Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
MOBILE COMPUTING Paper Presentation
Caricato da
Hatim Nagarwala0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
977 visualizzazioni6 pagineA cellular network consists of mobile units linked together to switching equipment, mobile voice communication is widely interconnecting the different parts of established throughout the world and has the network and allow access to the fixed network. The technology is hidden from networks over the last few years. It's incorporated in a number of extension of this technology is the ability transceivers called Base Stations (BS) to send and receive data across these networks. This is the principle of selected place and covers a given area or mobile computing.
Descrizione originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoA cellular network consists of mobile units linked together to switching equipment, mobile voice communication is widely interconnecting the different parts of established throughout the world and has the network and allow access to the fixed network. The technology is hidden from networks over the last few years. It's incorporated in a number of extension of this technology is the ability transceivers called Base Stations (BS) to send and receive data across these networks. This is the principle of selected place and covers a given area or mobile computing.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
977 visualizzazioni6 pagineMOBILE COMPUTING Paper Presentation
Caricato da
Hatim NagarwalaA cellular network consists of mobile units linked together to switching equipment, mobile voice communication is widely interconnecting the different parts of established throughout the world and has the network and allow access to the fixed network. The technology is hidden from networks over the last few years. It's incorporated in a number of extension of this technology is the ability transceivers called Base Stations (BS) to send and receive data across these networks. This is the principle of selected place and covers a given area or mobile computing.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 6
MOBILE COMPUTING
Hatim Mazhar Husain Nagarwala
Department of Computer Science, Vishwabharati Academy’s College of Engineering,
Ahmednagar.
.
large number of users. During the 1980's
analogue technology was used. Among the
ABSTRACT most well known systems were the
The Paper Contains the knowledge about NMT900 and 450 (Nordic Mobile
the Mobile Computing which includes its Telephone) and the AMPS (Advanced
Definition its use and the common Mobile Phone Service). In the 1990's the
information about its technologies. Next it digital cellular technology was introduced
Summarizes the GSM technology and its with GSM (Global System Mobile) being
technical Specifications & the required the most widely accepted system around
knowledge about the GSM technology. It the world. Other such systems are the
Moreover contains the Applications of DCS1800 (Digital Communication
Mobile computing in general and also the System) and the PCS1900 (Personal
Future of Mobile computing. Communication System).
A cellular network consists of mobile units
INTRODUCTION linked together to switching equipment,
Mobile voice communication is widely which interconnect the different parts of
established throughout the world and has the network and allow access to the fixed
had a very rapid increase in the number of Public Switched Telephone Network
subscribers to the various cellular (PSTN). The technology is hidden from
networks over the last few years. An view; it's incorporated in a number of
extension of this technology is the ability transceivers called Base Stations (BS).
to send and receive data across these Every BS is located at a strategically
cellular networks. This is the principle of selected place and covers a given area or
mobile computing. cell, hence the name cellular
Mobile computing is a generic describing communications. A number of adjacent
one’s ability to use technology while cells grouped together form an area and
moving, as opposed to portable computers, the corresponding BSs communicate
which are only practical for use while through a so called Mobile Switching
deployed in a stationary configuration. Centre (MSC). The MSC is the heart of a
Mobile data communication has become a cellular radio system. It is responsible for
very important and rapidly evolving routing, or switching, calls from the
technology as it allows users to transmit originator to the destinator. It can be
data from remote locations to other remote thought of managing the cell, being
or fixed locations. This proves to be the responsible for set-up, routing control and
solution to the biggest problem of business termination of the call, for management of
people on the move - mobility. inter-MSC hand over and supplementary
services, and for collecting charging and
TAXONOMY accounting information. The MSC may be
Mobile telephony took off with the connected to other MSCs on the same
introduction of cellular technology which network or to the PSTN.
allowed the efficient utilization of The frequencies used vary according to the
frequencies enabling the connection of a cellular network technology implemented.
