Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Drug Interactions of Digoxin - P-Glycoprotein
Caricato da
PharmazellDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Drug Interactions of Digoxin - P-Glycoprotein
Caricato da
PharmazellCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Drug Interactions: Insights and Observations
Drug Interactions with Digoxin:
The Role of P-glycoprotein
John R. Horn, PharmD, FCCP, and Philip D. Hansten, PharmD
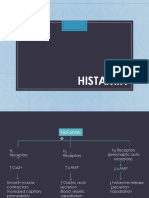
Figure
Drs. Horn and Hansten are both professors
of pharmacy at the University of Washington P-glycoprotein and Digoxin
School of Pharmacy. For an electronic ver-
sion of this article, including references if Small Intestine Biliary Excretion
Diffusion
any, visit www.hanstenandhorn.com.
P-gp
P-gp
O
ne of the most widely studied
Bile Hepatocyte Plasma
drug interactions is the interac-
tion between digoxin and quini- Lumen Enterocyte Plasma
dine. Patients who receive the combina-
tion almost always will have a significant Renal Tubular Secretion
elevation in their digoxin plasma con-
centrations and can suffer digoxin- P-gp = Digoxin
induced toxicity, including arrhythmias,
Urine Tubular Cell Plasma
anorexia, altered color vision, and men-
tal changes. One of the first case reports
of this interaction was published in
1968.1 In 1978, several prospective stud- P-gp = P-glycoprotein. P-gp is found in the enterocytes, hepatocytes, and renal tubular cells. It acts by pumping digoxin out of
cells, resulting in a reduction in digoxin absorption and an increase in its biliary and urinary excretion.
ies of the interaction were published,
noting a 2- to 3-fold increase in digoxin would be 100%, and no further increase Table
concentrations following the coadminis- in concentration could occur by this
tration of quinidine. mechanism. Another mechanism for Selected Drugs That
Since that time, several other drugs— the interaction was needed to explain Affect P-glycoprotein
including cyclosporine, erythromycin, the large changes in digoxin concentra-
Inhibitors Inducers
clarithromycin, propafenone, itracona- tions that had been reported.
Amiodarone Rifampin
zole, amiodarone, verapamil, and dilti- Starting in 1993, a series of studies
azem—were noted to increase digoxin identified a mechanism that appears to Clarithromycin St. John’s wort
Cyclosporine
plasma concentrations. Although some underlie the digoxin interactions report-
Diltiazem
investigators noted a reduction in ed with a wide variety of precipitant
digoxin renal and total body clearance, drugs. It was first noted that Erythromycin
the underlying mechanism for these cyclosporine reduced the renal tubular Felodipine
interactions remained undefined. secretion of digoxin by inhibiting a Indinavir
Some investigators suggested that renal transporter protein—P-glycopro- Itraconazole
antibiotics might increase digoxin tein (P-gp).3 In 1996, it was demonstrat- Ketoconazole
absorption by inactivating gastrointesti- ed that the effect of quinidine on plasma Nicardipine
nal bacteria thought to metabolize digoxin concentrations was the result of Quinidine
digoxin in the gut.2 This mechanism, quinidine-induced inhibition of P-gp in Ritonavir
however, would appear to be incapable the intestine, as well as at sites of digox- Sirolimus
of raising digoxin concentrations 2- to in elimination such as the kidney.4
Tacrolimus
3-fold, because digoxin is well absorbed P-glycoprotein is an energy-depend-
Verapamil
with a bioavailability of about 75%. ent efflux transporter. Simply stated, P-
Adapted from Hansten PD, Horn JR. The Top 100 Drug
Assuming that the intestinal bacteria gp pumps drug molecules out of cells. Interactions: A Guide to Patient Management. Edmonds,
were responsible for this reduction of P-gp is found in the epithelial cells of WA: H&H Publications; 2004:157-169.
