Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM Kelantan 2010 Peraturan Pemarkahan Physics Paper 1
Caricato da
nik mohamad solehinTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM Kelantan 2010 Peraturan Pemarkahan Physics Paper 1
Caricato da
nik mohamad solehinCopyright:
Formati disponibili
PEPERIKSAAN PERCUBAAN SPM KELANTAN 2010 PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN PHYSICS PAPER 1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9. 10 11 12 D C D C C A A C A D C C 13 14 15 16 17 18. 19. 20 21 22 23 24 C C B B C A C C A C D A 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 C C A B B C D B A A C A 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 C D C B D B C C D A A C 49 50 C B
MARKING SCHEME (PAPER 2) SECTION A Question No. 1 (a) (i) (ii) (b) (i) Answer Increases Metal sphere absorbs heat from boiling water. The rate of heat flows from boiling water = the rate of heat flows from metal sphere. Kadar pengaliran haba dari air mendidih = kadar pengaliran haba dari sfera logam. Marks 1 1
(ii)
Thermal equilibrium TOTAL
1 4
2 (a) (b) (c)
Pressure = Force Area Depth / Density / gravity P = hg = 0.12 x 1000 x 10 = 1200 Pa.
1 1
1 1
(d)
TOTAL 3 (a) Beam of electron moving at high speed Alur elektron berhalaju tinggi 1. Light from the filament is blocked by the cross Cahaya dari filament dihalang oleh palang // Cathode ray is blocked by the cross Sinar katod dihalang oleh palang
5 1
(b)
(c)
1.
Correct substitution 2 (1.6 x 10
-19 -31
) ( 3000) 1
9 x 10 2. Correct answer with unit 3.27 x 10 7 ms-1 (d) (i)
(ii)
Flemings left- hand rule // Peraturan tangan kiri Fleming TOTAL
1 6 1 1 1 1
4 (a) (i) (ii) (b) (i) (ii) (c) (i)
A region in which there is an electric force // a region around a charged object which gives electric force on another charged object. Increases Negative charged Attracted to positive plate // Repelled away from negative plate Note : The flame flatten and spread out more toward negative plate
(ii)
1. The heat of burning candle produces positive and negative ions. 2. The positive ions which are heavier is pulled towards negative plate with a large proportion flame TOTAL
1 1 7 1
5 (a) (b) (i) (ii) (iii) (c) (d)
Number of oscillations in one second. Mass of plasticine in Diagram 5.1 < in Diagram 5.2 Frequency in Diagram 5.1 > frequency in Diagram 5.2 The greater the mass the lower the frequency Inertia Increase
1 1 1 1 1
(e) (i) (ii)
T = t = 10 = 0.5 s n 20 F = 1 = 1 = 2 Hz T 0.5 TOTAL
1 1 8 1
6 (a)
(b) (c ) (i) (ii)
An electromagnet is a solenoid which can produce magnetic field when current passes through it. When the current is switch off, the solenoid loses its magnetism. Due to left In diagram 6.2 the number of turns of the coils more than 6.1 In diagram 6.2 the number of magnetic field line is more than that in Diagram 6.1 The current flow in Diagram 6.1 and Diagram 6.2 are the same As the number of turns of solenoid increase the strength of an electromagnet increase The strength of electromagnet increase The magnetic field line are closer // magnetic field line will be concentrate TOTAL
1 1 1
(iii) (d)
1 1
(e) (i) (ii)
1 1
8 1
7. (a)
Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of unstable nucleus with the emission of energetic particles or photons. X - alpha particle Z beta particle Z is lighter than X Nuclear Fission
(b) (i)
1 1 1 1
(ii) (c) (i) (ii)
1 (iii) E = mc2 = (2.988 x 10 -11 )(3 x 108) 2 = 2.67 x 10 -11 J -strong radioactive substances are handled using remote controlled mechanical arms from a safe distance // -weak radioactive substance can be handled by forceps 1 1 1
(d) (i)
-workers should wear a special badge // -wearing protective suits and gears such as gloves, eye glasses// (ii) -to avoid direct contact - detect the amount of radiation they are exposed to// * the reason should be related to the answer given in (d)(i) TOTAL 8. (a)(i) (ii) (iii) (b) Longitudinal wave / mechanical wave No sound / sound cannot be heard Sound wave cannot propagate // sound energy cannot be transferred 10 1 1 1
