Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Unit I and Unit II Multiple Choice Practice Test
Caricato da
Christian FirschingDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Unit I and Unit II Multiple Choice Practice Test
Caricato da
Christian FirschingCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Test: Unit I and II- Mechanics, Fluids and Thermal Name: Date: 1.
5 hours Note: To simplify calculations, you may use g = 10 2 m / s in all problems. Questions 1-4 (D) It is upward and increases in magnitude from 0 to 3 s, then decreases. (E) It is upward and decreases in magnitude from 0 to 3 s, then increases.
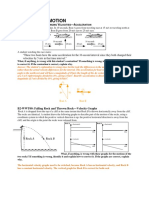
A ball is thrown straight up by a student at rest on the surface of Earth. A graph of the position y as a function of time t, in seconds, is shown above. Air resistance is negligible. 1. At which of the following times is the ball farthest from the student? (A) 1 s (B) 2 s (C) 3 s (D) 4 s (E) 5 s 2. At which of the following times is the speed of the ball the least? (A) 1 s (B) 2 s (C) 3 s (D) 4 s (E) 5 s 3. Which of the following best describes the acceleration of the ball? (A) It is downward and constant from 0 to 6 s. (B) It is downward and increases in magnitude from 0 to 3 s, then decreases. (C) It is downward and decreases in magnitude from 0 to 3 s, then increases.
4. What is the initial speed of the ball? (A) 30 m/s (B) 45 m/s (C) 60 m/s (D) 90 m/s (E) 180 m/s ______________________________________ 5. Two boxes of different masses in an orbiting space station appear to float at restone above the otherwith respect to the station. An astronaut applies the same force to both boxes. Can the boxes have the same acceleration with respect to the space station? (A) No, because the boxes are moving in orbits of different radius. (B) No, because the box of greater mass requires more force to reach the same acceleration. (C) Yes, because both boxes appear weightless. (D) Yes, because both boxes are accelerating toward Earth at the same rate. (E) It cannot be determined without knowing whether the boxes are being pushed parallel or perpendicular to Earths gravity. 6. An object is dropped from rest from a certain height. Air resistance is negligible. After falling a distance d, the objects
kinetic energy is proportional to which of the following? (A) 1/d2 (B) 1/d (C) d (D) d (E) d2 7. An object is projected vertically upward from ground level. It rises to a maximum height H. If air resistance is negligible, which of the following must be true for the object when it is at a height H/2 ? (A) Its speed is half of its initial speed. (B) Its kinetic energy is half of its initial kinetic energy. (C) Its potential energy is half of its initial potential energy. (D) Its total mechanical energy is half of its initial value. (E) Its total mechanical energy is half of its value at the highest point.
statements is true for the two objects after the impact? (A) The total momentum is Mv and the total kinetic energy is Mv2. (B) The total momentum is Mv and the total kinetic energy is less than Mv2. (C) The total momentum is less than Mv and the total kinetic energy is Mv2. (D) The momentum of each object is Mv. (E) The kinetic energy of each object is Mv2. 10. A spherical planet has mass greater than that of Earth, but its density is unknown. The weight of an object on that planet compared with its weight on Earth is which of the following? (A) Larger (B) The same (C) Smaller (D) It cannot be determined without information about the planets size. (E) It cannot be determined without information about the planets atmosphere.
