Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Seminar On Bluetooth Technology
Caricato da
anuprk0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
67 visualizzazioni12 pagineBluetooth is a wireless distances from fixed and mobile devices, creating networks (PANs) it was originally conceived as a wireless alternative to RS232 data cables. Bluetooth takes small-area networking to the next level by removing the need for user intervention.
Descrizione originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoBluetooth is a wireless distances from fixed and mobile devices, creating networks (PANs) it was originally conceived as a wireless alternative to RS232 data cables. Bluetooth takes small-area networking to the next level by removing the need for user intervention.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
67 visualizzazioni12 pagineSeminar On Bluetooth Technology
Caricato da
anuprkBluetooth is a wireless distances from fixed and mobile devices, creating networks (PANs) it was originally conceived as a wireless alternative to RS232 data cables. Bluetooth takes small-area networking to the next level by removing the need for user intervention.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 12
Seminar On Bluetooth Technology (Professional Practices IV) Page 1
A Seminar Report On
Bluetooth Technology
Submitted By – Sanjay Dudani
Roll No. - 419
Under The Guidance of Prof.
P.B. Dehenkar
Seminar On Bluetooth Technology
Bluetooth is a wireless
distances from fixed and mobile devices, creating
networks (PANs). It was originally conceived as a wireless
alternative
to RS232 data cables. It can connect several devices,
overcoming problems
of synchronization.
Origin of the name and Logo
Bluetooth was named after a 10th Century King, Harald
Bluetooth,
King of Denmark and Norway.
The Bluetooth Logo contains the Latin letters H and B (H for
Harald, B
for Bluetooth)
means H
means B
Working of Bluetooth-
Bluetooth uses a radio
spectrum, which chops up the data being sent and
transmits chunks of it on
up to 79 frequencies. In its basic mode, the modulation is
frequency-shift keying (GFSK). It can achieve a gross
Bluetooth provides a way to connect and exchange
information between
devices such as
computers, printers, Global Positioning System
cameras, and video game consoles
(Professional Practices IV)
protocol for exchanging data over short
personal area
e Logo-
radio-technology frequency-hopping spread
, data rate
mobile phones, telephones, laptops
(GPS) receivers
consoles.
Page 2
Gaussian
of 1Mbps.
laptops, personal
receivers, digital
Seminar On Bluetooth Technology (Professional Practices IV) Page 3
How Bluetooth Creates a Connection?
Bluetooth takes small-area networking to the next level by
removing the
need for user intervention and keeping transmission power
extremely low
to save battery power.
Picture this: You're on your Bluetooth-enabled cell phone,
standing outside
the door to your house. You tell the person on the other
end of the line to
call you back in five minutes so you can get in the house
and put your stuff
away. As soon as you walk in the house, the map you
received on your cell
phone from your car's Bluetooth-enabled GPSsystem is
automatically sent to
your Bluetooth-enabled computer, because your cell phone
picked up a
Bluetooth signal from your PC and automatically sent the
data you
designated for transfer. Five minutes later, when your
friend calls you back,
your Bluetooth-enabled home phone rings instead of your
cell phone. The
person called the same number, but your home phone
picked up the
Bluetooth signal from your cell phone and automatically re-
routed the call
because it realized you were home. And each transmission
signal to and
from your cell phone consumes just 1 milliwatt of power, so
your cell phone
charge is virtually unaffected by all of this activity.
Bluetooth is essentially a networking standard that works
at two levels:
• It provides agreement at the physical level -- Bluetooth is
a radiofrequency
standard.
• It provides agreement at the protocol level, where
products have to
agree on when bits are sent, how many will be sent at a
time, and
how the parties in a conversation can be sure that the
message
received is the same as the message sent.
The big draws of Bluetooth are that it is wireless,
inexpensive and
automatic. There are other ways to get around using wires,
including
infrared communication. Infrared (IR) refers to light waves
of a lower
frequency than human eyes can receive and interpret.
Infrared is used in
most television remote controlsystems. Infrared
communications are fairly
reliable and don't cost very much to build into a device, but
there are a
couple of drawbacks. First, infrared is a "line of sight"
technology.
Seminar On Bluetooth Technology (Professional Practices IV) Page 4
For example, you have to point the remote control at the
television or DVD
player to make things happen. The second drawback is that
infrared is
almost always a "one to one" technology. You can send
data between your
desktop computer and your laptop computer, but not your
laptop computer
and your PDA at the same time. (SeeHow Remote Controls
Work to learn
more about infrared communication.)
