Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Introduction To Trigonometry
Caricato da
Richa GulatiDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Introduction To Trigonometry
Caricato da
Richa GulatiCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Introduction to Trigonometry
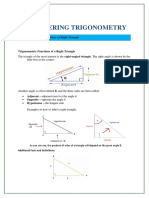
Introduction: Trigonometry is an important branch of Mathematics. The word Trigonometry has been derived from three Greek words Tri (Three), Goni (Angles), Metron (Measurement). Literally it means measurement of triangles The origin of trigonometry have benn traced back to the Egyptians of the 13 century B.C., whose tables of shadow lengths correspond to today's tangent and cotangent functions. The Babylonians and Greeks trigonometry to study of heavens. Travelers of recent centuries used trigonometry to navigate, and physicist use trigonometry to study sound, light, and other waves. TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS The relationships between the angles and the sides of a right triangle are expressed in terms of TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS. For example, in figure 19-7, the sides of the triangle are named in accordance with their relationship to angle . In trigonometry, angles are usually named by means of Greek letters. The Greek name of the symbol is theta. The six trigonometric ratios for the angle are listed in table 19-1. The-ratios are defined as follows:
Figure 19-1.-Relationship of sides and angles in a right triangle. (A) Names of the sides; (B) symbols used to designate the sides. Table 19-1.-Trigonometric ratios.
The other acute angle in figure 19-7 (B) is labeled (Greek alpha). The side opposite is x and the side adjacent to is y. Therefore the six ratios for are as follows:
Suppose that the sides of triangle (B) in figure 19-7 are as follows: x = 3, y.= 4, r = 5. Then each of the ratios for angles and may be expressed as a common fraction or as a decimal. For example,
Decimal values have been computed for ratios of angles between 0 and 90, and values for angles above 90" can be expressed in terms of these same values by means of conversion formulas. Appendix II of this training coursegives the sine, cosine, and tangent of angles from 0 to 90. The secant, cosecant, and cotangent are calculated, when needed, by using their relationships to the three principal ratios. These relationships are as follows:
Trigonometric Ratios of Some Specific Angles:
Method to find the sine of some specific angles (0, 30, 45, 60 & 90):
Table of Trigonometric Ratios of Some Specific Angles:
Remark: From the table, you can observe that as increases from 0 to 90, sin A increases from 0 to 1 and cos A decreases from 1 to 0.
Trigonometric Ratios of Complementary Angles: Two angles are complementary, if the sum of angles is 90.
In a right angled triangle, measure of one angle is 90 and sum of other two angles is also 90. So, these angles are complementary angles.
For any angle A, trigonometric ratios of complementary angle are:
Trigonometric Identities: An equation involving trigonometric ratios of an angle is called a trigonometric identity, if it is true for all values of the angle(s) involved.
For any angle
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Mathematics 10 DLS 26-27Documento6 pagineMathematics 10 DLS 26-27Ivan Miguel MariNessuna valutazione finora
- Project On Basic Trigonometry: Presented byDocumento14 pagineProject On Basic Trigonometry: Presented byRajesh Kumar SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- TrigonometryDocumento7 pagineTrigonometryRagav VijayNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometry WorksheetDocumento4 pagineTrigonometry Worksheetapi-143521979Nessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometry - WikiDocumento46 pagineTrigonometry - WikiNikhil RajNessuna valutazione finora
- TrigonometryDocumento40 pagineTrigonometryThawdar TunNessuna valutazione finora
- E - ContentDocumento8 pagineE - ContentSomasundariNessuna valutazione finora
- Applications of Trigonometry in ConstructionDocumento33 pagineApplications of Trigonometry in ConstructionKeval PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Diocton Edward ADocumento46 pagine3 Diocton Edward AgdhehhhdbdbdnhwNessuna valutazione finora
- SOHCAHTOADocumento17 pagineSOHCAHTOAYsa BurguillosNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 Radian and Degree MeasureDocumento16 pagine1.1 Radian and Degree MeasureJOVANIE CLAVERONessuna valutazione finora
- TrigonometryDocumento36 pagineTrigonometryYoshika GNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometry: "Trig" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocumento10 pagineTrigonometry: "Trig" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeAurelio BuenaventuraNessuna valutazione finora
- TrigonometryDocumento16 pagineTrigonometrysarojtiwary7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of TriangleDocumento10 pagineProperties of Triangleapi-3709966Nessuna valutazione finora