8. A boy of mass m and a girl of mass 2m are initially at rest at the center of a frozen pond. They push each other so that she slides to the left at speed v across the frictionless ice surface and he slides to the right as shown above. What is the total work done by the children? (A) Zero (B) mv (C) mv2 (D) 2mv2 (E) 3mv2 9. An object of mass M travels along a horizontal air track at a constant speed v and collides elastically with an object of identical mass that is initially at rest on the track. Which of the following
11. A 2 kg object initially moving with a constant velocity is subjected to a force of magnitude F in the direction of motion. A graph of F as a function of time t is shown above. What is the increase, if any, in the velocity of the object during the time the force is applied? (A) 0 m/s (B) 2.0 m/s (C) 3.0 m/s (D) 4.0 m/s (E) 6.0 m/s
(B) 20 N (C) 40 N (D) 50 N (E) 60 N 15. What is the force exerted on the upper block by the lower string? (A) Zero (B) 10 N upward (C) 10 N downward (D) 20 N upward (E) 20 N downward ________________________________________ 16. In any physically correct equation, the units of any two quantities must be the same whenever these quantities are (A) added or multiplied only (B) subtracted or divided only (C) multiplied or divided only (D) added or subtracted only (E) added, subtracted, multiplied, or divided 17. An object initially at rest is subjected to a constant net force. Measurements are taken of its velocity v at different distances d from the starting position. A graph of which of the following should exhibit a straight-line relationship? (A) d2 versus v-2 (B) d2versus v (C) d versus v (D) d versus v-1 (E) d versus v2 18. A disk slides to the right on a horizontal, frictionless air table and collides with another disk that was initially stationary. The figures below show a top view of the initial path I of the sliding disk and a hypothetical path H for each disk after the collision. Which figure shows an impossible situation? (A)
12. A particle P moves around the circle of radius R shown above under the influence of a radial force of magnitude F. What is the work done by the radial force as the particle moves from position 1 to position 2 halfway around the circle? (A) Zero (B) RF (C) 2RF (D) RF (E) 2 RF 13. An object of mass m hanging from a spring of spring constant k oscillates with a certain frequency. What is the length of a simple pendulum that has the same frequency of oscillation? (A) (mk)/g (B) (mg)/k (C) (kg)/m (D) k/(mg) (E) g/(mk) Questions 14-15
Two blocks of wood, each of mass 2 kg, are suspended from the ceiling by strings of negligible mass, as shown above. 14. What is the tension in the upper string? (A) 10 N
(B)
(C)
(D) 21. The figure above shows a cart of mass M accelerating to the right with a block of mass m held to the front surface only by friction. The coefficient of friction between the surfaces is . What is the minimum acceleration a of the cart such that the block will not fall? (A) g (B) g / (C) gm / ( (M + m)) (D) gM / ( (M + m)) (E) gM / (M+ m) _______________________________________
(E)
19. A meter stick of negligible mass is placed on a fulcrum at the 0.60 m mark, with a 2.0 kg mass hung at the 0 m mark and a 1.0 kg mass hung at the 1.0 m mark. The meter stick is released from rest in a horizontal position. Immediately after release, the magnitude of the net torque on the meter stick about the fulcrum is most nearly (A) 2.0 Nm (B) 8.0 Nm (C) 10 Nm (D) 14 Nm (E) 16 Nm
20. A car of mass 900 kg is traveling at 20 m/s when the brakes are applied. The car then comes to a complete stop in 5 s. What is the average power that the brakes produce in stopping the car? (A) 1800 W (B) 3600 W (C) 7200 W (D) 36,000 W (E) 72,000 W
22. A platform of mass 2 kg is supported by a spring of negligible mass as shown above. The platform oscillates with a period of 3 s when the platform is pushed down and released. What must be the mass of a block that when placed on the platform doubles the period of oscillation to 6 s? (A) 1 kg (B) 2 kg (C) 4 kg (D) 6 kg (E) 8 kg 23. The acceleration of a satellite of mass m in a circular orbit of radius R around a planet of mass M is equal to which of the following? (A) GM / R2 (B) Gm / R2 (C) GMm / R2
(D) G mM / R (E) GmMR
volume decreases by 0.20 m3. What is the work done by the system on its environment? (A) 14 kJ (B) 35 kJ (C) -14 kJ (D) -35 kJ (E) -72 kJ 27. A 2.0 mole ideal gas system is maintained at a constant volume of 4.0 liters. If 100 J of thermal energy is transferred to the system, what is the change in the internal energy of the system? (A) 0 (B) 400 J (C) 70 J (D) 100 J (E) -0.100 J 28. If an ideal gas undergoes an adiabatic expansion, which of the following statements is true? (A) The temperature of the gas doesnt change. (B) No work is done by the gas. (C) No energy is delivered to the gas by heat. (D) The internal energy of the gas doesnt change. (E) The pressure increases. 29. If an ideal gas is compressed isothermally, which of the following statements is true? (A) Energy is transferred to the gas by heat. (B) No work is done on the gas. (C) The temperature of the gas increases. (D) The internal energy of the gas remains constant. (E) The pressure remains constant. 30. An engine does 15 kJ of work while rejecting 37 kJ to the cold reservoir. What is the efficiency of the engine? (A) 0.15 (B) 0.29 (C) 0.33 (D) 0.45 (E) 1.2
24. A ball of mass m with speed v strikes a wall at an angle with the normal, as shown above. It then rebounds with the same speed and at the same angle. The impulse delivered by the ball to the wall is (A) zero (B) mvsin (C) mvcos (D) 2mvsin (E) 2mvcos
25. An object of mass m hangs from a string that is fixed to the ceiling of a car. At the instant shown above, the car is moving into the plane of the page at constant speed v as it turns to the left around a horizontal curve of radius r. Which of the following is a correct expression for the angle of the string with respect to the vertical? (A) cos = mg / r (B) cos =mv / r (C) sin = mv2 / r (D) tan = v2 / (gr) (E) tan = gr / v2 26. An ideal gas is maintained at a constant pressure of 70.0 kPa during an isobaric process while its
