Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
NCP 2 Qi
Caricato da
Karlo Tuazon SedigoDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
NCP 2 Qi
Caricato da
Karlo Tuazon SedigoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
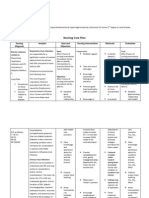
NURSING CARE PLAN
Assessment Analysis
Subjective: Nanghihinatal agaakokadala san as verbalized by the client. Mahiluhinnga din ako e as verbalized by the client, Objective: Pale skin Fatigue Increased respiratory rate RR: 28 Laboratory results: Hemoglobin: 81 Hematocrit: 0.25 WBC: 23.1 x10 g/l Sepsis is a clinical term used to describe symptomatic bacteremia, with or without organ dysfunction. Sustained bacteremia, in contrast to transient bacteremia, may result in a sustained febrile response that may be associated with organ dysfunction. Septicemia refers to the active multiplication of bacteria in the bloodstream that
Diagnosis
Risk for infection related to compromised immune.
Planning
Goal: After 8 hours of nursing intervention the infection must be eliminated or controlled. Objectives: After 1 hour of nursing intervention the client will able to: y Understand the risk of infection Determine the techniques to reduce the risk of infection
Intervention
Independent: Provide isolation or monitor visitors as indicated.
Rationale
Evaluation
Infection was eliminated or controlled. Client able to understand risk of infection. Client able to determine the techniques to reduce the risk of infection.
Body substance isolation (BSI) should be used for all infectious patients. Wound/linen isolation and hand washing may be all that is required for draining wounds. Patients with diseases transmitted through air may also need airborne and droplet precautions. Reverse isolation/restriction of visitors may be needed to protect the immunosuppressed patient. Reduces risk of crosscontamination because gloves may have unnoticeable defects, get torn or damaged during use. Good pulmonary toilet may reduce respiratorycompromis
Wash hands with antimicrobial soap/ after each care activity, even if gloves are used.
Encourage/provide frequent position changes, deep-
Salud, Rausan J. BSN216/ Group 64
Ms. Liza Villacorte Clinical Insrtuctor
NURSING CARE PLAN
results in an overwhelming infection. breathing/coughing exercises. Encourage patient to cover mouth and nose with tissue during coughs/sneezes. Wear mask when providing direct care as appropriate. Dispose of soiled dressings/materials in double bag. e. Prevents spread of infection via airborne droplets.
Reduces contamination/soilage of area; limits spread of airborne organisms. To increase awareness and to minimize spread of infection.
Instruct the client in techniques in prevention of spread of infection.
Collaborative: Obtain specimens of urine, blood, sputum, wound, invasive lines/tubes as indicated for Gram stain, culture, and sensitivity. Monitor laboratory studies, e.g., WBC count with Salud, Rausan J. BSN216/ Group 64
Identification of portal of entry and organism causing the septicemia is crucial to effective treatment.
The normal ratio of neutrophils to total WBCs is at least Ms. Liza Villacorte Clinical Insrtuctor
NURSING CARE PLAN
neutrophil and band counts. 50%; however, when WBC count is markedly decreased, calculating the absolute neutrophil count is more pertinent to evaluating immune status.