These two qualities of infrared are actually advantageous
in some regards.
Because infrared transmitters and receivers have to be
lined up with each
other, interference between devices is uncommon. The
one-to-one nature
of infrared communications is useful in that you can make
sure a message
goes only to the intended recipient, even in a room full of
infrared receivers.
Bluetooth is intended to get around the problems that
come with infrared
systems. The older Bluetooth 1.0 standard has a maximum
transfer speed of
1 megabit per second (Mbps), while Bluetooth 2.0 can
manage up to 3
Mbps. Bluetooth 2.0 is backward-compatible with 1.0
devices.
Seminar On Bluetooth Technology (Professional Practices IV) Page 5
How Bluetooth Operates?
Bluetooth networking transmits data via low-power radio
waves. It
communicates on a frequency of 2.45 gigahertz (actually
between 2.402 GHz
and 2.480 GHz, to be exact). This frequency band has been
set aside by
international agreement for the use of industrial, scientific
and medical
devices (ISM).
A number of devices that you may already use take
advantage of this
same radio-frequency band. Baby monitors, garage-door
openers and the
newest generation of cordless phones all make use of
frequencies in the ISM
band. Making sure that Bluetooth and these other devices
don't interfere
with one another has been a crucial part of the design
process.
One of the ways Bluetooth devices avoid interfering with
other systems is by
sending out very weak signals of about 1 milliwatt. By
comparison, the most
powerful cell phones can transmit a signal of 3 watts. The
low power limits
the range of a Bluetooth device to about 10 meters (32
feet), cutting the
chances of interference between your computer system
and your portable
telephone or television. Even with the low power, Bluetooth
doesn't require
line of sight between communicating devices. The walls in
your house won't
stop a Bluetooth signal, making the standard useful for
controlling several
devices in different rooms.
Bluetooth can connect up to eight devices simultaneously.
With all of those
devices in the same 10-meter (32-foot) radius, you might
think they'd
interfere with one another, but it's unlikely. Bluetooth uses
a technique
called spread-spectrum frequency hopping that makes it
rare for more than
one device to be transmitting on the same frequency at the
same time. In
this technique, a device will use 79 individual, randomly
chosen frequencies
within a designated range, changing from one to another
on a regular basis.
In the case of Bluetooth, the transmitters change
frequencies 1,600 times
every second, meaning that more devices can make full
use of a limited slice
of the radio spectrum. Since every Bluetooth transmitter
uses spreadspectrum
transmitting automatically, it’s unlikely that two
transmitters will
be on the same frequency at the same time. This same
technique minimizes
Seminar On Bluetooth Technology (Professional Practices IV) Page 6
the risk that portable phones or baby monitors will disrupt
Bluetooth
devices, since any interference on a particular frequency
will last only a tiny
fraction of a second.
When Bluetooth-capable devices come within range of one
another, an
electronic conversation takes place to determine whether
they have data to
share or whether one needs to control the other. The user
doesn't have to
press a button or give a command -- the electronic
conversation happens
automatically. Once the conversation has occurred, the
devices -- whether
they're part of a computer system or a stereo -- form a
network. Bluetooth
systems create a personal-area network (PAN), or piconet,
that may fill a
room or may encompass no more distance than that
between the cell phone
on a belt-clip and the headset on your head. Once a
piconet is established,
the members randomly hop frequencies in unison so they
stay in touch with
one another and avoid other piconets that may be
operating in the same
room. Let's check out an example of a Bluetooth-connected
system.
Bluetooth Security
In any wireless networking setup, security is a concern.
Devices can easily
grab radio waves out of the air, so people who send
sensitive information
over a wireless connection need to take precautions to
make sure those
signals aren't intercepted. Bluetooth technology is no
different -- it's
wireless and therefore susceptible to spying and remote
access, just
like WiFi is susceptible if the network isn't secure. With
Bluetooth, though,
the automatic nature of the connection, which is a huge
benefit in terms of
time and effort, is also a benefit to people looking to send
you data without
your permission.
