Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Lactated Ringers
Caricato da
E100%(5)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (5 voti)
18K visualizzazioni3 pagineSodium chloride, sodium lactate, potassium chloride, and calcium chloride. Calcium chloride in water dissociates to provide calcium (Ca++) and chloride (Cl-) ions. Potassium is found in low concentration in plasma and extracellular fluids.
Descrizione originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoSodium chloride, sodium lactate, potassium chloride, and calcium chloride. Calcium chloride in water dissociates to provide calcium (Ca++) and chloride (Cl-) ions. Potassium is found in low concentration in plasma and extracellular fluids.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
100%(5)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (5 voti)
18K visualizzazioni3 pagineLactated Ringers
Caricato da
ESodium chloride, sodium lactate, potassium chloride, and calcium chloride. Calcium chloride in water dissociates to provide calcium (Ca++) and chloride (Cl-) ions. Potassium is found in low concentration in plasma and extracellular fluids.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
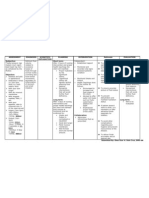
NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications Worksheets
(You will need to make additional copies of these forms)
Generic Name Trade Name Classification Dose Route Time/frequency
sodium chloride, Lactated Ringers Fluid/electrolyte 1000 mL IV Q 24 hrs @ 42 mL/hr
sodium lactate, replacement, blood
potassium volume expander
chloride, and
calcium chloride
Peak Onset Duration Normal dosage range
Unknown Unknown Unknown The dose is dependent upon the age, weight and clinical
(several sources (several (several sources condition of the patient as well as laboratory
checked) sources checked) determinations.
checked)
Why is your patient getting this medication For IV meds, compatibility with IV drips and/or
Extracellular fluid/ electrolyte replacement solutions
There are many drugs that are incompatible with LR, some
commonly used emergency medications that are
incompatible are nitroglycerin, nitroprusside,
norepinephrine, mannitol, procainamide, propranolol,
methylprednisolone.
Mechanism of action and indications Nursing Implications (what to focus on)
(Why med ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactions
Isotonic Solution. When administered No known contraindications. Use precaution with CHF,
intravenously, these solutions provide sources of renal insufficiency, edema states with sodium retention,
water and electrolytes. Their electrolyte content Hyperkalemia, metabolic or respiratory alkalosis, DO NOT
resembles that of the principal ionic constituents of administer simultaneously with blood through same
normal plasma and the solutions therefore are administration set because of the likelihood of coagulation.
suitable for parenteral replacement of extracellular
losses of fluid and electrolytes. Calcium chloride in Common side effects
water dissociates to provide calcium (Ca++) and Fever, infection at administration site, venous thrombosis,
chloride (Cl−) ions. They are normal constituents of extravasation, hypervolemia.
the body fluids and are dependent on various
physiologic mechanisms for maintenance of balance
between intake and output. Approximately 80% of
body calcium is excreted in the feces as insoluble
salts; urinary excretion accounts for the remaining
20%. Potassium chloride in water dissociates to
provide potassium (K+) and chloride (Cl−) ions.
Potassium is found in low concentration in plasma
and extracellular fluids (3.5 to 5.0 mEq/liter in a
healthy adult). It is the chief cation of body cells
(160 mEq/liter of intracellular water). Potassium
plays an important role in electrolyte balance.
Normally about 80 to 90% of the potassium intake is
excreted in the urine; the remainder in the stools and
to a small extent, in the perspiration. The kidney
does not conserve potassium well so that during
fasting or in patients on a potassium-free diet,
potassium loss from the body continues resulting in
potassium depletion. Sodium chloride in water
dissociates to provide sodium (Na+) and chloride
(Cl−) ions. Sodium (Na+) is the principal cation of
the extracellular fluid and plays a large part in the
therapy of fluid and electrolyte disturbances.
Chloride (Cl−) has an integral role in buffering
action when oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange
occurs in the red blood cells. The distribution and
excretion of sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) are
largely under the control of the kidney which
maintains a balance between intake and output.
Sodium lactate provides sodium (Na+) and lactate
(C3H5O3−) ions. The lactate anion is in equilibrium
with pyruvate and has an alkalizing effect resulting
from simultaneous removal by the liver of lactate
and hydrogen ions. In the liver, lactate is
metabolized to glycogen which is ultimately
converted to carbon dioxide and water by oxidative
Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or Lab value alterations caused by medicine
herbal medicines (ask patient specifically) Serum electrolytes ↑
None for this patient
Be sure to teach the patient the following about this
medication
Report any adverse effects, edema, difficulty breathing,
angina to provider.
