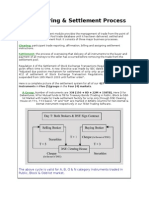
Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Technical Analysis
Caricato da
Alvin TanDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Technical Analysis
Caricato da
Alvin TanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
TECHNICAL ANALYSIS y y y y y Technical analysts or technicians develop technical trading rules from observations of past (prior) price movements
of the stock market and individual stocks. The philosophy behind technical analysis is in sharp contrast to the efficient market hypothesis. It also differs from fundamental analysis. Technical analysis involves the examination of past market data such as prices and the volume of trading, which leads to an estimate of future price trends and therefore an investment decision. The technical analyst uses data from the market itself because they contend that the market is its own best predictor. Technical analysis is an alternative method of making the investment decision and answering the questions: What securities should an investor buy or sell? When should these investments be made? Technical analysts see no need to study the multitude of economic, industry, and company variables to arrive at an estimate of future value because they believe that past price movements will signal future price movements. Technicians also believe that a change in the price trend may predict a forthcoming change in the fundamental variables such as earning and risk before the change is perceived by most fundamental analysts. Underlying assumptions of technical analysis: 1. The market value of any good or service is determined solely by the interaction of supply and demand. 2. Supply and demand are governed by numerous rational and irrational factors. Included are those economic variables as well as moods, opinions, and guesses. The market weighs all these factors continually and automatically. 3. The prices for individual securities and the overall value of the market tend to move in trends, which persist for appreciable lengths of time. 4. Prevailing trends change reaction to shifts in supply and demand relationships. These shifts no matter why they occur can be detected sooner or later in the action of the market itself. Technical analysts expect stock prices to move trends that persist for long periods because they believe that new information does not come to the market at one point in time but rather enters the market over a period of time. Technicians expect a gradual price adjustment to reflect the gradual dissemination of information. Technicians look for the beginning of a movement from one equilibrium to new equilibrium value but do not attempt to predict the new equilibrium value. According to technical analysts, it is important to recognize that the fundamental analysts can experience superior returns only if they obtain new information before other investors and process it correctly and quickly. Technical analysts do not depend heavily on financial accounting statements the major source of information about the past performance of a firm or industry. Major problems with accounting statements: 1. Lack a great deal of information needed by security analysts
y y y
y y
y y
y y
y y y y y y y y y y y y y
2. Corporations may choose among several procedures for reporting expenses, assets or liabilities which can produce vastly different values for expenses, income, ROA, and ROE. Investors can have trouble comparing the statements of two firms. 3. Many psychological factors and other non-quantifiable variables do not appear in the financial statements. Examples are employee training and loyalty, customer goodwill, and general investor attitude towards an industry. While fundamentalists need to process new information quickly and correctly to derive a new intrinsic value for the stock before other investors, technicians only need to quickly recognize a movement to a new equilibrium value for whatever reason. Because most technicians do not invest until the move to the new equilibrium is under way, they contend that they are more likely than a fundamentalist to experience ideal timing. Challenges to technical analysis: 1. Challenge some of its basic assumptions 2. Challenge some specific technical trading rules and their long run usefulness The major challenge to technical analysis is based on the empirical tests of the efficient market hypothesis (EMH). Weak form efficient market hypothesis the market would have to be slow to adjust prices to the arrival of new information that is it would have to be inefficient to generate superior riskadjusted returns after taking account of transaction costs. Two sets of tests of the weak-form EMH: (a) statistical analysis of prices to determine if prices moved in trends or