Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
10 Catchup Schedule PR
Caricato da
drsaharpakzadDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
10 Catchup Schedule PR
Caricato da
drsaharpakzadCopyright:
Formati disponibili
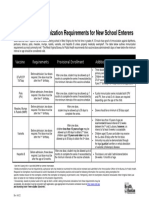
Catch-up Immunization Schedule for Persons Aged 4 Months Through 18 Years Who Start Late or Who Are More
Than 1 Month Behind—United States • 2010
The table below provides catch-up schedules and minimum intervals between doses for children whose vaccinations have been delayed. A vaccine
series does not need to be restarted, regardless of the time that has elapsed between doses. Use the section appropriate for the child’s age.
PERSONS AGED 4 MONTHSTHROUGH 6 YEARS
Minimum Age Minimum Interval Between Doses
Vaccine
for Dose 1 Dose 1 to Dose 2 Dose 2 to Dose 3 Dose 3 to Dose 4 Dose 4 to Dose 5
8 weeks
Hepatitis B1 Birth 4 weeks
(and at least 16 weeks after first dose)
Rotavirus2 6 wks 4 weeks 4 weeks2
Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis3 6 wks 4 weeks 4 weeks 6 months 6 months3
4 weeks 4 weeks4
if first dose administered at younger than age 12 months if current age is younger than 12 months
8 weeks (as final dose)
8 weeks (as final dose) 8 weeks (as final dose)4 This dose only necessary
if first dose administered at age 12–14 months if current age is 12 months or older and first dose for children aged 12 months
Haemophilus influenzae type b4 6 wks
administered at younger than age 12 months and through 59 months who
No further doses needed
second dose administered at younger than 15 months received 3 doses before
if first dose administered at age 15 months or older
age 12 months
No further doses needed
if previous dose administered at age 15 months or older
4 weeks 4 weeks
if current age is younger than 12 months 8 weeks (as final dose)
if first dose administered at younger than age 12 months
This dose only necessary
8 weeks (as final dose for healthy children) 8 weeks for children aged 12 months
if first dose administered at age 12 months or older (as final dose for healthy children) through 59 months who
Pneumococcal5 6 wks
or current age 24 through 59 months if current age is 12 months or older received 3 doses before
age 12 months or for high-
No further doses needed No further doses needed risk children who received
for healthy children if first dose for healthy children if previous dose administered at age 3 doses at any age
administered at age 24 months or older 24 months or older
Inactivated Poliovirus6 6 wks 4 weeks 4 weeks 6 months
Measles,Mumps, Rubella7 12 mos 4 weeks
Varicella8 12 mos 3 months
Hepatitis A9 12 mos 6 months
PERSONS AGED 7 THROUGH 18 YEARS
4 weeks
if first dose administered at younger than age 12 months 6 months
Tetanus,Diphtheria/
7 yrs10 4 weeks if first dose administered at
Tetanus,Diphtheria,Pertussis10 6 months younger than age 12 months
if first dose administered at 12 months or older
Human Papillomavirus11 9 yrs Routine dosing intervals are recommended11
Hepatitis A9 12 mos 6 months
8 weeks
Hepatitis B1 Birth 4 weeks
(and at least 16 weeks after first dose)
Inactivated Poliovirus6 6 wks 4 weeks 4 weeks 6 months
Measles,Mumps, Rubella7 12 mos 4 weeks
3 months
if person is younger than age 13 years
Varicella8 12 mos
4 weeks
if person is aged 13 years or older
1. Hepatitis B vaccine (HepB). • A fourth dose is not necessary if the third dose was administered at age 4 years
• Administer the 3-dose series to those not previously vaccinated. or older and at least 6 months following the previous dose.
• A 2-dose series (separated by at least 4 months) of adult formulation Recombivax • In the first 6 months of life, minimum age and minimum intervals are only recom-
HB is licensed for children aged 11 through 15 years. mended if the person is at risk for imminent exposure to circulating poliovirus (i.e.,
2. Rotavirus vaccine (RV). travel to a polio-endemic region or during an outbreak).
• The maximum age for the first dose is 14 weeks 6 days. Vaccination should not be 7. Measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine (MMR).
initiated for infants aged 15 weeks 0 days or older. • Administer the second dose routinely at age 4 through 6 years. However, the second
• The maximum age for the final dose in the series is 8 months 0 days. dose may be administered before age 4, provided at least 28 days have elapsed
• If Rotarix was administered for the first and second doses, a third dose is not since the first dose.
indicated. • If not previously vaccinated, administer 2 doses with at least 28 days between
3. Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis vaccine (DTaP). doses.