Nursing Process- Assessment Assessment Evaluation
(Pre-administration assessment) Why would you hold or not give this Check after giving
Assess level of hydration med? Hydration/electrolyte status
Occurrence of an adverse reaction.
Overdose (overhydration, solute
overload).
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento11 pagineNursing Care Planaycee0316100% (1)
- NCP Bed MobilityDocumento1 paginaNCP Bed MobilityDiana Laura Lei100% (2)
- Silvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)Documento1 paginaSilvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)ENessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento2 pagineNCP - Fluid Volume DeficitPatrice LimNessuna valutazione finora
- D5LRDocumento2 pagineD5LRLouiseville Ann Arcilla PilNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolDocumento1 paginaDrug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolmikErlh100% (2)
- NCP FdarDocumento11 pagineNCP FdarJhaymee PinedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Discharge Plan For Dengue Fever 1Documento4 pagineDischarge Plan For Dengue Fever 1Cecille Ursua0% (1)
- (NCP) Deficient Fluid Volume - HypovolemiaDocumento3 pagine(NCP) Deficient Fluid Volume - HypovolemiaMacaRonie PepeRownie del Rio100% (4)
- NCPDocumento2 pagineNCPDidith AbanNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBDocumento3 pagineNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (1)
- NCP - Acute PainDocumento3 pagineNCP - Acute PainErine Emmanuelle Cawaling Hetrosa100% (1)
- KalimateDocumento3 pagineKalimateJàson Vòrhees100% (1)
- PnssDocumento2 paginePnssFrances Oscar GaviolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 13 - Cystoclysis (Student)Documento4 pagineModule 13 - Cystoclysis (Student)Raymond Edge100% (2)
- Patriarca, Janna Mae H. Nursing Care Plan Client: Mr. YingDocumento1 paginaPatriarca, Janna Mae H. Nursing Care Plan Client: Mr. Yingjanna mae patriarca100% (1)
- Short Term: Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 pagineShort Term: Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationChristy BerryNessuna valutazione finora
- MultivitaminDocumento1 paginaMultivitaminKatie McPeek88% (8)
- NCP RiskDocumento3 pagineNCP RiskMaricar Azolae MascualNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Burn Risk InfectionDocumento1 paginaNCP Burn Risk InfectionBraingie Racho50% (4)
- Case Scenario (Pedia)Documento2 pagineCase Scenario (Pedia)Hamima Azis PandapatanNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP LymphedemaDocumento1 paginaNCP Lymphedemayasira50% (2)
- Ncp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasDocumento4 pagineNcp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasFran LanNessuna valutazione finora
- D 5 IMBDocumento2 pagineD 5 IMBAloyan Rose JoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan (Compartment Sydnrome)Documento6 pagineNursing Care Plan (Compartment Sydnrome)Zyiv BalogalNessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento1 paginaIneffective Tissue PerfusionRhae RaynogNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento4 pagineNCP - Impaired Skin IntegrityColette Marie PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Tia DrugsDocumento2 pagineTia DrugsPorxa MalolosNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP. Deficient Fluid Volume by Eben D.C.Documento1 paginaNCP. Deficient Fluid Volume by Eben D.C.dominoredwing2024100% (1)
- NCPDocumento3 pagineNCPeun kyung shinNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento7 pagineNCPChris Denver BancaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Aminoleban Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaAminoleban Drug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento4 pagineCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjomsportg0% (1)
- Er NCPDocumento9 pagineEr NCPEden Marie FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento1 paginaNCPJ. ishtelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroidectomy NCPDocumento1 paginaThyroidectomy NCPkzbreakerrNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP About Fluid IntakeDocumento5 pagineNCP About Fluid IntakeWild Rose100% (1)
- NCP BkaDocumento4 pagineNCP BkaKeeshia CesnerosNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Acute Pain FURUNCOLOSISDocumento2 pagineNCP Acute Pain FURUNCOLOSISMaria Imogen MilambilingNessuna valutazione finora
- Paracetamol Drug StudyDocumento4 pagineParacetamol Drug StudyDennis Nyambane MomanyiNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperthermia NCPDocumento2 pagineHyperthermia NCPMatthew Emmanuel M. Martinez0% (1)
