Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Sample Paper Biology
Caricato da
Mini PGDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Sample Paper Biology
Caricato da
Mini PGCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Q.1: Define the term tissue?
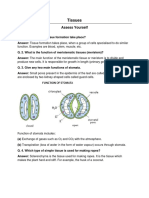
Ans: The group of cells similar in structure that work together to achieve a particular function forms a tissue. This group of cells has a common origin. Q.2: How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them. Ans: Xylem is a complex tissue. It is made up of following four kinds of cells or elements: (a) Tracheids (b) Vessels (c) Xylem parenchyma (d) Xylem fibres. Q.3: How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants? Ans: Simple tissues are made up of one type of cells which coordinate to perform a common function. Complex tissues are made up of more than one type of cells. all these coordinate to perform a common function. Q.4: Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchymas and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall. Ans: The differences between cell walls of parenchyma, collenchymas and sclerenchyma are given in the following table: Parenchyma 1. Cell wall is primary 2. Cells have thin walls and made up of cellulose. Collenchyma 1. Cell wall is primary. 2. Cell walls are thickened at the corners due to protein deposition. Q.5: What are the functions of Stomata? Ans: The small pores present in the epidermis of the leaf are stomata. Stomata are enclosed by two kidney shaped cells called guard cells. Functions of Stomata 1. Exchange of gases, particularly CO2 and O2, with atmosphere. 2. Loss of water in the form of vapour during transpiration. Q.6: Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres. Ans: Fig: Striated muscles Sclerenchyma 1. Cell wall is secondary. 2. Cell wall is very thick due to lignin deposition.
Fig: Smooth (Un-striated) muscles
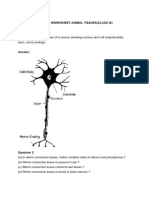
Fig: Cardiac muscles Q.7: What is the specific function of cardiac muscle? Ans: Cardiac muscles are involuntary muscles which show characteristics of both smooth and striated muscles. These muscles occur in the walls of the heart. Functions of Cardiac Muscles 1. Cardiac muscles contract and relax rapidly, rhythmically and tirelessly throughout life. They contract endlessly from early embryonic stage until death. 2. The contraction and relaxation of heart muscles help to pump and distribute blood to various parts of body. Q.8: Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site / location in the body. Ans: Striated, Unstriated and Cardiac muscles are three types of muscle tissues. Their different characteristics are as follows: Character 1. Shape of cells 2. Nucleus 3. Striation 4. Mode of Contraction 5. Example of location Striated Muscles Cells are long cylindrical, non-tapering and un-branched Many nuclei (multi-nucleated) which are situated towards the periphery of muscle fibre. Transverse alternate light and dark bands present. Voluntary contract rapidly but soon undergo fatigue. Hands, legs and other skeletal muscles. Q9: Draw a labeled diagram of neuron. Ans: Unstriated Muscles Cells are long with tapering ends (spindle shape) and un-branched. The cells have only one nucleus (uni-nucleated) situated in the center. Striations or strips are absent. Involuntarily not at our will. Contract comparatively slow but do not fatigue. Stomach wall, intestine, ureter, bronchi etc. Cardiac Muscles Cells are non-tapering, cylindrical and branched. Each cell contains one or two nuclei situated in the center. Cells have faint striations. Involuntary, rhythmically contract and relax throughout life without fatigue under normal conditions. Present in heart.