In 1982, the European Conference of
Postal and Telecommunications
administrations(CEPT) created the Groupe
Special Mobile (GSM) to develop a
standard for a mobile telephone system
that could be used across Europe. In 1989,
For GSM, 890 - 915 MHz range is used GSM responsibility was transferred to the
for transmission and 935 -960 MHz for Europeans Telecommunications Standards
reception. The DCS technology uses Institute (ETSI). By the End of 1993 over
frequencies in the 1800MHz range while a million subscribers and GSM phone
PCS in the 1900MHz range. network was being operated by 70 carriers
Each cell has a number of channels across 48 countries.
associated with it. These are assigned to
subscribers on demand. When a Mobile TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS OF
Station (MS) becomes 'active' it registers GSM NETWORK
with the nearest BS. The corresponding
MSC stores the information about that MS GSM is a cellular Network, which means
and its position. This information is used that mobile phones connect it by searching
to direct incoming calls to the MS. for cells in the immediate vicinity.
If during a call the MS moves to an
adjacent cell then a change of frequency There are five different cell sizes in GSM
will necessarily occur - since adjacent cells network, macro, micro, pico, femto and
never use the same channels. This umbrella cells. The coverage area of each
procedure is called hand over and is the cell varies according to the implementation
key to Mobile communications. As the MS environment. Macro cells can be regarded
is approaching the edge of a cell, the BS as cells where the base station antenna is
monitors the decrease in signal power. The installed on a mast or a building above
strength of the signal is compared with average roof top level. Micro cells are
adjacent cells and the call is handed over cells whose antenna height is under
to the cell with the strongest signal. average roof top level; they are typically
During the switch, the line is lost for about used in urban areas. Picocells are small
400ms. When the MS is going from one cells whose coverage diameter is a few
area to another it registers itself to the new dozen meters; they are mainly used
MSC. Its location information is updated, indoors. Femtocells are cells designed for
thus allowing MSs to be used outside their use in residential or small business
'home' areas. environments and connect to the service
provider’s network via a broadband
GSM TECHNOLOGIES internet connection. Umbrella cells are
used to cover shadowed regions of smaller
GSM communications is the most popular cells and fill in gaps in coverage between
standard for mobile phone in the world. Its those cells.
Promoter, the GSM Association, estimates
that 80% of the global mobile market uses Cell horizontal radius varies depending on
the standard. GSM differs from its antenna height, antenna gain and
predecessors in that both signaling and propagation conditions from a couple of
speech channels are digital, and thus is hundred meters to several tens of
considered a second generation (2G) kilometres. The longest distance the GSM
mobile phone system. specification supports in practical use is
35 kilometres (22 mi). There are also
several implementations of the concept of
an extended cell, where the cell radius multiplexing is used to allow eight full-
could be double or even more, depending rate or sixteen half-rate speech channels
on the antenna system, the type of terrain per radio frequency channel. There are
and the timing advance. eight radio timeslots (giving eight burst
periods) grouped into what is called a
The modulation used in GSM is Gaussian TDMA frame. Half rate channels use
minimum-shift keying (GMSK), a kind of alternate frames in the same timeslot. The
continuous-phase frequency shift keying. channel data rate for all 8 channels is
In GMSK, the signal to be modulated onto 270.833 kbit/s, and the frame duration is
the carrier is first smoothed with a 4.615 ms.
Gaussian low-pass filter prior to being fed
to a frequency modulator, which greatly The transmission power in the handset is
reduces the interference to neighboring limited to a maximum of 2 watts in
channels (adjacent channel interference). GSM850/900 and 1 watt in
GSM1800/1900.
GSM FREQUENCIES
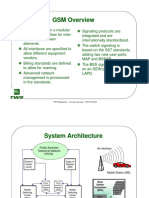
THE STRUCTURE OF GSM
GSM networks operate in a number of NETWORK
different frequency ranges (separated into The network behind the GSM seen by the
GSM frequency ranges for 2G and UMTS customer is large and complicated in order
frequency bands for 3G). Most 2G GSM to provide all of the services which are
networks operate in the 900 MHz or 1800 required. It is divided into a number of
MHz bands. Some countries in the sections and these are each covered in
Americas (including Canada and the separate articles.
