Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
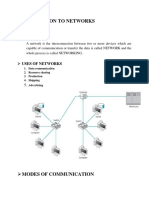
Networking
Caricato da
Dheeraj KushwahaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Networking
Caricato da
Dheeraj KushwahaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Routing or routeing is the process of selecting paths in a network along which to send network traffic.
Routing is performed for many kinds of networks, including the telephone network (Circuit switching) , electronic data networks (such as the Internet), and transportation networks. In packet switching networks, routing directs packet forwarding, the transit of logically addressed packets from their source toward their ultimate destination through intermediate nodes, typically hardware devices called routers, bridges, gateways, firewalls, or switches. Generalpurpose computers can also forward packets and perform routing, though they are not specialized hardware and may suffer from limited performance. The routing process usually directs forwarding on the basis of routing tables which maintain a record of the routes to various network destinations. Thus, constructing routing tables, which are held in the router's memory, is very important for efficient routing. Most routing algorithms use only one network path at a time, but multipath routing techniques enable the use of multiple alternative paths. Circuit switching is a telecommunications technology by which two network nodes establish a dedicated communications channel (circuit) before the nodes may communicate. A telecommunications network is a collection of terminals, links and nodes which connect together to enable telecommunication between users of the terminals. A router is connected to two or more data lines from different networks. When data comes in on one of the lines, the router reads the address information in the packet to determine its ultimate destination. Then, using information in its routing table or routing policy, it directs the packet to the next network on its journey or drops the packet. A data packet is typically forwarded from one router to another through networks that constitute the internetwork until it gets to its destination node.[1]
IP - is responsible for moving packet of data from node to node. IP forwards each packet based on a four byte destination address (the IP number). The Internet authorities assign ranges of numbers to different organizations. The organizations assign groups of their numbers to departments. IP operates on gateway machines that move data from department to organization to region and then around the world. TCP - is responsible for verifying the correct delivery of data from client to server. Data can be lost in the intermediate network. TCP adds support to detect errors or lost data and to trigger retransmission until the data is correctly and completely received. Sockets - is a name given to the package of subroutines that provide access to TCP/IP on most systems.
Network of Lowest Bidders
The Army puts out a bid on a computer and DEC wins the bid. The Air Force puts out a bid and IBM wins. The Navy bid is won by Unisys. Then the President decides to invade Grenada and the armed forces discover that their computers cannot talk to each other. The DOD must build a "network" out of systems each of which, by law, was delivered by the lowest bidder on a single contract.
The Internet Protocol was developed to create a Network of Networks (the "Internet"). Individual machines are first connected to a LAN (Ethernet or Token Ring). TCP/IP shares the LAN with other uses (a Novell file server, Windows for Workgroups peer systems). One device provides the TCP/IP connection between the LAN and the rest of the world. To insure that all types of systems from all vendors can communicate, TCP/IP is absolutely standardized on the LAN. However, larger networks based on long distances and phone lines are more volatile. In the US, many large corporations would wish to reuse large internal networks based on IBM's SNA. In Europe, the national phone companies traditionally standardize on X.25. However, the sudden explosion of high speed microprocessors, fiber optics, and digital phone systems has created a burst of new options: ISDN, frame relay, FDDI, Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM). New technologies arise and become obsolete within a few years. With cable TV and phone companies competing to build the National Information Superhighway, no single standard can govern citywide, nationwide, or worldwide communications. The original design of TCP/IP as a Network of Networks fits nicely within the current technological uncertainty. TCP/IP data can be sent across a LAN, or it can be carried within an internal corporate SNA network, or it can piggyback
on the cable TV service. Furthermore, machines connected to any of these networks can communicate to any other network through gateways supplied by the network vendor.
Addresses
Each technology has its own convention for transmitting messages between two machines within the same network. On a LAN, messages are sent between machines by supplying the six byte unique identifier (the "MAC" address). In an SNA network, every machine has Logical Units with their own network address. DECNET, Appletalk, and Novell IPX all have a scheme for assigning numbers to each local network and to each workstation attached to the network. On top of these local or vendor specific network addresses, TCP/IP assigns a unique number to every workstation in the world. This "IP number" is a four byte value that, by convention, is expressed by converting each byte into a decimal number (0 to 255) and separating the bytes with a period. For example, the PC Lube and Tune server is 130.132.59.234.