1. Amplitude of the wave drawn is bigger 1 (c) (i) (ii) (iii) Note: accept as long as the amplitude drawn is slightly bigger. P Infrared Q - Ultraviolet Gamma ray / ultraviolet / x-Ray Can kills the life cell / skin burn or skin cancer / Note: the reason given must be related to the answer in (c) (ii) Radio wave / microwave High frequency / high energy / high penetrating power / less diffracted Gamma Ray high energy / high penetrating power TOTAL 1 1 1 1
(iv) (v) (vi) (vii)
1 1 1 1 12
SECTION B No 9 (a) i) ii)
Suggested Answer The temperature in which a solid substance change to liquid at atmospheric pressure 1. The mass of substance in Diagram 9.1 < in Diagram 9.2 2. Time taken to reach the melting point in Diagram 9.1 < in Diagram 9.2 3. Time taken by the substance to change into liquid completely in Diagram 9.1 < in Diagram 9.2 4. The greater the mass the longer the time taken by the substance to change into liquid completely. 5. The greater the mass the greater the latent heat of fusion absorbed 1. 2. 3. 4. In daytime the sun warms the land to higher temperature than the sea. The land has a lower specific heat capacity than sea-water. The air above the land is heated and rises The cooler air above the sea moving to land.
Mark 1 1 1 1 1 1 5 1 1 1 1 4 1
(b)
(c) Aspect High specific heat capacity of liquid High boiling point of liquid Low rate of rusting material Strong material The size of the fan is big Explanation Becomes hot faster Not easily change into vapour Long lasting // not easily rust Not easily breaks To blow large amount of heat TOTAL 20 2 2 2 2 2 10
No 10 (a) (b) (i)
Suggested Answer 24 J of energy is consumed in 1 s if connected to a 6V power supply // if the voltage is 6 V the power produced is 24 W Reading of ammeter is the same The brightness of filament lamp in Diagram 10.1 is brighter than Diagram 10.2 // vice versa // Filament M is brighter The thickness of wire in Diagram 10.4 is bigger than in Diagram 10.3 // vice versa // Filament M is thinner The thinner the wire the brighter the lamp // vice versa The thinner the wire the more the heat produced by the lamp. 1 Two pin plug has no earth wire // three pin plug has earth wire 2 using 2 pin plug, if there is leakege of current it will also flow through the metal body // using 3 pin plug if there is leakege of current it will flow to the ground 3 The person who touches the metal body will experiences electric shock // using 3 pin plug, the current will be earthed 4 using 2 pin is not safe to the consumer // Using 3 pin plug is more safer to the consumer Aspect Use tungsten Coiled Explanation High melting point longer wire, increase the resistance not easy to melt under high temperature Does not get rust easily
Mark 1 1 1 1 5 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 1
(ii) (iii)
(c)
(d)
2 10
high melting point
Low rate of rusting use termostat
2 When temperature reach 100 C, the water heater will automatically turned off TOTAL 20
o
No 11 (a) (b)
Suggested Answer Distance between focal pint and the optical centre of a lens 1. The convex lens is aimed/focused to a distant object (infinity) 2. The screen is adjusted until a sharp image is formed on the screen 3. The distance between the screen and the lens is measured 4. Focal length = distance between the screen and the lens
Mark 1 1 1 1 1 1
(c) Aspect Longer focal length High magnification Distance = fo + fe Bigger diameter J is chosen Explanation To produce real, inverted and smaller image Produce bigger image Produce image at normal adjustment // image at infinity More light can enter objective lens // more brighter Longer focal length, higher magnification, Distance between two lenses = fo + fe and bigger diameter
2 2 2
2 2 10
(d)
(i)
1 =1 + 1 f u v 1 = 1 1 v 5 400 v = 5.063 cm h2 = v2 h1 v1 h 2 = 5.063 100 400 h 2 = 1.27 cm
1 1
(ii)
1 1
(iii)
Real , inverted and diminished. TOTAL
20
No 12 (a)
Suggested Answer
Mark 1 1
Electrical energy (b) (i)
1.
