oris- encircles mouth, closes lips, protrudes lips as in kissing. O: Modiolus of mouth, I: submucosa and dermis of lips, N: Facial Levator labii superioris- Elevates and everts upper lip in sad, sneering, or serious expressions. O: Zygomatic bone and maxilla near inferior margin of orbit, I: Muscles of upper lip. Depressor labii inferioris- draws lower lip downward and laterally in chewing and expressions of doubt. O: Mandible near mental protuberance, I: Skin and mucosa of lower lip. Buccinator- compresses cheek against teeth and gums; directs food between molars, expels air and liquid. O: alveolar processes on lateral surfaces of maxialla and mandible, I: orbicularis oris; submucosa of cheek and lips. Mentalis- Elevates and protrudes lower lip in drinking, pouting, and expressions of doubt, elevates and wrinkles skin of chin. O: mandible near inferior incisors, I: skin of chin at mental protuberance. Nasalis-widens nostrils; narrows internal air passage between vestibule and nasal cavity. O: maxilla just lateral to nose, I: bridge and alar cartilage of nose. Platysma- draws lower lip angel of the mouth downward in expressions of horror or surprise; may aid in opening mouth widely. O: Fascia of deltoid and pectoralis major, I: Mandible, skin and subcutaneous tissue of lower face. Orbicularis oculi- sphicter of the eyelids; closes eye in blinking, squinting; and sleep; aids in flow of tears across eye. O: Lacrimal bone, adjacent regions of frontal bone and maxilla, medial angle of eyelids, I: upper and lower eyelids, skin around margin of orbit. Zygomaticus major- Draws angle of the mouth upward and laterally in laughing. O: Zygomatic bone, I: superolateral angle of mouth. Zygomaticus minor- Elevates upper lip, exposes upper teeth in smiling or sneering. O: Zygomatic bone, I: Muscles of upper lip.
Risorius-Draws angle of the mouth
laterally in expressions of laughing, horror, or disdain. O: Zygomatic arch, fascia near ear. I: Modiolus of mouth.
Muscles that move the mandible
Masseter- Elevation of the mandible,
with smaller roles in protraction, retraction, and lateral and medial excursion. O: Zygomatic arch, I: Lateral surface of mandibular ramus and angle, N: Mandibular. Temporalis- Elevation, retraction, and lateral and medial excursion of the mandible. O: Temporal line and temporal fossa of cranium, I: Coronoid process and anterior border of mandibular ramus, N: Mandibular
Occipital belly Occipitalis-
Muscles of the neck
Suprahyoid muscles- composed of
four pairs superior to hyoid- digastric, geniohyoid,mylohyoid, stylohyoid. Digastric- depresses mandible when hyoid is fixed; opens mouth widely, as when ingesting foud or yawning; elevates hyoid when mandible is fixed. O: Mastoid notch of temporal bone, digstric fossa of mandible, I: Hyoid bone via fascial sling, N: Posterior belly: fascial n. Anteror belly: mylohyoid n. Infrahyoid muscles- inferior to the hyoid bone, enable the suprahyoid muscles to open the mouth. Depresses hyoid. Omohyoid, Sternohyoid, Thyrohyoid, Sternothyroid. I: Hyoid bone. Pharyngeal constrictors- (Three Muscles) During swallowing, contract in order from superior to middle to inferior constrictor to drive food into esophagus. O: Medial pterygoid plate, mandible,hyoid, stylohyoid ligament, cricoid and thyroid cartilages of larynx, I: Median pterygoid raphe (seam on posterior side of pharynx) basilar part of occipital bone, N: Glossopharyngeal vagus nn.