- TrigonometryDocumento14 pagineTrigonometryaditya9463178650173100% (4)
- The Six Trigonometric RatiosDocumento30 pagineThe Six Trigonometric Ratiosmaligaya evelynNessuna valutazione finora
- Q4-Week-12-Grade-9Documento21 pagineQ4-Week-12-Grade-9manueldale0915Nessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometry (1)Documento20 pagineTrigonometry (1)biconyorNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometric Functions 2Documento34 pagineTrigonometric Functions 2Sahil JindalNessuna valutazione finora
- Incircle and Excircles of A Triangle - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento10 pagineIncircle and Excircles of A Triangle - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedianeiljain421Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plane Trigonometry in Modern ApplicationsDocumento12 paginePlane Trigonometry in Modern ApplicationsJOVANIE CLAVERONessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometric Functions - WikipediaDocumento34 pagineTrigonometric Functions - WikipediaDeniz KütükerNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometric Ratios LessonDocumento6 pagineTrigonometric Ratios LessonShaun PattersonNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperbolic Triangle TrigonometryDocumento9 pagineHyperbolic Triangle TrigonometrySakrani SukroNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometry and Its Applications: U. DeepikaDocumento22 pagineTrigonometry and Its Applications: U. Deepikaletter2lalNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths 6Documento19 pagineMaths 6rNessuna valutazione finora
- The Six Trigonometric RatiosDocumento30 pagineThe Six Trigonometric Ratiosmaligaya evelynNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan Trigo Class X by ManishaDocumento20 pagineLesson Plan Trigo Class X by Manishamansiha agrawal82% (17)
- Spherical Trigonometry: Reuleaux TriangleDocumento3 pagineSpherical Trigonometry: Reuleaux TriangleAchandraNessuna valutazione finora
- TrigonometryDocumento101 pagineTrigonometryMarilyn LiconoNessuna valutazione finora
- B2 Module 1 Lesson 2Documento11 pagineB2 Module 1 Lesson 2Kate RellitaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 - Trigonometric FunctionsDocumento26 pagine3 - Trigonometric FunctionsZamanoden D. UndaNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometry WorksheetsDocumento4 pagineTrigonometry Worksheetsapi-150536296Nessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometry Project Explains Its History, Functions and ApplicationsDocumento13 pagineTrigonometry Project Explains Its History, Functions and ApplicationsA for Arunabha33% (3)
- The World of Triangles and Circles: Alyanna Jozeah G. AmbalongDocumento1 paginaThe World of Triangles and Circles: Alyanna Jozeah G. AmbalongAlyanna JozeahNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Holiday Homework (Trigonometric Ratios) X-A Roll No 3Documento11 pagineMaths Holiday Homework (Trigonometric Ratios) X-A Roll No 3daxe ytNessuna valutazione finora
- Cartesian PlaneDocumento39 pagineCartesian PlaneBol Mën NhialNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometry ExplainedDocumento1 paginaTrigonometry ExplainedRuel Lictao Gonzales Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- TrigonometryDocumento12 pagineTrigonometryGwyneth Lei T. ManaoisNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometric FunctionsDocumento3 pagineTrigonometric Functionsapi-150539480Nessuna valutazione finora
- Trig No Metric FunctionDocumento24 pagineTrig No Metric FunctionShishpal SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Law of tangents relationship between tangents and triangle sidesDocumento9 pagineLaw of tangents relationship between tangents and triangle sidesfrawler22Nessuna valutazione finora
- Law of Sine and CosineDocumento10 pagineLaw of Sine and CosineSherpork LoriNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Numerical Skills: Triangles and Trigonometric FunctionsDocumento7 pagineBasic Numerical Skills: Triangles and Trigonometric FunctionshiryanizamNessuna valutazione finora
- Story of Trigonometry: BY:-Name: Rakshit Gupta Class: - XTH - B ROLL NO.: - 13Documento13 pagineStory of Trigonometry: BY:-Name: Rakshit Gupta Class: - XTH - B ROLL NO.: - 13Akshat JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Script Phytagorean Similarity TheoremDocumento4 pagineMath Script Phytagorean Similarity TheoremMarian Nicole NalicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Everything You Need to Know About TrigonometryDocumento10 pagineEverything You Need to Know About Trigonometryjohn sinnyNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Functions and The Right TriangleDocumento15 pagineBasic Functions and The Right TriangleChetan Tolia100% (1)