Fig: Neuron Q.10: Name the following: (a) Tissue that forms inner lining of our mouth. (b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans. (c) Tissue that transports food in plants. (d) Tissue that stores fat in our body. (e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix. (f) Tissue present in brain. Ans: (a) Squamous epithelium (b) Tendon (c) Phloem (d) Adipose tissue (e) Blood (f) Nervous tissue. Q.11: Identify the type of tissue in the following: Skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle. Ans: (i) Skin - Striated Squamous epithelium (ii) Bark of tree - Cork protective tissue (iii) Bone - Connective tissue (iv) Lining of kidney tubule - Cuboidal epithelium (Cuboidal epithelial tissue) (v) Vascular bundle - Complex permanent tissue (Xylem and Phloem) Q.12: Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present. Ans: Parenchyma is a simple permanent tissue of angiospermic plants. It is present in cortex and pith of stem and roots. It is also present in mesophyll of leaves. When it contains chlorophyll, it is called Chlorenchyma, found in green leaves. Q.13: What is the role of epidermis in plants? Ans: Epidermis is a protective tissue of angiospermic plants. It provides protections to underlying tissues. Epidermis forms outer covering of various plant organs such as roots, stem, leaves, and flowers and remains in direct contact with the environment. Any substance whether solid, liquid or gas can enter into the plant or move outside only after passing through this layer. Epidermis helps in absorption, secretion, gaseous exchange and transpiration. It helps in preventing the entry of pathogens. Q.14: How does the cork act as a protective tissue? Ans: The cork cells are dead cells and do not have any intercellular spaces. The cell wall of the cork cells are coated with suberin (a waxy substance). Suberin makes these cells impermeable to water and gases. Cork is protective in function; it protects underlying tissues from desiccation, infection and mechanical injury. NCERT (CBSE) Class IX Science
Q.1: the end of a long bone is connected to another bone by (a) Ligament (b) Tendon (c) Cartilage (d) Muscle Q.2: Ligaments and Tendons are formed of (a) Epithelial tissue (b) Muscular tissue (c) Cartilage (d) Connective tissue Q.3: When boiled in water collagen changes into (a) Gelatin (b) Reticulin (c) Elastin (d) Myosin Q.4: Processes of osteoblasts are found in (a) Lamella (b) Canaliculi (c) Dendrites (d) Haversian canals Q.5: A group of cells alike in form, function and origin is called (a) Tissue (b) Organ (c) Organelle (d) None of these Q.6: Plant length is increased by (a) Apical meristems (b) Lateral meristems (c) Periblem (d) Parenchyma Q.7: The cell division is restricted to (a) Merismatic cells (b) Permanent cells (c) Secretory cells (d) All of the above Q.8: Active divisions take place in the cells of (a) Phloem (b) Sclerenchyma (c) Xylem (d) Cambium Q 9: Grass stem elongates by the activity of (a) Apical meristem (b) Hypodermis (c) Intercalary meristem (d) Primary meristem Q.10: Water and minerals are conducted by (a) Xylem (b) (c) (d) Q.11: In higher plants food is conducted by (a) Root (b) Phloem (c) Xylem (d) Leaves Q.12: Blood is a (a) Fibre (b) Non-connective tissue (c) Organ (d) Connective tissue Q.13: Bone consists of the following type of cells (a) Chondrocyte (b) Connective (c) Osteocyte (d) None of these Q.14: Cartilage consists of which type of cells (a) Chondrocyte (b) Osteocyte (c) Cambium (d) None of these Q.15: A nerve impulse passes from one neuron to another across a (a) Synapse (b) Dendrite (c) Axion (d) Cell body Q.16: Collenchyma mainly forms (a) Hypodermis (b) Epidermis (c) Phloem (d) Inner cortex Q.17: Whose living cells provide tensile and mechanical strength? (a) Collenchyma (b) Sclerenchyma (c) Phloem (d) Sclereids Q.18: Lignified elongated dead cells are (a) Parenchyma (b) Collenchyma (c) Sclerenchyma (d) None of these Q 19: Which of these contains dead cells mainly? (a) Phloem (b) Epidermis (c) Xylem (d) Endodermis Q.20: Phloem performs the function of (a) Conduction of food (b) Conduction of water (c) Providing support (d) Photosynthesis Q.21: Simple epithelium is a tissue composed of cells which are (a) Hardened and provide support to organs (b) Continuously diving to provide to form an organ (c) Cemented directly to one another to form an irregular layer (d) Loosely connected to one another to form an irregular layer Q.22: Which one of the following is living but non-nucleated (a) Sieve