were a random walk, (b) the analysis of specific trading rules to determine if their use could beat a buy-and-hold policy after considering transactions costs and risk An obvious challenge to technical analysis is that the past price patterns or relationships between specific market variables and stock prices may not be repeated. Another problem is that the success of a particular trading rule will encourage many investors to adopt it. Specific trading rules all require a great deal of subjective judgment. The standard values that signal investment decisions can change over time. The end of a declining (bear) market finishes in a trough. Confirmation that the declining trend has reversed would be a buy signal. As long as the stock price stayed in the rising trend channel, the technician would hold the stocks. Technicians would sell the stocks at the peak of the cycle until after the trend changes. If the stock begins trading in a flat pattern (flat trend channel), it will necessarily break out of its rising trend channel. If the stock were to break out of the channel on the downside, it is a sell signal. Almost all technical analysts watch many alternative rules and decide on a buy or sell decision based on a consensus of the signals because complete agreement of all rules is rare. Contrary-opinion rules assume that the majority of investors are wrong as the market approaches peaks and troughs. These technicians trade in the opposite direction of the majority. Mutual funds hold some part of their portfolio in cash for several reasons: 1. Need cash to liquidate shares
y y y
y y
y y y y y y y y y y y y
y y
y y
2. New investments in the mutual fund may not have been invested 3. Portfolio manager might be bearish on the market and want to increase the funds defensive cash position Mutual funds ratios of cash as a percentage of the total assets in their portfolios, cash ratio, are reported in press. (Range: 4% - 11%) Contrary opinion technicians believe that mutual funds usually are wrong at peaks and troughs. Mutual funds have a high percentage of cash near a market trough the time when they should be fully invested. At the market peak, mutual funds are expected to be almost fully invested with a low percentage of cash. Technicians tend to buy when the cash ratio approaches 11% and sell when the cash ratio approaches 4%. A high cash position is a bullish indicator because of potential buying power. A low cash ratio would mean that the institutions have bought heavily and are left with little potential buying power. Credit balances result when investors sell stocks and leave the proceeds with their brokers, expecting to reinvest them shortly. Technical analysts view them as potential purchasing power. A decline in credit balances is considered bearish because it indicates lower purchasing power as the market approaches peak. A build up in credit balances indicates an increase in buying power and is a bullish signal. Many technicians believe that if a large proportion of investment advisory services are bearish; this signals the approach of a market trough and onset of a bull market. Number of bears is greatest when market bottoms are approaching (bullish indicator). Number of bulls is greatest when market tops are approaching (bearish indicator). Speculative trading typically peaks at market peaks. Contrary opinion technicians use put options which give the holder the right to sell stock at a specified price for a given time period, as signals of a bearish attitude. A higher put-call option indicates a pervasive bearish attitude for investors. In terms of stock index futures, technicians would consider it a bearish sign when more than 70% of the speculators are bullish, and a bullish sign when this ratio declines to 30% or lower. Smart money is a set of indicators and corresponding rules that technicians believe indicate the behaviour of smart, sophisticated investors. Confidence index is the ratio of Barrons average yield on 10 top-grade corporate bonds to the yield on the Dow Jones average of 40 bonds. This ratio is a bullish indicator (during periods of high confidence, investors are willing to invest in lower quality bonds which cause a decrease in yield spread, confidence index increases). A popular measure of investor attitude or confidence on a global basis the spread between T-bill yields and Eurodollar rates measured as the ratio of T-bill/Eurodollar yields. Debit balances in brokerage accounts represent borrowing (margin debt) by knowledgeable investors from their brokers; indicate the attitude of sophisticated investors who engage in margin transactions. Increase in debit balances indicates buying and is considered a bullish sign. Decrease in debit balances indicates selling and is considered a bearish sign.
