Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Typhoid Fever
Caricato da
MarkChesterSaguidNagen100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
1K visualizzazioni1 paginaSalmonella typhi transmitted by: ingestion of contaminated foods, water or milk. Risk factor: age - 2 years old Susceptible host because of immature body defenses. Bacteria grow and multiply invasion of reticulo endothelial organs Local multiplication in the walls of the gallbladder infected bile causes positive stool culture.
Descrizione originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoSalmonella typhi transmitted by: ingestion of contaminated foods, water or milk. Risk factor: age - 2 years old Susceptible host because of immature body defenses. Bacteria grow and multiply invasion of reticulo endothelial organs Local multiplication in the walls of the gallbladder infected bile causes positive stool culture.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
1K visualizzazioni1 paginaTyphoid Fever
Caricato da
MarkChesterSaguidNagenSalmonella typhi transmitted by: ingestion of contaminated foods, water or milk. Risk factor: age - 2 years old Susceptible host because of immature body defenses. Bacteria grow and multiply invasion of reticulo endothelial organs Local multiplication in the walls of the gallbladder infected bile causes positive stool culture.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
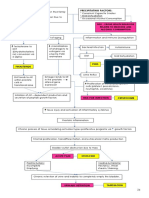
Pathophysiology:
Reference: Atlas of Pathophysiology 2nd Edition: pp.178-179; Medical-Surgical Nursing by Black 7th Edition
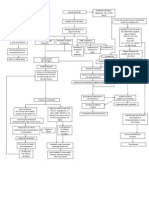
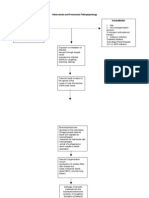
Salmonella typhi 1. ingestion of contaminated foods, water or milk (most common)
transmitted by: 2. fecal contamination of food stuff
3. human carriers (infected individuals)
Risk factor: age – 2 years old Ingestion of spring water which is
Bacterial invasion possibly contaminated with salmonella
Susceptible host because of
typhi from feces etc.
immature body defenses to
Direct invasion of microvilli
protect one’s self from foreign
invaders Invasion of interstitial epithelium
Invasion of ilial brush borders through Peyer’s patches
Organism travel to mesenteric lymph nodes
Infectious process
Risk for constipation anorexia Multiplication of microorganisms
TYPHOID FEVER
Enter blood stream via thoracic duct
Risk for imbalanced Bacteria grow and multiply
nutrition: less than body
requirements Invasion of reticulo endothelial organs
Body’s immune system is activated Local multiplication in the walls of the gallbladder
Elevated WBC Release of IgE Infected bile causes positive stool culture
Inflammation process Maculopapular rashes (“rose Infiltration of Peyer’s patches
spots”)
Mucosal ulceration
Risk for pruritus Vomiting
Hyperthermia episodes Severe diarrhea Abdominal pain Acute Pain
Discomfort, inability to sleep
Causes weakness and electrolyte loss Fatigue
Disturbed sleep pattern
Risk for fluid volume deficit
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocumento4 pagineUrinary Tract InfectionGerardLum100% (2)
- Pathophysiology Acute Bacterial MeningitisDocumento2 paginePathophysiology Acute Bacterial MeningitisNadira Farah PrayogoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology Schistosomiasis: Table in New WindowDocumento7 paginePathophysiology Schistosomiasis: Table in New WindowKaren Leigh MagsinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Liver AbscessDocumento6 pagineLiver AbscessKenneth SunicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of DMDocumento4 paginePathophysiology of DMNicole Louise N. VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Leptospirosis FinalDocumento5 pagineLeptospirosis FinalufrieNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophy of Appendicitis (Or) by Mizzy BaylonDocumento2 paginePathophy of Appendicitis (Or) by Mizzy BaylonmizzybaylonNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Typhoid FeverDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of Typhoid FeverRiandino Suryo RNessuna valutazione finora
- Clarithromycin Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaClarithromycin Drug StudyJanine Joy Orpilla100% (4)
- Pathophysiology of Typhoid FeverDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of Typhoid FeverKristofer Karlo Cabrera Castillo0% (1)
- Case Scenario Dengue FeverDocumento2 pagineCase Scenario Dengue FeverJaslir MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- DiarrheaDocumento24 pagineDiarrheaash ashNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology (Client Base) :: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology (Client Base) :: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factorsleslie_macasaetNessuna valutazione finora
- Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocumento12 pagineDengue Hemorrhagic FeverJohn Maurice AbelNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Pott'S DiseaseDocumento4 paginePathophysiology of Pott'S Diseasee3runeNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Nursing Research Alpha 2017Documento8 pagine4 Nursing Research Alpha 2017Nicole DimarucutNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology: School OF Health AND Allied Sciences Bachelor of Science in Nursing - Level IiiDocumento4 paginePathophysiology: School OF Health AND Allied Sciences Bachelor of Science in Nursing - Level IiiLadybelle GototosNessuna valutazione finora