tube (b) Companion cell (c) Phloem cell (d) Phloem parenchyma Q.23: Which one of the following is a function of white blood cells? (a) Help in transport of oxygen (b) Act as soldiers, scavengers and builders of the body (c) Help in blood clotting (d) None of these Q.24: In human beings, muscle cells (a) Conduct food and water (b) Carry message from brain (c) Contract and relax to cause movement (d) Transport oxygen and other gases Q.25: Muscles contain special protein called (a) Tubulin (b) Contractile (c) Carrier (d) Globulins Q.26: Bone is an example of (a) Epithelial tissue (b) Muscular tissue (c) Connective tissue (d) Nervous tissue Q.27: Areolar connective tissue is found between (a) Skin and muscles (b) Blood vessels and nerves (c) In the bone marrow (d) All of these Q.28: The hardness of the bone tissue is due to the phosphates and carbonates of (a) Calcium and sodium (b) calcium and magnesium (c) Magnesium and sodium (d) Magnesium and potassium Q 29: Ciliated epithelium is present in (a) Trachea (b) Tongue (c) Uterus (d) Heart Q.30: Husk of coconut is made of (a) Sclerechymatous tissue (b) Parenchyma (c) Collenchyma (d) Chlorenchyma Ans: 1-a. 2-d. 3-a. 4-b. 5-a. 6-a. 7-a. 8-d. 9-c. 10-a. 11-b. 12-d. 13-c. 14-a. 15-a 16-a. 17-a. 18-c. 19-c. 20-a. 21-c. 22-a. 23-b. 24-c. 25-b. 26-c. 27-d. 28-b. 29-a. 30-a NCERT (CBSE) Class IX Science Chapter 6, Tissues - Further study
1: What is a tissue? Ans: A tissue is a group or collection of similar cells which work together to achieve a particular function and have common origin. Blood, phloem and muscles are all examples of tissues. Q.2: What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms? Ans: In multicellular organisms there are millions of cells. Most of these cells are specialized to carry out a few functions. Each specialized function is taken up by a different group of cells or tissues. Since these cells of a tissue carry out only a particular function, they do it very efficiently. The tissues are arranged and designed so as to give the highest possible efficiency of function. For example, in human beings, muscle cells contract and relax to cause movement, nerve cells carry messages and blood flows to transport oxygen, food, hormones and waste materials etc. Likewise in plants, vascular tissues (xylem, phloem) conduct water and food from one part of the plant to other parts. So, multicellular organisms exhibit division of labour. Q.3: Name types of simple tissues. Ans: Types of simple tissues: Parenchyma, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma. Q.4: Where is apical meristem found? Ans: Apical meristem is found in shoot apex and root apex of an angiospermic plant. Q.5: Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut? Ans: Sclerenchymatous tissue Q.6: What are the constituents of phloem? Ans: Phloem is a complex tissue. It transports food from leaves to other parts of the plant. Phloem is made up of four types of elements: Sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres and the phloem parenchyma. Q.7: Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body. Ans: Muscular tissue. Q.8: What does a neuron look like? Ans: Refer to the NCERT Textbook Exercise Solution Q.No.9 of this chapter. Q9: Give the three features of cardiac muscles. Ans: Three features of cardiac muscles are as follows (i) Cardiac muscle cells are cylindrical branched and uninucleate. (ii) They show rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout life. (iii) They are involuntary muscles. Q.10: What are the functions of areolar tissue? Ans: Areolar tissues are connective tissues found between the skins and muscle around blood vessels and nerves and in the bone marrow. It fills space inside the organs, support internal organs and help in repair of the tissues
Human cheek cells are commonly stained with a. methylene blue b. safranin c. acetocarmine d. eosine 2. Definite shape of cell is seen in case of a. animal cell b. plant cells c. both animal and plant cells d. neither animal nor plant cells 3. Coverslip is put on the mounted material on a slide very gently to a. avoid oozing of stain b. avoid oozing of glycerine c. avoid entry of air bubbles d. avoid the crushing of mounted materials 4. Name the stain which is commonly used to study plant cells a. methylene blue b. cotton blue c. safranin d. acetocarmine 5. Plant cells generally have a. No vacuoles at all b. all equal sized vacuoles c. small but large number of vacuoles d. big but less number of vacuoles 6. We generally mount the