A network gateway is an internetworking system capable of joining together two networks that use different base protocols. A network gateway can be implemented completely in software, completely in hardware, or as a combination of both. Depending on the types of protocols they support, network gateways can operate at any level of the OSI model.
router vs gateway ROUTER
network device that forwards packets from one network to another. Based on internal routing tables, routers read each incoming packet and decide how to forward it. Routers work at the network layer (layer 3) of the protocol
GATEWAY device that converts one protocol or format to another. A network gateway converts packets from one protocol to another.the gateway functions as an entry/exit point to the network.An earlier name for router. The term commonly refers to a multi-port network bridge that processes and routes data at the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model. Switches that additionally process data at thenetwork layer
a switch is a device that channels incoming data from any of multiple input ports to the specific output port that will take the data toward its intended destination. In the traditional circuit-switched telephone network, one or more switches are used to set up a dedicated though temporary connection or circuit for an exchange between two or more parties. On an Ethernet local area network (LAN), a switch determines from the
Domain Name System (DNS) is a system for naming computers and network services that is organized into a hierarchy of domains. TCP/IP networks, such as the Internet, use DNS to locate computers and services through user-friendly names.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server, the server that lets client computers that are connected to a network acquire IP addresses dynamically.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Packet Switching Is The Dividing Of: MessagesDocumento31 paginePacket Switching Is The Dividing Of: MessagesShokin AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Layer Samia'Documento10 pagineNetwork Layer Samia'Dark GardianNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networking AssignmentDocumento9 pagineComputer Networking AssignmentSibgat Ul HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Name - Prajwal Ghale Roll On - NP000477 Section - B: Question No.1Documento4 pagineName - Prajwal Ghale Roll On - NP000477 Section - B: Question No.1Prajwal GhalezNessuna valutazione finora
- IPv4 - Quick GuideDocumento21 pagineIPv4 - Quick GuidemispanshieNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Assignment: 3: Be 5 Section B Subject: CCNDocumento6 pagineLab Assignment: 3: Be 5 Section B Subject: CCNIqraJahanNessuna valutazione finora
- IPv4 and Addressing CompleteDocumento24 pagineIPv4 and Addressing CompleteusamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Logical Addressing: IPV4 Addressing - Computer NetworksDocumento19 pagineLogical Addressing: IPV4 Addressing - Computer Networksblessing pakachenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Logical Addressing: IPV4 Addressing - Computer NetworksDocumento19 pagineLogical Addressing: IPV4 Addressing - Computer Networksblessing pakachenaNessuna valutazione finora
- IT Notes Unit 5Documento14 pagineIT Notes Unit 5Deepankar Anil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1: Networking Theory & Java Overview: Prepared By: Siti Nur Ain FTK 2016Documento38 pagine1.1: Networking Theory & Java Overview: Prepared By: Siti Nur Ain FTK 2016ainnNessuna valutazione finora
- IPv 4Documento20 pagineIPv 42224 Momynul IslamNessuna valutazione finora
- A Local Area NetworkDocumento4 pagineA Local Area Networkwvejuynq100% (1)
- Module 1-2 TakenotesDocumento9 pagineModule 1-2 TakenotesAries VenturaNessuna valutazione finora
- TCP-IP Part-1Documento38 pagineTCP-IP Part-1Aadya SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Networks: Modes of CommunicationDocumento24 pagineIntroduction To Networks: Modes of CommunicationamitNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 STDocumento60 pagine1 STmayank barsenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1 - Network BasicsDocumento47 pagineLecture 1 - Network BasicsYahya MakarimNessuna valutazione finora
- Network ProtocolDocumento5 pagineNetwork ProtocolNeenetoots GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Manual: Computer Network IDocumento35 pagineLaboratory Manual: Computer Network ITedNessuna valutazione finora