Muscles that move the head
Sternocleidomastoid- unilateral action
tilts head slightly upward and toward the opposite side, as looking over ones contralateral shoulder. The most common action is probably rotating the head to the left or right. Bilateral action draws the head straight forward and down, as when eating or reading. Aids in deep breathing. O: Manubrium of sternum, medial one third of clavicle, I: Mastoid process and lateral half of superior nuchal line. N: Accessory n., spinal nerves C2-C3. Scalenes- Unilateral contraction causes ipsilateral flexion or contralateral rotation (tilts head toward the same shoulder, or rotates face away), depending on the action of other muscles. Bilateral contraction flexes neck. If spine is fixed,
scalenes elevate ribs 1-2 and aid and breathing. O: Transverse process of all cervical vertebrae (C1- C7), I: Ribs 1-2, N: Anterior rami of C3-C8. Splenius capitis- acting unilaterally, produces ipsilateral flexion and slight rotation of the head, extend head when acting bilaterally. O: inferior half on nuchal ligament, spinous processes of vertebrae C7-T6, I: Mastoid process and occipital bone just inferior to superior nuchal line; vervical vertebrae C1-C2 or C3, N: Posterior rami of middle cervical nn. Semispinalis capitis- extend and contralaterally rotate head. O: articular processes of vertebrae C4-C7, trasverse processes of T1-T6, I: Occipital bone between nuchal lines, spinous processes of vertebrae C2-C5, N: Posterior rami of cervical and thoracic nn.
the ribs and expanding the thoracic cavity; in expiration, the interosseus part depresses and retracts the ribs, compressing the thoracic cavity and expelling air; the latter occurs only in forceful expiration not in relaxed breathing. O: Superior margins and costal cartilages of ribs 2-12; margin of sternum, I: inferior margin of next higher rib, N: Intercostal nn. External intercostals- When scalenes fix rib 1, external intercostals elevate and protract ribs 2-12, expanding the thoracic cavity and creating a partial vacuum causing inflow of air; exercise a braking action during expiration so that expiration is not overly abrupt. O: Inferior margins of ribs 1-11, I: superior margin of next lower rib, N:Intercostal nn.
Muscles of the abdominal wall
Rectus abdominis- Flexes lumbar
Muscles that move the pectoral girdle
Pectoralis minor- with serratus
anterior, draws scapula laterally and forward around chest wall; with other muscles, rotates scapula and depresses apex of shoulder. O: Ribs 3-5 and overlying fascia, I: Coracoid process of scapula, N:Medial and lateral pectoral nn. Serratus anterior- with pectoralis minor, draws scapula laterally and forward around chest wall; protracts scapula, and is the prime mover in all forward reaching and pushing actions; aids in rotating scapula to elevate apex of shoulder; fixes scapula during abduction of arm. O: All of ribs, I: Medial border of scapula, N: Long thoracic n. Trapezius- Stabilizes scapula and shoulder during arm movements; elevates and depresses apex of shoulder; acts with other muscles to rotate and retract scapula. O: external occipital protuberance, medial one third of superior nuchal line, nuchl ligament, spinous process of vertebrae C7-T3 or T4, I: Acromion and spine of scapula, lateral one-third of clavicle, N: Accesory n. , anterior rami of C3-C4. Rhomboid major-Retracts scapula and braces shoulder; fixes scapula during arm movements. O: spinous processes of vertebrae T2-T5, I: Medial border of scapula, N: Dorsal scapular n. Rhomboid minor- same as rhomboideus major. O: spinous processes of vertebrae C7-T1, nuchal ligament, I: Medial border of scapula, N: same^ Levator scapulae- elevates the scapula if cervical vertebrae are fixed; flexes neck laterally if scapula is fixed; retracts scapula and braces shoulder; rotates scapula and depresses apex of shoulder. O: Transverse processes of vertebrae C1-C4, I: Superior anfle to medial border of scapula, N: C3-c4, and C5 via dorsal scapular n.