material on slide a. on left side of slide b. on right side of slide c. in the centre d. both (a) and (b) 7. Cells are focused in microscope under a. 40X b. 100X c. 10X d. any of these 8. In animal cheek cells, nucleus is generally located a. near the plasma membrane b. on one side c. in the centre d. any where in the cell 9. In plant cell, nucleus is generally placed a. in the centre b. on one side of the cell c. attached to cell membrane d. on one corner of the cell 10.Temporary mount of a tissue is made in a. wax b. alcohol c. xylene d. glycerine 11. The outermost covering of a plant cell is a. cell wall b. nuclear membrane c. plasma membrane d. middle lamella 12. The organelle not present in human cheek cell is a. nucleus b. mitochondria c. cell membrane d. chloroplast 13. The outer most layer of human cheek cell is a. cell wall b. nuclear membrane c. plasma membrane d. middle lamella 14. The shape of onion peel cells taken for observation under microscope is a. round b. elliptical c. rectangular d. round 15. The shape of nucleus in a plant cell is a. round b. elliptical c. rectangular d. triangular
16. The number of lenses in a compound microscope is a. 2 b. 1 c. 3 d. 4 17. During observation of an onion peel, cells are first seen under a. high power b. low power c. medium power d. none of the above 18. To prepare a mount of human cheek cell, the sample is collected from a. outer side of cheek with a blade b. inner side of cheek with a blade c. outer side of cheek with a toothpick d. inner side of cheek with a toothpick. 19. Which one of the following cell constituents cannot be seen while observing a human cheek cell? a. nucleus b. cell wall c. cytoplasm d. cell membrane 20. To observe cells in an onion peel, we must prepare the slide by mounting on it a. crushed pulp of onion b. dry scale leaf c. green leaf of onion d. thin layer of fleshy onion 21. The cellular component not seen under a compound microscope while observing onion peel a. chromosome b. cell wall c. nucleus d. cytoplasm 22. Cells are stained to a. nourish the cell b. highlight the cell organelles c. make the cell turgid d. help in cell multiplication 23. human cheek cell stained in methylene blue and mounted in glycerine were observed under a compound microscope. The components of cell which would be seen are a. cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus b. plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus c. plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria d. plasma membrane, nucleus, mitochondria lysosomes 24. Magnifying power of a microscope is calculated by a. multiplying the power of objective lens and eye piece b. multiplying the power of objective lens with the distance between the objective lens and the specimen c. adding up the power of objective lens and eye piece d. subtracting the power of objective lens from that of eye piece. 25. Glycerine is used to prepare a temporary mount of a tissue due to the following reason a. to colour the specimen b. to avoid drying up of the specimen quickly c. to avoid entry of air bubbles d. none of the above 26.The less stained central part of onion peel cell is a. nucleus b. cytoplasm c. vacuole d. cell wall 27.Which one of the following is the correct sequence for preparing a mount of onion peel a. (i) take out onion peel (ii) keep the peel on the slide (iii) add a few drop of glycerine on it (iv) add few drops of safranin stain (v) cover it up with a coverslip b. (i) take out onion peel (ii) keep the peel in water in a petridish (iii) add a few drops of safranin stain and transfer to a slide (iv) add a drop of glycerine (v) cover it up with a coverslip c. (i) take out onion peel (ii) Keep it on a slide and add safranin stain (iii) transfer it to water in a petridish (iv) remove water and add glycerine (v) cover it up with a coverslip d. (i) take out onion peel (ii) cover it up with a coverslip (iii) on a petridish, add water to clean (iv) add a drop of glycerine (v) add a few drops of safranin stain 28. Given below four operations for preparing a temporary mount of human cheek cells- (i) taking scraping from inner side of cheek and spreading it on a clean slide. (ii) putting a drop of glycerine on the material. (iii) adding 2-3 drops of methylene blue. (iv) rinsing the mouth with fresh water and disinfectant solution. The correct sequence of these operation is a. i ii iii iv b. iv i iii ii c. iv i ii iii d. i iii ii iv
ANSWERS TO MCQs BIOLOGY CLASS IX
