Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
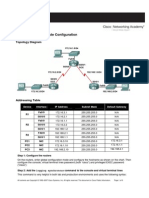
Basic Router Configuration and Network Addressing
Caricato da
Md SyahidDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Basic Router Configuration and Network Addressing
Caricato da
Md SyahidCopyright:
Formati disponibili
ITT459 Data Communication Essentials Lab Exercise Basic Router Configuration and Network Addressing
1. 2.
Select the relevant devices and add them to the working space inside Packet Tracer. Use the labels as a guide as to where to place the devices. Based on the network requirements shown in the topology, design an appropriate addressing scheme. (Note: Remember that the interfaces of network devices are also host IP addresses and are included in the above addressing requirements.) Starting with the largest LAN, determine the size of each subnet you will need for the given host requirement After the addresses have been determined for all the LAN subnets, assign the first available address space to the WAN link between B1 and HQ. Assign the second available address space to the WAN link between HQ and B2 Use the addressing table below to document the IP addresses, subnet masks and default gateway addresses. For the LANs, assign the first IP address to the router interface, Assign the last IP address to the PC. For the WAN links, assign the first IP address to HQ
3.
Enter the basic configurations for the routers. To enter router configurations, a user needs to be in privileged EXEC mode. To enter the privileged EXEC mode, Router>enable Router#
Next, enter the global configuration mode Router#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)# To change the router name from the default Router to, for example, R1 Router(config)#hostname R1 R1(config)# To enable the FastEthernet0/0 Interface R1(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0 R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#no shutdown %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up R1(config-if)# For a serial interface, the one labeled DCE must be additionally configured with a clock rate. For example, to configure a Serial0/0/0 interface R1(config-if)#interface serial 0/0/0 R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#clock rate 64000 R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)# Note: The interface will not be activated until the serial interface on the other end is configured and activated To return to the privileged EXEC mode from the global configuration mode R1(config-if)#end R1# To save the configuration R1#copy running-config startup-config Building configuration... [OK] R1# 4. 5. Configure the host PCs Verify and test the configuration. To verify that the routing tables have the routes R1#show ip route Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 To verify that the interface configuration is correct R1#show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol FastEthernet0/0 192.168.1.1 YES manual up up FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down Serial0/0/0 192.168.2.1 YES manual up up Serial0/0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down Vlan1 unassigned YES manual administratively down down
6.
Test the connectivity. From the host attached to HQ, is it possible to ping the default gateway? From the host attached to B1, is it possible to ping the default gateway? From the host attached to B2, is it possible to ping the default gateway? From the host connected to HQ attempt to ping the host connected to B1 and B2. Is it successful? Attempt to do this with all other hosts. 7. Identify Layer 2 and Layer 3 addresses used to switch packets. Enter Simulation Mode Use the Add Simple PDU button to create a ping from PC1 to PC3 Change Edit Filters so that only ICMP is simulated Record the addresses used by PC1 to send the ping packet to B1 Addresses at PC1 Record the addresses used by PC1 to send the ping packet to B1 Layer 3 Source: Layer 3 Destination: Layer 2 Source: Layer 2 Destination: Addresses at B1 Record the addresses used by B1 to switch the ping packet to HQ: Layer 3 Source: Layer 3 Destination: Layer 2 Source: Layer 2 Destination: Addresses at HQ Record the addresses used by HQ to switch the ping packet to B2: Layer 3 Source: Layer 3 Destination: Layer 2 Source: Layer 2 Destination: Addresses at B2 Record the addresses used by B2 to switch the ping packet to PC3: Layer 3 Source: Layer 3 Destination: Layer 2 Source: Layer 2 Destination:
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Lab 4 Static Default RouteDocumento8 pagineLab 4 Static Default RouteLipp00 M0MANessuna valutazione finora
- P4 (Static Routing - Configuration)Documento6 pagineP4 (Static Routing - Configuration)Huda GhaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Configure IP Address and Default RouteDocumento77 pagineConfigure IP Address and Default RouteAman SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab: Basic Static Route Configuration: Topology DiagramDocumento6 pagineLab: Basic Static Route Configuration: Topology Diagramchanda_banda272Nessuna valutazione finora
- Configuring HSRP and GLBPDocumento9 pagineConfiguring HSRP and GLBPRajwecNessuna valutazione finora
- P5 (RIP Configuration)Documento7 pagineP5 (RIP Configuration)Huda GhaziNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative AccessDocumento11 pagine4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative AccessJesús EnriqueNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.4.7 Lab Configure Secure Administrative AccessDocumento10 pagine4.4.7 Lab Configure Secure Administrative AccessHector De Jesus Tapia GorgonioNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.1.5.8 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesDocumento9 pagine5.1.5.8 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesJozeph Abod67% (3)
- Lab 1Documento10 pagineLab 1Israel EliasNessuna valutazione finora
- Configure Router and End DevicesDocumento23 pagineConfigure Router and End DevicesSam JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Configuration Cisco Router CCNA Introduction To Networks V7.02Documento6 pagineConfiguration Cisco Router CCNA Introduction To Networks V7.02Kim WorldNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 1: Basic Router Configuration: Topology DiagramDocumento7 pagineLab 1: Basic Router Configuration: Topology DiagramDat LCNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 4 - Static RoutingDocumento5 pagineLab 4 - Static RoutingdaveNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.3.3.2 Lab - Troubleshoot LAN Traffic Using SPANDocumento6 pagine5.3.3.2 Lab - Troubleshoot LAN Traffic Using SPANYaser Samer0% (6)
- 4.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring HSRP and GLBPDocumento9 pagine4.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring HSRP and GLBPLex Schneider0% (1)
- Lab 5.2.3 Configuring Ripv2 With VLSM, and Default Route PropagationDocumento4 pagineLab 5.2.3 Configuring Ripv2 With VLSM, and Default Route Propagationmohammad_shahzad_iiuiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 4Documento8 pagineLab 4pzydf6wjxvNessuna valutazione finora
- Configuring OSPF Brandon&KatieDocumento8 pagineConfiguring OSPF Brandon&KatieLuis GonzalezNessuna valutazione finora
- Configuracion Router CiscoDocumento3 pagineConfiguracion Router Ciscofernandomh2028Nessuna valutazione finora
- Static Routing - Part 1: CIS 82 Routing Protocols and Concepts Rick Graziani Cabrillo College Graziani@cabrillo - EduDocumento125 pagineStatic Routing - Part 1: CIS 82 Routing Protocols and Concepts Rick Graziani Cabrillo College Graziani@cabrillo - EduJulio Cesar EMNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPDocumento7 pagine4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPLeo Leo17% (6)
- ICND1 Practice Questions 9tutDocumento56 pagineICND1 Practice Questions 9tutnicolelemmimgNessuna valutazione finora
- LAN-to-LAN routing with static and RIPDocumento166 pagineLAN-to-LAN routing with static and RIPSaravanan Nallusamy100% (2)
- 07-BCMSN-Layer 3 Switching PDFDocumento7 pagine07-BCMSN-Layer 3 Switching PDFChoubane LamineNessuna valutazione finora
- Static Routing and Basic Router ConfigurationsDocumento11 pagineStatic Routing and Basic Router ConfigurationsJoseph NegranzaNessuna valutazione finora
- HRRPDocumento7 pagineHRRPJavier CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.4.3.4 Packet TracerDocumento11 pagine2.4.3.4 Packet TracercoleparksNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.3.8 LabDocumento10 pagine6.2.3.8 LabAutumn TillmanNessuna valutazione finora