- The Pathophysiology of Peptic UlcerDocumento15 pagineThe Pathophysiology of Peptic UlcerKike Meneses100% (1)
- POTTs Disease PathoDocumento3 paginePOTTs Disease PathoEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- Bacterial and Viral MeningitisDocumento12 pagineBacterial and Viral Meningitisapi-3704562Nessuna valutazione finora
- ChlamydiaDocumento45 pagineChlamydiaCesar Toribio GamuzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Patho DengueDocumento3 paginePatho DengueKayshey Christine ChuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Communicablediseases 110227001506 Phpapp02 PDFDocumento30 pagineCommunicablediseases 110227001506 Phpapp02 PDFCrystal Ann Monsale TadiamonNessuna valutazione finora
- Case StudyDocumento21 pagineCase StudyLuige AvilaNessuna valutazione finora
- MeningococcemiaDocumento15 pagineMeningococcemiaJoma CabiLdo ﭢNessuna valutazione finora
- RabiesDocumento25 pagineRabiesAdindapauliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Meningococcal Meningitis and SepticaemiaDocumento8 paginePathophysiology of Meningococcal Meningitis and SepticaemiaEugen TarnovschiNessuna valutazione finora
- International QuarantineDocumento72 pagineInternational QuarantineBEISAL BABY PNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Leptospirosis and Dengue FeverDocumento5 paginePathophysiology of Leptospirosis and Dengue FeverKenneth Lagman100% (1)
- Pa Tho Physiology of Typhoid Fever Client BasedrtyytyttyDocumento3 paginePa Tho Physiology of Typhoid Fever Client Basedrtyytyttyangeliejoy_1109Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology: Non-Hodgkin's LymphomaDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology: Non-Hodgkin's LymphomaExernest Joever ZausaNessuna valutazione finora
- Amoebiasis Is An Infection in The Bowel, Particularly The Colon, Characterized byDocumento8 pagineAmoebiasis Is An Infection in The Bowel, Particularly The Colon, Characterized byJamie JunioNessuna valutazione finora
- CiprobayDocumento2 pagineCiprobayianecunar100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of AmoebiasisDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of AmoebiasisCathy AcquiatanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pa Tho Physiology of RaDocumento7 paginePa Tho Physiology of Ralisalmar2008Nessuna valutazione finora
- Typhoid FeverDocumento30 pagineTyphoid FeversakuarNessuna valutazione finora
- Pa Tho Irritable Bowel SyndromeDocumento1 paginaPa Tho Irritable Bowel Syndromekaye0403Nessuna valutazione finora
- PathophysiologyDocumento5 paginePathophysiologyJessyl GirayNessuna valutazione finora
- Patho DengueDocumento3 paginePatho DengueLindy Shane BoncalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Hypersensitivity Type IIDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of Hypersensitivity Type IItwin_smartyNessuna valutazione finora
- Buerger DiseaseDocumento3 pagineBuerger DiseaseElmer DizonNessuna valutazione finora
- Cancer of The ColonDocumento8 pagineCancer of The Colonnot your medz duranNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdominal TraumaDocumento24 pagineAbdominal TraumaSurgeryClassesNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Cause or Etiology of Pott's DiseaseDocumento5 pagineCommon Cause or Etiology of Pott's DiseaseStan Aves GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology: HIV Infection and AIDSDocumento7 paginePathophysiology: HIV Infection and AIDSmeylin SNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of DiarrheaDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of DiarrheaFathur RahmatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology and Schematic Diagram of Typhoid FeverDocumento3 paginePathophysiology and Schematic Diagram of Typhoid FeverCyrus De AsisNessuna valutazione finora
- Geographical Area - Tropical Islands in Thepacific (Philippines) and AsiaDocumento1 paginaGeographical Area - Tropical Islands in Thepacific (Philippines) and AsiaGenevang SeaweedsNessuna valutazione finora
- Vii. Pathophysiology A. AlgorithmDocumento2 pagineVii. Pathophysiology A. AlgorithmJonna Mae TurquezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Ruptured Ectopic PregnancyDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancybowki namoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic PyelonephritisDocumento5 pagineChronic PyelonephritisIsak ShatikaNessuna valutazione finora
- PathophysiologyDocumento6 paginePathophysiologyElbert Hermogino ﭢNessuna valutazione finora
- Liver AbscessDocumento3 pagineLiver AbscessLyiuiu TranNessuna valutazione finora
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever PathophysiologyDocumento4 pagineDengue Hemorrhagic Fever PathophysiologylylasherliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Presentation of Acute PyelonephritisDocumento1 paginaCase Presentation of Acute PyelonephritisANALYN ANUBNessuna valutazione finora
