Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Main Functions of Protein
Caricato da
sweetwaffleDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Main Functions of Protein
Caricato da
sweetwaffleCopyright:
Formati disponibili
The Main Functions of Proteins
Function Class of Protein Examples Use
Structure Fibers Collagen Cartilage
Metabolism Enzymes Lysosomes Cleve polysaccharide
Proteases Breakdown protein
Polymerases Produce nucleic acid
Kinases Phophorylate sugars
and proteins
Membrane Channels Sodium-potassium Exitable membrane
transport pump
Anion channel Transport chlorine
Osmotic Albumin Serum Albumin Maintains osmotic
regulation concentration of blood
Regulation of Repressor genes Lac repressor Regulates transcription
gene action
Regulation of Hormones Insulin Controls blood glucose
body function level
Vasopressin Increases water
retention by kidney
Oxytocin Regulates milk
production
Transport Globins Hemoglobin Carries oxygen and
throughout the carbon dioxide in the
body blood
Myoglobin Carries oxygen and
carbon dioxide in the
muscle
Cytochrome Electron transport
Storage Ion-binding Ferritin Stores ion specially
spleen
Casein Stores ion in milk
Calmodulin Binds calcium ion
Contraction Muscle Actin Contraction of muscle
Myosin fibers
Defense Immunoglobulins Antibodies Mark foreign proteins
for elimination
Toxins Snake venom Blocks nerve function
Biologically Important Macro Molecules and their Repeating Units
Biological Polymer
PROTEINS NUCLEIC ACID POLYSACCHARIDE
Kind of Informational Informational Storage
macromolecule Structural
Examples Enzymes DNA Starch
Hormones RNA Glycogen, Cellulose
Antibodies
Repeating Amino acid Nucleotides Mono-saccharide
monomers Mono-saccharide
Number and kinds 20 4 DNA One or few
of repeating units 4 RNA One or few
The 30 most Common Small Molecules in Cells
Kind of molecule Number Name of molecules Role in
present cell
Amino acid 20 Alanine Leucine
Arginine Lysine Monomeric units
Asparagine Methionine of all proteins
Aspartate Phenylalanine
Cysteine Proline
Glutamate Serine
Glutamine Threonine
Glycine Tryptophan
Histidine Valine
Isoleucine Thymine
Uracil
Acromatic base Components of
5 Adenosine, Guanine, nucleic acid
Purine Pyrimidine Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil DNA
RNA
Sugar Ribose Component of
(monosaccharides) 2 nucleic acid
Glucose Energy
metabolism,
component of
starch and
glycogen
Lipid 3 Choline, Glycerol, Components of
Palmitate phospholipids
Biological Importance
Organic Compound Significance
PROTEINS Essential in building and repairing of body cells and
tissues
Enzymes are proteins, they aid in speeding up almost all
chemical reactions in the body
Brings about individual differences because each of us is
made up of different proteins in our body
Serves as transport molecules, reserve food and provide
protection as antibodies
Hormones as proteins controls body function
CARBOHYDRATES Serve as backbone of other molecules
Act as energy storage such as starch, cellulose, and
glycogen
Combined with proteins to form structural components
of living cells
Provides fuel for muscles and organs
FATS Energy storage
Key component of cell membrane
Carriers of vitamin A, D, E and K as raw materials for
hormones
- This copy of abbreviation is also joined for further uses and also as part of the reviewer,
but is not a remainder out of the original copy. As for the latter reason, underneath the
amino acid is its two abbreviations (the 3-letter and the 1-letter). -YT
Alanine Glutamic Acid Leucine Serine
Ala Glu Leu Ser
A E L S
Arginine Glutamine Lysine Threonine
Arg Gln Lys Thr
R Q K T
Asparagine Glycine Methionine Tryptophan
Asn Gly Met Trp
N G M W
Aspartic acid Histidine Phenylalanine Tyrosine
Asp His Phe Tyr
D H F Y
Cysteine Isoleucine Proline Valine
Cys Ile Pro Val
C I P V
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Project Geek To Freak 5-31-11Documento43 pagineProject Geek To Freak 5-31-11Benny Carroll80% (5)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Heirarchy of AngelsDocumento5 pagineHeirarchy of AngelssweetwaffleNessuna valutazione finora