Reference: http://www.scribd.com/d oc/ 9658938/ Sepsis-Septicemia
Salud, Rausan J. BSN216/ Group 64
Ms. Liza Villacorte Clinical Insrtuctor
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Fundamental Aspects of Infection Prevention and ControlDa EverandFundamental Aspects of Infection Prevention and ControlNessuna valutazione finora
- Infections in ICUDocumento7 pagineInfections in ICUNikolay ToméNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Neonatal SepsisDocumento1 paginaNCP Neonatal SepsisGen-GenMedranoGirayNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Lab Unit 11Documento7 pagineCourse Lab Unit 11FREVILYN ABASTANessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Nadia Aziz C.A.B.C.M Baghdad Medical CollegeDocumento39 pagineDr. Nadia Aziz C.A.B.C.M Baghdad Medical CollegeMazinNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan (Risk For Infection) CVADocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan (Risk For Infection) CVAawesomedawn50% (4)
- Assessmen T Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocumento1 paginaAssessmen T Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationKurtt Evan ValinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Adenomyosis NCPDocumento2 pagineAdenomyosis NCPBrainan Aquino100% (2)
- Module 8Documento2 pagineModule 8Tricia Mae GutibNessuna valutazione finora
- I and I MODULE INFECTIOUS DISORDERSDocumento23 pagineI and I MODULE INFECTIOUS DISORDERSJeffrey GazmenNessuna valutazione finora
- I and I Module Infectious DisordersDocumento23 pagineI and I Module Infectious DisordersCaitlynNessuna valutazione finora
- Intensive Care Unit: DR Amr KandeelDocumento46 pagineIntensive Care Unit: DR Amr KandeelPranav UppadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- M. Tuberculosis M. LepraeDocumento47 pagineM. Tuberculosis M. LepraeFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationPaul Cubacub100% (1)
- Infection and Prevention Control-2Documento14 pagineInfection and Prevention Control-2NIKHIL RAJNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Foundation: Unit Xi Infection Control in Clinicl SettingDocumento45 pagineNursing Foundation: Unit Xi Infection Control in Clinicl Settingbemina jaNessuna valutazione finora
- Infection PreventionDocumento64 pagineInfection PreventionAnonymous Iyf0Rjmdm3Nessuna valutazione finora
- NR 224 Week 1 Instuctor Unit 1 Questions and AnswersDocumento7 pagineNR 224 Week 1 Instuctor Unit 1 Questions and AnswersJesse JohnsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Anesthaesia and Intensive CareDocumento139 pagineAnesthaesia and Intensive CareIvan Kurniadi100% (2)
- Infection Control Policies and ProceduresDocumento9 pagineInfection Control Policies and ProceduresKelly J WilsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Candida AurisDocumento5 pagineCandida Aurisarunkumar76Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anaesthesia & Intensive Care: For Fcai, Frca EdaicDocumento139 pagineAnaesthesia & Intensive Care: For Fcai, Frca EdaicMuhammad Farid100% (1)
- Module Infectious and InflammatoryDocumento6 pagineModule Infectious and InflammatoryMerald PerdigonNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal Club Discussion - Sep 2014: Jegen Kandasamy MD Pgy-6, NPMDocumento23 pagineJournal Club Discussion - Sep 2014: Jegen Kandasamy MD Pgy-6, NPMjaydoc_paed@yahoo.co.inNessuna valutazione finora
- Ventilator Associated Pneumonia 1Documento14 pagineVentilator Associated Pneumonia 1Tulus ArisonoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP InfectionDocumento3 pagineNCP InfectionPrince AhmirNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality & Safety Issues in BMW Quality & Accreditation Standards Bio Medical Waste Handlers SafetyDocumento12 pagineQuality & Safety Issues in BMW Quality & Accreditation Standards Bio Medical Waste Handlers SafetyParth SoniNessuna valutazione finora
- RN Lesson 2 Safety & Infection Control Practice Test (Required)Documento11 pagineRN Lesson 2 Safety & Infection Control Practice Test (Required)Ruthmarie CatarajaNessuna valutazione finora
- Infection Control Care BundlesDocumento3 pagineInfection Control Care BundlesvikramadityapeepreNessuna valutazione finora