- NCP - Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento1 paginaNCP - Impaired Skin Integrityjanelee28240% (2)
- NCP For DehydrationDocumento1 paginaNCP For Dehydrationjxhel63% (8)
- D5LR VS PLRDocumento27 pagineD5LR VS PLRgerrilynwayneNessuna valutazione finora
- Senna Concentrate: The Medicine at BedtimeDocumento2 pagineSenna Concentrate: The Medicine at BedtimeTempoNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk For FallsDocumento1 paginaRisk For FallsEugene UCNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento1 paginaNCP For Impaired Physical Mobilityitzme_andreaNessuna valutazione finora
- ASSESSMENT S: "Nanghihina Ako, Hindi Ko Magawa Yung Mga GustoDocumento1 paginaASSESSMENT S: "Nanghihina Ako, Hindi Ko Magawa Yung Mga GustoCherie MayNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Impaired SkinDocumento2 pagineNCP Impaired Skinarjay2306_obcq100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocumento7 pagineDrug StudyKim GalamgamNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Ferrous SulfateDocumento1 paginaDrug Ferrous SulfateSrkocherNessuna valutazione finora
- DS PNSSDocumento2 pagineDS PNSSCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNessuna valutazione finora
- 0.9% NaCl or Plain NSSDocumento13 pagine0.9% NaCl or Plain NSSJeannette Richelle DacilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study Sodium ChlorideDocumento4 pagineCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study Sodium ChloridehahahahaaaaaaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Zaroxolyn MetolazoneDocumento1 paginaZaroxolyn MetolazoneCassieNessuna valutazione finora
- Sodium Chloride (IV/oral) : (Soe-Dee-Um Klor-Ide)Documento2 pagineSodium Chloride (IV/oral) : (Soe-Dee-Um Klor-Ide)anon_340279231Nessuna valutazione finora
- FATMADocumento8 pagineFATMAAmr Ramazan IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Potassium ChlorideDocumento1 paginaDrug Potassium ChlorideSrkocherNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Potassium Chloride KCLDocumento1 paginaDrug Potassium Chloride KCLSrkocher100% (3)
- Aki Inn EmergencyDocumento52 pagineAki Inn EmergencyHamza DossaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperparathyroidism PathoDocumento2 pagineHyperparathyroidism PathoENessuna valutazione finora
- Pyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISDocumento4 paginePyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISENessuna valutazione finora
- Influenza B PathoDocumento4 pagineInfluenza B PathoENessuna valutazione finora
- Iron Deficiency Anemia PathoDocumento6 pagineIron Deficiency Anemia PathoENessuna valutazione finora
- Hyponatremic Dehydration PathoDocumento4 pagineHyponatremic Dehydration PathoENessuna valutazione finora
- Left-Side CHF PathoDocumento5 pagineLeft-Side CHF PathoENessuna valutazione finora
- Autonomic DysreflexiaDocumento2 pagineAutonomic DysreflexiaENessuna valutazione finora
- Bowel Resection PathoDocumento7 pagineBowel Resection PathoENessuna valutazione finora
- Congestive Heart Failure-ABDocumento3 pagineCongestive Heart Failure-ABENessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Burns PathoDocumento2 pagineChemical Burns PathoENessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Pancreatitis PathoDocumento5 pagineAcute Pancreatitis PathoENessuna valutazione finora
- FiberCon (Polycarbophil)Documento1 paginaFiberCon (Polycarbophil)ENessuna valutazione finora
- Congestive Heart FailureDocumento4 pagineCongestive Heart FailureENessuna valutazione finora
- Pneumonia Short PathoDocumento2 paginePneumonia Short PathoENessuna valutazione finora
- Zosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)Documento2 pagineZosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)E67% (3)
- Pancreatitis Short PathoDocumento2 paginePancreatitis Short PathoENessuna valutazione finora
- Subluxation c6c7 Short PathoDocumento1 paginaSubluxation c6c7 Short PathoENessuna valutazione finora
- Geodon (Ziprasidone)Documento2 pagineGeodon (Ziprasidone)ENessuna valutazione finora
- Buspar (Buspirone)Documento1 paginaBuspar (Buspirone)ENessuna valutazione finora
- Campral (Acamprosate Calcium)Documento1 paginaCampral (Acamprosate Calcium)E100% (1)
- Darvocet (Propoxyphene Napsylate/Acetaminophen)Documento1 paginaDarvocet (Propoxyphene Napsylate/Acetaminophen)ENessuna valutazione finora
- Lexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)Documento2 pagineLexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)ENessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocumento1 paginaClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsENessuna valutazione finora
