Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
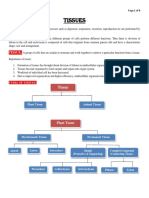
CBSE Class 9 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Chapter - 6 Tissue
Caricato da
NaliniKumaresanTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CBSE Class 9 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Chapter - 6 Tissue
Caricato da
NaliniKumaresanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CBSE
Class 9 Science
NCERT Exemplar Solutions
Chapter - 6
Tissue
Long Answer Questions
49. Differentiate between sclerenchyma and parenchyma tissues. Draw well labelled
diagram.
Ans.
Parenchyma Sclerenchyma
(1) Cells are thin walled and unspecialized. (1) Cells are thick walled and lignified.
(2) These are living cells. (2) Tissues are made up of dead cells.
(3) Cells are usually loosely packed with large (3) No intercellular spaces between the
intercellular space. cells are found.
(4) Stores nutrient and water in stem and
(4) Provides strength to the plant parts.
roots.
(5) Some cells contain chlorophyll called (5) The cells are long and narrow, make the
chlorenchyma and perform photosynthesis. plant hard and stiff. The tissue is present in
Other cells have large air cavities called the stem around vascular bundles, in
aerenchyma which provide buoyancy to the veines of leaves and hal'd covering of seeds
hydrophytic plants. and nuts.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 1 / 6
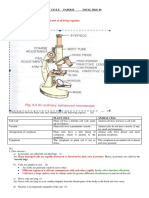
50. Describe the structure and function of different types of epithelial tissues. Draw
diagram of each type of epithelial tissue.
Ans. Epithelial tissues are the covering or protective tissues in the animal body. Epithelium
covers most organs and cavities within the body and keep different body systems separate.
The skin, the lining of the mouth, the lining of blood vessels, lung alveoli and kidney tubules
are all made of epithelial tissue.
Epithelial tissue cells are tightly packed and form a continuous sheet. They have only a small
amount of cementing material between them and almost no intercellular spaces. The
permeability of the cells of various epithelia play an important role in regulating the
exchange of materials between the body and the external environment and also between
different parts of the body. Regardless of the type, all epithelia are usually separated from
the underlying tissue by an extracellular fibrous basement membrane.
Epithelial tissues are of following types:
(1) Simple squamous epithelium
(2) Stratified squamous epithelium
(3) Columnar epithelium, and
(4) Cubodial epithelium.
These tissues differ in structure that correlate with their unique functions. For example, in
cells lining blood vessels or lung alveoli, where transportation of substances occurs through
a selectively permeable surface, there is a simple flat kind of epithelium. This is called the
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 2 / 6
simple squamous epithelium. Simple squamous epithelial cells are extremely thin and flat
and form a delicate lining. The skin, oesophagus and the lining of the mouth are also covered
with squamous epithelium.
Skin epithelial cells are arranged in many layers to prevent wear and tear. Since, they are
arranged in a pattern of layers, the epithelium is called stratified squamous epithelium.
Where absorption and secretion occur, as in the inner lining of the intestine, tall epithelial
cells are present. This columnar epithelium facilitates movement across the epithelial
barrier. In the respiratory tract, the columnar epithelial tissue also has cilia, which are hair-
like projections on the outer surfaces of epithelial cells. These cilia can move, and their
movement pushes the mucus forward to clear it. This type of epithelium is thus ciliated
columnar epithelium.
Cuboidal epithelium forms the lining of kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands, where it
provides mechanical support. Epithelial cells often acquire additional specialisation as gland
cells, which can secrete substances at the epithelial surface. Sometimes a portion of the
epithelial tissue folds inward, and a multicellular gland is formed. This is glandular
epithelium.
51. Draw well labelled diagrams of various types of muscles found in human body.
Ans.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 3 / 6
52. Give reasons for
(a) Meristematic cells have a prominent nucleus and dense cytoplasm but they lack vacuole.