- Epithelial Tissue Teaching DemoDocumento40 pagineEpithelial Tissue Teaching DemoFrancis Salcedo100% (1)
- 24 PG Study Guide Study Guide Afaa 1Documento20 pagine24 PG Study Guide Study Guide Afaa 1api-599067855Nessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (DSMQ)Documento2 pagineDiabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (DSMQ)Wayan SugitaNessuna valutazione finora
- 100 Past QuestionsDocumento37 pagine100 Past QuestionsNasif Basher0% (1)
- A Text - Book of Histology: Descriptive and Practical. For the Use of StudentsDa EverandA Text - Book of Histology: Descriptive and Practical. For the Use of StudentsNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Remember The Brachial PlexusDocumento4 pagineHow To Remember The Brachial PlexusAmanda PachecoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Laymans Guide To Steroids 12Documento164 pagineThe Laymans Guide To Steroids 12plgrodrigues100% (2)
- Medical Cell Biology: Xiaoying LiuDocumento44 pagineMedical Cell Biology: Xiaoying LiuSayan KonarNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Mock Test MDCAT-2021 - by RKian MCAT ServiceDocumento15 pagine1st Mock Test MDCAT-2021 - by RKian MCAT ServiceKhan100% (1)
- Drvnbody HandbookDocumento29 pagineDrvnbody HandbookVlad KrasNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry Saeed Oraby Part 1Documento248 pagineBiochemistry Saeed Oraby Part 1Go Hell100% (2)
- Monomers Polymers/ Different Name Elements Examples / Real Life Examples / Real Life Use Special Characteristics Synthesis ReactionDocumento2 pagineMonomers Polymers/ Different Name Elements Examples / Real Life Examples / Real Life Use Special Characteristics Synthesis ReactionNxlaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Anatomy, Histology and Development of The Pancreas PDFDocumento6 pagineThe Anatomy, Histology and Development of The Pancreas PDFredderdatNessuna valutazione finora
- BLOOD PHYSIOLOGY Study Notes For Medical StudentsDocumento3 pagineBLOOD PHYSIOLOGY Study Notes For Medical StudentsBijay Kumar MahatoNessuna valutazione finora
- ProteinDocumento23 pagineProteinsamantha garciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Physiology - Kapitola 21 PDFDocumento41 pagineHuman Physiology - Kapitola 21 PDFpummygNessuna valutazione finora
- Gastrointestinal HormonesDocumento46 pagineGastrointestinal HormonesTaufiq Singgih BaskoroNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry TheoryDocumento198 pagineBiochemistry TheorysgajendranNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are The Functions of ProteinsDocumento12 pagineWhat Are The Functions of ProteinsQue TenederoNessuna valutazione finora
- Acids Bases LessonDocumento16 pagineAcids Bases LessonAndy TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry 1001 V J Temple PDFDocumento12 pagineBiochemistry 1001 V J Temple PDFAmjad Ali50% (2)
- 115 MCAT Biology QuestionsDocumento14 pagine115 MCAT Biology QuestionsmengNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Exam BiologyDocumento4 pagineSample Exam BiologyHamsaNessuna valutazione finora
- HORT 111 Fundamentals of Horticulture Credit Hours: 2 (1+1)Documento13 pagineHORT 111 Fundamentals of Horticulture Credit Hours: 2 (1+1)AnuragNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolic Bioquem Kaplan NotesDocumento6 pagineMetabolic Bioquem Kaplan NotesDrbee10100% (1)
- FST Undergraduate Handbook 2020-2021Documento392 pagineFST Undergraduate Handbook 2020-2021Robin WilliamsNessuna valutazione finora
- PHYSIOLOGYDocumento10 paginePHYSIOLOGYapi-1986354875% (4)
- MSAR Medical School MCATs and GPAsDocumento7 pagineMSAR Medical School MCATs and GPAsDavi CavalcNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Physiology in Physio-1 On BmeDocumento47 pagineBlood Physiology in Physio-1 On BmeGUIDE ON BIO-MEDICAL ENGINEERING UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAM:Nessuna valutazione finora
