Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
The Role of The Student in The Instructional Process
Caricato da
Rahshen R BarberDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
The Role of The Student in The Instructional Process
Caricato da
Rahshen R BarberCopyright:
Formati disponibili
THE ROLE OF THE STUDENT IN THE INSTRUCTIONAL PROCESS
1. Adapt to and thrive in diverse teaching/learning environments.
2. Be actively engaged in the learning process both inside and outside the
classroom.
3. Create, develop, and evaluate an individualized academic plan and life goals.
4. Respect the learning environment and rights of all learners.
5. Abide by the Student Code of Conduct.
6. Interact with peers.
7. Participate in or support student organizations and school activities.
8. Be aware of and use student support services and resources.
9. Assume responsibility for academic and personal choices.
10.Use what you have learned to become a viable and contributing member of
the community.
TRAITS OF STUDENTS DURING THE INSTRUCTIONAL PROCESS
INSTRUCTIONAL DIRECTION:
• Students can explain the posted expectations (SWBAT)
• Students can articulate WHY they have been asked to attempt the task
KNOWLEDGE OF PERFORMANCE AND ABILITY:
• Students can acknowledge their individualized assessment data and baseline
performance data including how they will be assessed(Rubrics, Assessment
Guidelines)
ENGAGEMENT AND PARTICIPATION:
• Students are sharing knowledge and constructing solutions (Centers,
Responses, Projects)
• Students will activate prior knowledge and apply it to tasks (Aha Moments)
• Students will be involved in the curriculum selection by providing an element
of what they want to learn via self-selection activities, KWL charts, Project
Based Learning, etc.
DEMONSTRATED KNOWLEDGE AND PARTICIPATION:
• Students will be able to demonstrate learning via classroom participation,
Socratic questioning, and Blooms Taxonomy (must recall, comprehend, apply,
analyze, synthesize, and evaluate).
• Use of prior knowledge to make connections
• Student inquiry
• In-depth vs. superficial awareness
• Expressing new or revising old ideas
• Finding a value beyond the classroom (Real-world applications)
TEACHERS WILL BE ABLE TO: Evaluate the dynamics of the student instructional process
by using the previously discussed elements and Bloom’s Taxonomy to design a
model lesson/dialogue between a teacher and his/her students. Please include an
activity, student grouping, and learning objective (SWBAT).
• What are the students doing and saying when they are engaged in learning?
• What role(s) should the student play in the classroom?
• What is the teacher doing and saying?
• How do I know that the student is engaged in a rigorous activity?
Example Response
SWBAT: differentiate among fact/opinion, bias and propaganda in newspapers,
periodicals, & electronic texts by analyzing the rational behind the first political
cartoons.
STUDENT FRIENDLY SWBAT: Evaluate the reasons behind the first political cartoons.
GROUPING: Small learning groups (center activity)
ACTIVITY: Students will be placed in small groups where they will …………
ASSESSMENT: Recognizing bias & propaganda vs. fact (worksheet) and group rubric
ANSWERS TO BULLETED QUESTIONS:
BLOOM'S TAXONOMY
(Original Version)
1. Knowledge: arrange, define, duplicate, label, list, memorize, name, order,
recognize, relate, recall, repeat, reproduce state.
2. Comprehension: classify, describe, discuss, explain, express, identify,
indicate, locate, recognize, report, restate, review, select, translate,
3. Application: apply, choose, demonstrate, dramatize, employ, illustrate,
interpret, operate, practice, schedule, sketch, solve, use, write.
4. Analysis: analyze, appraise, calculate, categorize, compare, contrast,
criticize, differentiate, discriminate, distinguish, examine, experiment,
question, test.
5. Synthesis: arrange, assemble, collect, compose, construct, create, design,
develop, formulate, manage, organize, plan, prepare, propose, set up, write.