y y y y y y
Breadth of market measures the number of issues that have increased each day and the number of issues that have declined. Advance-decline index is typically a cumulative index of net advances or net declines. To examine individual stocks, the 200 day moving average of prices has been popular. Overbought negative correction greater percentage above their 200 day moving average Oversold positive correction lesser percentage above their 200 day moving average
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- CFA QuicksheetDocumento6 pagineCFA QuicksheetAlvin TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Hbo - CH3Documento3 pagineHbo - CH3Alvin TanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- ACCT1B - Prelims ReviewerDocumento2 pagineACCT1B - Prelims ReviewerAlvin TanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- TQM - BenchmarkingDocumento7 pagineTQM - BenchmarkingAlvin TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Final PrimoDocumento5 pagineFinal Primoaissel50% (2)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- CRANBERRY PLC Scenario Chapter 12Documento3 pagineCRANBERRY PLC Scenario Chapter 12Nguyễn Thanh Thanh HươngNessuna valutazione finora
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Money Banking and Financial Markets 4th Edition Cecchetti Test Bank DownloadDocumento119 pagineMoney Banking and Financial Markets 4th Edition Cecchetti Test Bank DownloadJean Standridge100% (23)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Adani Group - How The World's 3rd Richest Man Is Pulling The Largest Con in Corporate History - Hindenburg ResearchDocumento147 pagineAdani Group - How The World's 3rd Richest Man Is Pulling The Largest Con in Corporate History - Hindenburg ResearchmanusolomonNessuna valutazione finora
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Abdos Credit Rating CARE 2020Documento5 pagineAbdos Credit Rating CARE 2020Puneet367Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- DSE ClearingDocumento6 pagineDSE ClearingMohammed Anwaruzzaman100% (1)
- ACCT550 Homework Week 6Documento6 pagineACCT550 Homework Week 6Natasha DeclanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Careers in Banking and Finance PDFDocumento84 pagineCareers in Banking and Finance PDFJohn AngNessuna valutazione finora
- GR 10 Test Posting To Ledger From CashDocumento10 pagineGR 10 Test Posting To Ledger From CashStars2323Nessuna valutazione finora
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Prelim L1 Assignment TestDocumento3 paginePrelim L1 Assignment TestEMELY EMELYNessuna valutazione finora
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- NDICs Deposit Insurance Scheme in Nigeria - Problems Prospects PDFDocumento17 pagineNDICs Deposit Insurance Scheme in Nigeria - Problems Prospects PDFDaniel AdegboyeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Cost of Capital and Capital Structure PlanningDocumento32 pagineCost of Capital and Capital Structure PlanningAshiq NobitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Security Analysis and Portfolio Management by Rohini SinghDocumento442 pagineSecurity Analysis and Portfolio Management by Rohini SinghNishant Dogra67% (3)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Scrip Bitcoin v1Documento5 pagineScrip Bitcoin v1Mostafa KamjooNessuna valutazione finora
- Dubai Land Department Transfer Fees - 1Documento4 pagineDubai Land Department Transfer Fees - 1praveenNessuna valutazione finora
- Finance PDFDocumento125 pagineFinance PDFRam Cherry VMNessuna valutazione finora
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Bond and Stock ValuationDocumento5 pagineBond and Stock ValuationCh SibNessuna valutazione finora
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- LAS ABM - FABM12 Ia B 1 Week 1Documento9 pagineLAS ABM - FABM12 Ia B 1 Week 1ROMMEL RABONessuna valutazione finora
- Maria Theresia ThalerDocumento5 pagineMaria Theresia ThalerZoltan NagyNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Account: Invoice/Statement of Account Service Tax REG. NO:B16-1808-31031789Documento4 pagineSummary of Account: Invoice/Statement of Account Service Tax REG. NO:B16-1808-31031789NKNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To FinanceDocumento31 pagineIntroduction To FinanceJean FlordelizNessuna valutazione finora
- International Financial Management 7th Edition Eun Test BankDocumento25 pagineInternational Financial Management 7th Edition Eun Test BankMatthewRosarioksdf100% (60)
- Thornado Partnership Statement of Liquidation August 1, 2016 To October 31, 2016Documento3 pagineThornado Partnership Statement of Liquidation August 1, 2016 To October 31, 2016Joannah maeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Sebi SharemarketDocumento19 pagineSebi SharemarketbhavyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Date: November 9, 2020: Bill To: Wuhan Fiberhome International Technologies Philippines, LNCDocumento2 pagineDate: November 9, 2020: Bill To: Wuhan Fiberhome International Technologies Philippines, LNCMartine Amos AntonioNessuna valutazione finora
- Q4 2022 PitchBook Analyst Note 2023 US Private Equity OutlookDocumento14 pagineQ4 2022 PitchBook Analyst Note 2023 US Private Equity Outlookmayowa odukoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Audit Walkthrough QuestionnaireDocumento3 pagineAudit Walkthrough QuestionnaireRey Sabado100% (1)
- Pro Forma Invoice: Chemxo Trading FZEDocumento1 paginaPro Forma Invoice: Chemxo Trading FZErmautomobiles.dhkNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Statement Analysis Wipro LTDDocumento35 pagineFinancial Statement Analysis Wipro LTDAnitha PanneerselvamNessuna valutazione finora
- 26ASDocumento4 pagine26ASYash KavteNessuna valutazione finora
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)