31. How much net work is done by the gas undergoing the cyclic process illustrated above? Choose the best estimate.
35. A hole is drilled in a metal plate. When the metal is heated what happens to the diameter of the hole? (A) It decreases. (B) It increases. (C) It remains the same. (D) The answer depends on the initial temperature of the metal. (E) None of these. 36. The Statue of Liberty is 93 m tall on a summer morning when the temperature is 20C. If the temperature of the statue rises from 20C to 30C, what is the order of magnitude of the statues increase in height? Choose the best estimate, treating the statue as though it were solid copper (coefficient of linear expansion = 17 x 10-6 /C) (A) 0.1 mm (B) 1 mm (C) 1 cm (D) 10 cm (E) 1 m 37. If the temperature of an ideal gas is increased from 200 K to 600 K, what happens to the rms speed of the molecules? (A) It increases by a factor of 3. (B) It remains the same. (C) It is one third of the original speed. (D) It is 3 times the original speed. (E) It increases by a factor of 6. 38. A person shakes a sealed, insulated bottle containing coffee for a few minutes. What is the change in the temperature of the coffee? (A) a large decrease (B) a slight decrease (C) no change (D) a slight increase (E) a large increase 39. A glass windowpane in an otherwise perfectly insulated house is replaced with another glass windowpane which is twice the area, and twice as thick. The rate of heat loss between the inside of the house and the outside is now (A) the same (B) twice (C) 4 times (D) half (E) a quarter
(A) 1 x 105 J (B) 2 x 105 J (C) 3 x 105 J (D) 4 x 105 J (E) 5 x 105 J
32. A steam turbine operates at a boiler temperature of 450 K and an exhaust temperature of 3.0 x 102 K. What is the maximum theoretical percent efficiency of this system?
(A) 24% (B) 50% (C) 33% (D) 67% (E) 15% 33. On a very cold day in upstate New York, the temperature is -25C, which is equivalent to what temperature in Fahrenheit?