- Best Physiology TextbookDocumento3 pagineBest Physiology TextbookPeterNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepare Vegetable and Seafood DishesDocumento60 paginePrepare Vegetable and Seafood DishesAlodie Dela Raiz Asuncion89% (9)
- Kaplan Biochemistry: Study Online atDocumento2 pagineKaplan Biochemistry: Study Online atShaz Chindhy100% (1)
- Osmolarity&tonicitypracticeproblemsfrominternetDocumento14 pagineOsmolarity&tonicitypracticeproblemsfrominternetbsktblbabe88Nessuna valutazione finora
- L 17 Structure and Functions of ProteinsDocumento43 pagineL 17 Structure and Functions of ProteinssNessuna valutazione finora
- Selected Topics in the History of Biochemistry. Personal Recollections. Part IIIDa EverandSelected Topics in the History of Biochemistry. Personal Recollections. Part IIIValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- Pages From 1-Molecular Cell Biology Lodish 5Th EdDocumento4 paginePages From 1-Molecular Cell Biology Lodish 5Th Edapi-3733156100% (1)
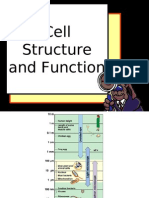
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocumento41 pagineCell Structure and FunctionAhkyluzLaniaz100% (1)
- Quiz 1: Introduction To Molecular BiologyDocumento4 pagineQuiz 1: Introduction To Molecular BiologyLuis MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis of Dr. AKM Maruf Raza PDFDocumento95 pagineThesis of Dr. AKM Maruf Raza PDFMaruf Raza DarubagiNessuna valutazione finora
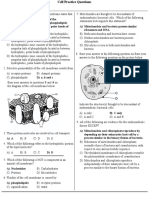
- Cell Practice Questions-Answer KeyDocumento7 pagineCell Practice Questions-Answer KeyJoohyun LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- XI BIO CH# 1 Worksheet 01 Sir Adeeb Rattar - 1Documento19 pagineXI BIO CH# 1 Worksheet 01 Sir Adeeb Rattar - 1kaleel Abbasi100% (5)
- The Edaphic Factors and The Soil Inhabitants: Exercise No.. 2Documento7 pagineThe Edaphic Factors and The Soil Inhabitants: Exercise No.. 2Sakib R SiddiqueNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA: The Genetic Material: A Molecular Approach 2 EditionDocumento63 pagineDNA: The Genetic Material: A Molecular Approach 2 Editionhomerina933379Nessuna valutazione finora
- Content Lehninger Biochemistry BookDocumento2 pagineContent Lehninger Biochemistry BookPingkan Liana MaharaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Examn of Molecular BiologyDocumento11 pagineExamn of Molecular BiologycegfracNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam - 2011, Class: XI, Subject: BiologyDocumento4 pagineExam - 2011, Class: XI, Subject: BiologyAnand RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Bonding: (A Step Towards Smart Education)Documento33 pagineChemical Bonding: (A Step Towards Smart Education)RANJEET SHARMANessuna valutazione finora
- Topic of Entrance ExaminationDocumento3 pagineTopic of Entrance ExaminationNguyễnHuânNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Notes 1Documento15 pagineBiology Notes 1MylesBeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology MCQsDocumento11 pagineBiology MCQs555angel100% (1)
- Lecture 19 Notes - Mucosal ImmunityDocumento5 pagineLecture 19 Notes - Mucosal ImmunityAlbert Mao LiNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Design: Medicinal Chemistry: A Series of Monographs, Vol. 2Da EverandDrug Design: Medicinal Chemistry: A Series of Monographs, Vol. 2E. J. AriënsNessuna valutazione finora
- Cytology and Cell PhysiologyDa EverandCytology and Cell PhysiologyGeoffrey BourneNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd Year Course OutlineDocumento19 pagine2nd Year Course OutlineMiliyon TilahunNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology - Questions & Answers CSIR NET Paper II Life-ScienceDocumento112 pagineBiology - Questions & Answers CSIR NET Paper II Life-ScienceNikhil Zope100% (1)
- 1.04 Biochemistry Trans - EnzymesDocumento11 pagine1.04 Biochemistry Trans - EnzymesApril AramNessuna valutazione finora