- Arjumand Zargar Anp@AARUSIMIDocumento69 pagineArjumand Zargar Anp@AARUSIMIArjumand ZargarNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar in PN - Infection Control Practices2Documento93 pagineSeminar in PN - Infection Control Practices2Sara HamzaNessuna valutazione finora
- All Short Notes of ICDocumento30 pagineAll Short Notes of ICaarti HingeNessuna valutazione finora
- Belluomini - Clean Needle TechniqueDocumento81 pagineBelluomini - Clean Needle Techniquealbertomtch75% (4)
- Vasquez - Bsn4a - Case Studies - Optional Credit (30 Points) - NCM 120 & Ic 7Documento4 pagineVasquez - Bsn4a - Case Studies - Optional Credit (30 Points) - NCM 120 & Ic 7Mari Sheanne M. VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is PlagueDocumento3 pagineWhat Is Plagueanon_959000253Nessuna valutazione finora
- How Is A Wound Infection Treated?Documento5 pagineHow Is A Wound Infection Treated?Haider JulailiNessuna valutazione finora
- How Is A Wound Infection Treated?Documento5 pagineHow Is A Wound Infection Treated?Haider JulailiNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento5 pagineNCPf_jm06_gNessuna valutazione finora
- Universal PrecautionDocumento39 pagineUniversal PrecautionSyifa MustikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Septicemia NCPDocumento3 pagineSepticemia NCPJaessa Feliciano0% (1)
- Unit - Two - Infection Control - Universal PrecautionsDocumento31 pagineUnit - Two - Infection Control - Universal Precautionsvirtus_kuwaitNessuna valutazione finora
- 0907 UniversalDocumento6 pagine0907 UniversalRenisa HutahaeanNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 - Infection ControlDocumento45 pagine4 - Infection ControlNoura RihanNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocumento26 pagineRespiratory Tract InfectionsyousefismailrootNessuna valutazione finora
- Ovarian Cancer NCPDocumento3 pagineOvarian Cancer NCPEm Emer Emerson0% (5)
- Methods of Prevention and Control of InfectionDocumento5 pagineMethods of Prevention and Control of InfectionDauda Muize AdewaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Five Summary of Findings, Conclusion and RecommendationsDocumento5 pagineChapter Five Summary of Findings, Conclusion and RecommendationsKojo AduNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study On Knowledge and Practice of Nursing Staff Towards Infection Control MeasuresDocumento17 pagineA Study On Knowledge and Practice of Nursing Staff Towards Infection Control MeasuresPriyanka SatalkarNessuna valutazione finora
- HandwashingDocumento36 pagineHandwashingidelleequibalNessuna valutazione finora
- Ssi Presentation 1226839149141241 9Documento36 pagineSsi Presentation 1226839149141241 9Wasim R. IssaNessuna valutazione finora
- Universal PrecautionDocumento10 pagineUniversal PrecautionParth VasaveNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study: Patient With Appendicitis: Submitted By: Farzaneh Yeganeh Submitted To: Ms. Amara SabriDocumento19 pagineCase Study: Patient With Appendicitis: Submitted By: Farzaneh Yeganeh Submitted To: Ms. Amara Sabrifarzaneh yeganehNessuna valutazione finora
- Annexure-XX Clinical Management Protocol: (Novel Influenza A H1N1)Documento3 pagineAnnexure-XX Clinical Management Protocol: (Novel Influenza A H1N1)Ramadi PrameelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Microbiology Assignment 1Documento3 pagineMicrobiology Assignment 1Bia BlancaNessuna valutazione finora
- Respi, GI, GU, Repro DiseasesDocumento6 pagineRespi, GI, GU, Repro DiseasesAngela OngNessuna valutazione finora
- Surgical InfectionsDocumento20 pagineSurgical InfectionsDr-Mohammad Ali-Fayiz Al TamimiNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP and DrugsDocumento13 pagineNCP and DrugsApRil ANn ChUa BingcangNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 1 VapDocumento1 paginaGroup 1 VapMoon KillerNessuna valutazione finora
- Infection Control - LESSON PLANDocumento53 pagineInfection Control - LESSON PLANJincy JohnyNessuna valutazione finora