(A) -46F (B) -77F (C) 18F (D) 298 K (E) -13F 34. A container holds 0.50 m3 of oxygen at absolute pressure of 4.0 atm. A valve is opened, allowing the gas to drive a piston, increasing the volume of the gas until the pressure drops to 1.0 atm. If the temperature remains constant, what new volume does the gas occupy? (A) 1.0 m3 (B) 1.5 m3 (C) 2.0 m3 (D) 0.12 m3 (E) 2.5 m3
40. A hydraulic jack has an input piston of area 0.050 m2 and an output piston of area 0.70 m2. How much force on the input piston is required to lift a car weighing 1.4 x 103 N? (A) 50 N (B) 100 N (C) 200 N (D) 19600 N (E) 49 N 41. What is the pressure at the bottom at Loch Ness, which is as much as 230 m deep. The surface of the lake is almost at sea level, at 1 x 105 Pa. The density of water is 1.00 x 103 kg/m3. (A) 2.3 x 105 Pa (B) 2.4 x 106 Pa (C) 1 x 106 Pa (D) 4.3 x 106 Pa (E) 4.3 x 105 Pa 42. A horizontal pipe narrows from a radius of r to 0.5r. If the speed of the water in the pipe is 1.00 m/s in the larger-radius pipe, what is the speed in the smaller pipe? (A) 1.00 m/s (B) 2.00 m/s (C) 0.25 m/s (D) 4.00 m/s (E) 0.5 m/s
44. A hose is pointed straight up, with water flowing from it at a steady volume flow rate and reaching a maximum height of h. Neglecting air resistance, which of the following adjustments to the nozzle will result in the water reaching a height of 4h? (A) Decrease area of the opening by a factor of 16. (B) Decrease the area by a factor of 8. (C) Decrease the area by a factor of 4. (D) Decrease the area by a factor of 2. (E) The water cannot reach a height of 4h. 45. A student at the top of a building throws a red ball upward with a speed v0 and then throws a blue ball downward with the same initial speed v0. Immediately before the two balls reach the ground, which of the following statements is true, assuming no air resistance: (A) the speed of the red ball is less than that of the blue. (B) the speed of the red ball is greater than that of the blue. (C) their velocities are equal. (D) the acceleration of the blue ball is greater than that of the red ball. (E) the acceleration of the red ball is greater than that of the blue ball. 46. A ball is thrown straight up in the air. For which situation are both the instantaneous velocity and the acceleration zero? (A) on the way up (B) at the top of the flight path (C) on the way down (D) halfway up and halfway down (E) none of these 47. A large truck collides head-on with a small compact car. During the collision: (A) the truck exerts a greater amount of force on the car than the car exerts on the truck. (B) the car exerts a greater amount of force on the truck than the truck exerts on the car. (C) neither exerts a force on the other, the car gets smashed simply because it gets in the way of the truck. (D) the truck exerts a force on the car but the car does not exert a force on the truck. (E) the truck exerts the same amount of force on the car as the car exerts on the truck.
43. Three cups of different shapes are filled to the same level with water as in the figure above. The area of the base is the same for all three vessels. Which of the following statements is valid? (A) The pressure at the top surface of cup A is greatest because it has the largest surface area. (B) The pressure at the bottom of the cup C is greatest because it contains the most water. (C) The pressure at the bottom of each cup is the same. (D) The force on the bottom of each cup is not the same. (E) At a given depth below the surface of each cup, the pressure on the side of cup A is greatest because of its slope.
3. A force in the direction of the boys motion.
Elevator going up at constant speed
4. A force pointing from O to A. Which of the above forces is (are) acting on the boy when he is at position A? (A) 1 only. (B) 1 and 2. (C) 1 and 3. (D) 1, 2, and 3. (E) 1, 3, and 4. 51. A block of mass m is dropped from the fourth floor of an office building, subsequently hitting the sidewalk at speed v. From what floor should the mass be dropped to double to impact speed? (A) the sixth floor (B) the eighth floor (C) the tenth floor (D) the twelfth floor (E) the sixteenth floor
48. An elevator is being lifted up an elevator shaft at a constant speed by a steel cable as shown in the figure above. All frictional effects are negligible. In this situation, forces on the elevator are such that: (A) upward force by the cable is greater than the downward force of gravity. (B) upward force by the cable is equal to the downward force of gravity. (C) upward force by the cable is smaller than the downward force of gravity. (D) upward force by the cable is greater than the sum of the downward force of gravity and downward force due to the air. (E) none of the above. (The elevator goes up because the cable is being shortened, not because an upward force is exerted on the elevator by the cable). 49. A certain truck has twice the mass of a car. Both are moving at the same speed. If the kinetic energy of the truck is K, what is the kinetic energy of the car? (A) K/4 (B) K/2 (C) 0.71 K (D) K (E) 2K
52. A 5 kg cart moving to the right with a speed of 6 m/s collides with a concrete wall and rebounds with a speed of 2m/s. Is the change in momentum of the cart (A) 0 (B) 40 kg.m/s (C) -40 kg.m/s (D) -30 kg.m/s (E) -10 kg.m/s 53. A ball falls straight down through the air under the influence of gravity. There is a retarding force F on the ball with magnitude given by F = bv, where v is the speed of the ball and b is a positive constant. The magnitude of the acceleration a of the ball at any time is equal to which of the following? (A) g - b (B) g - bv/m (C) g + bv/m (D) g/b (E) bv/m 54. An ideal spring obeys Hooke's law, F = -kx. A mass of 0.50 kilogram hung vertically from this
50. The figure above shows a boy swinging on a rope, starting at a point higher than A. Consider the following distinct forces: 1. A downward force of gravity 2. A force exerted by the rope pointing from A to O.