Ans. Cells of meristematic tissue are capable of division. Hence, prominent nucleus and
dense cytoplasm are present in these cells. Since these cells continuously undergo division
hence they do not need to maintain a particular shape and store food or deposit any waste
material. Due to this, vacuoles are not required in these cells.
(b) Intercellular spaces are absent in sclerenchymatous tissues.
Ans. Cell wall in sclerenchyma is lignified. They are arranged as closely organised hexagonal
cells meant to provide strength and protection to the plant parts. Due to this, intercellular
spaces are absent in sclerenchymatous tissues.
(c) We get a crunchy and granular feeling, when we chew pear fruit.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 4 / 6
Ans. In a pear fruit, cells of scelerenhyma are small and called stone cells. They are hard
with highly thickened cell wall . So we get the crunchy feeling due to these stone cells.
(d) Branches of a tree move and bend freely in high wind velocity.
Ans. Collenchyma is present at junction of a branch. Collenchyma provides rigidity with
flexibility. Due to this, branches of tree move and bend freely in high wind velocity.
(e) It is difficult to pull out the husk of a coconut tree.
Ans. The husk of coconut tree is composed of sclerenhyma. Due to this, the husk is very hard
and is difficult to be pulled out.
53. List the characteristics of cork. How are they formed? Mention their role.
Ans. a) Characteristics of cork are following :
Cells of cork are dead at maturity
These cells are compactly arranged
Cells do not possess intercellular spaces.
Cells possess a chemical substances suberin in their walls
They are several layers thick.
b) As plants grow older, a strip of secondary meristem replaces the epidermis of the stem.
Cells which are cut on the outer side by this meristem are called cork.
c) They are protective in function for older stem/twigs/branches. They are impervious to
gases and water.
54. Why are xylem and phloem called complex tissues? How are they different from
one other?
Ans. Both xylem and phloem consist of more than one type of cells, which coordinate to
perform a common function.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 5 / 6
55. (a) Differentiate between meristematic and permanent tissues in plants.
Ans.
(b) Define the process of differentiation.
Ans. The loss of ability to divide by taking up a permanent shape, size and function is called
differentiation. Cells develop into tissues and organs with the help of differentiation.
(c) Name any two simple and two complex permanent tissues in plants.
Ans. The two simple and two complex permanent tissues in plants are as follows:
Simple tissues: Parenchyma/collenchyma/sclerenchyma.
Complex tissues: Phloem/xylem.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 6 / 6
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 9th Bio MTG Tissue QuesDocumento13 pagine9th Bio MTG Tissue QuesData ShareNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue ClassworkDocumento5 pagineTissue ClassworkRajesh Kanna A亗Nessuna valutazione finora
- English Task 2Documento3 pagineEnglish Task 2Tiara ArmiliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Q&ADocumento6 pagineTissue Q&ASuman DasNessuna valutazione finora
- TISSUESDocumento9 pagineTISSUEStyrtNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7th TissueDocumento6 pagineChapter 7th Tissuenakulvyan708Nessuna valutazione finora
- PDF 20221214 190246 0000Documento11 paginePDF 20221214 190246 0000Hiba ZiziNessuna valutazione finora
- TissuesDocumento7 pagineTissuesRohitNessuna valutazione finora
- 9th Bio Important QuesDocumento12 pagine9th Bio Important QuesData ShareNessuna valutazione finora
- PLANTDocumento7 paginePLANTKhaleeq KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Delhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Cell:Structure and FunctionDocumento4 pagineDelhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Cell:Structure and FunctionSaket TNessuna valutazione finora
- Ix Plant Tissues 1Documento7 pagineIx Plant Tissues 1ayushiguptab0406Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues: PS Verma and V.K. Agarwal Biology Class 9 Page No - 165Documento14 pagineTissues: PS Verma and V.K. Agarwal Biology Class 9 Page No - 165Thikshika . NNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6: "Tissues"Documento5 pagineChapter 6: "Tissues"Anil TripathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-8 Cell: Structure and FuctionDocumento12 pagineChapter-8 Cell: Structure and FuctionTopNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER-TISSUES (Class-9) Self Instructional Material S. P Model Higher Secondary School, M.A Road, Srinagar (Teacher: Burhana Rashid)Documento4 pagineCHAPTER-TISSUES (Class-9) Self Instructional Material S. P Model Higher Secondary School, M.A Road, Srinagar (Teacher: Burhana Rashid)MuzafarNessuna valutazione finora