digoxin absorption, the greatest the intestine (enterocytes) along the enter the blood. As the molecules dif-
increase in bioavailability one could apical (luminal) side of the cell. When fuse through the enterocyte, P-gp can
expect would be about 25%. At that a drug is taken orally, drug molecules
point, the bioavailability of digoxin have to pass through the enterocyte to continued on page 114
Pharmacy Times October 2004 45
Pg 28-30-114 Rx Focus Diabetes 10/1/04 2:50 PM Page 114
continued from page 30
trials of these analogues have shown positive results. scription for diabetes medications for the first time, the
Gene therapy research also is currently being conduct- pharmacist can play a crucial role in educating the patient
ed. The first area of research involves the conversion of about diabetes. Patients often have heard about diabetes
stem cells to insulin-producing islet cells. Gene research is but will have many questions that the pharmacist can help
underway to promote inactivation of SHIP2, a gene that answer. Patients who know more about their disease are
increases insulin sensitivity. better prepared to play a role in the decision-making
process and in establishing goals of therapy with their
Opportunities for the Pharmacist physician.
In the community setting, when the pharmacist notes According to an Institute for Safe Medication
that a patient is filling prescriptions for diabetes medica- Practices study, 11% of serious medication errors are
tions, he or she should assess the effectiveness of the ther- due to insulin misadministration.7 The pharmacist
apy, the patient’s compliance with it, and the presence of should educate the patient about the type of insulin used,
any adverse effects. Reviewing the frequency at which including the brand, duration of action, onset of action,
medications are refilled is a simple tool to gauge the and proper storage. Patients should demonstrate to the
patient’s compliance. The refilling of glucagon or pur- pharmacist that they are able to accurately measure
chasing of glucose tablets should prompt the pharmacist insulin in the syringe. If a patient uses multiple insulins
to question the patient about side effects or difficulties and is required to mix them, the pharmacist should
with the therapy. ensure that the patient demonstrates the correct tech-
Because a patient often visits the pharmacist more often nique. The pharmacist also should educate the patient on
than the physician, the pharmacist can offer to review the which insulins never should be mixed.
patient’s log of daily glucose readings. If the pharmacist
notes erratic control, he or she can offer options to
For a list of references, send a stamped, self-addressed envelope to:
improve adherence to therapy or recommend an appoint- References Department, Attn. A. Stahl, Pharmacy Times,
ment with the physician to alter the treatment plan. 241 Forsgate Drive, Jamesburg, NJ 08831;
When the pharmacist notices that a patient is filling pre- or send an e-mail request to: astahl@mwc.com.
Drug Interactions: Insights and Observations
continued from page 45
pick up the molecules and carry them back to the luminal side An inducer of P-gp could reduce digoxin plasma concen-
of the cell, where they are dumped back into the lumen of the trations by limiting its absorption from the GI tract and/or
intestine. This action prevents drug molecules from reaching by increasing the elimination of digoxin. The effect of
the systemic circulation, effectively limiting bioavailability. rifampin on digoxin plasma concentrations is greater fol-
Because P-gp is found throughout the intestinal tract, it affects lowing oral digoxin than intravenous digoxin, indicating
the absorption of all susceptible oral drugs, including sustained- that the effect of rifampin may be greater on the absorption
release formulations. P-gp also is present in the liver and kidney, of digoxin than on its renal elimination.5 Both rifampin and
where it acts to increase the excretion of drugs by transporting St. John’s wort have been demonstrated to increase P-gp in
the molecules into the bile and urine, respectively (Figure). the intestine and to result in lower plasma digoxin concen-
If the activity of P-gp is inhibited, more drug will be trations.
absorbed through the enterocytes, and plasma concentra- The Table lists some P-gp inhibitors and inducers. Any of
tions will increase. In addition, drug that is normally elimi- these substances will affect digoxin elimination and absorp-
nated by P-gp in the bile or urine will accumulate in the tion, although, as with other interactions, the magnitude of
body. Thus, when quinidine is coadministered with digox- the effect will vary considerably. Much more study is need-
in, quinidine inhibition of P-gp results in an increase in ed to evaluate other potential interactions involving digox-
digoxin absorption and a reduction of digoxin elimination, in and inhibitors or inducers of P-gp. In the interim, phar-
primarily via the kidney. The elimination of digoxin is so macists should be on the alert for drugs that alter P-gp
dependent on P-gp that it can be used as a test substance to activity, for they may also cause clinically important
see whether other drugs affect P-gp activity. changes in digoxin plasma concentrations.