• The fifth dose is not necessary if the fourth dose was administered at age 4 years 8. Varicella vaccine.
or older. • Administer the second dose routinely at age 4 through 6 years. However, the second
4. Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine (Hib). dose may be administered before age 4, provided at least 3 months have elapsed
• Hib vaccine is not generally recommended for persons aged 5 years or older. No since the first dose.
efficacy data are available on which to base a recommendation concerning use of • For persons aged 12 months through 12 years, the minimum interval between
Hib vaccine for older children and adults. However, studies suggest good immu- doses is 3 months. However, if the second dose was administered at least 28 days
nogenicity in persons who have sickle cell disease, leukemia, or HIV infection, or after the first dose, it can be accepted as valid.
who have had a splenectomy; administering 1 dose of Hib vaccine to these persons • For persons aged 13 years and older, the minimum interval between doses is 28
who have not previously received Hib vaccine is not contraindicated. days.
• If the first 2 doses were PRP-OMP (PedvaxHIB or Comvax), and administered at 9. Hepatitis A vaccine (HepA).
age 11 months or younger, the third (and final) dose should be administered at • HepA is recommended for children aged older than 23 months who live in areas
age 12 through 15 months and at least 8 weeks after the second dose. where vaccination programs target older children, who are at increased risk for
• If the first dose was administered at age 7 through 11 months, administer the second infection, or for whom immunity against hepatitis A is desired.
dose at least 4 weeks later and a final dose at age 12 through 15 months. 10. Tetanus and diphtheria toxoids vaccine (Td) and tetanus
5. Pneumococcal vaccine. and diphtheria toxoids and acellular pertussis vaccine (Tdap).
• Administer 1 dose of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) to all healthy children • Doses of DTaP are counted as part of the Td/Tdap series
aged 24 through 59 months who have not received at least 1 dose of PCV on or • Tdap should be substituted for a single dose of Td in the catch-up series or as a
after age 12 months. booster for children aged 10 through 18 years; use Td for other doses.
• For children aged 24 through 59 months with underlying medical conditions, admin- 11. Human papillomavirus vaccine (HPV).
ister 1 dose of PCV if 3 doses were received previously or administer 2 doses of • Administer the series to females at age 13 through 18 years if not previously
PCV at least 8 weeks apart if fewer than 3 doses were received previously. vaccinated.
• Administer pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV) to children aged 2 years • Use recommended routine dosing intervals for series catch-up (i.e., the second and
or older with certain underlying medical conditions, including a cochlear implant, third doses should be administered at 1 to 2 and 6 months after the first dose). The
at least 8 weeks after the last dose of PCV. See MMWR 1997;46(No. RR-8). minimum interval between the first and second doses is 4 weeks. The minimum
6. Inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV). interval between the second and third doses is 12 weeks, and the third dose should
• The final dose in the series should be administered on or after the fourth birthday be administered at least 24 weeks after the first dose.
and at least 6 months following the previous dose.
CS207330-A
Information about reporting reactions after immunization is available online at http://www.vaers.hhs.gov or by telephone, 800-822-7967. Suspected cases of vaccine-preventable diseases should be reported to the state
or local health department. Additional information, including precautions and contraindications for immunization, is available from the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases at http://www.cdc.gov/
vaccines or telephone, 800-CDC-INFO (800-232-4636).