light energy 1 1 1 1 4
When an a.c. voltage is supplied to the primary coil, the soft iron core is magnetized 2. The magnet produced varies in magnitude and direction 3. This causes a changing magnetic flux to pass through the secondary coil 4. Induced e.m.f across the secondary coil is produced. Aspect Soft iron core Laminated Thick wire Copper wire Explanation Easy to magnetized and demagnetised Less eddy current/ reduce energy lost Reduce the resistance/more current Low resistance/ reduce the lost of heat Soft iron core, Laminated , thick wire, Copper wire
(c)
2 2 2
2 Q (d) (i) (ii) 12 V Np = Vp Ns Vs Np = 240 x 200 12 = 4000 Efficiency = Po x 100 Pi = 240 x 0.2 x 100 48 = 100 % TOTAL 20 2 1 10
1 1
(iii)
1 5
PAPER 3 TRIAL KELANTAN 2010 FIZIK PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
SECTION A Answer (i) number of turn // N (ii) induced current//current // I (iii) height of magnet, h 16 A 24 A 32 A 40 A 48 A 5 are correct - 3 m 4 - 2m <3 - 1m
No 1 (a)
Mark 1 1 1
(b)
(c)
N/ turns 40 60 80 100 120
I / A 16 24 32 40 48
Topic (N and I ) Unit (turns and A) Value-N ( No d.p ) Value-I (consistency)
(d)
Correct axis --- Correct unit - Even scale All 5 point transfer correctly on graph or 4 point transfer correctly on graph Draw one best fit straight line with y-intercept Graph size used ( > 50 percent )
Skor 7 6 or 5 4 or 3 2 1
Markah 5 4 3 2 1
(e)
I is directly proportional to N TOTAL MARK
1 16
2 (a)
(i) h increased linearly with N. (ii) -Extrapolate line intercept h axis. - show on graph the value of h (with unit) - state the value of h = 12.6 cm (iii) show horizontal line from 13.4 cm touches the graph then vertical line until it touches the n axis. - N = 9 (from the graph = 9.2)
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
(b)
- show with an acceptable size. ( > 8 cm x 8 cm) - substitute correctly 13.2 -11.0 y 2 y1 -------- = ----------12.0 2.0 x2 x1 - state the value of gradient and its value k = 0.22 cm m = 5.455 d2 k = 5.455 (2.5)2 (0.22) .. gantian betul = 7.5 (tanpa unit) The position of eye should be in line with the scale reading to be taken TOTAL MARK
(c)
1 1 1 12
(d)
SECTION B 3 (a) Inference : Apparent depth depends on the density/type of block/material Hypothesis : When the density (of material) increase , the apparent depth decrease/depth of image (i) Aim : To investigate the relationship between density and apparent depth/depth of the image (ii)Variables : manipulated V : density// mass of salt responding V : apparent depth/depth of image fixed V : real depth , volume water(ignore the change of volume of water + salt ) (iii)Apparatus and materials : Tall Beaker/cylinder, pin, retort stand , water , salt , meter 1 1
1 1 No Mark
rule, triple beam balance
(iv) Set up apparatus
(v)procedure Fill the beaker with ( V = 1000 cm3 ) water. Put the 20 g of salt into the beaker and stir . Place a pin O into the water. Adjust the position of the pin I (at the retort stand) by observing above the beaker until it appears in line with the image Measure the apparent depth of the straight line,d. Repeat the experiment with( different four densities of liquids) by mixing the mass of salt , m = 30g , 40g, 50g, and 60g . (vi) Mass of salt,m/g 30 40 50 60 70 Density of liquid, / kgm-3 1 2 3 4 5 (vii) graph Apparent depth,d /cm
Apparent depth,d /cm
Accept : Correct axis and unit only
TOTAL MARK 4 (a) Inference: Resistance// brightness of bulb depends on the diameter/thickness of the conductor wire Hypothesis When the diameter/thickness increase , the resistance decrease Aim : To investigate the relationship between the diameter /thickness of the conductor wire and resistance Variable : Manipulated : diameter / thickness Responding : resistance / voltage Fixed : length of conductor
12
1 1
1 1 No mark
Apparatus and material Dry cells, insulated constantan wire, connector wire, ammeter, voltmeter, rheostat , switch, meter rule Set up apparatus 1
1
Dawai konstantan
Procedure: A 20 cm length of constantan wire of diameter of 0.1 mm is connected to a circuit as shown in diagram above. Adjust the rheostat and until the ammeter reading is I = (0.2A). Measure the corresponding reading on the voltmeter, V Calculate the resistance of conductor using equation; R = V/I 1
Repeat the experiment with the diameter of constantan wire , 0.2 mm , 0.3 mm, 0.4mm and 0.5mm.