United States) use the 850 MHz and 1900
MHz bands because the 900 and 1800 • the Base Station Subsystem (the
MHz frequency bands were already base stations and their controllers).
allocated. Most 3G GSM networks in • the Network and Switching
Europe operate in the 2100 MHz Subsystem (the part of the network
frequency band most similar to a fixed network).
This is sometimes also just called
The rarer 400 and 450 MHz frequency the core network.
bands are assigned in some countries • the GPRS Core Network (the
where these frequencies were previously optional part which allows packet
used for first-generation systems. based Internet connections).
• all of the elements in the system
GSM-900 uses 890–915 MHz to send combine to produce many GSM
information from the mobile station to the services such as voice calls and
base station (uplink) and 935–960 MHz SMS.
for the other direction (downlink),
providing 124 RF channels (channel
numbers 1 to 124) spaced at 200 kHz.
Duplex spacing of 45 MHz is used. In
some countries the GSM-900 band has
been extended to cover a larger frequency
range. This 'extended GSM', E-GSM, uses
880–915 MHz (uplink) and 925–960 MHz
(downlink), adding 50 channels (channel
numbers 975 to 1023 and 0) to the original
GSM-900 band. Time division
database services, where they can
gather information on the case and
APPLICATIONS OF MOBILE related precedents. Therefore
COMPUTING mobile computers allow immediate
access to a wealth of information,
The question that always arises when a making people better informed and
business is thinking of buying a mobile prepared.
computer is "Will it be worth it?"
In Companies
In many fields of work, the ability to keep
on the move is vital in order to utilise time • Managers can use mobile
efficiently. Efficient utilisation of computers in, say, critical
resources (ie: staff) can mean substantial presentations to major customers.
savings in transportation costs and other They can access the latest market
non quantifyable costs such as increased share information. At a small
customer attention, impact of on site recess, they can revise the
maintenance and improved presentation to take advantage of
intercommunication within the business. this information. They can
communicate with the office about
The importance of Mobile Computers has possible new offers and call
been highlighted in many fields of which a meetings for discussing responds to
few are described below. the new proposals. Therefore,
mobile computers can leverage
For Estate Agents competitive advantages.
• Estate agents can work either at Stock Information Collation/
home or out in the field. With Control
mobile computers they can be
more productive. They can obtain • In environments where access to
current real estate information by stock is very limited ie: factory
accessing multiple listing services, warehouses. The use of small
which they can do from home, portable electronic databases
office or car when out with clients. accessed via a mobile computer
They can provide clients with would be ideal.
immediate feedback regarding
specific homes or neighborhoods, Credit Card Verification
and with faster loan approvals,
since applications can be submitted At Point of Sale (POS) terminals in
on the spot. Therefore, mobile shops and supermarkets, when
computers allow them to devote customers use credit cards for
more time to clients. transactions, the intercommunication
required between the bank central
In Courts computer and the POS terminal, in
order to effect verification of the card
• Defense counsels can take mobile usage, can take place quickly and
computers in court. When the securely over cellular channels using a
opposing counsel references a case mobile computer unit. This can speed
which they are not familiar, they up the transaction process and relieve
can use the computer to get direct, congestion at the POS terminals.
real-time access to on-line legal
Electronic Mail/Paging that, even in social spheres, people will
interact via mobile stations, eliminating
• Usage of a mobile unit to send and the need to venture outside of the house.
read emails is a very useful asset
for any business individual, as it This scary concept of a world full of
allows him/her to keep in touch inanimate zombies sitting, locked to their
with any colleagues as well as any mobile stations, accessing every sphere of
urgent developments that may their lives via the computer screen
affect their work. Access to the becomes ever more real as technology,
Internet, using mobile computing especially in the field of mobile data
technology, allows the individual communications, rapidly improves and, as
to have vast arrays of knowledge at shown below, trends are very much
his/her fingertips. towards ubiquitous or mobile computing.