- Term 1 - Grade 8 Science CH 7 Cell Structure and FunctionDocumento3 pagineTerm 1 - Grade 8 Science CH 7 Cell Structure and Functionprakashjoshi23aprilNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade Nine Biology Cell AnswersheetDocumento4 pagineGrade Nine Biology Cell AnswersheetHitakshi BhanushaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer - Bio - Class 7 Chap 1Documento6 pagineAnswer - Bio - Class 7 Chap 1Laiq Ur RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue 11Documento5 pagineTissue 11Adnan Al-asbahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 9 Science CH 6 NotesDocumento13 pagineClass 9 Science CH 6 NotesChetan GargNessuna valutazione finora
- Aakash Institute: NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 TissuesDocumento13 pagineAakash Institute: NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 TissuesNischay MahamanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 Plant Tissues - Class 9th - BiologyDocumento6 pagineChapter 6 Plant Tissues - Class 9th - BiologyPreeti BhullarNessuna valutazione finora
- 642020112334AM-Class 9 Biology Notes-Chapter-6 Plant TissueDocumento14 pagine642020112334AM-Class 9 Biology Notes-Chapter-6 Plant Tissuekmdmohideen2297100% (1)
- Part 3 - Laboratory ManualDocumento50 paginePart 3 - Laboratory ManualBianca AnguloNessuna valutazione finora
- Living TissuesDocumento18 pagineLiving Tissuesdissanayakeinduwara2008Nessuna valutazione finora
- Yellow Green Blue and Red Handwritten Zones of Regulation SEL Social and Emotional Learning Education PresentationDocumento15 pagineYellow Green Blue and Red Handwritten Zones of Regulation SEL Social and Emotional Learning Education PresentationAngel ChrisleneNessuna valutazione finora
- TissueDocumento14 pagineTissueBarkha Agrawal100% (1)
- Animal TissuesDocumento14 pagineAnimal Tissuesjitendragandhi250Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kebo 106Documento8 pagineKebo 106Mohamed Fayaz Sheik DawoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Science FinalDocumento96 pagineScience FinalChitransh GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues - NotesDocumento14 pagineTissues - Notesphysicsbooks.storeNessuna valutazione finora
- L-2 Tissues - 210822Documento22 pagineL-2 Tissues - 210822hridaanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues Class 9Documento5 pagineTissues Class 9Arnav PatangeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Science-9 CombinedDocumento20 pagineChapter Science-9 CombinedAnushkaNessuna valutazione finora
- A P Topic 5 SummaryDocumento9 pagineA P Topic 5 SummaryMax Delvalle100% (1)
- 09 Science Notes ch06 Tissues-UnlockedDocumento5 pagine09 Science Notes ch06 Tissues-UnlockedShekhar UpadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- JihijiojhiDocumento5 pagineJihijiojhiGaurav Kumar GoyalNessuna valutazione finora
- TissuesDocumento5 pagineTissuesDarshilNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organization in Plants: Form 4 Biology Chapter 2 (B) Cell OrganisationDocumento9 pagineCell Organization in Plants: Form 4 Biology Chapter 2 (B) Cell OrganisationMei QiiNessuna valutazione finora
- PS Verma Biology Class 9 Chapter 3 Tissues CBSEDocumento2 paginePS Verma Biology Class 9 Chapter 3 Tissues CBSEhemac717Nessuna valutazione finora
- Science Chapter-6-TissueDocumento11 pagineScience Chapter-6-TissueJEETNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues NotesDocumento7 pagineTissues NotesHarshitNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise-6.1: NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science - Chapter 6 TissuesDocumento9 pagineExercise-6.1: NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science - Chapter 6 TissuesShah RukhNessuna valutazione finora
- 642020112334AM-Class 9 Biology Notes-Chapter-6 Plant TissueDocumento11 pagine642020112334AM-Class 9 Biology Notes-Chapter-6 Plant TissueL Sri Madhi100% (1)
- Gist of The Topic: BiologyDocumento14 pagineGist of The Topic: BiologyDhanya BalasundarrajNessuna valutazione finora
- Review For Test - Biology Use This One - Answer KeyDocumento12 pagineReview For Test - Biology Use This One - Answer Keybettina wNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 TissuesDocumento7 pagineChapter 6 Tissuesh8631259Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues: ClassDocumento4 pagineTissues: ClassShail KumariNessuna valutazione finora