region of vertebral column, producing forward bending at the waist. O: Pubic symphysis and superior margin of pubis. I: Xiphoid process, costal cartilages 5-7, N: Anterior rami of spinal nerves T6-T12 External oblique- supports abdominal viscera against pull of gravity, stabilizes vertebral column during heavy lifting; maintains posture; compresses abdominal organs, thus aiding in expiration of contents during childbirth, urination, defecation, and vomiting; unilateral contraction causes contralateral rotation of waist.O: ribs 5-12, I: Anterior half of iliac crest, pubic symphysis, and superior margin of pubis, N: anterior rami of spinal nerves T7-T12 Internal oblique- same as external oblique except that unilateral contraction causes ipsilateral rotation of waist. O: Inguinal ligament, iliac crest, thoracolumbar fascia, costal cartilages 712, I: Ribs 10-12, costal cartilages 7-10, pubis, N:anterior rami of spinal nerves T7L1. Transversus abdominis- compresses abdominal contents, with same effects as external oblique, but does not contribute to movements of vertebral column. O: inguinal ligament, iliac crest, thoracolumbar fascia, costal cartilages 712, I: Linea alba, pubis, aponeurosis of internal oblique, N: ^
Muscles used in breathing
Diaphragm- prime mover of inspiration;
contracts in preparation for sneezing, coughing, crying, laughing, and weight lifting; contraction compresses abdominal viscera and aids in childbirth and expulsion of urine and feces. O: Xiphoid process of sternum, ribs and costal cartilages 7-12; lumbar vertebrae. I: central tendon of diaphragm, N: Phrenic nn. Internal intercostals- In inspiration, the intercarilaginous part aids in elevating
Muscles that move the humerus
Pectoralis major- Flexes, adducts, and
medially rotates humerus, as in climbing or hugging. Aids in deep inspiration. O: Medial half of clavicle, costal cartilages 1-7, aponeurosis of external oblique, I: Lateral lip of intertubercular sulcus of humerus, N: Medial and lateral pectoral nn. Latissimus dorsi- adducts and medially rotates humerus, extends the shoulder joint as in pulling on oars in a boat; produces backward swing of rm in actions such as walking or bowling; with hands grasping overhead objects, pulls body forward and upward, as in climbing; aids in deep inspiration, sudden expiration such as sneezing or coughing, and rolonged forceful expiration as in singing or blowing. O: vertebrae T7-L5, lower 3 or 4 ribs, iliac crest, thoracolumbar fascia, I: floor of intertubercular sulcus of humerus, N: Thoracodorsal n. Deltoid- Anterior fiers flex and medially rotate arm ; lateral fibers abduct arm; posterior fibers extend and laterally rotte arm; involved in arm swinging during actions as walking or bowling, and in adjustment of hand height for carious manual tasks. O: Acomion and spine of scapula; clavicle, I: Deltoid tuberosity of humerus, N: Lower suprascapular n. Supraspinatus- Aids deltoid in abduction of arm; resists downward slippage of humeral head when arm is relaxed or when carrying wight. O: supraspinous fossa of scapula, I: greater tubercle of humerus, N: suprascapular n. Infraspinatus- modulates action of deltoid, preventing humeral head from sliding upward; rotates himerus laterally. O:infraspinous fossa of scapula, I: greater tubercle of humerus, N: suprascapular Teres major-extends and medially rotates humerus; contributes to arm swinging. O: inferior angle of scapula, I:medial aspect of humeral shaft, N: musculocutaneous n. Teres minor- modulates action of deltoid, preventing humeral head from sliding upward as arm is abducted; rotates humerus laterally. O: Lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of scapula, I: Greater tubercle of humerus; posterior surface of joint capsule, N: Axillary n. Subscapularis- modulates action of deltoid, preventing humeral head from sliding upward as arm is abducted; rotates humerus medially. O:subscapular fossa of scaula, I: Lessertubercle of humerus, anterior surface of joint capsule, N: upper and lower subscapular. Coracobrachialis- flexes and medially rotates arm, resists deviation of arm from frontal plane during abduction. O: coracoid process, I: Medial aspect of humeral shaft, N: Musculocutaneous n.