EXPERIMENT NO1 1 a 15 b 2 b 16 a 3 c 17 b 4 c 18 d 5 d 19 b 6 c 20 d 7 a 21 a 8 c 22 b 9 b 23 b 10 d 24 a 11 a 25 b 12 d 26 b 13 c 27 b 14 c 28 b
EXPERIMENT NO2 1 a 9 d 2 d 10 b 3 c 11 d 4 c 12 a 5 d 13 a 6 b 14 c 7 c 15 b 8 d 16 c
EXPERIMENT NO3 1 c 8 a 2 a 9 c 3 d 10 c 4 a 11 c 5 c 12 b 6 c 13 b 7 c 14 b
EXPERIMENT NO4 1 b 6 c 2 a 7 d 3 b 8 d 4 c 9 a 5 d 10 -
EXPERIMENT NO5 1 d 5 d 2 d 6 a 3 c 7 c 4 d
STUDENTS-LEARN.BLOGSPOT.COM
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 6Documento16 pagineImportant Questions For CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 6VI A 19 Aaryan JadhavNessuna valutazione finora
- TissuesDocumento23 pagineTissuesAadarsh RameshNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Chapter-6-TissueDocumento11 pagineScience Chapter-6-TissueJEETNessuna valutazione finora
- BiologyDocumento19 pagineBiologyBhavyaraj GohilNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 09 Biology - Chapter Tissue Solved Questions - 6Documento2 pagineClass 09 Biology - Chapter Tissue Solved Questions - 6Anusha AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- 9th Bio Important QuesDocumento12 pagine9th Bio Important QuesData ShareNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - Tissues: Plant and Animal Tissues ExerciseDocumento8 pagineChapter 3 - Tissues: Plant and Animal Tissues ExerciseArpan KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- 9th TissueDocumento6 pagine9th TissueRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues: Assess YourselfDocumento16 pagineTissues: Assess YourselfGamer JiNessuna valutazione finora
- NCERT Exemplar For Class 9 Science Chapter 6Documento30 pagineNCERT Exemplar For Class 9 Science Chapter 6Vidhan PanwarNessuna valutazione finora
- TissuesDocumento22 pagineTissuesmustafathegreat02Nessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Test-1class Ix TissuesDocumento5 pagineRevision Test-1class Ix TissuesAnwesh NayakNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 9TH Biology TissueDocumento4 pagineClass 9TH Biology TissueChirag KashyapNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Q&ADocumento6 pagineTissue Q&ASuman DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Paper of TissuesDocumento9 pagineSample Paper of TissuesPritamprakash JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 9 Chapter 6Documento22 pagineNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 9 Chapter 6harshitsingh433379Nessuna valutazione finora
- Selina Solutions For Class 9 Biology Chapter 3 Tissues Plant and Animal TissuesDocumento12 pagineSelina Solutions For Class 9 Biology Chapter 3 Tissues Plant and Animal TissuesleenaapNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 BiologyDocumento8 pagineChapter 6 BiologyMohammed mahfuzNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues Class 9 Mcqs Questions With AnswersDocumento13 pagineTissues Class 9 Mcqs Questions With AnswersSCIENCE WORK [AMP] ActivitiesNessuna valutazione finora
- ST - John'S School Greater Noida West Subject: Science CLASS IX: BIOLOGY (2020 - 21) Chapter - 6 Tissues (Answer Key - 2)Documento6 pagineST - John'S School Greater Noida West Subject: Science CLASS IX: BIOLOGY (2020 - 21) Chapter - 6 Tissues (Answer Key - 2)India Tech with AstitvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues MCQDocumento9 pagineTissues MCQtraptisharma3342Nessuna valutazione finora
- Aakash Institute: NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 TissuesDocumento13 pagineAakash Institute: NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 TissuesNischay MahamanaNessuna valutazione finora
- 9th Bio MTG Tissue QuesDocumento13 pagine9th Bio MTG Tissue QuesData ShareNessuna valutazione finora
- 910th Bio QuesDocumento19 pagine910th Bio QuesData ShareNessuna valutazione finora
- Epithelial TissueDocumento2 pagineEpithelial Tissueapi-295869261Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Tissues G-IXDocumento3 pagineBiology Tissues G-IXSrinivas VenkataramanNessuna valutazione finora
- 9bio AssignmentDocumento2 pagine9bio AssignmentKrishna GovilNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOLOGY WORKSHEET-ANIMAL TISSUES (Launch Pad 1)Documento11 pagineBIOLOGY WORKSHEET-ANIMAL TISSUES (Launch Pad 1)RaashiNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue ClassworkDocumento5 pagineTissue ClassworkRajesh Kanna A亗Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Mat PDFDocumento13 pagineTissue Mat PDFAyushman TripathyNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice Questions: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 12Documento12 pagineMultiple Choice Questions: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 12NaliniKumaresanNessuna valutazione finora