Bluetooth offers several security modes, and device
manufacturers
determine which mode to include in a Bluetooth-enabled
gadget. In almost
all cases, Bluetooth users can establish "trusted devices"
that can exchange
data without asking permission. When any other device
tries to establish a
connection to the user's gadget, the user has to decide to
allow it. Servicelevel
security and device-level security work together to
protect Bluetooth
Seminar On Bluetooth Technology (Professional Practices IV) Page 7
devices from unauthorized data transmission. Security
methods include
authorization and identification procedures that limit the
use of Bluetooth
services to the registered user and require that users make
a conscious
decision to open a file or accept a data transfer. As long as
these measures
are enabled on the user's phone or other device,
unauthorized access is
unlikely. A user can also simply switch his Bluetooth mode
to "nondiscoverable"
and avoid connecting with other Bluetooth devices entirely.
If
a user makes use of the Bluetooth network primarily for
synching devices at
home, this might be a good way to avoid any chance of a
security breach
while in public.
Still, early cell-phone virus writers have taken advantage of
Bluetooth's
automated connection process to send out infected files.
However, since
most cell phones use a secure Bluetooth connection that
requires
authorization and authentication before accepting data
from an unknown
device, the infected file typically doesn't get very far. When
the virus arrives
in the user's cell phone, the user has to agree to open it
and then agree to
install it. This has, so far, stopped most cell-phone viruses
from doing much
damage. SeeHow Cell-phone Viruses Work to learn more.
Other problems like "bluejacking," "bluebugging" and "Car
Whisperer" have
turned up as Bluetooth-specific security issues.
Bluejacking involves
Bluetooth users sending a business card (just a text
message, really) to other
Bluetooth users within a 10-meter (32-foot) radius. If the
user doesn't
realize what the message is, he might allow the contact to
be added to his
address book, and the contact can send him messages that
might be
automatically opened because they're coming from a
known contact.
Bluebugging is more of a problem, because it allows
hackers to remotely
access a user's phone and use its features, including
placing calls and
sending text messages, and the user doesn't realize it's
happening. The Car
Whisperer is a piece of software that allows hackers to
send audio to and
receive audio from a Bluetooth-enabled car stereo. Like a
computer security
hole, these vulnerabilities are an inevitable result of
technological
innovation, and device manufacturers are releasing
firmware upgrades that
address new problems as they arise.
Seminar On Bluetooth Technology (Professional Practices IV) Page 8
If communications security is a concern of yours, then click
here to learn
how phone conferencing security works. To learn more
about Bluetooth
security issues and solutions, see Bluetooth.com: Wireless
Security.
Applications Of Bluetooth-
1) Wireless control of and communication between a
mobile phone and
a hands-free headset. This was one of the earliest
applications to
become popular.
2) Wireless networking between PCs in a confined space
and where little
bandwidth is required.
3) Wireless communication with PC input and output
devices, the most
common being the mouse, keyboard and printer.
4) Transfer of files, contact details, calendar appointments,
and
reminders between devices with OBEX i.e. Object
Exchange
technology.
5) Replacement of traditional wired serial communications
in test
equipment, GPS receivers, medical equipment, bar code
scanners, and
traffic control devices.
6) For controls where infrared was traditionally used.
7) Two seventh-generation game consoles, Nintendo's Wii
and Sony's
PlayStation 3, use Bluetooth for their respective wireless
controllers.
8) Dial-up internet access on personal computers or PDAs
using a datacapable
mobile phone as a modem.
Seminar On Bluetooth Technology (Professional Practices IV) Page 9
Advantages Of Bluetooth Technology-
1) Bluetooth Technology is Inexpensive-
Bluetooth technology is cheap for companies to implement,
which results in
lower over-all manufacturing Costs. These savings are then
passed on to
you, the consumer.
The end result: Bluetooth devices are relatively
inexpensive.
2) Bluetooth is Automatic-
Bluetooth doesn't require you to think about setting up a
connection or to
push any buttons. When two or more Bluetooth devices
enter a range (Up
to 30 feet) of one another, they automatically begin to
communicate
without you having to do anything. Once the
communicating begins,
Bluetooth devices will setup Personal Area Networks or
Piconets.
The best part is: The devices take care of the entire setup
process, and you
can go about your business.
3) Low Energy Consumption -
Bluetooth uses low power signals. As a result, the
technology requires little
energy and will therefore use less battery or electrical
power. Obviously, this
is a great benefit for mobile devices because Bluetooth
won't drain the life
of your device's battery.
4) Information Privacy is in your control -
Even though you are able to exchange data across your
cell phones, you still
have the ability to keep your information private. In this
technology, a
password is sent to the receiver by the sender, and the
information is sent
to the receiver if and only if the both ends’ passwords are
matched
correctly.
