Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Ps 10
Caricato da
Sahil Madaan0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
17 visualizzazioni2 pagineAssembly drawing is a drawing which displays the parts of a machine or a machine unit assembled in their relative working positions. The assembly drawing should be such that it should satisfy (i) Manufacturing requirements (ii) Operational requirement and (iii) Maintenance requirement. A Gate Valve controls the flow by operating a gate, which slides up and down across the section to clear or obstruct the flow passage.
Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
ps10
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoAssembly drawing is a drawing which displays the parts of a machine or a machine unit assembled in their relative working positions. The assembly drawing should be such that it should satisfy (i) Manufacturing requirements (ii) Operational requirement and (iii) Maintenance requirement. A Gate Valve controls the flow by operating a gate, which slides up and down across the section to clear or obstruct the flow passage.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
17 visualizzazioni2 paginePs 10
Caricato da
Sahil MadaanAssembly drawing is a drawing which displays the parts of a machine or a machine unit assembled in their relative working positions. The assembly drawing should be such that it should satisfy (i) Manufacturing requirements (ii) Operational requirement and (iii) Maintenance requirement. A Gate Valve controls the flow by operating a gate, which slides up and down across the section to clear or obstruct the flow passage.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
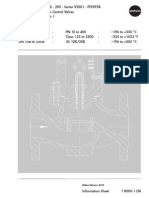
ME-211
Problem Sheet No: 10
Assembly Drawings:
A drawing which displays the parts of a machine or a machine unit assembled in their relative
working positions is known as assembly drawing. The assembly drawing should be such that it
should satisfy (i) Manufacturing requirements (ii) Operational requirement and (iii) Maintenance
requirement
Sequence of preparing the assembly drawing
1. Study functional requirements of each components and their inter-relationship. Learn the
actual working of a machine
2. Study carefully the views of each component in the detailed drawing and decide the relative
location of each part for the proper functioning of the machine.
3. Decide the mating dimensions between two components which are required to be assembled.
4. Prepare free-hand sketch of the main view or an important view (generally front view). Add
additional views, if necessary.
5. Select a suitable scale for the entire assembly drawing.
6. Lay out the views of the assembly drawing so that it becomes easier to understand.
7. Prepare the list of components, their quantities and materials.
Gate Valve assembly:
A valve is a device, which is used to check or control the flow of fluid through a passage such as
pipes or ducts. The valve is operated by the pressure of the fluid or by hand or by some external
mechanism. There are different types of valves. Some of them are (i) Gate valve (ii) Globe valve
(iii) Swing-check valve and (iv) Stop valve. A gate valve controls the flow by operating a gate,
which slides up and down across the section to clear or obstruct the flow passage. The schematic
diagram of a gate valve with its main parts is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of a gate valve
Figure 2 shows the actual details of different parts of a gate valve. The wedge or gate valve 4 in this
design is guided by the control screw 5. When fully opened, the wedge valve clears-off the passage
in the valve body 1 for the flow of fluid. The inside union 8 is slipped onto the stem from below.
This is placed in the union 2 and screwed. The wedge valve is threaded on the stem and the
assembly is placed in the valve body and screwed. The gland is placed from the top of the stem so
that it enters the union. It is fixed in position by the union ring 3. Finally, the hand wheel 6 is placed
on the square end of the screw and fixed in position by means of a nut (not shown). The gate valve
may be fixed for any direction of the fluid flow.