Biceps brachii- rapid or forceful
supination of forearm; synergist in elbow flexion; slight shoulder flexion; tendon of long head stabilizes shoulder by holding humeral head against glenoid cavity. O:long head: superior margin of glenoid cavity, short head: coracoid process, I: Tuberosity of radius, fascia of forearm, N: musculocutaneous. Brachialis- prime mover of elbow flexion. O: anterior surface of distal half of humerus, I:coronoid process and tuberosity of ulna, N: Musculocutaneous n. radial n. Brachioradialis-flexes elbow. O: latera supracondylar ridge of humerus, I:lateral surface of radius near styloid process, N: radial n. Triceps brachii- Extends elbow; long head extends and adducts humerus. O: Long head: inferior margin of glenoid cavity and joint capsule, Lateral Head: posterior surface of proximal end of humerus, Medial head:posterior surface of entire humeral shaft, I: Olecranon, fascia of forearm, N: Radial n. Anconeus- Extends elbow; may help to control ulnar movement during pronation, O: Lateral epicondyle of humerusm I:Olecranon and posterior surface of ulna, N: radial. Pronator quadratus- prime mover of forearm pronation, also resists separation of radius and ulna when force is applied to the forearm through wrist, as in doing push ups. O:Anterior surface of distal ulna, I: Anterior surface of distal radius, N: Median n. Pronator teres-Assists pronator quadratus in pronation, but only in rapid or forceful action; weakly flexes elbow. O:Humeral shaft near medial epicondyle, coronoid process of ulna, I:Lateral surface of radial shaft, N: Median n. Supinator- supintes forearm. O: Lateral epicondyle of humerus; supinator crest and fossa of ulna just distal to radial notch; anular and radial collateral ligaments of elbow, I: proximal one-third of radius, N: Posterior interosseus.
Muscles that move the femur
IliopsoasPsoas major- Flexes thigh at hip
Muscles that move the forearm
when trunk is fixed; flexes trunk at hip when thigh is fixed, as in bending forward in a chair or sitting up in bed; balances trunk during sitting. O: iliac crest and fossa, superolateral region of sacrum, anterior sacroiliac and iliolumbar ligaments, I: lesser trochanter and nearby shaft of femur, N: Femoral n. Iliacus- Same as Psoas major. O: Bodies and intervertebral discs of vertebrae T12-L5, transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae, I: same as psoas, N: anterior rami of lumbar spinal nn. Gluteus maximus- extends thigh at hip as in stair climbing or running nd walking
(backswing of limb); abducts thigh; elevates trunk after stooping; prevents trunk from pitching forward during walking and running; helps stabilize femur on tibia. O: Posterior gluteal line of ilium, on posterior surface from iliac crest to posterior superior spine; coccyx; posterior surface of lowr sacrum; aponeurosis of erector spinae, I: Gluteal tuberosity of femor; lateral condyle of tibia via iliotibial band, N: inferior gluteal n. Gluteus medius- abduct and medially rotate thigh; during walking, shift weight of trunk toward limb with foot on the ground as other foot is lifted. O: Most of lateral surface of ilium between crest and acetabulum, I: greater trochanter of femur, N: superior gluteal n. Gluteus minimus- SAB Tensor fasciae latae- extends knee, laterally rotates tibia, aids in abduction and medial rotation of femur, during standing, steadies pelvis on femoral head and steadies femoral condyles on tibia. O: iliac crest anterior superior spine, deep surface of fascia lata. I: Lateral condyle of tibia via iliotibial band, N: Superior gluteal n. Adductor longus- adducts and medially rotates thight; flexes thigh at hip. O: body and inferior ramus of pubis, I: linea aspera of femur, N: obturator. Adductor magnus- adducts and medially rotates thigh; extends thigh at hip. O: inferior ramus of pubis; ramus and tuberosity of ischium, I: linea aspera, gluteal tuberosity, and medial supracondylar line of femur, N: obturator, tibial n. Pectineus- flexes and adducts thigh. O: superior ramus of pubis, I: spiral line of femur, N: femoral.
knew movements. O: Femur at greater trochanter and intertrochanteric line, gluteal tuberosity, linea aspera, I: Same as rectus femoris, N: Same. Vastus intermedius- extends knee, O: Anterior and lateral surfaces of femoral shaft, I: same, N: same. Vastus medialis- Same as vastus lateralis, I: same, N: same Sartorius- aids in knee and hip flexion, as in sitting or climbing; abducts and laterally rotates thigh, O: On and near anterior superior spine of ilum, I: medial surface of proximal end of tibia, N: femoral.