Paging is also achievable here, The future of Mobile Computing is very
giving even more promising indeed, although technology
intercommunication capability may go too far, causing detriment to
between individuals, using a single society.
mobile computer device.
REFERENCES
FUTURE OF MOBILE COMPUTING
“GSM World Statistics” GSM Association
With the rapid technological 2007 retrived on 01-10-2008
advancements in Artificial Intelligence,
Integrated Circuitry and increases in “About GSM Association” GSM
Computer Processor speeds, the future of association
mobile computing looks increasingly
exciting. “DOMINO: Databases for Moving Objects
Traking” by Ouri Wolfson, Bo Xu, Sam
With the emphasis increasingly on Chaamberlain, Liqin Jiang and Prasad
compact, small mobile computers, it may Sistla
also be possible to have all the practicality
of a mobile computer in the size of a hand “MobSQL, An SQL Like Query Language
held organizer or even smaller. for Mobile Objets Databases” by Ahmed
Lbath and Mourad Ouziri
Use of Artificial Intelligence may allow
mobile units to be the ultimate in personal “Why Mobile Computing? Where can it be
secretaries, which can receive emails and Used?” Article by Vasilis koudounas,
paging messages, understand what they are 1996.
about, and change the individuals personal
schedule according to the message. This Communication Systems, Third Edition
can then be checked by the individual to 1994, By Simon Haykin.
plan his/her day.
“Mobile Computing” By R.K.Ghosh, April
The working lifestyle will change, with the 2005.
majority of people working from home,
rather than commuting. This may be WWW Links:
beneficial to the environment as less
transportation will be utilised. This http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~nd/surprise_96/j
mobility aspect may be carried further in ournal/vol4/ vk5/report.html
http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~nd/surprise_96/j
ournal/vol1/vk5/article1.html
http://www.cs.ucsb.edu/~ebelding/courses/
284/w04/slides/intro.pdf
http://www.ansa.co.uk/ANSATech/ANSA
html/98-
ansa/external/9807tb/9807mose.pdf
http://www.danishtechnology.dk/it/9238
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GSM
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- WDM Technologies: Passive Optical ComponentsDa EverandWDM Technologies: Passive Optical ComponentsAchyut K. DuttaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Telephony 2Documento118 pagineCellular Telephony 2mc chesterNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar On GSM 34Documento39 pagineSeminar On GSM 34shikha140Nessuna valutazione finora
- GSM SignalingDocumento11 pagineGSM SignalingAmruthVarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 UMTS Intro Ws10Documento45 pagine01 UMTS Intro Ws10alemayehu w. teferaNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Electronic Communication Systems: Third EditionDocumento57 paginePrinciples of Electronic Communication Systems: Third EditionErwin Roquid IsagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Artificial Intelligence Vehicle: Fundamentals and ApplicationsDa EverandArtificial Intelligence Vehicle: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Green Communication PresentationDocumento16 pagineGreen Communication PresentationSoha Ayaz MehmoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Tecore Icore 2G / 3G / 4G Multi-Technology Core Network SpecificationsDocumento2 pagineTecore Icore 2G / 3G / 4G Multi-Technology Core Network Specificationsyuyong717Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile CommunicationDocumento57 pagineMobile Communicationrphanikumar chintalapudi100% (1)
- Ram Shanti Vidya MandirDocumento17 pagineRam Shanti Vidya MandirChetan DigarseNessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless and Mobile Network ArchitectureDocumento45 pagineWireless and Mobile Network Architecturepruthvi mpatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture6 PLMNDocumento34 pagineLecture6 PLMNNatnael MesheshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Communication: Unit-I Two Marks Q&ADocumento20 pagineMobile Communication: Unit-I Two Marks Q&AKarthika NarasimanNessuna valutazione finora
- Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Asad AliDocumento66 pagineGlobal System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Asad AliMuhammadwaqasnaseemNessuna valutazione finora
- 5G - Fifth-Generation ExplanationDocumento5 pagine5G - Fifth-Generation ExplanationSertse Dingle ShewandagnNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic GSM Frame StructureDocumento42 pagineBasic GSM Frame StructureDawit SeleshNessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless ComuunicationDocumento13 pagineWireless ComuunicationNimra MazharNessuna valutazione finora
- 3G Overview: - UMTS Radio Network Planning & Optimization DeptDocumento54 pagine3G Overview: - UMTS Radio Network Planning & Optimization DeptEdy SupriyantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nokia Is Your Backbone Network Ready For FRMCS? White Paper ENDocumento13 pagineNokia Is Your Backbone Network Ready For FRMCS? White Paper ENdtb5rcknq9Nessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Word FileDocumento11 pagineGSM Word FileevilanubhavNessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless Technology (Includes Practicals)Documento2 pagineWireless Technology (Includes Practicals)Dreamtech Press0% (1)
- A Review: Wireless Sensor Networks and Its Application, Platforms, Standards and ToolsDocumento7 pagineA Review: Wireless Sensor Networks and Its Application, Platforms, Standards and ToolsseventhsensegroupNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM System OverviewDocumento12 pagineGSM System Overviewvemala vandanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lte Ofdm, Ofdma and Sc-FdmaDocumento5 pagineLte Ofdm, Ofdma and Sc-FdmaSamsher SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Ab Ansys Hfss For Antenna Simulation PDFDocumento9 pagineAb Ansys Hfss For Antenna Simulation PDFغريب في بلاد الفرنجهNessuna valutazione finora
- A Survey of Energy-Efficient Techniques For 5G Networks and Challenges AheadDocumento13 pagineA Survey of Energy-Efficient Techniques For 5G Networks and Challenges AheadtroibktroibkNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.12 Questions (GSM) : Answers For Chapter 1 Answer - 1Documento11 pagine1.12 Questions (GSM) : Answers For Chapter 1 Answer - 1edwinNessuna valutazione finora
- Abis Link SignallingDocumento7 pagineAbis Link Signallingsrikanth.2335528Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cs 718 Wireless Networks Syllabus - Virtual University of PakistanDocumento4 pagineCs 718 Wireless Networks Syllabus - Virtual University of PakistanTaran AulakhNessuna valutazione finora
- Millimeter Wave Mobile Communications For 5G CellularDocumento15 pagineMillimeter Wave Mobile Communications For 5G CellularFrancesco GrassiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Communication ComputingDocumento11 pagineMobile Communication ComputingvenkateshmukharjiNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 - Wireless NetworkDocumento25 pagineUnit 1 - Wireless NetworkZappYNessuna valutazione finora
- PSTN PLMNDocumento220 paginePSTN PLMNDr.Hesham El-BadawyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch-4 GSM Channels - and Interfaces LectureDocumento105 pagineCh-4 GSM Channels - and Interfaces LectureShubham GargNessuna valutazione finora
- It2402 Mobile CommunicationDocumento1 paginaIt2402 Mobile Communicationomprakkash1509Nessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Network SignallingDocumento59 pagineGSM Network SignallingAbdullah AbidNessuna valutazione finora
- Radio Over Fiber & WCDMADocumento33 pagineRadio Over Fiber & WCDMASyed Shahzaib RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- UmtsDocumento23 pagineUmtsMitz PaminNessuna valutazione finora
- MLBAM RF Performance Acceptance Criteria For Venues - V2 - 12!6!12 RDJDocumento75 pagineMLBAM RF Performance Acceptance Criteria For Venues - V2 - 12!6!12 RDJculeros1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lte FDD & TDDDocumento16 pagineLte FDD & TDDebrao100% (1)
- SDH Vs PDHDocumento5 pagineSDH Vs PDHTayyab RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- ICS Telecom LeafletDocumento2 pagineICS Telecom LeafletMelania Dîmbeanu100% (1)
- Rappaport GSMDocumento18 pagineRappaport GSMUsman100% (1)