6. Evaluation: appraise, argue, assess, attach, choose compare, defend
estimate, judge, predict, rate, core, select, support, value, evaluate.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Distance Learning Through Modular Approach: Nerissa O. RoqueDocumento15 pagineDistance Learning Through Modular Approach: Nerissa O. RoqueSuertz Zaragosa0% (1)
- Declaration Education 2030Documento11 pagineDeclaration Education 2030Vipul GoelNessuna valutazione finora
- Special Educational Needs ReflectionDocumento3 pagineSpecial Educational Needs ReflectionEmma FubuWarrioh Bloor100% (1)
- Humanism-Education Thought - Sweta, ShreyashiDocumento2 pagineHumanism-Education Thought - Sweta, ShreyashiShreya SanyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Environment and Teaching StrategiesDocumento3 pagineLearning Environment and Teaching StrategiesJovie MasongsongNessuna valutazione finora
- Education EssayDocumento2 pagineEducation Essayapi-510179166Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Demands of Society From The Teacher As A ProfessionalDocumento7 pagineThe Demands of Society From The Teacher As A ProfessionallorenzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Social and Technological Foundations 1Documento34 pagineSocial and Technological Foundations 1Nidzar Zulfriansyah BahariNessuna valutazione finora
- Report in The Teaching ProfessionDocumento9 pagineReport in The Teaching ProfessionAiza C. Abungan-GalzoteNessuna valutazione finora
- The Learner Centered ClassroomDocumento16 pagineThe Learner Centered ClassroomJanine CanlasNessuna valutazione finora
- Synthesis Reaction Paper 1Documento4 pagineSynthesis Reaction Paper 1api-353957387100% (1)
- Roles of A Teacher in Colleges of EducationDocumento7 pagineRoles of A Teacher in Colleges of EducationIlayaraja SubbiahNessuna valutazione finora
- The 21st Century TeacherDocumento6 pagineThe 21st Century TeacherAngilly LibreaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Influece of School Environment On Students AchivementDocumento9 pagineThe Influece of School Environment On Students AchivementEdward Clarence LimNessuna valutazione finora
- The Teaching Learning ProcessDocumento5 pagineThe Teaching Learning ProcessСтрэнгхэид Рои РоналдNessuna valutazione finora
- Speech CovidDocumento3 pagineSpeech CovidAnanda SaviraNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching PhilosophyDocumento5 pagineTeaching Philosophyapi-272013505Nessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Values Reflection, AngkananDocumento2 pagineTypes of Values Reflection, AngkananMahathma Dalandas - AngkananNessuna valutazione finora
- Peace Education: An Important Aspect of CurriculumDocumento7 paginePeace Education: An Important Aspect of CurriculumAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes Educational TechnologyDocumento27 pagineLecture Notes Educational TechnologyMPORANANAYO NOEL100% (1)
- Answer:: Describe WDocumento3 pagineAnswer:: Describe WAurea Jasmine Dacuycuy100% (1)
- Code of Ethucs EssayDocumento10 pagineCode of Ethucs Essayapi-434739441Nessuna valutazione finora
- Personal Education Philosophy PaperDocumento4 paginePersonal Education Philosophy Paperapi-316502259Nessuna valutazione finora
- Field Study 1: University of Caloocan CityDocumento7 pagineField Study 1: University of Caloocan CityLovelyn MaristelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Engagement in Online LearningDocumento5 pagineStudent Engagement in Online Learningapi-495889137Nessuna valutazione finora
- QualitiesDocumento15 pagineQualitiesDarwin PatricioNessuna valutazione finora
- Philosophy of EducationDocumento7 paginePhilosophy of Educationapi-288966220Nessuna valutazione finora
- EducTech Ref6Documento3 pagineEducTech Ref6Dennis Arthur S. LeonorNessuna valutazione finora
- Educational Technology OutputDocumento17 pagineEducational Technology OutputFelyn Garbe YapNessuna valutazione finora