114 Pharmacy Times October 2004
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Mechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingDa EverandMechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingH. RaškováNessuna valutazione finora
- 15 PharmaDocumento32 pagine15 PharmaGilbert OfeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug InteractionDocumento2 pagineDrug InteractionNicole EncinaresNessuna valutazione finora
- AntihistaminDocumento44 pagineAntihistaminDWI RAHMA HALIDANessuna valutazione finora
- Kinetik LengkapDocumento133 pagineKinetik Lengkapreczky HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Pharmacology Chapter 1Documento37 paginePrinciples of Pharmacology Chapter 1Muhammad ZakriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Review On Chemical Permeation Enhancer Used in Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemDocumento14 pagineReview On Chemical Permeation Enhancer Used in Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemijsidonlineinfoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacokinetic Drug Interactions: Syed Imran Prof. Mrs. Vidya. P. SableDocumento20 paginePharmacokinetic Drug Interactions: Syed Imran Prof. Mrs. Vidya. P. SableDALI SAPARI 2021Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics 40Documento40 paginePharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics 40Shoaib BiradarNessuna valutazione finora
- Computational Methods For Prediction of Drug LikenessDocumento10 pagineComputational Methods For Prediction of Drug LikenesssciencystuffNessuna valutazione finora
- Organ Bath ReportDocumento13 pagineOrgan Bath ReportYusri Yusoff100% (1)
- Advantage of FDC Atozet-Sv - EditDocumento31 pagineAdvantage of FDC Atozet-Sv - EditSuardy Ciayadi100% (1)
- Excretion of DrugDocumento36 pagineExcretion of DrugYeni SuwitaNessuna valutazione finora
- PharmacologyDocumento57 paginePharmacologyarun231187Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Absorption and DistributionDocumento30 pagineDrug Absorption and DistributionaelmowafyNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharm Manuf Drug LitDocumento1 paginaPharm Manuf Drug LitHannah Jean LemorenasNessuna valutazione finora
- EcosanoidsDocumento21 pagineEcosanoidsfmduniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexilor RangeDocumento31 pagineFlexilor RangekurutalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Parameter FarmakokinetikDocumento12 pagineParameter FarmakokinetikNnay AnggraeniNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Receptor and PharmacodynamicsDocumento45 pagineDrug Receptor and PharmacodynamicsFebrianaMNessuna valutazione finora
- Farmakologi III (Antivirus)Documento44 pagineFarmakologi III (Antivirus)candhawidiya santikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Therapy Assessment Worksheet (Dtaw) : 1. A Problem ExistsDocumento6 pagineDrug Therapy Assessment Worksheet (Dtaw) : 1. A Problem ExistsputriNessuna valutazione finora
- DiltiazemDocumento10 pagineDiltiazemSari Puspita DewiNessuna valutazione finora
- Bp503t Pcol Unit-IIIDocumento38 pagineBp503t Pcol Unit-IIIAakkkNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs Interaction1Documento13 pagineDrugs Interaction1Akshay MandhotraNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation of Proteins and Peptides PDFDocumento19 pagineEvaluation of Proteins and Peptides PDFMehnaz Mohammad100% (1)
- Drug Related ProblemsDocumento40 pagineDrug Related Problemsfauzul husnaNessuna valutazione finora
- DRUG Interactions of Veterinary ImportanceDocumento8 pagineDRUG Interactions of Veterinary ImportanceSunil100% (1)
- Autocoids and Their AntagonistsDocumento19 pagineAutocoids and Their AntagonistsHossein Sehati100% (1)
- REVIEW SOLUBILITY Admin - Articles - Review-On-Better-Solubility-Enhancement-Of-Poorly-Water-Soluble-DrugsDocumento7 pagineREVIEW SOLUBILITY Admin - Articles - Review-On-Better-Solubility-Enhancement-Of-Poorly-Water-Soluble-Drugsdini hanifaNessuna valutazione finora