spring stretches the spring 0.075 meter. The value of the force constant for the spring is most nearly (A) 0.33 N/m (B) 0.66 N/m (C) 6.6 N/m (D) 33 N/m (E) 66 N/m
(E) None of the above, because the acceleration is constant
55. The figure above shows a rough semicircular track whose ends are at a vertical height h. A block placed at point P at one end of the track is released from rest and slides past the bottom of the track. Which of the following is true of the height to which the block rises on the other side of the track? (A) It is equal to h/2 (B) It is equal to h/4 (C) It is equal to h/2 (D) It is equal to h (E) It is between zero and h; the exact height depends on how much energy is lost to friction. 56. An object is released from rest on a planet that has no atmosphere. The object falls freely for 3.0 meters in the first second. What is the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity on the planet? (A) 1.5 m s2 (B) 3.0 m/s2 (C) 6.0 m/s2 (D) 10.0 m/s2 (E) 12.0 m/s2
58. A block of mass 3m can move without friction on a horizontal table. This block is attached to another block of mass m by a cord that passes over a frictionless pulley, as shown above. If the masses of the cord and the pulley are negligible, what is the magnitude of the acceleration of the descending block? (A) Zero (B) g/4 (C) g/3 (D) 2g/3 (E) g 59. A car initially travels north and then turns to the left along a circular curve. This causes a package on the seat of the car to slide toward the right side of the car. Which of the following is true of the net force on the package while it is sliding? (A) The force is directed away from the center of the circle. (B) The force is directed north. (C) There is not enough force directed north to keep the package from sliding. (D) There is not enough force tangential to the car's path to keep the package from sliding. (E) There is not enough force directed toward the center of the circle to keep the package from sliding.
57. A particle oscillates up and down in simple harmonic motion. Its height y as a function of time t is shown in the diagram above. At what time t does the particle achieve its maximum positive acceleration? (A) 1 s (B) 2 s (C) 3 s (D) 4 s
60. Two objects, of masses 6 and 8 kilograms, are hung from the ends of a stick that is 70 centimeters long and has marks every 10 centimeters, as shown above. If the mass of the stick is negligible, at which of the points indicated should a cord be attached if the stick is to remain horizontal when suspended from the cord? (A) A (B) B (C) C
(D) D (E) E
61. A T-shaped tube with a constriction is inserted in a vessel containing a liquid, as shown above. What happens if air is blown through the tube from the left, as shown by the arrow in the diagram? (A) The liquid level in the tube rises to a level above the surface of the liquid surrounding the tube. (B) The liquid level in the tube falls below the level of the surrounding liquid. (C) The liquid level in the tube remains where it is. (D) The air bubbles out at the bottom of the tube. (E) Any of the above depending on how hard the air flows. 62. Two objects, A and B, initially at rest, are "exploded" apart by the release of a coiled spring that was compressed between them. As they move apart, the velocity of object A is 5 m/s and the velocity of object B is -2 m/s. The ratio of the mass of object A to the mass of object B, mA/mB, is (A) 4/25 (B) 2/5 (C) 1/1 (D) 5/2 (E) 25/4 63. In time t, an amount of heat Q flows through the solid door of area A and thickness d represented above. The temperatures on each side of the door are T2 and T1, respectively. Which of the following changes would be certain to decrease Q ? (A) Increasing A only (B) Decreasing d only (C) Increasing d and T2 T1 only (D) Decreasing A and T2 T1 only (E) Increasing d, A, and T2 T1 Questions 64-66
A ball is thrown and follows the parabolic path shown above. Air friction is negligible. Point Q is the highest point on the path. Points P and R are the same height above the ground. 64. How do the speeds of the ball at the three points compare? (A) vp < vQ < vR (B) vR < vQ < vP (C) vQ < vR < vP (D) vQ< vP = vR (E) vP = vR < vQ 65. Which of the following diagrams best shows the direction of the acceleration of the ball at point P? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 66. Which of the following best indicates the direction of the net force, if any, on the ball at point Q ? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) There is no net force on the ball at point Q. 67. A gas with a fixed number of molecules does 32 J of work on its surroundings, and 16 J of heat are transferred from the gas to the surroundings. What happens to the internal energy of the gas? (A) It decreases by 48 J. (B) It decreases by 16 J. (C) It remains the same. (D) It increases by 16 J. (E) It increases by 48 J.