- Spherical TrigonometryDocumento19 pagineSpherical Trigonometryjohn tanNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Trigonometry IntroductionDocumento4 pagineMaths Trigonometry IntroductionDivyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometric Functions - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento18 pagineTrigonometric Functions - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadaniyalhassan2789Nessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometry Came From Three Greek Words, Tri Which Means Three, Gono Which MeansDocumento1 paginaTrigonometry Came From Three Greek Words, Tri Which Means Three, Gono Which MeansRoberto C. DiscutidoNessuna valutazione finora
- Project 2 1C03Documento6 pagineProject 2 1C03Steven LiNessuna valutazione finora
- I DunnoDocumento71 pagineI DunnoJulius Patrick MallanaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Right Triangle DefinitionsDocumento4 pagineRight Triangle DefinitionsArki TektureNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- AUSL/NLU Lesson Plan TemplateDocumento4 pagineAUSL/NLU Lesson Plan Templateapi-253587612Nessuna valutazione finora
- DM No. 134 S. 2023 Schedule of Division Checking of School Forms For Sy 22 23Documento1 paginaDM No. 134 S. 2023 Schedule of Division Checking of School Forms For Sy 22 23A-jaye CelesenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Report - ResponsesDocumento9 pagineReport - Responseskuruba sairamNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis Statments PDFDocumento8 pagineThesis Statments PDFzkalel_mNessuna valutazione finora
- Bcas BulletinDocumento4 pagineBcas BulletinJay-Jay JapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Cie Igcse o Level Maths Topic 4Documento24 pagineCie Igcse o Level Maths Topic 4Nayeem HakimNessuna valutazione finora
- Bahasa Inggris - Fikri Fauzi KhoirullohDocumento2 pagineBahasa Inggris - Fikri Fauzi KhoirullohFikri FauziNessuna valutazione finora
- Budding Mathematician AwardDocumento7 pagineBudding Mathematician AwardAlvin BugayongNessuna valutazione finora
- Descriptive ReportDocumento2 pagineDescriptive Reportapi-250424750Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final End of Year Grade 4.mathematics.Documento5 pagineFinal End of Year Grade 4.mathematics.nkosi.mkwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Slac Training DesignDocumento6 pagineSlac Training DesignMcjo YasyagasNessuna valutazione finora
- Yearly Math Plan Year 6Documento8 pagineYearly Math Plan Year 6jusipsNessuna valutazione finora
- Children - Patricia Clark Kenschaft - Teaching Elementary School Teachers More MathematicsDocumento5 pagineChildren - Patricia Clark Kenschaft - Teaching Elementary School Teachers More MathematicstamtolemolaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2013 MacDuffie Alumni Magazine (English)Documento18 pagine2013 MacDuffie Alumni Magazine (English)macduffieNessuna valutazione finora
- Packing Methods: Mathematics in The Modern World Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocumento1 paginaPacking Methods: Mathematics in The Modern World Mathematics in The Modern WorldJercell Mae CunananNessuna valutazione finora
- ResumeDocumento2 pagineResumeapi-269981895Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2023 AIMO Prepratory Program Problem Sheet 1 Number TheoryDocumento2 pagine2023 AIMO Prepratory Program Problem Sheet 1 Number TheoryFulcycNessuna valutazione finora
- 2018 AMEP QualifiersDocumento14 pagine2018 AMEP QualifierslilibethNessuna valutazione finora
- Islamic 5 FoldDocumento21 pagineIslamic 5 FoldJun Moss100% (1)
- Boisselle - ResumeDocumento4 pagineBoisselle - Resumeapi-302335965Nessuna valutazione finora
- Term 3 MathsDocumento72 pagineTerm 3 MathsJoshna Rhea BhargavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Poudre School District Long Range Plan (March 2015 Draft)Documento70 paginePoudre School District Long Range Plan (March 2015 Draft)ColoradoanNessuna valutazione finora
- Equations Linear, Quadratic, Cubic and Higher Orders: 86. Degree of AnDocumento60 pagineEquations Linear, Quadratic, Cubic and Higher Orders: 86. Degree of AnFghjbfdxc FnkczvkcxxNessuna valutazione finora
- Maclaurin 14Documento3 pagineMaclaurin 14ichkhuyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Square/Circle Constant: Earth/MatrixDocumento21 pagineThe Square/Circle Constant: Earth/Matrixtrea1701Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Short CutsDocumento4 pagineMaths Short CutsShailesh SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Effectiveness of Using Recount Text To Improve Writing SkillDocumento9 pagineThe Effectiveness of Using Recount Text To Improve Writing SkillSopiahUlfahIINessuna valutazione finora
- Still Life Lesson PlanDocumento2 pagineStill Life Lesson Planapi-2859415070% (1)
- Paper Praktikum Teknik PemrogramanDocumento6 paginePaper Praktikum Teknik Pemrogramanbenny pradanaNessuna valutazione finora
- PDS 1Documento4 paginePDS 1Gian C. GuzmanNessuna valutazione finora