- 2021 Chapter 6 Tissue Most IMP QuestionsDocumento11 pagine2021 Chapter 6 Tissue Most IMP QuestionsGauravNessuna valutazione finora
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues - .Documento9 pagineNCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues - .AshchatNessuna valutazione finora
- Ncert Solutions June6 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocumento10 pagineNcert Solutions June6 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsdrathod4653Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cell - Structure and Function Class 8 Notes: CellsDocumento26 pagineCell - Structure and Function Class 8 Notes: CellsPrabal SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- The Fundamental Unit of Life - Short NotesDocumento5 pagineThe Fundamental Unit of Life - Short Notesas9922889709Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue - Class 9Documento9 pagineTissue - Class 9Rohit Jain100% (1)
- 910th Bio QuesDocumento19 pagine910th Bio QuesData ShareNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocumento16 pagineAnatomy of Flowering PlantsSadik FsNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 BiologyDocumento8 pagineChapter 6 BiologyMohammed mahfuzNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Solutions Textual Questions and Answers: Is Called A TissueDocumento11 pagineTissue Solutions Textual Questions and Answers: Is Called A TissueMr Pan GamingNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice Questions: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 12Documento12 pagineMultiple Choice Questions: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 12NaliniKumaresanNessuna valutazione finora
- Kadal Viralgal - 1 PDFDocumento25 pagineKadal Viralgal - 1 PDFNaliniKumaresanNessuna valutazione finora
- Kadal Viralgal - 2 PDFDocumento20 pagineKadal Viralgal - 2 PDFNaliniKumaresanNessuna valutazione finora
- Athisaya Ragam - 1 PDFDocumento22 pagineAthisaya Ragam - 1 PDFNaliniKumaresanNessuna valutazione finora
- Section - A Very Short Answer Questions: Social ScienceDocumento5 pagineSection - A Very Short Answer Questions: Social ScienceNaliniKumaresanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nizhal Thedum Marangal-KCDocumento42 pagineNizhal Thedum Marangal-KCNaliniKumaresanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hlry WMLD: For ShlffidffignDocumento34 pagineHlry WMLD: For ShlffidffignNaliniKumaresanNessuna valutazione finora
- Biblical World ViewDocumento15 pagineBiblical World ViewHARI KRISHAN PALNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 Closing The Gap ReportDocumento64 pagine2016 Closing The Gap ReportAllan ClarkeNessuna valutazione finora
- Produktkatalog SmitsvonkDocumento20 pagineProduktkatalog Smitsvonkomar alnasserNessuna valutazione finora
- Delonghi Esam Series Service Info ItalyDocumento10 pagineDelonghi Esam Series Service Info ItalyBrko BrkoskiNessuna valutazione finora
- TriPac EVOLUTION Operators Manual 55711 19 OP Rev. 0-06-13Documento68 pagineTriPac EVOLUTION Operators Manual 55711 19 OP Rev. 0-06-13Ariel Noya100% (1)
- Lecture 2 Effects of Operating Conditions in VCCDocumento9 pagineLecture 2 Effects of Operating Conditions in VCCDeniell Joyce MarquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Biography Thesis ExamplesDocumento7 pagineBiography Thesis Examplesreneewardowskisterlingheights100% (2)
- Apple Change ManagementDocumento31 pagineApple Change ManagementimuffysNessuna valutazione finora
- A Survey On Security and Privacy Issues of Bitcoin-1Documento39 pagineA Survey On Security and Privacy Issues of Bitcoin-1Ramineni HarshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of the pulp cavity กย 2562-1Documento84 pagineAnatomy of the pulp cavity กย 2562-1IlincaVasilescuNessuna valutazione finora
- Speech On Viewing SkillsDocumento1 paginaSpeech On Viewing SkillsMera Largosa ManlaweNessuna valutazione finora
- Guyana and The Islamic WorldDocumento21 pagineGuyana and The Islamic WorldshuaibahmadkhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 13 (Automatic Transmission)Documento26 pagineChapter 13 (Automatic Transmission)ZIBA KHADIBINessuna valutazione finora
- Injections Quiz 2Documento6 pagineInjections Quiz 2Allysa MacalinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Configuring BGP On Cisco Routers Lab Guide 3.2Documento106 pagineConfiguring BGP On Cisco Routers Lab Guide 3.2skuzurov67% (3)
- Impact of Pantawid Pamilyang Pilipino Program On EducationDocumento10 pagineImpact of Pantawid Pamilyang Pilipino Program On EducationEllyssa Erika MabayagNessuna valutazione finora
- Fds-Ofite Edta 0,1MDocumento7 pagineFds-Ofite Edta 0,1MVeinte Años Sin VosNessuna valutazione finora