- CCN Lab 5-IP NamingDocumento14 pagineCCN Lab 5-IP NamingTanveer KhadimNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 8Documento5 pagineExperiment 8Rohan 7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ospf ChallangeDocumento7 pagineOspf ChallangeDave RojasNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 10.2 - Configure IPv6 Addresses On Network DevicesDocumento4 pagineLab 10.2 - Configure IPv6 Addresses On Network DevicesRecky JimmyNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPDocumento7 pagine4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPjb100% (1)
- 6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocumento11 pagine6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesntutaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 4.9.4 Configuring ISDN PRI: ObjectiveDocumento5 pagineLab 4.9.4 Configuring ISDN PRI: ObjectiveCharles MorrisonNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Configure Routing Information Protocol RIP Routing Information Protocol Version 2 RIPv2 Lab PRDocumento7 pagineHow To Configure Routing Information Protocol RIP Routing Information Protocol Version 2 RIPv2 Lab PRshinde_jayesh2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.7 Lab Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocumento11 pagine6.2.7 Lab Configure Automated Security FeaturesCesar Lazo DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- 12.9.2 Lab - Configure Ipv6 Addresses On Network DevicesDocumento4 pagine12.9.2 Lab - Configure Ipv6 Addresses On Network Devicessouaifi yosraNessuna valutazione finora
- 12.9.2 Lab - Configure IPv6 Addresses On Network DevicesDocumento4 pagine12.9.2 Lab - Configure IPv6 Addresses On Network DevicesCRISTIAN DAVID VIASUS VEGANessuna valutazione finora
- Connecting Router With 2 PCSDocumento165 pagineConnecting Router With 2 PCSBhargavNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab NetworkDocumento9 pagineLab NetworkPro NebyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Latest Real CCNA Simulations QuestionsDocumento95 pagineLatest Real CCNA Simulations QuestionsTara CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Practica para SkillsDocumento10 paginePractica para SkillsyoyonjuanNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA 2 v503 v60 Chapter 1 Exam Answers 2018 100 FullDocumento23 pagineCCNA 2 v503 v60 Chapter 1 Exam Answers 2018 100 FullEdwinNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA Config QuestionDocumento4 pagineCCNA Config QuestionAsnake MekonnenNessuna valutazione finora
- CNS Lab Manual 2019 Course - UpdatedDocumento96 pagineCNS Lab Manual 2019 Course - Updatedswapnil khandareNessuna valutazione finora
- Konfigurasi Static Routing LABDocumento18 pagineKonfigurasi Static Routing LABDhani msNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRP - ILMDocumento18 pagine4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRP - ILMjanakp2004Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 11Documento4 pagineLab 11chaukietnguyen74Nessuna valutazione finora
- ICND1 Review – Configure Cisco Network InfrastructureDocumento3 pagineICND1 Review – Configure Cisco Network InfrastructureJaja Jajagf0% (4)
- 12.9.2-Lab-Configure-Ipv6-Addresses-On-Network (Resuelto)Documento5 pagine12.9.2-Lab-Configure-Ipv6-Addresses-On-Network (Resuelto)Esteban RcNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocumento11 pagine6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesHani GoytomNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 3Documento26 pagineExperiment 3Ellaine SouribioNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF AuthenticationDocumento7 pagine6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF AuthenticationGISTSalehuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Information Security Management: Lab Assessment - 4Documento9 pagineInformation Security Management: Lab Assessment - 4asmit guptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationDa EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNessuna valutazione finora
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkDa EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNessuna valutazione finora