- Fourc's 21st CenturyDocumento5 pagineFourc's 21st CenturyZeus OngNessuna valutazione finora
- Sarah Lesson Plan 2Documento2 pagineSarah Lesson Plan 2api-260894328Nessuna valutazione finora
- TTL 1 L3 ModuleDocumento6 pagineTTL 1 L3 ModuleAllyssa JhaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Media and Cyber or Digital LiteraciesDocumento3 pagineMedia and Cyber or Digital LiteraciesDale Francis Dechavez RutagenesNessuna valutazione finora
- Cognitive Load Theory (John Sweller) : Information ProcessingDocumento2 pagineCognitive Load Theory (John Sweller) : Information ProcessingNik ZazlealizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module1 191124131758 PDFDocumento18 pagineModule1 191124131758 PDFjade tagabNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 Educ 3Documento29 pagineModule 1 Educ 3Selle Albero100% (1)
- Glova, Angeline B. Bsed English 1Documento4 pagineGlova, Angeline B. Bsed English 1Angeline GlovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Importance of Educational TechnologyDocumento4 pagineImportance of Educational Technologywichupinuno100% (1)
- 21st Century Skills Curriculum and Instruction PDFDocumento5 pagine21st Century Skills Curriculum and Instruction PDFsyifa nurjanahNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Behavior Problems in The ClassroomDocumento2 pagineCommon Behavior Problems in The ClassroomJaycel Abrasado DaganganNessuna valutazione finora
- HOTS IT-based ProjectsDocumento14 pagineHOTS IT-based ProjectsmarygracejaspesiarotNessuna valutazione finora
- The Computer As A TutorDocumento18 pagineThe Computer As A TutorKai MasaglangNessuna valutazione finora
- Bioecological TheoryDocumento3 pagineBioecological TheoryJ BNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 The Teaching ProfessionDocumento7 pagineModule 1 The Teaching ProfessionOshuu desuNessuna valutazione finora
- Instructional PlanningDocumento30 pagineInstructional PlanningTyrone O. GilNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter2 The Teacher in The Classroom and CommunityDocumento84 pagineChapter2 The Teacher in The Classroom and Communitychristopher d. balubayan100% (1)
- Module 2 Activities of Leonard Ray R. MendozaDocumento2 pagineModule 2 Activities of Leonard Ray R. MendozaLeonardray MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- M.ed PPT Gagandeep KaurDocumento18 pagineM.ed PPT Gagandeep KaurAnuradha sethNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching StrategiesDocumento16 pagineTeaching StrategiesGomonan RosannaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Impact of Social Media On Educational Performance With Reference To College StudentsDocumento5 pagineThe Impact of Social Media On Educational Performance With Reference To College StudentsIjcams PublicationNessuna valutazione finora
- Module in MathDocumento8 pagineModule in MathJoey Bojo Tromes Bolinas100% (1)
- Behavioral EngagementDocumento1 paginaBehavioral EngagementAriah TugadoNessuna valutazione finora
- My Mother Is My Hero TabusaresDocumento3 pagineMy Mother Is My Hero TabusaresAgnes PablicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Reflective Essay On AssessmentDocumento6 pagineReflective Essay On AssessmentPremier PublishersNessuna valutazione finora
- M7 - ON BECOMING A GLOBAL TEACHER (Responded)Documento8 pagineM7 - ON BECOMING A GLOBAL TEACHER (Responded)June LegaspiNessuna valutazione finora
- Reflection On ICT PrinciplesDocumento4 pagineReflection On ICT PrinciplesNerjone AlveroNessuna valutazione finora
- The Importance of Educational Goals: Education and LearningDa EverandThe Importance of Educational Goals: Education and LearningNessuna valutazione finora
- Progressive Education In Nepal: The Community Is the CurriculumDa EverandProgressive Education In Nepal: The Community Is the CurriculumNessuna valutazione finora
- Educational Leadership: a Student-Centered ApproachDa EverandEducational Leadership: a Student-Centered ApproachNessuna valutazione finora