Figure 2: Details of parts of a Gate valve
Q.1. Figure 2 shows the details of different parts of a gate valve. Assemble the parts and draw
to full scale, (i) half-sectional view from the front, (ii) the view from above and (iii) the view
from the left.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Gasket CatalogoDocumento242 pagineGasket CatalogoAnand KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- C-14 Selection and Limitation of Piping ComponentsDocumento14 pagineC-14 Selection and Limitation of Piping ComponentscristhianNessuna valutazione finora
- Report On ValvesDocumento15 pagineReport On ValvesAnonymous b9J5NMNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-Piping Manual-Pdms12Documento413 pagine1-Piping Manual-Pdms12MOHSEN2005IBNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods, Processes and Equipment Involved in Handling of SolidsDocumento137 pagineMethods, Processes and Equipment Involved in Handling of SolidsRhadel Gantuangco100% (1)
- Asl Ga 90-160 Aif-056813 PDFDocumento85 pagineAsl Ga 90-160 Aif-056813 PDFFernando Guaman Remache100% (10)
- Control Valves: by Hans D. BaumannDocumento17 pagineControl Valves: by Hans D. BaumannAida PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- PWHT of Socket Weld Valves, Vogt (Flowserv)Documento8 paginePWHT of Socket Weld Valves, Vogt (Flowserv)Gábor BacsaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kitz Bronze Gate ValveDocumento9 pagineKitz Bronze Gate ValveRyte EchanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Brochure - Valco - Power Valves - EnglishDocumento16 pagineBrochure - Valco - Power Valves - EnglishMeet JaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Series FS-CFC-S FloodSafe Specification SheetDocumento2 pagineSeries FS-CFC-S FloodSafe Specification SheetWattsNessuna valutazione finora
- CatalogueDocumento184 pagineCatalogueysinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Instalacion Belmont SP CielaDocumento18 pagineInstalacion Belmont SP CielaTecnico BuhosNessuna valutazione finora
- Product Catalog Samson at A Glance: Production Sites StaffDocumento174 pagineProduct Catalog Samson at A Glance: Production Sites Staffkhaled saeedNessuna valutazione finora
- ProValve Cast SteelDocumento12 pagineProValve Cast SteelHarry HonchoNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of ValvesDocumento13 pagineTypes of ValvesRajkumar ANessuna valutazione finora
- Valve - Check - Globe - StopDocumento288 pagineValve - Check - Globe - StopveneethgeoNessuna valutazione finora
- T 80001 enDocumento24 pagineT 80001 enGumersindo MelambesNessuna valutazione finora
- Toyo Valve PN TypeDocumento12 pagineToyo Valve PN Typent_long76Nessuna valutazione finora
- FlowserveDocumento118 pagineFlowserveCesar Cedano VivarNessuna valutazione finora
- Valtek Maxflo 3: High Capacity Eccentric Rotary Plug Control ValveDocumento8 pagineValtek Maxflo 3: High Capacity Eccentric Rotary Plug Control Valvesaroat moongwattanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Instruction Manual For Control ValvesDocumento13 pagineInstruction Manual For Control ValvesBruno RachidNessuna valutazione finora
- Valves Used in Fire Protection SystemDocumento20 pagineValves Used in Fire Protection SystemrashalNessuna valutazione finora
- Flow Coefficients CV Values: Bolted Bonnet Globe Valves API 623 & B 16.34 Class: 150 - 2500 Size: 2" - 18"Documento1 paginaFlow Coefficients CV Values: Bolted Bonnet Globe Valves API 623 & B 16.34 Class: 150 - 2500 Size: 2" - 18"Mohamed NabilNessuna valutazione finora
- Valvula Neumatica Honeywell PC1Documento8 pagineValvula Neumatica Honeywell PC1DAVIDNessuna valutazione finora
- Cat AXCATDocumento80 pagineCat AXCATgazwang478Nessuna valutazione finora
- Newco Pressure Seal Valves BrochureDocumento4 pagineNewco Pressure Seal Valves Brochuremax_powerNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4 Water Pipe Sizing PDFDocumento26 pagineLecture 4 Water Pipe Sizing PDFAlchea Aldeguer100% (1)
- Valvulas de Control Schroedahl Broschure Regelarmaturen Uk 012Documento20 pagineValvulas de Control Schroedahl Broschure Regelarmaturen Uk 012cristobal_tl2277Nessuna valutazione finora
- Valve & Flange DeatilsDocumento28 pagineValve & Flange DeatilssppatilNessuna valutazione finora