68. A satellite of mass m and speed v moves in a stable, circular orbit around a planet of mass M. What is the radius of the satellite's orbit? GM (A) mv Gv (B) mM
(C)
GM v2
per second. The frictional force between the block and the floor is 10 newtons. The work done by the force F in 1 minute is most nearly (A) 0 J (B) 30 J (C) 600 J (D) 1,350 J (E) 1,800 J 70. The length of a simple pendulum with a period on Earth of one second is most nearly (A) 0.12 m (B) 0.25 m (C) 0.50 m (D) 1.0 m (E) 10.0 m
GmM (D) v GmM
(E)
v2
69. A horizontal force F is used to pull a 5-kilogram block across a floor at a constant speed of 3 meters
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Test - Unit 3 - Energy and MomentumDocumento4 pagineTest - Unit 3 - Energy and Momentumascd_msvuNessuna valutazione finora
- MatterDocumento7 pagineMatterCharmaine Wright100% (1)
- As Newtons Laws and Momentum QuestionsDocumento61 pagineAs Newtons Laws and Momentum Questionshasan_shahryar2008Nessuna valutazione finora
- Honors Physics Midterm Review: Exam DayDocumento8 pagineHonors Physics Midterm Review: Exam DayEarl averzosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework 3 PDFDocumento31 pagineHomework 3 PDFnaveena kumariNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 PDFDocumento34 pagineChapter 5 PDFQassem MohaidatNessuna valutazione finora
- PHYS 211 Exam 1 Sample 2 With Key PDFDocumento11 paginePHYS 211 Exam 1 Sample 2 With Key PDFAndrew TrolioNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 30 TestDocumento27 pagineCH 30 TestEliceth MosqueraNessuna valutazione finora
- Wolfson Eup3 ch09 Test BankDocumento15 pagineWolfson Eup3 ch09 Test Bank陳禹誌Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Test Circular Motion Anmd Universal Gravitation 1Documento4 pagineUnit Test Circular Motion Anmd Universal Gravitation 1Nandhu RamkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Testbank Chapter13Documento12 pagineTestbank Chapter13Doom RefugeNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison Between Weber's Electrodynamics and Classical ElectrodynamicsDocumento12 pagineComparison Between Weber's Electrodynamics and Classical ElectrodynamicsBruno RodriguesNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam Review 3Documento24 pagineExam Review 3api-223793512Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 PacketDocumento13 pagineUnit 4 Packetbobno23Nessuna valutazione finora
- AP Physics 1 Algebra Based Unit 4 EnergyDocumento7 pagineAP Physics 1 Algebra Based Unit 4 EnergyNikhita Rajesh100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Force and Newtons Laws of MotionDocumento23 pagineChapter 4 Force and Newtons Laws of MotionQassem MohaidatNessuna valutazione finora
- Ap Gov Practice TestDocumento47 pagineAp Gov Practice Testapi-255064087Nessuna valutazione finora
- PHY 151 Homework Practice Test Solutions 01Documento8 paginePHY 151 Homework Practice Test Solutions 01Dnhdj JdhsjdNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 03-01 Work and The Work-Energy TheoremDocumento2 paginePhysics 03-01 Work and The Work-Energy Theoremmechanical_lecturerNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Momentum Practice TestDocumento11 pagineEnergy Momentum Practice TestMohamad SotoudehNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 15 Electric FieldsDocumento17 pagineChapter 15 Electric FieldsdrewNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy 151 Pre-Test 03aDocumento3 paginePhy 151 Pre-Test 03aMurimi IrunguNessuna valutazione finora
- Hapter: Conceptual ProblemsDocumento52 pagineHapter: Conceptual ProblemsAmeen ShaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Elastic Collision With C++Documento12 pagineElastic Collision With C++qud86Nessuna valutazione finora
- PhysicsDocumento20 paginePhysicsAnthony HugillNessuna valutazione finora