Hamstrings Biceps femoris- flexes knee;
extends hip; elevates trunk from stooping posture; laterally rotates tibia on femur when knee is flexed; laterally rotates femur when hip is extended; counteracts forward bending at hips. O: Long head: ischial tuberosity, Short head: linea aspera and lateral supracondylar line of femur, I: Head of fibula, N: tibial n., common fibular n. Semitendinosus- flexes knee, medially rotates tibia on femur when knee is flexed; medially rotates femur when hip is extended; counteracts forward bending at hips. O: ischial tuberosity , I: Medial surface of upper tibia, N: tibial n. Semimembranosus- same as semitendinosus. O: ischial tuberosity, I: Medial condyle and nearby margin of tibia; intercondylar line and lateral condyle of femur; ligament of politeal region, N: tibial
Muscles that move the foot and toes
Tibialis anterior- dorsiflexes and inverts
the foot; resists backward tipping of body (as when standing on a moving boat deck) helps support medial longitudinal arch of foot. O: Latera l condyle and lateral margin of proximal half of tibia; interosseous membrane, I: Medial cuneiform, metatarsal I, N:Deep Fibular (peroneal) Gastrocnemius- Plantar flexes foot, flexes knee; active in walking, running, jumping. O: Condyles and popliteal surface of femur, lateral supracondylar line, capsule of knee joint, I: calcaneus, N:Tibial. Soleus- Plantar flexes foot; steadies leg on ankle during standing. O: Posterior surface of head and proximal one-fourth of fibula; middle one-third of tibia; interosseous membrane, I: calcaneus, N: Tibial
Muscles that move the femur, tibia, and fibula
Gracilis-flexes and medially rotates tibia
at the knee. O: body and inferior ramus of pubis; ramus of ischium.
Quadriceps femoris Rectus femoris- extends knee;
flexes thigh at hip; flexes trunk on hip if thigh is fixed. O: ilium at anterior inferior spine and superior margin of acetabulum; capsule of hip joint. I: Patella, tibial tuberosity, lateral and medial condyles of tibia, N: femoral . Vastus lateralis- extends knee; retains patella in groove on femur during
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Upper Limb MusclesDocumento6 pagineUpper Limb MusclesMarina CasavecchiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles OinaDocumento3 pagineMuscles Oinageldevera100% (2)
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy Review NotesDocumento9 pagineMusculoskeletal Anatomy Review Notessimone dumbrell100% (1)
- Muscles To RememberDocumento3 pagineMuscles To RememberKayla CunananNessuna valutazione finora
- AP MusclesDocumento14 pagineAP MusclesAlexandra NadinneNessuna valutazione finora
- The Influence of Bones and Muscles on FormDa EverandThe Influence of Bones and Muscles on FormValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Liceo de Cagayan University: WorksheetDocumento7 pagineLiceo de Cagayan University: WorksheetLol lolNessuna valutazione finora
- Praktikum Anatomi 3 (Muscle of Head and NeckDocumento36 paginePraktikum Anatomi 3 (Muscle of Head and NeckPutriIffahNessuna valutazione finora
- Kines Anatomy Ch. 14-16Documento36 pagineKines Anatomy Ch. 14-16icedragon727Nessuna valutazione finora
- ZoologyMuscular SystemDocumento11 pagineZoologyMuscular SystemBeyNessuna valutazione finora
- CanineDocumento47 pagineCanine0682816890Nessuna valutazione finora
- Canine Oi AnDocumento47 pagineCanine Oi AnAcherl NagnamiLlNessuna valutazione finora
- Origin Insertion Action InnervationDocumento4 pagineOrigin Insertion Action Innervationstereomix987Nessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles of MasticationDocumento8 pagineMuscles of Masticationوليد خالدNessuna valutazione finora
- Cat MusclesDocumento5 pagineCat MusclesKim DeiparineNessuna valutazione finora
- Project 2Documento19 pagineProject 2Dequan FloydNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles of Facial ExpressionDocumento21 pagineMuscles of Facial Expressiondan_dezideriuNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles of The NeckDocumento2 pagineMuscles of The NeckAncuta VijanNessuna valutazione finora
- Upper Extremity Attachments and ActionsDocumento3 pagineUpper Extremity Attachments and Actionsjjjj31Nessuna valutazione finora