- Selina Concise Biology Class 7 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 1 - Plant and Animal TissuesDocumento10 pagineSelina Concise Biology Class 7 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 1 - Plant and Animal Tissuesvedanthendre5Nessuna valutazione finora
- PD 4 WJ SBJ UE7 XAASH4 U KZDocumento11 paginePD 4 WJ SBJ UE7 XAASH4 U KZPrincy GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- G10 Mid-Term RevisionDocumento239 pagineG10 Mid-Term RevisionMartria EhabNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7th TissueDocumento6 pagineChapter 7th Tissuenakulvyan708Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue SubjectiveDocumento1 paginaTissue SubjectiveKHUSHKARAN SANDHUNessuna valutazione finora
- CLS Aipmt-15-16 XI Zoo Study-Package-1 SET-1 Chapter-2A PDFDocumento16 pagineCLS Aipmt-15-16 XI Zoo Study-Package-1 SET-1 Chapter-2A PDFAnonymous Too8UuiNessuna valutazione finora
- TissuesDocumento7 pagineTissuesRohitNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 9 PWDocumento16 pagineClass 9 PW2982Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues Notes Class IxDocumento7 pagineTissues Notes Class Ixishaan singhNessuna valutazione finora
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues - .Documento9 pagineNCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues - .AshchatNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 9 - Tissues - Revision WRKSHT - 23-24Documento3 pagineGrade 9 - Tissues - Revision WRKSHT - 23-24Yashvi PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant and Animal Tissue TestDocumento5 paginePlant and Animal Tissue TestSri Suhartini100% (1)
- WS CH 6 - 2Documento2 pagineWS CH 6 - 2ayan.aggarwallNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 9 Biology Worksheet - TissuesDocumento4 pagineCBSE Class 9 Biology Worksheet - Tissuesankit anandNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues Class 9 Extra Questions Very Short Answer TypeDocumento31 pagineTissues Class 9 Extra Questions Very Short Answer TypeAyushi VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Text 92969AD289CB 1Documento2 pagineText 92969AD289CB 1glestudy28Nessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Human Physiology 6th Edition Stanfield Test BankDocumento25 paginePrinciples of Human Physiology 6th Edition Stanfield Test BankJeremySmithwrok100% (44)
- 2021 Chapter 6 Tissue Most IMP QuestionsDocumento11 pagine2021 Chapter 6 Tissue Most IMP QuestionsGauravNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer PrelimDocumento19 pagineReviewer PrelimALPEREZ, GRACE LYN C.Nessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ Exemplar - Cell StructureDocumento6 pagineMCQ Exemplar - Cell StructurenitikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocumento16 pagineAnatomy of Flowering PlantsSadik FsNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQDocumento24 pagineMCQiqra jabeenNessuna valutazione finora
- 9th Bio CHP 4 Animal TissueDocumento2 pagine9th Bio CHP 4 Animal TissueShanza HayatNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6: "Tissues"Documento5 pagineChapter 6: "Tissues"Anil TripathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Exam QnsDocumento4 pagineTissue Exam Qnsvarsha thakurNessuna valutazione finora
- cell and its structure (разработка)Documento8 paginecell and its structure (разработка)Ирина КривошеяNessuna valutazione finora
- Ix Plant Tissues 1Documento7 pagineIx Plant Tissues 1ayushiguptab0406Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quizch 04 TissuesqonlyproDocumento16 pagineQuizch 04 Tissuesqonlyproapi-282601291Nessuna valutazione finora
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsDa EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Review Article Is Antenatal Care Effective in Reducing Maternal Morbidity and Mortality?Documento15 pagineReview Article Is Antenatal Care Effective in Reducing Maternal Morbidity and Mortality?Mini PGNessuna valutazione finora
- m857 PDFDocumento11 paginem857 PDFMini PGNessuna valutazione finora
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Detection of Down SyndromeDocumento41 pagineNon-Invasive Prenatal Detection of Down SyndromeMini PGNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied & Translational Genomics: Philippos C. PatsalisDocumento6 pagineApplied & Translational Genomics: Philippos C. PatsalisMini PGNessuna valutazione finora