- XII - Computer Networks - NetworkDevicesDocumento30 pagineXII - Computer Networks - NetworkDevicesLakshya NayakNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking Data Link Protocol Networking Nodes Authentication Encryption CompressionDocumento9 pagineNetworking Data Link Protocol Networking Nodes Authentication Encryption CompressionAdit LalNessuna valutazione finora
- CNC ExperimentDocumento33 pagineCNC ExperimentNikita AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- The Bits and Bytes of Computer NetworkingDocumento23 pagineThe Bits and Bytes of Computer NetworkingAshish SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Networking - Cyber Security - Ethical HackingDocumento25 pagineBasic Networking - Cyber Security - Ethical HackingShanzida Anika MimNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking QuestionsDocumento4 pagineNetworking QuestionsShivanshu Kumar UpadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- CN Lab Viva QuestionsDocumento4 pagineCN Lab Viva QuestionsChetan Raj100% (1)
- A) Guided MediaDocumento12 pagineA) Guided Mediabharath5911Nessuna valutazione finora
- Data Com 1Documento26 pagineData Com 1Pedro OleskoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11: Wide Area Networks and The InternetDocumento12 pagineChapter 11: Wide Area Networks and The InternetDanny OxinaNessuna valutazione finora
- NetworksDocumento8 pagineNetworksGaby MbuguaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Networking.Documento40 pagineIntroduction To Networking.Md Fareed JuneidNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Computer NetworksDocumento13 pagine2 Computer Networksthapliyallaxmi72Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computer NetworkDocumento20 pagineComputer NetworkAnsh VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- CN Unit1 8-7-10Documento20 pagineCN Unit1 8-7-10nallapatiharika0% (1)
- WT Unit 1 & 2 NotesDocumento37 pagineWT Unit 1 & 2 NotesKeshavNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of NetworksDocumento13 pagineTypes of NetworkssumitNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Devices NotesDocumento14 pagineNetwork Devices NotesGonella KameshNessuna valutazione finora
- The Network LayerDocumento14 pagineThe Network Layerpeter_joonNessuna valutazione finora
- Viva VoceDocumento5 pagineViva VocesathishNessuna valutazione finora
- DCN FileDocumento50 pagineDCN FileArpit KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- CN-Unit-1 - Part2 NotesDocumento9 pagineCN-Unit-1 - Part2 NotesMeghnadhNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A Network?Documento9 pagineWhat Is A Network?amrit singhaniaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 NetworksDocumento81 pagine4 NetworksSaurabh JainNessuna valutazione finora
- 17BCS2998 Assignment1Documento7 pagine17BCS2998 Assignment1samswag2898Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction of Computer Networks and InternetDocumento24 pagineIntroduction of Computer Networks and InternetChristy RagayNessuna valutazione finora
- Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineCheat SheetDevan TillyNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Communication ProtocolsDocumento111 pagineNetwork Communication ProtocolsignatvaseaNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Network DevicesDocumento14 pagineComputer Network DevicesArham ZeshanNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 05Documento10 pagineCH 05Hari PrasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking AucseDocumento8 pagineNetworking Aucseapi-3804388Nessuna valutazione finora
- TCP IpDocumento36 pagineTCP IpMonisha MoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Distributed Communications SystemsDocumento36 pagineDistributed Communications SystemsRavi AroraNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Networking ConceptsDocumento30 pagineBasic Networking ConceptsQamar KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Network Long Questions & AnswerDocumento12 pagineComputer Network Long Questions & Answersravan123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Data Communication and Computer NetworksDocumento151 pagineData Communication and Computer NetworksmandviNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To NetworkingDocumento17 pagineIntroduction To NetworkingGraceNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Da EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyDa EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Hacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisDa EverandHacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisNessuna valutazione finora