- BIO 516-Advance Molecular Biology-Shaper MirzaDocumento4 pagineBIO 516-Advance Molecular Biology-Shaper MirzaAnonymous sF8ZuiGNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice Questions-Cancers: AdvertisementDocumento5 pagineMultiple Choice Questions-Cancers: AdvertisementSp PpvNessuna valutazione finora
- BiochemistryDocumento113 pagineBiochemistryMohammed Faizuddin siddiqui100% (1)
- Bmat Biology KnowledgeDocumento22 pagineBmat Biology KnowledgeAngel SyNessuna valutazione finora
- BRS BiochemistryDocumento345 pagineBRS Biochemistrysxymd321100% (1)
- VNS Faculty of Pharmacy: Mentors - Presented byDocumento1 paginaVNS Faculty of Pharmacy: Mentors - Presented bypoplu100% (1)
- Name Pi R Group: Characteristic Three LetterDocumento1 paginaName Pi R Group: Characteristic Three LetterAloysius QuitaligNessuna valutazione finora
- Gunshot Wound ScenariosDocumento19 pagineGunshot Wound Scenariossweetwaffle50% (2)
- PathophysiologyDocumento2 paginePathophysiologyapi-19762967100% (1)
- Pharmacology Exam ReviewDocumento4 paginePharmacology Exam Reviewapi-3721078100% (3)
- Module 1Documento12 pagineModule 1Rth CMglNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Effects of Non-Centrifugal Sugar - A ReviewDocumento10 pagineHealth Effects of Non-Centrifugal Sugar - A ReviewAsmita AtreNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3 Biomolecules ReviewerDocumento15 pagineLesson 3 Biomolecules Reviewerjohnromar VilasNessuna valutazione finora
- SCIENCE 10 4th QuarterDocumento7 pagineSCIENCE 10 4th QuarterJezha Mae NelmidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Interview Questions For Sport NutritionDocumento4 pagineInterview Questions For Sport NutritionUmi RaihanahNessuna valutazione finora
- CarbohydrtesDocumento2 pagineCarbohydrtesCassandra NaragNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.1 Chemical Basis of Life - 05th JanDocumento15 pagine10.1 Chemical Basis of Life - 05th JanManupa PereraNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 10 4th QeDocumento2 pagineScience 10 4th QeIris LeuterioNessuna valutazione finora
- Vi CH2 Components of Food All QuestionsDocumento5 pagineVi CH2 Components of Food All Questionspriya sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- AsuhanDocumento52 pagineAsuhanDedi KurniawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition Intervention - What's AvailableDocumento39 pagineNutrition Intervention - What's AvailablesitihawamtNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Weekender Issue 55Documento32 pagineIndian Weekender Issue 55Indian WeekenderNessuna valutazione finora
- BCM 202Documento49 pagineBCM 202Naufal QaweimNessuna valutazione finora
- Acellular CarbsDocumento15 pagineAcellular CarbsstarmittNessuna valutazione finora
- Infancy and NutritionDocumento1 paginaInfancy and NutritionGeneveive GuevaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Nutrition & FeedingDocumento16 pagineAnimal Nutrition & FeedingSager KambojNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Grade 7 - Ujian Mid Semester 2 (Mis)Documento3 pagineBiology Grade 7 - Ujian Mid Semester 2 (Mis)Maggie Y. MontungNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbohydrates and Its TypesDocumento64 pagineCarbohydrates and Its TypesAJ GabayNessuna valutazione finora
- The Sweet Science of CandymakingDocumento4 pagineThe Sweet Science of CandymakingSijan KattelNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Physical Education - Sports and Nutrition-MCQDocumento1 pagina12 Physical Education - Sports and Nutrition-MCQAjad SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- CPAP 413 Week 3Documento7 pagineCPAP 413 Week 3Agnes EvanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Isolation From Chicken Liver and Enzymatic Hydrolysis of GlycogenDocumento2 pagineIsolation From Chicken Liver and Enzymatic Hydrolysis of GlycogenKevin Magadia78% (9)
- Human Anatomy and Physiology 1st Edition Amerman Test BankDocumento15 pagineHuman Anatomy and Physiology 1st Edition Amerman Test BankKevinHarrisoncatjn100% (19)