- PharmecogenomicsDocumento21 paginePharmecogenomicsRatan Ratan100% (1)
- Bronchodilator & Other Drugs Used in AsthmaDocumento15 pagineBronchodilator & Other Drugs Used in AsthmaGenta JagadNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 4Documento5 pagineAssignment 4NIKITA0% (1)
- Typhoid Management Guidelines - 2019 - MMIDSPDocumento14 pagineTyphoid Management Guidelines - 2019 - MMIDSPhasnah shintaNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical PharmacokineticsDocumento31 pagineClinical PharmacokineticsArdiyanti Puspitasari100% (1)
- PK-PD of Antimicrobial Therapy-Lecture12 Oct11Documento37 paginePK-PD of Antimicrobial Therapy-Lecture12 Oct11Idrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- Aminoglycoside AntibioticsDocumento56 pagineAminoglycoside AntibioticsMaharani IndriatyNessuna valutazione finora
- Geriatric Drug TherapyDocumento48 pagineGeriatric Drug Therapywalt65Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transes PharmacodynamicsDocumento36 pagineTranses PharmacodynamicsGwyneth Koleen Lopez100% (1)
- Absolute Bioavailability & Relative Bioavailability PDFDocumento8 pagineAbsolute Bioavailability & Relative Bioavailability PDFNehaNessuna valutazione finora
- PHARM CARE PD SLE NewDocumento58 paginePHARM CARE PD SLE NewbrevmanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Toxicology PDFDocumento44 pagineToxicology PDFhuong LNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice ProblemsDocumento2 paginePractice ProblemsShemaj GurchumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Farmakokinetika Klinik Vancomycin: Riri Tifani 1201108Documento21 pagineFarmakokinetika Klinik Vancomycin: Riri Tifani 1201108Rahmatul HusnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To PharmacologyDocumento28 pagineIntroduction To Pharmacologynadar shahNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti Ulcer DrugsDocumento25 pagineAnti Ulcer DrugsPam LalaNessuna valutazione finora
- 44 85 1 SMDocumento9 pagine44 85 1 SMsilvanaanggraeniNessuna valutazione finora
- Floating Drug Delivery SystemDocumento27 pagineFloating Drug Delivery SystemGANESH KUMAR JELLA100% (1)
- Dr. Widyati ADR ANALYSIS-PERSIDocumento39 pagineDr. Widyati ADR ANALYSIS-PERSIHanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic Polymorphism FixDocumento63 pagineGenetic Polymorphism FixBiean gantengNessuna valutazione finora
- Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy and DiagnosisDocumento55 pagineNanoparticles in Cancer Therapy and Diagnosismimshin0% (1)
- Method Development and Validation of Roflumilast in TabletDocumento6 pagineMethod Development and Validation of Roflumilast in TabletjamonlineNessuna valutazione finora
- Shock Syndromes and Sepsis PDFDocumento61 pagineShock Syndromes and Sepsis PDFhuong LNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Related ProblemDocumento13 pagineDrug Related ProblemLinda Yuni LestariNessuna valutazione finora
- Chitosan-Based Systems for Biopharmaceuticals: Delivery, Targeting and Polymer TherapeuticsDa EverandChitosan-Based Systems for Biopharmaceuticals: Delivery, Targeting and Polymer TherapeuticsNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Physiology and Pharmacology: The EssentialsDa EverandClinical Physiology and Pharmacology: The EssentialsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Therapeutic Hypothermia - Principles, Indications, Practical ApplicationDa EverandTherapeutic Hypothermia - Principles, Indications, Practical ApplicationNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Jeemain - GuruDocumento29 pagineSolution Jeemain - GuruPankaj SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 3Documento12 pagineLec 3Shraddha JaiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- (Full List) Indian Stranded Code of Personal Protective Equipment Ppe - Rls Human CareDocumento7 pagine(Full List) Indian Stranded Code of Personal Protective Equipment Ppe - Rls Human CareHarshal Vaidya100% (2)