- Evs ProjectDocumento19 pagineEvs ProjectSaloni KariyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Progressive Muscle RelaxationDocumento4 pagineProgressive Muscle RelaxationEstéphany Rodrigues ZanonatoNessuna valutazione finora
- Amount of Casien in Diff Samples of Milk (U)Documento15 pagineAmount of Casien in Diff Samples of Milk (U)VijayNessuna valutazione finora
- EqualLogic Release and Support Policy v25Documento7 pagineEqualLogic Release and Support Policy v25du2efsNessuna valutazione finora
- MCI Approved Medical College in Uzbekistan PDFDocumento3 pagineMCI Approved Medical College in Uzbekistan PDFMBBS ABROADNessuna valutazione finora
- Friction: Ultiple Hoice UestionsDocumento5 pagineFriction: Ultiple Hoice Uestionspk2varmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Promotion-Mix (: Tools For IMC)Documento11 paginePromotion-Mix (: Tools For IMC)Mehul RasadiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- What's New in CAESAR II: Piping and Equipment CodesDocumento1 paginaWhat's New in CAESAR II: Piping and Equipment CodeslnacerNessuna valutazione finora
- PresentationDocumento27 paginePresentationMenuka WatankachhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Comp PPT 1Documento12 pagineCloud Comp PPT 1Kanishk MehtaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Production Engineer Samphhhhhle ResumeDocumento2 pagineMechanical Production Engineer Samphhhhhle ResumeAnirban MazumdarNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution Army 3 R DadDocumento341 pagineEvolution Army 3 R DadStanisław DisęNessuna valutazione finora
- SLA in PEGA How To Configue Service Level Agreement - HKRDocumento7 pagineSLA in PEGA How To Configue Service Level Agreement - HKRsridhar varmaNessuna valutazione finora
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesDa EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (397)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerDa EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (393)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDa EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceDa EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (517)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeDa EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessDa Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (33)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceDa EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (18)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsDa EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionDa EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (812)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseDa EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (52)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperDa EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (16)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainDa EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (65)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Da EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (411)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedDa EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (11)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomDa EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (216)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveDa EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (66)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorDa EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNessuna valutazione finora
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainDa EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (110)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueDa EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (38)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemDa EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (115)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldDa EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (595)
- Minds Make Societies: How Cognition Explains the World Humans CreateDa EverandMinds Make Societies: How Cognition Explains the World Humans CreateValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (23)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouDa EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (62)
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightDa EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (5)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildDa EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (44)