Seminar On Bluetooth Technology (Professional Practices IV) Page 10
Disadvantages Of Bluetooth Technology-
Every coin has its both ends i.e. positive and negative. So,
Bluetooth has its
Disadvantages as follows:
1) Battery Use –
This problem occurs on your cell phones. Your cell phone’s
battery will be
rapidly decreasing rapidly when you leave your phone’s
Bluetooth enabled
for number of hours. The best way to overcome this is
disable the Bluetooth
immediately after completing the data transfer. It takes
only a few seconds
to enable and disable it.
2) Slow Bluetooth Internet-
Throughout all devices, when using Bluetooth Internet, the
connection can
run sometimes run very slow, so Bluetooth Internet is not
highly suggested
for all cases.
Conclusion-
As you can notice that there are lot of advantages and few
disadvantages of Bluetooth Technology.
Overall, Bluetooth is a great thing to be using on all your
devices that
supports it. You can do so much with it and includes cutting
all the wires and
cords attached to your phone.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- C Program To Read The File and Display Contents On The ScreenDocumento22 pagineC Program To Read The File and Display Contents On The ScreenanuprkNessuna valutazione finora
- Arduino Liquid Crystal Library LCD Interface: Materials NeededDocumento4 pagineArduino Liquid Crystal Library LCD Interface: Materials NeededanuprkNessuna valutazione finora
- Service Oriented ArchitectureDocumento16 pagineService Oriented ArchitectureanuprkNessuna valutazione finora
- Off. No. 46, 1st Floor, Kadamba Complex Gamma-I, Greater Noida (India) - 201308 Contact UsDocumento7 pagineOff. No. 46, 1st Floor, Kadamba Complex Gamma-I, Greater Noida (India) - 201308 Contact UsSaurabh AwasthiNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM TutorialDocumento19 pagineGSM TutorialMuhammad Rauf AkramNessuna valutazione finora
- SMS Based Enotice Board For CollegeDocumento21 pagineSMS Based Enotice Board For CollegeNaveed AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Time Table May 2014Documento6 pagineTime Table May 2014anuprkNessuna valutazione finora
- Arduino Liquid Crystal Library LCD Interface: Materials NeededDocumento4 pagineArduino Liquid Crystal Library LCD Interface: Materials NeededanuprkNessuna valutazione finora
- List of I-Visa Agents NewDocumento12 pagineList of I-Visa Agents NewanuprkNessuna valutazione finora
- New Device Drivers QBDocumento3 pagineNew Device Drivers QBanuprkNessuna valutazione finora
- SMS Based Enotice Board For CollegeDocumento21 pagineSMS Based Enotice Board For CollegeNaveed AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Resume SampleDocumento5 pagineResume SampleanuprkNessuna valutazione finora
- ReportDocumento40 pagineReportanuprkNessuna valutazione finora
- SMS Based Notice BoardDocumento85 pagineSMS Based Notice BoardAnand Cool100% (1)
- Mathematics IIDocumento11 pagineMathematics IIanuprk100% (2)
- Mathematics IIDocumento11 pagineMathematics IIanuprk100% (2)
- Basic AerodynamicsDocumento5 pagineBasic AerodynamicsanuprkNessuna valutazione finora
- Your Order Summary: Order Number: 24079885 Order Date: 31-Mar-12 12:26:53Documento2 pagineYour Order Summary: Order Number: 24079885 Order Date: 31-Mar-12 12:26:53anuprkNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics IIDocumento11 pagineMathematics IIanuprk100% (2)
- UsersDocumento1 paginaUsersanuprkNessuna valutazione finora
- AcademicCALENDAR 2010ODDRevisedDocumento1 paginaAcademicCALENDAR 2010ODDRevisedanuprkNessuna valutazione finora
- SDMCET: Academic Program Handbook General Information Page NoDocumento32 pagineSDMCET: Academic Program Handbook General Information Page NoanuprkNessuna valutazione finora
- Radar NotesDocumento97 pagineRadar Notessrikanth497100% (2)