- Types of CellDocumento2 pagineTypes of CellAmit Singh TomarNessuna valutazione finora
- Atm Vs TDMDocumento2 pagineAtm Vs TDMjsdoodnathNessuna valutazione finora
- Smart AntennaDocumento20 pagineSmart AntennaJeyachitra SusanNessuna valutazione finora
- Personal Communication Services - PDF Reasearch PaperDocumento48 paginePersonal Communication Services - PDF Reasearch Paperamitgoyal19899633Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ue Role SequenceDocumento6 pagineUe Role SequenceKarnnan KamarajNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento32 pagineChapter 1Niraj ShresthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Software Defined Networking Enabled Wireless Network Virtualization - Challenges and Solutions - Ning Zhang Et Al PDFDocumento16 pagineSoftware Defined Networking Enabled Wireless Network Virtualization - Challenges and Solutions - Ning Zhang Et Al PDFguimanolNessuna valutazione finora
- Welcome All Trainees: Course No. 270 by Rajesh Suwalka Engineer (WMTDC)Documento29 pagineWelcome All Trainees: Course No. 270 by Rajesh Suwalka Engineer (WMTDC)Rajesh Suwalka100% (1)
- Cdma Deepak Final 1Documento83 pagineCdma Deepak Final 1deepak18mNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Protocol Layers For SignalingDocumento5 pagineGSM Protocol Layers For SignalingProf. P. P. AdivarekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3 - Wireless NetworkDocumento13 pagineUnit 3 - Wireless NetworkZappYNessuna valutazione finora
- EEE4121F - Solution Totutorial - 1 - 2019Documento3 pagineEEE4121F - Solution Totutorial - 1 - 2019ObusitseNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 - Introduction To Nokia Base StationsDocumento25 pagine04 - Introduction To Nokia Base Stationsdesperado1001Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4.3 GERAN Technical Proposal For BSNLDocumento33 pagine4.3 GERAN Technical Proposal For BSNLSunny BSNLNessuna valutazione finora
- HUAWEI CHC-U03 Descripción Del Producto (Inglés)Documento11 pagineHUAWEI CHC-U03 Descripción Del Producto (Inglés)Ramon MTNessuna valutazione finora
- Gsma Hspa/Lte Devices Tracking February 2011: Approval Frequency (MHZ) Data Rate (MB/S)Documento13 pagineGsma Hspa/Lte Devices Tracking February 2011: Approval Frequency (MHZ) Data Rate (MB/S)Luca GiulianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless Communication: Dr. B.Rebekka Assistant Professor Dept. of ECE, NIT, TrichyDocumento86 pagineWireless Communication: Dr. B.Rebekka Assistant Professor Dept. of ECE, NIT, TrichyRithanathithNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.15 Ho PDFDocumento6 pagine1.15 Ho PDFMuhammad HarisNessuna valutazione finora
- Airtel Customer SatisfactionDocumento71 pagineAirtel Customer SatisfactionSomkishore KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- PTA StandardsDocumento2 paginePTA Standardsanamq1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alcatel-Lucent GSM b11 GSM Radio Fine Tuning D0sgdeni1.0Documento466 pagineAlcatel-Lucent GSM b11 GSM Radio Fine Tuning D0sgdeni1.0Waqas AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Ericsson Bts Installation ManualDocumento3 pagineEricsson Bts Installation Manualcastoresime50% (4)
- HPSS Datasheet 100604 Final PrintDocumento2 pagineHPSS Datasheet 100604 Final PrintIdoz SpNessuna valutazione finora
- Keynote Sigos Product Guide 2013 PDFDocumento68 pagineKeynote Sigos Product Guide 2013 PDFSantha KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless Mobile CommunicationDocumento2 pagineWireless Mobile CommunicationRAVALINessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Lecture Notes - Wire & Wireless CommunicationDocumento22 pagine1st Lecture Notes - Wire & Wireless CommunicationJordan-James OlivoNessuna valutazione finora
- 'Evolution of Services and Architectures Throughout Mobile Generations''Documento147 pagine'Evolution of Services and Architectures Throughout Mobile Generations''Carlos León AraujoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Info in VietnamDocumento14 pagineMobile Info in VietnamAlexandar ApishaNessuna valutazione finora
- EE: 451 Mobile Communications: Syed Ali HassanDocumento38 pagineEE: 451 Mobile Communications: Syed Ali Hassansaadi khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Open Radio Equipment InterfaceDocumento2 pagineOpen Radio Equipment Interfaceagung.kusumaw269Nessuna valutazione finora