- SYPHILISDocumento6 pagineSYPHILISKhristine Dyanne San JoaquinNessuna valutazione finora
- Liver CancerDocumento1 paginaLiver CancerTarantado67% (3)
- Bacolod, Queen Elizabeth G. Bsn3A ESSAY About Community Health Network System in The PhilippinesDocumento2 pagineBacolod, Queen Elizabeth G. Bsn3A ESSAY About Community Health Network System in The PhilippinesQueenie BacolodNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus: LentiruvirusDocumento5 pagineHuman Immunodeficiency Virus: Lentiruvirusjoyrena ochondraNessuna valutazione finora
- Jocel D. Oclarit-Pbs5 Finals ProjectDocumento5 pagineJocel D. Oclarit-Pbs5 Finals ProjectJocel OclaritNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Typhoid FeverDocumento4 paginePathophysiology of Typhoid FeverIan ParrochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Person With Silicosis, DM, Post Gastrectomy StateDocumento6 paginePerson With Silicosis, DM, Post Gastrectomy StatekhleeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Final Patho No NotesDocumento1 paginaFinal Final Patho No NotesVanessa IbekweNessuna valutazione finora
- Igas Flow ChartDocumento1 paginaIgas Flow ChartYi Wei KoNessuna valutazione finora
- Deteksi Sistiserkosis Pada Babi Yang Dipotong Di Rumah Potong Hewan Kota So'eDocumento9 pagineDeteksi Sistiserkosis Pada Babi Yang Dipotong Di Rumah Potong Hewan Kota So'eDavid Prasetyo KutilNessuna valutazione finora
- A Case Report FormatDocumento3 pagineA Case Report FormatMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tylomix 250 Tylosine Feed PremixDocumento1 paginaTylomix 250 Tylosine Feed PremixLalit ChaudhariNessuna valutazione finora
- HIV - AIDS Quiz - Health Encyclopedia - University of Rochester Medical CenterDocumento1 paginaHIV - AIDS Quiz - Health Encyclopedia - University of Rochester Medical CenterWz bel DfNessuna valutazione finora
- DR Nur Farhanah SPPD - Penggunaan AB Rasional 1 PDFDocumento16 pagineDR Nur Farhanah SPPD - Penggunaan AB Rasional 1 PDFFlorantia Setya NugrohoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hiv V/S Aids: Other Differences Between HIV and AIDS Are Mentioned Below: HIV Is A Virus ThatDocumento1 paginaHiv V/S Aids: Other Differences Between HIV and AIDS Are Mentioned Below: HIV Is A Virus ThatTanya Gupta Srivastava100% (1)
- Sangguniang Panlungsod: Republic of The PhilippinesDocumento2 pagineSangguniang Panlungsod: Republic of The PhilippinesClarisse Marion DenilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Swab GuideDocumento1 paginaSwab GuideMoe Zaw LinNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Id71915 Coronavirus Covid 19 PhilippinesDocumento61 pagineStudy Id71915 Coronavirus Covid 19 PhilippinesBarneyNessuna valutazione finora
- Japanese EncephalitisDocumento8 pagineJapanese EncephalitisSaifNessuna valutazione finora
- Your Test Result Is Available:: Lapadat Darius Calin Eurofins Lifecodexx GMBHDocumento2 pagineYour Test Result Is Available:: Lapadat Darius Calin Eurofins Lifecodexx GMBHDarius LăpădatNessuna valutazione finora
- Bacteriology Edited 1Documento65 pagineBacteriology Edited 1Ali AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Veterinary Medicines ReportDocumento28 pagineVeterinary Medicines Reportvikram chhabraNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibiotic Prophylaxis OrthoDocumento4 pagineAntibiotic Prophylaxis OrthoDonNessuna valutazione finora
- Brochure For World Health Day 7 April 2011Documento2 pagineBrochure For World Health Day 7 April 2011Dody FirmandaNessuna valutazione finora
- MictobiologyDocumento26 pagineMictobiologySaransh GhimireNessuna valutazione finora
- ROOM ASSIGNMENT-NOV. 2021 CIVIL ENGINEER - Rosales, PangasinanDocumento38 pagineROOM ASSIGNMENT-NOV. 2021 CIVIL ENGINEER - Rosales, PangasinanMatt Julius CorpuzNessuna valutazione finora
- Leptospirosis: Divisi Penyakit Tropik Dan Infeksi Departemen Penyakit Dalam FK USU/RSU HAMDocumento20 pagineLeptospirosis: Divisi Penyakit Tropik Dan Infeksi Departemen Penyakit Dalam FK USU/RSU HAMJoice RumondangNessuna valutazione finora
- Mapeh 8 3RD Quarter ExamDocumento3 pagineMapeh 8 3RD Quarter ExamMelva JuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Parasitology LabDocumento28 pagineMedical Parasitology LabJanielle Medina FajardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Assess and Classify The Sick Child Age 2 Months Up To 5 YearsDocumento76 pagineAssess and Classify The Sick Child Age 2 Months Up To 5 YearsTaniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Group Task-Topic SentenceDocumento2 pagineGroup Task-Topic SentenceajengdwiprasantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Maternal Blood Test Report: Name of Client: CrmnoDocumento3 pagineMaternal Blood Test Report: Name of Client: CrmnoHemanth KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2020-3P-Mycoplasma PneumoniaeDocumento18 pagine2020-3P-Mycoplasma PneumoniaeSin SeutNessuna valutazione finora
- Background of The StudyDocumento4 pagineBackground of The StudyFerreze AnnNessuna valutazione finora
- The Impact of Covid-19 On RestaurantsDocumento4 pagineThe Impact of Covid-19 On RestaurantsIJRASETPublicationsNessuna valutazione finora