Department of Health and Human Services • Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Catchup Schedule PR PDFDocumento2 pagineCatchup Schedule PR PDFGama Adi SafutraNessuna valutazione finora
- Catchup Schedule BWDocumento4 pagineCatchup Schedule BWlcmurilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Vax 0-6Documento2 pagineVax 0-6alvinmhNessuna valutazione finora
- Catch Up VaccinationDocumento3 pagineCatch Up VaccinationSara Ilyas KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Dtap, Tdap, and TD Catch-Up Vaccination Recommendations by Prior Vaccine History and AgeDocumento1 paginaDtap, Tdap, and TD Catch-Up Vaccination Recommendations by Prior Vaccine History and AgeLaurensia Erlina NataliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Catchup Schedule PR 1Documento1 paginaCatchup Schedule PR 1MichelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Recommendations For Pneumococcal Vaccine Use in Children and TeensDocumento1 paginaRecommendations For Pneumococcal Vaccine Use in Children and TeensuknandiNessuna valutazione finora
- Figure 2. Catch-Up Immunization Schedule For Persons Ages 4 Months Through 18 Years Who Start Late or Who Are More Than 1 Month Behind, U. S., 2013Documento1 paginaFigure 2. Catch-Up Immunization Schedule For Persons Ages 4 Months Through 18 Years Who Start Late or Who Are More Than 1 Month Behind, U. S., 2013Alvaro FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Hepatitis B: Gorgonia, Leanie Louise LDocumento3 pagineHepatitis B: Gorgonia, Leanie Louise LLeanie LouiseNessuna valutazione finora
- Pneumonia Vaccine For ChildrenDocumento1 paginaPneumonia Vaccine For ChildrenPrincess Gutierrez RositaNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 - ADDITIONAL NOTES FOR Pedia Handout by DR - Ian de VeraDocumento2 pagine11 - ADDITIONAL NOTES FOR Pedia Handout by DR - Ian de VeraMJ Arcilla100% (1)
- ImmunizationDocumento1 paginaImmunizationMicah Lou CalambaNessuna valutazione finora
- National Immunization Schedule: One Dose at 14 Weeks, Along With OPV3. Injectable Dose GivenDocumento1 paginaNational Immunization Schedule: One Dose at 14 Weeks, Along With OPV3. Injectable Dose GivenSandip PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes For Pedia HandoutDocumento2 pagineNotes For Pedia HandoutAiszel Angeli Pepito Ligo100% (2)
- School Vaccine RequirementsDocumento2 pagineSchool Vaccine RequirementsrkarlinNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunization Routine TableDocumento9 pagineImmunization Routine TablewenyinriantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) Catch-Up Guidance For Children 4 Months Through 18 Years of Age 2015Documento3 paginePneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) Catch-Up Guidance For Children 4 Months Through 18 Years of Age 2015phobicmdNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric Vac + NotesDocumento36 paginePediatric Vac + NotesTrang VuNessuna valutazione finora
- Childhood Immunization Schedule 2021Documento11 pagineChildhood Immunization Schedule 2021Paula QuiñonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Recommendations For All Immunization Programmes: Haemophilus Influenzae Type B 5Documento9 pagineRecommendations For All Immunization Programmes: Haemophilus Influenzae Type B 5Shadia NaLaNessuna valutazione finora
- Catchup Schedule PRDocumento1 paginaCatchup Schedule PRJesus A. Pineda GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Childhood Immunization Schedule 2021 EditedDocumento11 pagineChildhood Immunization Schedule 2021 EditedPatricia Bernadette PalenciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sara Michlle Immunization Tip SheetDocumento2 pagineSara Michlle Immunization Tip SheetJan FloydNessuna valutazione finora
- Recommended Immunization Schedule For Persons Aged 0-6 YearsDocumento3 pagineRecommended Immunization Schedule For Persons Aged 0-6 YearsAlvaro FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunization ScheduleDocumento2 pagineImmunization ScheduleTrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunization ScheduleDocumento2 pagineImmunization Schedulerere choiNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunization ScheduleDocumento2 pagineImmunization Schedulerere choiNessuna valutazione finora
- VACCINESDocumento3 pagineVACCINESVannesa TarifaNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunization Routine Table3Documento7 pagineImmunization Routine Table3MukundNessuna valutazione finora