- C Tificate: Raveendra Konnur S/O Ramchanora KonnurDocumento1 paginaC Tificate: Raveendra Konnur S/O Ramchanora KonnuranuprkNessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Programs For Multiplication and DivisionDocumento6 paginePrograms For Multiplication and DivisionAkhil KumawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Compensated Semiconductro PDFDocumento7 pagineCompensated Semiconductro PDFabhinavruhelaNessuna valutazione finora
- CoT Pro Instruction ManualDocumento20 pagineCoT Pro Instruction ManualSeno PatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2Documento26 pagineLecture 2alessio8Nessuna valutazione finora
- Philips 32PFL3403D-27 - Manual y Circuito Chasis TPM1.2UDocumento62 paginePhilips 32PFL3403D-27 - Manual y Circuito Chasis TPM1.2URoberto GeselinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Submittal For Al Barsha 363 Rev0 PDFDocumento54 pagineSubmittal For Al Barsha 363 Rev0 PDFGokulNessuna valutazione finora
- HEBT-5V - Manual Serviço (EN) (2016.11)Documento24 pagineHEBT-5V - Manual Serviço (EN) (2016.11)Thiago AzevedoNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Controllers and SensorsDocumento12 pagineElectronic Controllers and Sensorsfaizan abbasiNessuna valutazione finora
- CzoneDocumento2 pagineCzoneKhairun NisaqNessuna valutazione finora
- 701MRF de PDFDocumento92 pagine701MRF de PDFPetros TsenesNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulas PyroDocumento23 pagineFormulas PyroMyguEl MurrieTa100% (1)
- Courseoutline Chem 1701 2018 UpdatedDocumento15 pagineCourseoutline Chem 1701 2018 Updatedapi-405072615Nessuna valutazione finora
- IBW OverviewDocumento32 pagineIBW OverviewAbhay SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 063927Documento4 pagine063927mprice2461Nessuna valutazione finora
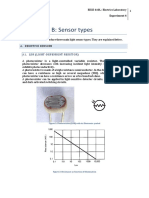
- APPENDIX B: Sensor Types: A1. LDR (Light-Dependent Resistor)Documento4 pagineAPPENDIX B: Sensor Types: A1. LDR (Light-Dependent Resistor)MostafaDilatyNessuna valutazione finora
- TR-808 Snare DIY perfboard layout <40Documento12 pagineTR-808 Snare DIY perfboard layout <40dse666Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bose Lifestyle 28 Repair - Schematics PDFDocumento32 pagineBose Lifestyle 28 Repair - Schematics PDFAurelio Machado75% (4)
- SARTDocumento3 pagineSARTKirtishbose Chowdhury100% (2)
- Manual Rele SickDocumento6 pagineManual Rele SickElian SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hutchison Effect ReportDocumento87 pagineHutchison Effect ReportKenny HaworthNessuna valutazione finora
- Lighting DomesticDocumento123 pagineLighting DomesticjifzerodotcomNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Organization and Architecture Module 1: Interconnection of ComponentsDocumento12 pagineComputer Organization and Architecture Module 1: Interconnection of ComponentsWINORLOSENessuna valutazione finora
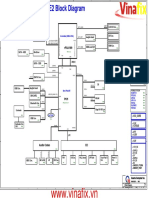
- Acer Aspire 4738G (Quanta ZQ9) Laptop SchematicsDocumento35 pagineAcer Aspire 4738G (Quanta ZQ9) Laptop SchematicsCempli BranomNessuna valutazione finora
- Yokogawa Flow Meter GS01R04B04-00E-EDocumento32 pagineYokogawa Flow Meter GS01R04B04-00E-Edhanu_lagwankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Jump and CarryDocumento8 pagineJump and CarryeekeekeekeekNessuna valutazione finora
- Procedure For SCC & OCC TestDocumento3 pagineProcedure For SCC & OCC TestAyan MajiNessuna valutazione finora
- 14Φ Series Metal Oxide Varistor (MOV) Data Sheet: FeaturesDocumento12 pagine14Φ Series Metal Oxide Varistor (MOV) Data Sheet: Featuresirensy vivasNessuna valutazione finora
- Com4 Satellite Communications ReviewersDocumento6 pagineCom4 Satellite Communications ReviewersKristine Ella BaduriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Generator - Avk Dig 142 E-4 - En-Tlnr593588Documento159 pagineGenerator - Avk Dig 142 E-4 - En-Tlnr593588சக்திவேல் கார்த்திகேயன்50% (2)
- Electrico ProStar PDFDocumento405 pagineElectrico ProStar PDFJ Angel Wolf Maketas50% (2)