- Postoperative Nursing Care Plan For Cesarian Section Patient Case Pres orDocumento6 paginePostoperative Nursing Care Plan For Cesarian Section Patient Case Pres orLoren EstefanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lynch Syndrome For The Gynaecologist, TOG-2021Documento12 pagineLynch Syndrome For The Gynaecologist, TOG-2021saeed hasan saeedNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry - Meaning & ScopeDocumento2 pagineBiochemistry - Meaning & ScopeBasudev GoswamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Scott 2003Documento10 pagineScott 2003evilelagNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Hemodynamic Monitoring: Basics and New Horizons: Mikhail Y. Kirov Vsevolod V. Kuzkov Bernd SaugelDocumento289 pagineAdvanced Hemodynamic Monitoring: Basics and New Horizons: Mikhail Y. Kirov Vsevolod V. Kuzkov Bernd SaugelIda Katarina75% (4)
- ĐA ĐỀ 124 (VIP 23)Documento23 pagineĐA ĐỀ 124 (VIP 23)thanhnam2982005Nessuna valutazione finora
- Proline HbA1c Net FS SP201909.00Documento4 pagineProline HbA1c Net FS SP201909.00TasrifNessuna valutazione finora
- P 6-ScienceDocumento8 pagineP 6-ScienceMonydit santinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibiotics and Drugs: Drug-Nutrient Interactions: KM Gura, Boston Children's Hospital, Boston, MA, USADocumento18 pagineAntibiotics and Drugs: Drug-Nutrient Interactions: KM Gura, Boston Children's Hospital, Boston, MA, USAEko SetNessuna valutazione finora
- National Board of Examinations Dated: 19 April 2018: Question Paper For NEET-SSDocumento6 pagineNational Board of Examinations Dated: 19 April 2018: Question Paper For NEET-SSrajvolgaNessuna valutazione finora
- BMED3100 Fall16 HW4-keyDocumento2 pagineBMED3100 Fall16 HW4-keyAnonymous yWHBqVa3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Complications of Local AnesthesiaDocumento80 pagineComplications of Local AnesthesiaRiya JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Intraoperative Surgical Complication During Cesarean SectionDocumento14 pagineIntraoperative Surgical Complication During Cesarean Sectioncarbolico100% (1)
- Underestanding Periods.Documento11 pagineUnderestanding Periods.Counseling BGANessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Treatment Planning Approach Facing A Failure of Conventional Treatment. Part I: Analysis of Treatment OptionsDocumento11 pagineModern Treatment Planning Approach Facing A Failure of Conventional Treatment. Part I: Analysis of Treatment OptionscdoskarNessuna valutazione finora
- Over The Counter MedicinesDocumento3 pagineOver The Counter MedicinesJhun Echipare100% (3)
- Breast Cancer Risks RecommendationsDocumento2 pagineBreast Cancer Risks RecommendationsYohannes GirmawNessuna valutazione finora
- Nnu 3112 Medical Physiology I 1Documento6 pagineNnu 3112 Medical Physiology I 1bosco kiuriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine Disorders PDFDocumento55 pagineEndocrine Disorders PDFAkram HusseinNessuna valutazione finora
- Orphan DrugsDocumento16 pagineOrphan Drugssakumar5678Nessuna valutazione finora
- Digestive and Respiratory System ExamDocumento3 pagineDigestive and Respiratory System ExamAnonymous zGjXogXNessuna valutazione finora
- Afalanga CVDocumento17 pagineAfalanga CVBagasNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolic Bone DisordersDocumento24 pagineMetabolic Bone Disordersbpt20% (1)
- CraniectomyDocumento5 pagineCraniectomytabanaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Causes of Death in BurnsDocumento9 pagineCauses of Death in Burnsniraj_sdNessuna valutazione finora
- Obat NefrotoksikDocumento5 pagineObat NefrotoksikIndah Nur LathifahNessuna valutazione finora
- Ovarian Dysgerminomas Pathology Overview of Ovarian DysgerminomasDocumento7 pagineOvarian Dysgerminomas Pathology Overview of Ovarian DysgerminomasDevi SyamNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Zonal Occult Outer Retinopathy A Classification Based On Multimodal ImagingDocumento10 pagineAcute Zonal Occult Outer Retinopathy A Classification Based On Multimodal ImagingStefanieNessuna valutazione finora
- Tropical AnemiaDocumento315 pagineTropical AnemiaRajesh BholaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs Used For GlaucomaDocumento40 pagineDrugs Used For GlaucomaAgust SalimNessuna valutazione finora
- Urtica Urens William Boericke Cyrus Maxwell Bogar Adolf Zur Lippe John Henry ClarkeDocumento9 pagineUrtica Urens William Boericke Cyrus Maxwell Bogar Adolf Zur Lippe John Henry ClarkeShah FaisalNessuna valutazione finora