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingDa EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit V Satellite Applications: INTELSAT SeriesDocumento76 pagineUnit V Satellite Applications: INTELSAT SeriesHemalatha NatarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Getting Started GuideDocumento24 pagineGetting Started GuideajfcardosoNessuna valutazione finora
- 00 - 2g - BTS - SCF - CIQ - xxBSCyyyy - Yymmdd - V1 4 - FORMULADocumento254 pagine00 - 2g - BTS - SCF - CIQ - xxBSCyyyy - Yymmdd - V1 4 - FORMULAPuneet KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- PCM CodigoDocumento14 paginePCM CodigoLeux GuillenNessuna valutazione finora
- White Paper: Mobile NFC in Transport: September 2012 Non ConfidentialDocumento31 pagineWhite Paper: Mobile NFC in Transport: September 2012 Non ConfidentialJoe NelsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Dedicated Bearer SetupDocumento2 pagineDedicated Bearer SetupAshuB08Nessuna valutazione finora
- IDM Crack - SerialsDocumento1 paginaIDM Crack - SerialsKiran KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Nexus 6000 Series Release Notes, Release 6.02Documento36 pagineCisco Nexus 6000 Series Release Notes, Release 6.02txNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework 1 Wireless NetworksDocumento2 pagineHomework 1 Wireless NetworkssjognipaNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Security and Penetration Testing Chapter 6 Encryption and Password CrackingDocumento88 pagineComputer Security and Penetration Testing Chapter 6 Encryption and Password CrackingEthan FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethical Hacking (Sem Vi) : Presented By: Ms. Drashti ShrimalDocumento11 pagineEthical Hacking (Sem Vi) : Presented By: Ms. Drashti ShrimalSunny PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- I C-Bus Specification and User ManualDocumento50 pagineI C-Bus Specification and User ManualDong NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- MessagesDocumento27 pagineMessagesCesar PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- AP-105 Wireless Access Point: Installation GuideDocumento2 pagineAP-105 Wireless Access Point: Installation GuideKalan KlNessuna valutazione finora
- VR4 05 GGS-000394-07E OM NoRestrictionDocumento340 pagineVR4 05 GGS-000394-07E OM NoRestrictionBuratNessuna valutazione finora
- Sipura SPA Administration GuideDocumento136 pagineSipura SPA Administration GuideHelen HelenopoulosNessuna valutazione finora
- GMDSS: Global Maritime Distress and Safety SystemDocumento110 pagineGMDSS: Global Maritime Distress and Safety SystemAmin Al Qawasmeh100% (1)
- Finite Impulse Response (Fir) : ObjectivesDocumento9 pagineFinite Impulse Response (Fir) : ObjectivesAldon JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- TMP 18035-Datasheet Autolog CP Gsm-Rtu-1484342593Documento2 pagineTMP 18035-Datasheet Autolog CP Gsm-Rtu-1484342593EugeneNessuna valutazione finora
- EC6602Documento1 paginaEC6602JothiEeshwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Shqip IptvDocumento8 pagineShqip IptvAsllan Bytyqi100% (1)
- Gotenna Mesh Spec SheetDocumento1 paginaGotenna Mesh Spec SheetPi LonNessuna valutazione finora
- Akshay - Irrigation & Fertilizer Control For Precision Agriculture Using WSN - Energy Efficient ApproachDocumento15 pagineAkshay - Irrigation & Fertilizer Control For Precision Agriculture Using WSN - Energy Efficient ApproachDenise NelsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Information Sources and Signals: Asst. Prof. Chaiporn Jaikaeo, PH.DDocumento34 pagineInformation Sources and Signals: Asst. Prof. Chaiporn Jaikaeo, PH.DDorian GreyNessuna valutazione finora
- R Rec M.2092 0 201510 I!!pdf e PDFDocumento146 pagineR Rec M.2092 0 201510 I!!pdf e PDFВлад ХмарукNessuna valutazione finora
- Ruckus R310: BenefitsDocumento6 pagineRuckus R310: Benefitswaseis81Nessuna valutazione finora
- GnuPG CheatsheetDocumento5 pagineGnuPG CheatsheetGiova RossiNessuna valutazione finora
- Using A Tacacs ServerDocumento4 pagineUsing A Tacacs Servermky212Nessuna valutazione finora
- Data Center Contact ListDocumento6 pagineData Center Contact Listganesh kondikireNessuna valutazione finora
- Prodelin 1.8m 1184 - Spec Sheet PDFDocumento2 pagineProdelin 1.8m 1184 - Spec Sheet PDFMario SegoviaNessuna valutazione finora