- Scalenes Palpating Scalenes Positioning: Client SupineDocumento4 pagineScalenes Palpating Scalenes Positioning: Client SupineSiti Rabiatul AdawiyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles of The Facial Expression, Face and NeckDocumento34 pagineMuscles of The Facial Expression, Face and NeckMorris KariukiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3 - AV - 2022Documento46 pagineLecture 3 - AV - 20222019190566Nessuna valutazione finora
- Openings in The Skull Bone of The Skull Structures TransmittedDocumento19 pagineOpenings in The Skull Bone of The Skull Structures TransmittedMacy Peralta100% (1)
- Plastic Surgery Board NotesDocumento69 paginePlastic Surgery Board Notesseandarcy600100% (1)
- Anatomy of Neck MusclesDocumento43 pagineAnatomy of Neck MusclesMahnoor malikNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Anatomy of The Shoulder Girdle OLUWADIYADocumento39 pagine2 Anatomy of The Shoulder Girdle OLUWADIYAADELAJA SAMUELNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of The ShoulderDocumento61 pagineAnatomy of The ShoulderChaman Lal KarotiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles of The Neck (Rerence PPT Only)Documento78 pagineMuscles of The Neck (Rerence PPT Only)francisalipio.medNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles of Facial ExpressionDocumento79 pagineMuscles of Facial ExpressionDr. Ektha PaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles of The Thorax That Assist in BreathingDocumento6 pagineMuscles of The Thorax That Assist in Breathinge jeighNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes For Muscles of The Head and NeckDocumento11 pagineLecture Notes For Muscles of The Head and NeckDrAhmed HamzaNessuna valutazione finora
- CatDocumento10 pagineCatKenneth SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles of The BackDocumento38 pagineMuscles of The BackPrashanth KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles of Upper Lims-Trunk - Ruan-2015Documento65 pagineMuscles of Upper Lims-Trunk - Ruan-2015Kw ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 14: Head, Face, Neck and Regional Lymphatics: Stucture & FunctionDocumento12 pagineChapter 14: Head, Face, Neck and Regional Lymphatics: Stucture & Functionelizabethen100% (1)
- Anat NotesDocumento94 pagineAnat NotesCarineHugz (CarineHugz)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles of Facial ExpressionDocumento63 pagineMuscles of Facial Expressionraphaelyohana140Nessuna valutazione finora
- MOINA Flashcards (Upper Limb)Documento63 pagineMOINA Flashcards (Upper Limb)jnthnrsj50% (2)
- 16 - Face (FF)Documento57 pagine16 - Face (FF)checkmateNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Exam 3 Study Guide UpdatedDocumento9 pagineAnatomy Exam 3 Study Guide Updatedvipul51190Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2b Facial Artery-Dr GosaiDocumento3 pagine2b Facial Artery-Dr GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Functions of Lateral V/s Medial Pterygoid Muscles: Branches of Facial NerveDocumento4 pagineFunctions of Lateral V/s Medial Pterygoid Muscles: Branches of Facial NerveMubashir SheriffNessuna valutazione finora
- Dental AnatomyDocumento73 pagineDental Anatomykajojo joyNessuna valutazione finora
- Part ADocumento14 paginePart AHammad -ullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Origins Insertions Muscle Jennyle1Documento6 pagineOrigins Insertions Muscle Jennyle1api-159564163Nessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles Reference GuideDocumento5 pagineMuscles Reference GuideVinceNessuna valutazione finora
- Temporomandibular JointDocumento3 pagineTemporomandibular JointFatima JamalNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomi 5 2.2 SaladinDocumento7 pagineAnatomi 5 2.2 SaladinwennyoktavNessuna valutazione finora
- Origin InsertionDocumento10 pagineOrigin InsertionPATRICE ANNE ALCOREZANessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of HipDocumento44 pagineAnatomy of Hipvijaykrishna59Nessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles of FaceDocumento51 pagineMuscles of FaceAyeth100% (1)
- CardiacMuscle&Head, Neck, and Trunk MusclesDocumento17 pagineCardiacMuscle&Head, Neck, and Trunk MusclesAshley ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- 4th Lecture HeadNeck and LympaticsDocumento77 pagine4th Lecture HeadNeck and LympaticsJeffrey Valdez Esteron100% (1)