- Diphtheria-, Tetanus-, and Pertussis-Containing Vaccines: Dtap/DtDocumento2 pagineDiphtheria-, Tetanus-, and Pertussis-Containing Vaccines: Dtap/DtVhjfxdhNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaccine Interval GuideDocumento2 pagineVaccine Interval GuideTabogon RHUNessuna valutazione finora
- Precept1 - Pulmo BlockDocumento15 paginePrecept1 - Pulmo BlockMary Christine IlangaNessuna valutazione finora
- COVID-19 Vaccine: Interim COVID-19 Immunization Schedule For 6 Months of Age and OlderDocumento4 pagineCOVID-19 Vaccine: Interim COVID-19 Immunization Schedule For 6 Months of Age and OlderBio EticaNessuna valutazione finora
- Raymund Christopher R. Dela Peña, RN, RM, MAN UNP-College of NursingDocumento32 pagineRaymund Christopher R. Dela Peña, RN, RM, MAN UNP-College of NursingrnrmmanphdNessuna valutazione finora
- Properly Yourself Family Deadly: You Been Vaccinated? Get Vaccinated Your Friends and Members From DiseasesDocumento2 pagineProperly Yourself Family Deadly: You Been Vaccinated? Get Vaccinated Your Friends and Members From DiseasesOmar FarukNessuna valutazione finora
- Con134921 PDFDocumento36 pagineCon134921 PDFMohamed AlomaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaccination Guide - Steyn SummaryDocumento1 paginaVaccination Guide - Steyn SummaryMichelle BrowneNessuna valutazione finora
- 0 6yrs Schedule BWDocumento1 pagina0 6yrs Schedule BWRyan ArdyantoNessuna valutazione finora
- BHW TRAINING Neonate and Infant HealthDocumento24 pagineBHW TRAINING Neonate and Infant HealthWilma BeraldeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 BingDocumento4 pagineChapter 3 BingDAVINA ELSA AURELLIANessuna valutazione finora
- Philippine Childhood Immunization Schedule 2019Documento8 paginePhilippine Childhood Immunization Schedule 2019Linius Cruz67% (3)
- Highlghts in Pediatric Infectious DiseasesDocumento37 pagineHighlghts in Pediatric Infectious DiseasesLibay Villamor IsmaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Pedia Osce Notes 2019 Med StudentDocumento30 paginePedia Osce Notes 2019 Med StudentBullet CanoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Pneumococcal Catch UpDocumento1 paginaPneumococcal Catch UpnzdocNessuna valutazione finora
- West Virginia School Immunization RequirementsDocumento1 paginaWest Virginia School Immunization RequirementsJeff MorrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Childhood Immunization Schedule 2019Documento8 pagineChildhood Immunization Schedule 2019Maribel LutzNessuna valutazione finora
- Hepatitis B (Hepb) Vaccine. (Min Age: Birth) at BirthDocumento5 pagineHepatitis B (Hepb) Vaccine. (Min Age: Birth) at Birthannu panchalNessuna valutazione finora
- Expanded Program of ImmunizationDocumento20 pagineExpanded Program of ImmunizationgwynNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunization Routine Table3Documento9 pagineImmunization Routine Table3oweesheeNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaccine Site Schedule Notes BCG DPT OPV Measles Hep B Hib PNCV/PPV Hep ADocumento5 pagineVaccine Site Schedule Notes BCG DPT OPV Measles Hep B Hib PNCV/PPV Hep AKevin AgbonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Paracetamol Safe Use of Paracetamol For Children July 2018Documento4 pagineParacetamol Safe Use of Paracetamol For Children July 2018Justin SamsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaccines!!!Documento6 pagineVaccines!!!Stephanie OngNessuna valutazione finora
- Demaprone: Identify The Generic Structures of The Label Above!Documento3 pagineDemaprone: Identify The Generic Structures of The Label Above!fauziahNessuna valutazione finora
- National Immunization Schedule (NIS) : For Infants, Children and Pregnant WomenDocumento13 pagineNational Immunization Schedule (NIS) : For Infants, Children and Pregnant WomenPrabir Kumar Chatterjee100% (1)
- Over-All Goal: To Reduce The Morbidity and Mortality Among Children Against The Most Common Vaccine-Preventable Specific GoalDocumento9 pagineOver-All Goal: To Reduce The Morbidity and Mortality Among Children Against The Most Common Vaccine-Preventable Specific GoalRetiza EllaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anticipatory Guidance - 18 MonthsDocumento4 pagineAnticipatory Guidance - 18 MonthsSolange AdamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaccination SchedDocumento9 pagineVaccination SchedDaihachi DaimeNessuna valutazione finora
- Hops (Humulus lupulus): Monograph on a herb reputed to be medicinalDa EverandHops (Humulus lupulus): Monograph on a herb reputed to be medicinalNessuna valutazione finora
- LASTING More in bed: Program of 7 Days To Eliminate forever Premature EjaculationDa EverandLASTING More in bed: Program of 7 Days To Eliminate forever Premature EjaculationNessuna valutazione finora