Tabulating data Resistance,R/ 1 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 (Accept : swg as a scale of diameter ) Analyzing data: R
Diameter,d/mm
1 d/mm TOTAL MARK 12
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Skema Fizik Kertas 2 Trial PerlisDocumento9 pagineSkema Fizik Kertas 2 Trial Perlisenasizuka100% (1)
- Vacuum Nanoelectronic Devices: Novel Electron Sources and ApplicationsDa EverandVacuum Nanoelectronic Devices: Novel Electron Sources and ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Trial SBP Physics SPM 2013 Paper 2Documento9 pagineAnswer Trial SBP Physics SPM 2013 Paper 2Cikgu FaizalNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Jawapan Kertas 2: Answer With The Correct UnitDocumento9 pagineSkema Jawapan Kertas 2: Answer With The Correct UnitNg Yew MengNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Section B and C and Paper 3Documento21 pagineAnswer Section B and C and Paper 3Adnan ShamsudinNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Chemistry of Oxides for Emerging ApplicationsDa EverandIndustrial Chemistry of Oxides for Emerging ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- 4531 FIZ - Skema Kertas 2Documento7 pagine4531 FIZ - Skema Kertas 2Yeow Pow Choo33% (3)
- 2011 SBP Fizik SkemaDocumento14 pagine2011 SBP Fizik SkemaAimi LiyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity from Sunlight: Photovoltaic-Systems Integration and SustainabilityDa EverandElectricity from Sunlight: Photovoltaic-Systems Integration and SustainabilityNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Modul 6Documento14 pagineSkema Modul 6nik mohamad solehinNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysDa EverandPhysics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Paper 1 Quarter Year Examination 2013 Marking SchemeDocumento23 paginePhysics Paper 1 Quarter Year Examination 2013 Marking SchemeAnonymous IyNfIgG4ZNessuna valutazione finora
- Bab 6: Gelombang Bahagian ADocumento20 pagineBab 6: Gelombang Bahagian AlapokNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Fizik Tingkatan 5 Kertas 2 Pep Percubaan SPM SBP 2011Documento8 pagineSkema Fizik Tingkatan 5 Kertas 2 Pep Percubaan SPM SBP 2011Chin Shee YanNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics P2 SPM 2014 A Modul Melaka GemilangDocumento9 paginePhysics P2 SPM 2014 A Modul Melaka GemilangCikgu FaizalNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Devices: The Simple Physics of Sophisticated TechnologyDa EverandModern Devices: The Simple Physics of Sophisticated TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Phyiscs Paper 2 Form 5 Midterm 2011Documento6 pagineAnswer Phyiscs Paper 2 Form 5 Midterm 2011Saidin HashimNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Physics Trial 08 - SchemeDocumento9 pagine02 Physics Trial 08 - SchemeSyafiq HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Trial SBP Physics 2007Documento15 pagineSkema Trial SBP Physics 2007Irfan Faiz100% (1)
- 15 Kelantan SkemaDocumento16 pagine15 Kelantan SkemaNadia SaidonNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM Trial 2011 Physics A TerengganuDocumento15 pagineSPM Trial 2011 Physics A TerengganunivethitacNessuna valutazione finora
- Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM Tahun 2011 Matapelajaran Fizik Skema Permarkahan Paper 2 Section A Marking Criteria Marks TotalDocumento7 paginePeperiksaan Percubaan SPM Tahun 2011 Matapelajaran Fizik Skema Permarkahan Paper 2 Section A Marking Criteria Marks TotalSiti Arbaiyah AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Kertas 2 Pep Pertengahan Tahun SBP 2011Documento8 pagineKertas 2 Pep Pertengahan Tahun SBP 2011KK-Yunn RuhNessuna valutazione finora
- (Spmsoalan) Skema Trial SPM 2014 MRSM PhysicsDocumento14 pagine(Spmsoalan) Skema Trial SPM 2014 MRSM PhysicsrockNessuna valutazione finora
- Trial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Skema Modul 2Documento5 pagineTrial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Skema Modul 2Cikgu FaizalNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Chemistry Trial Mara 2014Documento15 pagineAnswer Chemistry Trial Mara 2014RayChin0% (3)
- Trial Terengganu SPM 2014 Physics K1 K2 K3 SkemaDocumento16 pagineTrial Terengganu SPM 2014 Physics K1 K2 K3 SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Trial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics Skema K1 K2 K3Documento14 pagineTrial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics Skema K1 K2 K3NgauHWNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics P2 SPM 2014 MelakaDocumento9 paginePhysics P2 SPM 2014 MelakaLeeZiangNessuna valutazione finora
- Trial Terengganu SPM 2014 Physics K1 K2 K3 Skema PDFDocumento16 pagineTrial Terengganu SPM 2014 Physics K1 K2 K3 Skema PDFamadkacakNessuna valutazione finora
- 2015 PSPM Kedah Fizik2 W AnsDocumento32 pagine2015 PSPM Kedah Fizik2 W Ansjee2kk90% (10)
- Final Exam f4 Paper2 SkemaDocumento6 pagineFinal Exam f4 Paper2 SkemaJacklynlim LkcNessuna valutazione finora
- Bengkel Teknik Menjawab SPM 2016 PDFDocumento59 pagineBengkel Teknik Menjawab SPM 2016 PDFSuriyati Yusoff75% (4)
- Penang Trial SPM 2013 Physics K2 Skema PDFDocumento8 paginePenang Trial SPM 2013 Physics K2 Skema PDFbdy3372Nessuna valutazione finora
- SKEMA 7th Tips Physics SPM Success Modul Teknik Menjawab Kertas 2 Dan 3Documento13 pagineSKEMA 7th Tips Physics SPM Success Modul Teknik Menjawab Kertas 2 Dan 3Cikgu FaizalNessuna valutazione finora
- Mark Scheme Physics Trial SPM SBP 2016 Paper 2Documento8 pagineMark Scheme Physics Trial SPM SBP 2016 Paper 2Nor Azila Mohd Nasir50% (2)
- Marking Scheme Perfect Score Physics Module 2008Documento21 pagineMarking Scheme Perfect Score Physics Module 2008Shawal AwalNessuna valutazione finora
- 2012 Physics 5058 O-Level AnswersDocumento7 pagine2012 Physics 5058 O-Level AnswersheyitsvanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bengkel Teknik Menjawab Fizik SPM 2016Documento59 pagineBengkel Teknik Menjawab Fizik SPM 2016Suriyati Yusoff100% (2)
- Code r1 Ques Ans Neet 2022Documento41 pagineCode r1 Ques Ans Neet 2022AjNessuna valutazione finora
- PHYSICS Answer Key - English Medium SSLC EXAMINATION March 2019 by Arun Sir CHSS AdakkakunduDocumento4 paginePHYSICS Answer Key - English Medium SSLC EXAMINATION March 2019 by Arun Sir CHSS Adakkakundusafwan ahammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema 123 Fizik f4 Final 2009 MLKDocumento15 pagineSkema 123 Fizik f4 Final 2009 MLKShazreena ShazaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Marking Scheme Soalan Kertas 2 Set 2 Pecutan Akhir Fizik SPM 2010Documento6 pagineMarking Scheme Soalan Kertas 2 Set 2 Pecutan Akhir Fizik SPM 2010Chin Yit YeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Set 7Documento5 paginePhysics Set 7bijayakumal819Nessuna valutazione finora