- Signature Object Detection Based On YOLOv3Documento4 pagineSignature Object Detection Based On YOLOv3Lý Khánh NhưNessuna valutazione finora
- Open Letter To Hon. Nitin Gadkari On Pothole Problem On National and Other Highways in IndiaDocumento3 pagineOpen Letter To Hon. Nitin Gadkari On Pothole Problem On National and Other Highways in IndiaProf. Prithvi Singh KandhalNessuna valutazione finora
- Pioneer vsx-1020-k 1025-k SM PDFDocumento132 paginePioneer vsx-1020-k 1025-k SM PDFluisclaudio31Nessuna valutazione finora
- Exotic DVM 11 3 CompleteDocumento12 pagineExotic DVM 11 3 CompleteLuc CardNessuna valutazione finora
- School Based INSET Interim EvaluationDocumento8 pagineSchool Based INSET Interim Evaluationprinces arcangelNessuna valutazione finora
- Ci Thai RiceDocumento4 pagineCi Thai RiceMakkah Madina riceNessuna valutazione finora
- HFE0106 TraskPart2Documento5 pagineHFE0106 TraskPart2arunkr1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Numerical Modelling and Design of Electrical DevicesDocumento69 pagineNumerical Modelling and Design of Electrical Devicesfabrice mellantNessuna valutazione finora
- Bacacay South Hris1Documento7.327 pagineBacacay South Hris1Lito ObstaculoNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To BiogasDocumento5 pagineIntroduction To BiogasLouis EldertardNessuna valutazione finora
- Editan - Living English (CD Book)Documento92 pagineEditan - Living English (CD Book)M Luthfi Al QodryNessuna valutazione finora
- Brigade Product Catalogue Edition 20 EnglishDocumento88 pagineBrigade Product Catalogue Edition 20 EnglishPelotudoPeloteroNessuna valutazione finora
- EKC 202ABC ManualDocumento16 pagineEKC 202ABC ManualJose CencičNessuna valutazione finora
- Not A Toy Sample PDFDocumento37 pagineNot A Toy Sample PDFMartha Paola CorralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Babe Ruth Saves BaseballDocumento49 pagineBabe Ruth Saves BaseballYijun PengNessuna valutazione finora
- 82686b - LOAD SHARING MODULEDocumento2 pagine82686b - LOAD SHARING MODULENguyễn Đình ĐứcNessuna valutazione finora
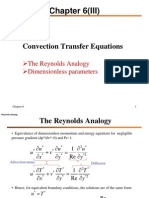
- Convection Transfer EquationsDocumento9 pagineConvection Transfer EquationsA.N.M. Mominul Islam MukutNessuna valutazione finora
- Pipe Cleaner Lesson PlanDocumento2 paginePipe Cleaner Lesson PlanTaylor FranklinNessuna valutazione finora
- A Noble Noose of Methods - ExtendedDocumento388 pagineA Noble Noose of Methods - ExtendedtomasiskoNessuna valutazione finora
- Axera D06Documento2 pagineAxera D06Cristián Fernando Cristóbal RoblesNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Sovereign States and Dependent Territories by Birth RateDocumento7 pagineList of Sovereign States and Dependent Territories by Birth RateLuminita CocosNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Some Common Surgical TermsDocumento5 pagineList of Some Common Surgical TermsShakil MahmodNessuna valutazione finora
- Codan Rubber Modern Cars Need Modern Hoses WebDocumento2 pagineCodan Rubber Modern Cars Need Modern Hoses WebYadiNessuna valutazione finora
- ADC of PIC MicrocontrollerDocumento4 pagineADC of PIC Microcontrollerkillbill100% (2)
- CLG418 (Dcec) PM 201409022-EnDocumento1.143 pagineCLG418 (Dcec) PM 201409022-EnMauricio WijayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Owners Manual Air Bike Unlimited Mag 402013Documento28 pagineOwners Manual Air Bike Unlimited Mag 402013David ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- S4 HANALicensing Model External V19Documento28 pagineS4 HANALicensing Model External V19Edir JuniorNessuna valutazione finora
- Bank Danamon Organization ChartDocumento4 pagineBank Danamon Organization ChartFaisal Agus NugrahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aakriti 1Documento92 pagineAakriti 1raghav bansalNessuna valutazione finora
- Jee MainsDocumento32 pagineJee Mainsjhaayushbhardwaj9632Nessuna valutazione finora