- Virtual Lab AnsweredDocumento6 pagineVirtual Lab Answeredrdixit2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics PE KE - Year 9Documento7 paginePhysics PE KE - Year 9inder191Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers Chapter 01Documento56 paginePhysics For Scientists and Engineers Chapter 01topwarmachineNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.0 Test On Circular MotionDocumento1 pagina1.0 Test On Circular Motionrsdiwane100% (1)
- CP Phys CH 2 Web RevDocumento8 pagineCP Phys CH 2 Web RevMichelle MuliawidjajaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-15-15 Kinematics AP1 - Review SetDocumento8 pagine1-15-15 Kinematics AP1 - Review SetLudwig Van Beethoven100% (1)
- Walker4 Ism Ch18Documento36 pagineWalker4 Ism Ch18Walter Ruby100% (2)
- Test Bank 6Documento13 pagineTest Bank 6LukeLi100% (1)
- Multiple Choice Questions For Physics 1Documento55 pagineMultiple Choice Questions For Physics 1OsamaHeshamNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 Work Energy and PowerDocumento7 pagineUnit 4 Work Energy and PowerSabia IdrisiNessuna valutazione finora
- Forces in One Dimension-2Documento3 pagineForces in One Dimension-2varaprasad100% (1)
- Chapter 30 - Magnetic Fields and TorqueDocumento26 pagineChapter 30 - Magnetic Fields and TorqueCrmz CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4-Motion in Two Dimensions: Multiple ChoiceDocumento18 pagineChapter 4-Motion in Two Dimensions: Multiple ChoiceDnhdj JdhsjdNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 8 ScienceDocumento2 pagineGrade 8 ScienceBart PorcadillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circulat Motion ProblemsDocumento15 pagineCirculat Motion ProblemsSadiki WallaceNessuna valutazione finora
- Two Dimensional Motion and VectorsDocumento5 pagineTwo Dimensional Motion and VectorsSriram ArumugamNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamics (Work and Energy) TutorialDocumento5 pagineDynamics (Work and Energy) TutorialYadana1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Displacement and Force in Two Dimensions-2Documento2 pagineDisplacement and Force in Two Dimensions-2varaprasad100% (1)
- Ch34 ISM 070623Documento56 pagineCh34 ISM 070623Ian GravesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5-The Laws of Motion: Multiple ChoiceDocumento31 pagineChapter 5-The Laws of Motion: Multiple ChoiceHasan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics B Form B 2010Documento12 paginePhysics B Form B 2010Michael CNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics Sheet SolutionDocumento60 pagineKinematics Sheet SolutiontHEhOODYgANGNessuna valutazione finora
- 18 Vector Word Problem Review PDFDocumento6 pagine18 Vector Word Problem Review PDFwade aryanNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Motion and GraphDocumento1 paginaLinear Motion and GraphmydadawalfnNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank 14Documento16 pagineTest Bank 14Brocksampson1983100% (2)
- Test Bank For Introduction To Physical Science 14th Edition Shipman Wilson Higgins TorresDocumento17 pagineTest Bank For Introduction To Physical Science 14th Edition Shipman Wilson Higgins TorresaimeeNessuna valutazione finora
- AP FR Quiz #5 2D MotionDocumento7 pagineAP FR Quiz #5 2D MotionRobbyNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Momentum TestDocumento5 paginePractice Momentum TestKinalPatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Work - Energy - PowerDocumento9 pagineWork - Energy - PowermaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank 7Documento20 pagineTest Bank 7LukeLi100% (1)
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento12 pagineMultiple Choice QuestionsGita GirihartaNessuna valutazione finora
- Test - Chapter 4 and 5 - Forces and Newton's LawsDocumento5 pagineTest - Chapter 4 and 5 - Forces and Newton's Lawsascd_msvu100% (1)
- AP Physics Chapter 3 Motion in Two DimensionsDocumento33 pagineAP Physics Chapter 3 Motion in Two DimensionsStewie Dog100% (1)