- Abi Research LpwansDocumento16 pagineAbi Research Lpwanstestuser5791Nessuna valutazione finora
- 54 GSM BSS Network Performance PS KPI (RTT Delay) Optimization ManualDocumento3 pagine54 GSM BSS Network Performance PS KPI (RTT Delay) Optimization ManualCarlos PazNessuna valutazione finora
- GUL SFP Throughput CalculationDocumento5 pagineGUL SFP Throughput Calculationazure_etherealNessuna valutazione finora
- How GPRS WorkDocumento5 pagineHow GPRS WorkparthieeeNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Based Train Reservation System: Technical SpecificationDocumento5 pagineGSM Based Train Reservation System: Technical SpecificationSandeep ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- DVR & Dr. HS MIC College of Technology 1: Arduino Based Smart LPG Gas Leakage Detector SystemDocumento83 pagineDVR & Dr. HS MIC College of Technology 1: Arduino Based Smart LPG Gas Leakage Detector SystemSanju StarcNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Banking SekDocumento141 pagineMobile Banking SekLoveday OsiagorNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 3Documento28 paginePart 3michaelliu123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Motor Speed Monitoring Control System & GSM ModemDocumento21 pagineMotor Speed Monitoring Control System & GSM ModemAditya TomarNessuna valutazione finora
- Thingsys - GPS TRACKER Quotation List V2.1.8Documento1 paginaThingsys - GPS TRACKER Quotation List V2.1.8Rakesh SahooNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Based Motor Control With 3 Phase Detection: PriceDocumento4 pagineGSM Based Motor Control With 3 Phase Detection: PriceSarath MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- IN3080502-01 MLog enDocumento6 pagineIN3080502-01 MLog enveeakumarNessuna valutazione finora
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionDa EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (4)
- Hacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxDa EverandHacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (67)
- CCNA Certification Study Guide, Volume 2: Exam 200-301Da EverandCCNA Certification Study Guide, Volume 2: Exam 200-301Nessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsDa EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Microsoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900Da EverandMicrosoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900Nessuna valutazione finora
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamDa EverandAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsDa EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Palo Alto Networks: The Ultimate Guide To Quickly Pass All The Exams And Getting Certified. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsDa EverandPalo Alto Networks: The Ultimate Guide To Quickly Pass All The Exams And Getting Certified. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNDa EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Cybersecurity: The Beginner's Guide: A comprehensive guide to getting started in cybersecurityDa EverandCybersecurity: The Beginner's Guide: A comprehensive guide to getting started in cybersecurityValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Computer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)Da EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (4)
- ITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationDa EverandITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Azure Networking: Command Line Mastery From Beginner To ArchitectDa EverandAzure Networking: Command Line Mastery From Beginner To ArchitectNessuna valutazione finora
- Cybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringDa EverandCybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (40)
- Terraform for Developers: Essentials of Infrastructure Automation and ProvisioningDa EverandTerraform for Developers: Essentials of Infrastructure Automation and ProvisioningNessuna valutazione finora
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamDa EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamNessuna valutazione finora