- Prozac (Fluoxetine) 40mgDocumento1 paginaProzac (Fluoxetine) 40mgENessuna valutazione finora
- ZofranDocumento1 paginaZofranKatie McPeek0% (1)
- Theragran (Multiple Vitamins)Documento3 pagineTheragran (Multiple Vitamins)ENessuna valutazione finora
- Reglan (Metoclopramide)Documento3 pagineReglan (Metoclopramide)E100% (1)
- Florinef (Fludrocortisone)Documento3 pagineFlorinef (Fludrocortisone)E100% (1)
- Keppra (Levetiracetam)Documento2 pagineKeppra (Levetiracetam)E100% (1)
- Pharma NotesDocumento69 paginePharma NotesJawad Ahmad100% (1)
- Ineffective Health MaintenanceDocumento6 pagineIneffective Health MaintenanceRYAN SAPLADNessuna valutazione finora
- Compatibility Between Space Analysis Methods of Kesling and Arch Length DiscrepancyDocumento6 pagineCompatibility Between Space Analysis Methods of Kesling and Arch Length DiscrepancynostaNessuna valutazione finora
- + +Sandra+Carter +TMJ+No+More+PDF+ (Ebook) PDFDocumento49 pagine+ +Sandra+Carter +TMJ+No+More+PDF+ (Ebook) PDFMassimiliano Marchionne0% (1)
- Strategies To Protect and Restore A Healthy GIT Microbiota (Dysbiosis Prevention and Treatment) .Documento61 pagineStrategies To Protect and Restore A Healthy GIT Microbiota (Dysbiosis Prevention and Treatment) .Nicoleta ButucNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Mechanics of The Normal andDocumento5 pagineBio Mechanics of The Normal andJuanolo Oo100% (1)
- TST Straight Volumed Modular Stem ENGDocumento16 pagineTST Straight Volumed Modular Stem ENGNorel Nicolae BalutaNessuna valutazione finora
- SofradexDocumento3 pagineSofradexWahidNessuna valutazione finora
- Hazardous Materials Management Plan SMDocumento26 pagineHazardous Materials Management Plan SMdarmayunitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Components of General Anesthesia: UnconsciousnessDocumento17 pagineComponents of General Anesthesia: UnconsciousnessDanieleNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 NCP Pressure UlcerDocumento6 pagine11 NCP Pressure UlcerICa MarlinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cancer PainDocumento52 pagineCancer PainIndraYudhi100% (1)
- NeurontinDocumento3 pagineNeurontinFesto HakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Holistic Solutions For Anxiety & Depression in Therapy - Peter BongiornoDocumento290 pagineHolistic Solutions For Anxiety & Depression in Therapy - Peter Bongiornojohnlived100% (2)
- LydiaDocumento219 pagineLydiatayabakhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cordymax Trifold BrochureDocumento2 pagineCordymax Trifold BrochureCherry San DiegoNessuna valutazione finora
- Phenylephrine HydrochlorideDocumento5 paginePhenylephrine HydrochlorideRoger Jr PumarenNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology of Oleanolic Acid and Ursolic Acid: Review ArticleDocumento12 paginePharmacology of Oleanolic Acid and Ursolic Acid: Review ArticlepunitNessuna valutazione finora
- T 1234029783 11845985 Nursing Crib Com Nursing Care Plan Dengue FeverDocumento2 pagineT 1234029783 11845985 Nursing Crib Com Nursing Care Plan Dengue Feversamantha cortezNessuna valutazione finora
- Strengthening Quality Midwifery Education For 2030 - Who Unfpa Unicef 20Documento4 pagineStrengthening Quality Midwifery Education For 2030 - Who Unfpa Unicef 20Sheilla Tania MarcelinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Management Flabby RidgeDocumento4 pagineManagement Flabby RidgeNidya Patricia Sembiring100% (1)
- Daniels and Jenkins - Therapy With Children 2e PDFDocumento2 pagineDaniels and Jenkins - Therapy With Children 2e PDFloubwoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Typing GameDocumento4 pagineBlood Typing GameWidjaya HS TeacherNessuna valutazione finora
- 18Th June 2019 Plab 1 Mock Test Plab ResourcesDocumento30 pagine18Th June 2019 Plab 1 Mock Test Plab Resourceskhashayar HajjafariNessuna valutazione finora
- Genotropin RefresherDocumento4 pagineGenotropin RefresherJessica BascoNessuna valutazione finora
- PNDFvol1ed7 2008Documento315 paginePNDFvol1ed7 2008Wilma de LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- A Report On Depression: Mental HealthDocumento12 pagineA Report On Depression: Mental HealthArchiev KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 3 Cot Filipino Pandiwa q4Documento9 pagineGrade 3 Cot Filipino Pandiwa q4Maricar FaralaNessuna valutazione finora
- FurosemideDocumento5 pagineFurosemideRaja Mashood ElahiNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Surgical Anatomy of TMJDocumento11 pagine8 Surgical Anatomy of TMJArchanaShenoyNessuna valutazione finora