- Dysphagia TreatmentDocumento122 pagineDysphagia TreatmentTiffani WallaceNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 MusclesDocumento43 pagine11 MusclesVasu Reddy ChallaNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 MusclesDocumento43 pagine11 MusclesFrank TuniNessuna valutazione finora
- The Face Gym: for a fresh and youthful lookDa EverandThe Face Gym: for a fresh and youthful lookValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Biomechanics: Finite Element Analysis of Tibia BoneDocumento6 pagineBiomechanics: Finite Element Analysis of Tibia BoneSathyamoorthi IlangovanNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Manual For Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual With Cat Dissections 7 e 7th EditionDocumento11 pagineSolution Manual For Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual With Cat Dissections 7 e 7th EditionJamesThomasngec100% (42)
- Introduction To Latin Language CourseDocumento6 pagineIntroduction To Latin Language CourseAlina AlinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Frequently Missed Fractures in Pediatric TraumaDocumento13 pagineFrequently Missed Fractures in Pediatric Traumaalejasuarez248Nessuna valutazione finora
- AANA Advanced Arthroscopy The Foot and Ankle PDFDocumento223 pagineAANA Advanced Arthroscopy The Foot and Ankle PDFsuny007_bond100% (2)
- Bernardo Fam To Be Continuednnn 2Documento43 pagineBernardo Fam To Be Continuednnn 2Luiezt BernardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Surgical RadiologyDocumento31 pagineSurgical RadiologyNeerupa KissoonNessuna valutazione finora
- 22-Surface Anatomy of The Upper and Lower LimbsDocumento24 pagine22-Surface Anatomy of The Upper and Lower LimbsMiahz Tv100% (1)
- Muscles of The Upper Limb Muscles of The Back Superficial Back Proximal Distal Action InnervationDocumento7 pagineMuscles of The Upper Limb Muscles of The Back Superficial Back Proximal Distal Action InnervationKris GulleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Blount Disease ImagingDocumento8 pagineBlount Disease ImagingGrace PombuNessuna valutazione finora
- V1 PLCDocumento18 pagineV1 PLCBartoszNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st GNM VivaDocumento144 pagine1st GNM VivaPatel MitanshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Tecnica Quirurgica PTG SygmaDocumento58 pagineTecnica Quirurgica PTG SygmaDS JeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Knee Replacement Prosthesis AssignmentDocumento33 pagineTotal Knee Replacement Prosthesis Assignmentdr neha gaggarNessuna valutazione finora
- KT TAPE English InstructionsDocumento24 pagineKT TAPE English InstructionsAlexandra ComanNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Test: Directions: One-BestDocumento8 pagineReview Test: Directions: One-BestFrederieNessuna valutazione finora
- Acupressure Points 1Documento10 pagineAcupressure Points 1Rajen MaharajNessuna valutazione finora
- Thoracic and Prothoracic Leg Neuromuscular System of The Praying Mantid, Sphodromantis Lineola (Burmeister)Documento14 pagineThoracic and Prothoracic Leg Neuromuscular System of The Praying Mantid, Sphodromantis Lineola (Burmeister)JoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lower Limb Mcqs MergedDocumento148 pagineLower Limb Mcqs MergedCaim ZNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Notes PhysiotherapyDocumento5 pagineAnatomy Notes PhysiotherapyMickey NgoNessuna valutazione finora
- Netter Anatomy Section 6-LOWER LIMBDocumento100 pagineNetter Anatomy Section 6-LOWER LIMBRickky MD100% (1)
- RADPOSDocumento59 pagineRADPOSLeahjen MaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ankle JointDocumento6 pagineAnkle JointIfeanyichukwu OgbonnayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Movement at The Ankle JointDocumento9 pagineMovement at The Ankle JointEsfahan BaclidNessuna valutazione finora
- GENESIS II Surgical Technique DCFDocumento46 pagineGENESIS II Surgical Technique DCFMazilo VictorNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal Sendi Dan Macam JointDocumento13 pagineJurnal Sendi Dan Macam JointN Nur AriniNessuna valutazione finora
- KN-5T TibiaDocumento21 pagineKN-5T TibiaJarinthon Armengot LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- SWJKJQWDocumento52 pagineSWJKJQWCyntia AndrinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cwu OrthopaedicDocumento13 pagineCwu OrthopaedicMuhammad HaziqNessuna valutazione finora