- National University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIDocumento11 pagineNational University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIYuhua SunNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Paper Two Year Medical 2017Documento9 pagineSample Paper Two Year Medical 2017kaushik ghoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper 2 Jun 2000 PhysicsDocumento4 paginePaper 2 Jun 2000 Physicssolarixe100% (3)
- Physics Perfect Score Module (Answer)Documento18 paginePhysics Perfect Score Module (Answer)Muhamad Syafiq Ab Muttalib100% (1)
- 6th Tips Physics SPM Success Tips Answer Paper 2Documento7 pagine6th Tips Physics SPM Success Tips Answer Paper 2Cikgu FaizalNessuna valutazione finora
- (PHY) 2021 Mock Paper 2 - AnswersDocumento13 pagine(PHY) 2021 Mock Paper 2 - Answerslohbernard168Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Paper 1 - AnskeyDocumento8 paginePractice Paper 1 - Anskeykim loveNessuna valutazione finora
- SKEMA Fizik Percubaan SPM 2012 SBP k123Documento0 pagineSKEMA Fizik Percubaan SPM 2012 SBP k123Ker HerNessuna valutazione finora
- Fizik K2Documento29 pagineFizik K2qq235100% (2)
- ImpulseDocumento3 pagineImpulsenik mohamad solehinNessuna valutazione finora
- Bernoulli's PrincipleDocumento11 pagineBernoulli's Principled-fbuser-23145914Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ding Thethe Effects of A ForceDocumento18 pagineDing Thethe Effects of A Forcenik mohamad solehinNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.9: Forces in EquilibriumDocumento11 pagine2.9: Forces in EquilibriumSyiera RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.1 Understanding PressureDocumento12 pagine3.1 Understanding Pressurenik mohamad solehinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4: Thermal EquilibriumDocumento18 pagineChapter 4: Thermal Equilibriumnik mohamad solehinNessuna valutazione finora
- Nota Padat Fizik F4 Forces and Pressure NotesDocumento24 pagineNota Padat Fizik F4 Forces and Pressure Notesslokkro98% (61)
- Introduction To Physics IDocumento10 pagineIntroduction To Physics ISyazwana ElleasNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Heat 4.2Documento13 pagineChapter 4 Heat 4.2nik mohamad solehinNessuna valutazione finora
- Modul 5 - SPM 2005 k1Documento10 pagineModul 5 - SPM 2005 k1nik mohamad solehinNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Modul 6Documento14 pagineSkema Modul 6nik mohamad solehinNessuna valutazione finora
- Jsi S1000 Modul 6Documento7 pagineJsi S1000 Modul 6nik mohamad solehinNessuna valutazione finora
- Nota Padat Fizik F4 Force and Motion NotesDocumento45 pagineNota Padat Fizik F4 Force and Motion Notesslokkro99% (67)
- Analysing Forces in EquilibriumDocumento18 pagineAnalysing Forces in Equilibriumnik mohamad solehinNessuna valutazione finora
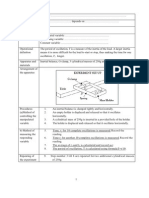
- PEKA EXpDocumento2 paginePEKA EXpnik mohamad solehinNessuna valutazione finora
- Peka 2+ Hooke's LawDocumento2 paginePeka 2+ Hooke's Lawnik mohamad solehinNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper 3 Physics PendulumDocumento2 paginePaper 3 Physics Pendulumnik mohamad solehinNessuna valutazione finora
- F4 ExperimentsDocumento52 pagineF4 ExperimentsKiTTy94% (16)