- Patient History Questionnaire: Last FirstDocumento4 paginePatient History Questionnaire: Last FirstMini PGNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Xi 2011Documento134 pagineChemistry Xi 2011Mini PGNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Paper - 2011 Class - XI Subject - Physics Time: 3 Hrs. MM: 70 General InstructionsDocumento4 pagineSample Paper - 2011 Class - XI Subject - Physics Time: 3 Hrs. MM: 70 General InstructionsMini PGNessuna valutazione finora
- CT'.WVV O Arw), D, Ttna Ri, O'W Al: T"RRRWX ( ": - /, Urrent Fvellrrct (YDocumento15 pagineCT'.WVV O Arw), D, Ttna Ri, O'W Al: T"RRRWX ( ": - /, Urrent Fvellrrct (YMini PGNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Chemical BondingDocumento5 pagineIntroduction To Chemical BondingMini PGNessuna valutazione finora
- Leukoplakia: Dr. Ishita Singhal Mds First YearDocumento70 pagineLeukoplakia: Dr. Ishita Singhal Mds First YearDR. ISHITA SINGHALNessuna valutazione finora
- Genesis - Biology (PHASE - 1) : (Crash Course - Jstse)Documento65 pagineGenesis - Biology (PHASE - 1) : (Crash Course - Jstse)Vinod AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2 Classification of EpitheliaDocumento43 pagineLesson 2 Classification of Epitheliabilal saminuNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of The Breast1Documento13 pagineAnatomy of The Breast1Shahinda Ahmed AdelNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundation Module d24Documento8 pagineFoundation Module d24Rabia OwaisNessuna valutazione finora
- Histo (MCQ) PDFDocumento6 pagineHisto (MCQ) PDFstuffNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 002 QuestionsDocumento17 pagineChapter 002 QuestionsCaitlin EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Single Squamous EpitheliumDocumento28 pagineSingle Squamous EpitheliumLyndonn Santos100% (1)
- BBMS1001 NotesDocumento41 pagineBBMS1001 NotesHelen WanNessuna valutazione finora
- Histology of GitDocumento56 pagineHistology of GitDoc On CallNessuna valutazione finora
- Tumor MarkersDocumento145 pagineTumor MarkersAnsh Dutta0% (1)
- Oral Mucosa and Complete DenturesDocumento8 pagineOral Mucosa and Complete DenturesANJALI TMU StudentNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (Lancet)Documento16 pagineChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (Lancet)marcos gamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gen. Zoo. Final ReviewerDocumento34 pagineGen. Zoo. Final ReviewerAshley FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Organization of The Cells TerminologiesDocumento3 pagineTissue Organization of The Cells TerminologiesskidamarinkNessuna valutazione finora
- Tabalba 1-Y1-2 Lab Exercise 3Documento4 pagineTabalba 1-Y1-2 Lab Exercise 3Shane V. TabalbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Training Course On Disease Diagnosis and Prevention PDFDocumento75 pagineTraining Course On Disease Diagnosis and Prevention PDFvctorvargas9383Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nasal Polyp DR Eva 2018Documento37 pagineNasal Polyp DR Eva 2018hudaNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Cytology (Compatibility Mode)Documento13 pagineAnimal Cytology (Compatibility Mode)AdarshBijapurNessuna valutazione finora
- Zoology 2008Documento91 pagineZoology 2008Ajmal Khan0% (2)
- First Nine Weeks ReviewDocumento19 pagineFirst Nine Weeks Reviewsuper novaNessuna valutazione finora
- HISTOLOGY Tongue and OsephagusDocumento8 pagineHISTOLOGY Tongue and OsephagusAkachukwu ObunikeNessuna valutazione finora
- TissuesDocumento9 pagineTissuesAtharv AggarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Asterion Practical Handbook of Anatomy-2eDocumento265 pagineAsterion Practical Handbook of Anatomy-2eMohammad AkhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- Fish Histology Manual v4Documento357 pagineFish Histology Manual v4vdcastillo13100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Sciences: ArticleinfoDocumento8 paginePharmaceutical Sciences: ArticleinfoMario CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer ANPH111 CandyDocumento21 pagineReviewer ANPH111 CandyRein TopacioNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 2 Prelab Tissues and IntegumentDocumento4 pagineLab 2 Prelab Tissues and IntegumentMareline MendietaNessuna valutazione finora
- MVW 020Documento9 pagineMVW 020SofyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Odontogenic Tumor PDFDocumento93 pagineOdontogenic Tumor PDFEmad Alriashy100% (1)