- Holistic Baby Acupressure System: 12 Acupressure Points for Pediatric Sleep Improvement and Wellness SupportDa EverandHolistic Baby Acupressure System: 12 Acupressure Points for Pediatric Sleep Improvement and Wellness SupportNessuna valutazione finora
- MSE DepressionDocumento3 pagineMSE DepressionSam Raven AndresNessuna valutazione finora
- Emergency Room 100 ItemsDocumento33 pagineEmergency Room 100 ItemsJillian EsquivelNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study SampleDocumento4 pagineCase Study SamplenivienneNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Circulation Disorders PDFDocumento69 pagine4 Circulation Disorders PDFSetiawan SukmadjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gastrointestinal Pharmacotherapy: Sarah Nelson, Pharm.D. March 3, 2009Documento45 pagineGastrointestinal Pharmacotherapy: Sarah Nelson, Pharm.D. March 3, 2009YainPanggaloNessuna valutazione finora
- 2010 Orthopaedic JournalDocumento80 pagine2010 Orthopaedic JournalPooria1989Nessuna valutazione finora
- Neo Pedia Guidelines Developmental CareDocumento29 pagineNeo Pedia Guidelines Developmental CareUlysses GamayonNessuna valutazione finora
- Obat Katalog Tahun 2017Documento96 pagineObat Katalog Tahun 2017Aqim Apa AdanyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Group الملزمة الاولىDocumento233 pagineStudy Group الملزمة الاولىMoustafa MagdyNessuna valutazione finora
- Modes of VentilatorDocumento10 pagineModes of VentilatorSatya Biomed100% (2)
- SBAR Communication Worksheet: SaferDocumento13 pagineSBAR Communication Worksheet: SaferBenny Riyan100% (1)
- GP Management Plan - Mbs Item No. 721 (Asthma)Documento3 pagineGP Management Plan - Mbs Item No. 721 (Asthma)Mohamed Rikarz Ahamed RikarzNessuna valutazione finora
- An Investigatory Project ProposalDocumento13 pagineAn Investigatory Project ProposalJeg B. Israel Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Nagpur Result NotificationDocumento4 pagineAll India Institute of Medical Sciences, Nagpur Result NotificationNayan ChaudhariNessuna valutazione finora
- Dilatation and Curettage ProcedureDocumento3 pagineDilatation and Curettage Proceduresagi muNessuna valutazione finora
- Abstracts of Literature: Some of The Papers On The Family Which Have Appeared Since 1960Documento7 pagineAbstracts of Literature: Some of The Papers On The Family Which Have Appeared Since 1960Fausto Adrián Rodríguez LópezNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurobiology of Hyper ReligiosityDocumento33 pagineNeurobiology of Hyper ReligiosityRavi KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- CP 4Documento79 pagineCP 4Kalichandren ArumugamNessuna valutazione finora
- Beauty-Care-9 q1 w4 Mod4Documento19 pagineBeauty-Care-9 q1 w4 Mod4AneNessuna valutazione finora
- My Own Life: by Oliver SacksDocumento4 pagineMy Own Life: by Oliver SacksAmerigo VespucciNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Plan For PidDocumento5 pagineTeaching Plan For PidokaciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ischemic Optic NeuropathyDocumento10 pagineIschemic Optic NeuropathyScerbatiuc CristinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric Assessment TriangleDocumento2 paginePediatric Assessment TriangleVanessa BergollaNessuna valutazione finora
- Shen Ling Bai Zhu San - 參苓白術散 - Ginseng, Poria and Atractylodis Macrocephalae Powder - 參苓白術散 - Ginseng and Atractylodes Formula - Chinese Herbs - American Dragon - Dr Joel Penner OMD, LAcDocumento9 pagineShen Ling Bai Zhu San - 參苓白術散 - Ginseng, Poria and Atractylodis Macrocephalae Powder - 參苓白術散 - Ginseng and Atractylodes Formula - Chinese Herbs - American Dragon - Dr Joel Penner OMD, LAcangelesarenas0% (1)
- Package Insert Roche c311Documento8 paginePackage Insert Roche c311Hassan Gill75% (4)
- Trauma Radiography Puteri Resort Melaka 2010Documento69 pagineTrauma Radiography Puteri Resort Melaka 2010Syuhada AzmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pmis BlankDocumento11 paginePmis BlankRudimar S. SabtulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acosta, Joyce Ara T. Week 7 & 8 Drug StudyDocumento11 pagineAcosta, Joyce Ara T. Week 7 & 8 Drug StudyJoyce Ara Tumbaga AcostaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gastrointestinal System Practice ExamDocumento53 pagineGastrointestinal System Practice Examcarina.pldtNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral Revalida: EmergenciesDocumento74 pagineOral Revalida: EmergenciesCynn AyoNessuna valutazione finora