- Bill NoDocumento2 pagineBill NoDheeraj KushwahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Windows Server 2003 Active Directory and Security QuestionsDocumento5 pagineWindows Server 2003 Active Directory and Security QuestionsDheeraj KushwahaNessuna valutazione finora
- 0 619 16023 3 03 OpDocumento40 pagine0 619 16023 3 03 OpDheeraj KushwahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment ISADocumento1 paginaAssignment ISADheeraj KushwahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Deposit Receipt ClerksDocumento1 paginaDeposit Receipt ClerksDheeraj KushwahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocumento593 pagineHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Question Bank of Financial Management - 2markDocumento16 pagineQuestion Bank of Financial Management - 2marklakkuMSNessuna valutazione finora
- Catherine The Great: Catherine II, Empress of RussiaDocumento7 pagineCatherine The Great: Catherine II, Empress of RussiaLawrence James ParbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Eumind Comparison ReportDocumento8 pagineEumind Comparison Reportapi-538632185Nessuna valutazione finora
- Books by Amy and Arny MindellDocumento24 pagineBooks by Amy and Arny Mindellrameshprema100% (1)
- A Skunk, A Weasel and A Rat!Documento174 pagineA Skunk, A Weasel and A Rat!WalliveBellair100% (1)
- A REPORT ON MIMO IN WIRELESS APPLICATIONS - FinalDocumento11 pagineA REPORT ON MIMO IN WIRELESS APPLICATIONS - FinalBha RathNessuna valutazione finora
- 250 Conversation StartersDocumento22 pagine250 Conversation StartersMarithe Le Blanc100% (2)
- Lesson 4 Theories of TruthDocumento25 pagineLesson 4 Theories of TruthKayeden CubacobNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes Mellitus in Pediatric: Dr. Wasnaa Hadi AbdullahDocumento30 pagineDiabetes Mellitus in Pediatric: Dr. Wasnaa Hadi AbdullahLily AddamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Lantolf Concept Based InstructionDocumento16 pagineLantolf Concept Based Instructionphdreadings39Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 6 Intercultural ComDocumento25 pagineLesson 6 Intercultural ComBrave MitraNessuna valutazione finora
- Two Steps From Hell Full Track ListDocumento13 pagineTwo Steps From Hell Full Track ListneijeskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Area Grade Level Quarter Date: English 10 4Documento4 pagineLearning Area Grade Level Quarter Date: English 10 4Yuki50% (8)
- Aarvee Denim & Export LTD.: CertificateDocumento46 pagineAarvee Denim & Export LTD.: CertificateVinita AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic Categorization Based On User Behaviour in Random Social Networks Using Firefly AlgorithmDocumento5 pagineTopic Categorization Based On User Behaviour in Random Social Networks Using Firefly AlgorithmBONFRINGNessuna valutazione finora
- Isl Isl StyleguideDocumento50 pagineIsl Isl StyleguideCole FranklinNessuna valutazione finora
- Krok1 EngDocumento27 pagineKrok1 Engdeekshit dcNessuna valutazione finora
- TIFR Pamphlet On Homological MethodsDocumento105 pagineTIFR Pamphlet On Homological MethodsRAMJANNessuna valutazione finora
- Mythbusters - Archimedes Cannon QuestionsDocumento2 pagineMythbusters - Archimedes Cannon QuestionsVictoria RojugbokanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tugas Pak Hendro PoemDocumento24 pagineTugas Pak Hendro PoemLaila LalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Opinion Essay: ECPE - Michigan Proficiency The (5) Types of ESSAYSDocumento4 pagineOpinion Essay: ECPE - Michigan Proficiency The (5) Types of ESSAYSelpidavekriNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurovascular Holding PointsDocumento8 pagineNeurovascular Holding PointsAlexandru Baciu100% (1)
- Torts and Damages Midterm ReviewerDocumento25 pagineTorts and Damages Midterm ReviewerErika-Anne ThereseNessuna valutazione finora
- Graph Theory and ApplicationsDocumento45 pagineGraph Theory and Applicationssubramanyam62Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamic Behavior of Closed-Loop Control Systems: 10.1 Block Diagram RepresentationDocumento26 pagineDynamic Behavior of Closed-Loop Control Systems: 10.1 Block Diagram Representationratan_nitNessuna valutazione finora
- Caldecott WinnersDocumento1 paginaCaldecott Winnersbenanas6Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrostatic PressureDocumento13 pagineHydrostatic Pressureapi-2859151810% (1)
- Streetcar - A Modern TradegyDocumento4 pagineStreetcar - A Modern Tradegyel spasser100% (2)
- Akbar Early YearsDocumento25 pagineAkbar Early YearsSandeep KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- The Myth of HITLER's POPE - Hubert - LunsDocumento13 pagineThe Myth of HITLER's POPE - Hubert - LunsHubert LunsNessuna valutazione finora