- AP Mechanics FLT2 PDFDocumento21 pagineAP Mechanics FLT2 PDFXtreme VitthalNessuna valutazione finora
- Center of Mass and The Motion of A SystemDocumento13 pagineCenter of Mass and The Motion of A SystemNitin SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Physics B Sample ExamDocumento17 pagineAP Physics B Sample ExamBob Smith100% (2)
- SVKM J.V. Parekh International School Grade: VI Div: Subject: Physics Topic: Gravity Name of The Student: Roll NoDocumento9 pagineSVKM J.V. Parekh International School Grade: VI Div: Subject: Physics Topic: Gravity Name of The Student: Roll NoWere WolfNessuna valutazione finora
- Masteringphys 13Documento22 pagineMasteringphys 13CarlosGomez25% (4)
- Module Checklist - Mechanics - Grade 12Documento7 pagineModule Checklist - Mechanics - Grade 12api-257324866Nessuna valutazione finora
- Enum Types JavaDocumento3 pagineEnum Types JavaAmandeep PuniaNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY413 GTR Final Notes Bijan BagchiDocumento103 paginePHY413 GTR Final Notes Bijan Bagchipranav gongiNessuna valutazione finora
- Quick Revision For o Level PhysicsDocumento28 pagineQuick Revision For o Level PhysicsRegie Sacil EspiñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mass ComparatorsDocumento32 pagineMass ComparatorspurwantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Newton's First and Second Laws - Print - QuizizzDocumento5 pagineNewton's First and Second Laws - Print - QuizizzZeinab ElkholyNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 9Documento2 pagineClass 9Ashutosh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ensayo CBR (D4429-09a)Documento7 pagineEnsayo CBR (D4429-09a)joake spasNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter No 14: (SECTIONS 14.1-14.4, 14.6)Documento63 pagineChapter No 14: (SECTIONS 14.1-14.4, 14.6)Farhan ShahriarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathworksheet of STD 5Documento3 pagineMathworksheet of STD 5rameshdorage12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 5 Unit 1 Overview Physical Science 2018.19Documento5 pagineGrade 5 Unit 1 Overview Physical Science 2018.19Mischelle 'mitch' PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Net 2020Documento48 pagineNet 2020Krishan pandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- TUMALIM NHS BMI Teachers Final VersionDocumento11 pagineTUMALIM NHS BMI Teachers Final VersionMayca Solomon GatdulaNessuna valutazione finora
- BSGS Sample Problems 1 - BB CollabDocumento11 pagineBSGS Sample Problems 1 - BB CollabNeo GarceraNessuna valutazione finora
- My First Experience in A Badminton CompetitionDocumento2 pagineMy First Experience in A Badminton CompetitionŇel DanNessuna valutazione finora
- SCI 111 HW 3 Solutions Fall 2011 JaquinDocumento7 pagineSCI 111 HW 3 Solutions Fall 2011 JaquinLawrrence LozanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 01 p001-011Documento11 pagineChapter 01 p001-011umamgis3304100% (3)
- Summary Notes Year 7Documento5 pagineSummary Notes Year 7Cinara Rahimova100% (1)
- Igcse 11 Movement&PositionDocumento36 pagineIgcse 11 Movement&PositionHany ElGezawy100% (1)
- Lab # 09Documento8 pagineLab # 09Muhammad WaqasNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5Documento29 pagineChapter 5Muhamad DanielNessuna valutazione finora
- How and Why Do Things FloatDocumento25 pagineHow and Why Do Things Floatswaglordswag123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 3: Kinematics in One DimensionDocumento40 pagineTopic 3: Kinematics in One DimensionUmar ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Motionmountain Volume1Documento604 pagineMotionmountain Volume1ritonga01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Operating Instruction Platform Scale: Kern deDocumento37 pagineOperating Instruction Platform Scale: Kern dedexterpoliNessuna valutazione finora