- Operation Management of Particle Board PlantDocumento18 pagineOperation Management of Particle Board PlantMainul AlamNessuna valutazione finora
- Vulpia MyurosDocumento5 pagineVulpia MyurosOana MikyNessuna valutazione finora
- MJC - H2 - Chem P2 - MSDocumento7 pagineMJC - H2 - Chem P2 - MSclarissa yeoNessuna valutazione finora
- 0610 s14 Ms 32 PDFDocumento8 pagine0610 s14 Ms 32 PDFCorinSaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Zupa Krusevac JSCDocumento19 pagineZupa Krusevac JSCLUIS XVNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbohydrate Polymers: Xiaobao Zhang, Yong Wang, Shitong YangDocumento9 pagineCarbohydrate Polymers: Xiaobao Zhang, Yong Wang, Shitong YangmatitaputyNessuna valutazione finora
- Synthesis of Methylamine - OrgSynDocumento5 pagineSynthesis of Methylamine - OrgSynzodd01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Civil Works MtoDocumento28 pagineCivil Works MtoNassim SabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise-Application of Nanotechnology in IndustryDocumento3 pagineExercise-Application of Nanotechnology in Industrysaadhana elangovan100% (1)
- Report 2 Material and Energy Balance - Doc FinalDocumento36 pagineReport 2 Material and Energy Balance - Doc Finalthembeka422100% (2)
- IB Biology IA: Enzymes and InhibitionDocumento16 pagineIB Biology IA: Enzymes and InhibitionMomina Amjad95% (73)
- Lab09 Catechol OxidaseDocumento9 pagineLab09 Catechol Oxidaseastromaze10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Brian L. Hamshere, Ian J. Lochert and Richard M. Dexter - Evaluation of PBXN-109: The Explosive Fill For The Penguin Anti-Ship Missile WarheadDocumento42 pagineBrian L. Hamshere, Ian J. Lochert and Richard M. Dexter - Evaluation of PBXN-109: The Explosive Fill For The Penguin Anti-Ship Missile WarheadYamveaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2007-04 NHT Reformer LOPADocumento195 pagine2007-04 NHT Reformer LOPARestoration2010100% (1)
- AHU Instalation Manual YorkDocumento36 pagineAHU Instalation Manual YorkBangto Yibsip50% (2)
- 1S Corrigendum For Schedul O Rates For Bu Ding Works Materi S and Labour (Vol-I) of PWD (W B) CTI F M 1st JUL 2014 Date:23.07.2014Documento6 pagine1S Corrigendum For Schedul O Rates For Bu Ding Works Materi S and Labour (Vol-I) of PWD (W B) CTI F M 1st JUL 2014 Date:23.07.2014Sougata DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Rpt-sales-Fundamentals of Sand ControlDocumento8 pagineRpt-sales-Fundamentals of Sand ControlDidier MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- KEPCO's First 5000 MW of Flue Gas Desulfurization: Babcock & Wilcox Barberton, Ohio, U.S.ADocumento6 pagineKEPCO's First 5000 MW of Flue Gas Desulfurization: Babcock & Wilcox Barberton, Ohio, U.S.AVishal RastogiNessuna valutazione finora
- P4 Oct Nov 21Documento11 pagineP4 Oct Nov 21Aini Munirah Muhamad ShudNessuna valutazione finora
- Marten Terpstra, Johan G. Van Veen (Auth.), Marten Terpstra, Johan G. Van Veen (Eds.) - Heat Pipes - Construction and Application - A Study of Patents and Patent Applications-Springer NetherlandsDocumento391 pagineMarten Terpstra, Johan G. Van Veen (Auth.), Marten Terpstra, Johan G. Van Veen (Eds.) - Heat Pipes - Construction and Application - A Study of Patents and Patent Applications-Springer NetherlandsJed MansouriNessuna valutazione finora
- OPerating MANUALDocumento149 pagineOPerating MANUALnobodymagdesignNessuna valutazione finora
- Auto DockDocumento13 pagineAuto DockKarthick YuvrajNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Data Sheet: Multitherm Pg-1 Heat Transfer FluidDocumento8 pagineSafety Data Sheet: Multitherm Pg-1 Heat Transfer FluidRoberto ZevallosNessuna valutazione finora
- Candace MaharajDocumento11 pagineCandace MaharajCharlotte BNessuna valutazione finora
- HRSG FundamentalsDocumento11 pagineHRSG Fundamentalschatuusumitava100% (1)
- The Ultimate Guide To 3D Printed JewelryDocumento69 pagineThe Ultimate Guide To 3D Printed JewelryjpNessuna valutazione finora