Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
DNA Structure Reveals Its Role in Heredity
Caricato da
Aishwarya ShuklaDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
DNA Structure Reveals Its Role in Heredity
Caricato da
Aishwarya ShuklaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
26
STRUCTURE SHOWS ACTION
x "It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a
possible copying mechanism for the genetic material" wrote Watson and Crick in the scientific
paper that was published in Nature, April 25, 1953.
x This was indeed a breakthrough in the study of how genetic material passes from generation to
generation.
x Once the model was established, its mere structure hinted that DNA was indeed the carrier of the
genetic code and thus the key molecule of heredity, developmental biology and evolution.
x The specific base pairing underlies the perfect copying of the molecule, which is essential for
heredity. During cell division, the DNA molecule is able to "unzip" into two pieces.
x One new molecule is formed from each half-ladder, and due to the specific pairing this gives rise to
two identical daughter copies from each parent molecule.
STRUCTURE
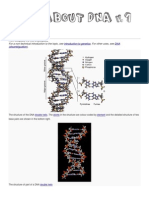
x In living organisms DNA does not usually exist as a single molecule, but instead as a pair of
molecules that are held tightly together.
x These two long strands entwine like vines, in the shape of a double helix.
x The nucleotide repeats contain both the segment of the backbone of the molecule, which holds the
chain together, and a nucleobase, which interacts with the other DNA strand in the helix.
x The backbone of the DNA strand is made from alternating phosphate and sugar residues.
x The sugar in DNA is 2-deoxyribose, which is a pentose (five-carbon) sugar.
x The sugars are joined together by phosphate groups that form phosphodiester bonds between the
third and fifth carbon atoms of adjacent sugar rings.
Gene It’s Nature Expression and Regulation
27
x These asymmetric bonds mean a strand of DNA has a direction.
x In a double helix the direction of the nucleotides in one strand is opposite to their direction in the
other strand: the strands are antiparallel.
x The asymmetric ends of DNA strands are called the 5′ (five prime) and 3′ (three prime) ends,
WATSON AND CRICK
x J. D Watson, an American biologist and F.Crick an English chemist in 1953 designed the model of
the DNA molecule to explain its structure.
x They got the 1962 Nobel prize for the same along with wilkins.
x They did not perform any new experiment but intelligently enough synthesized the data provided
by others.(Wilkins and Franklin, Chargaff).
x Watsons book, the double helix provides fascinating insight into their work.
x Acc to their model, the DNA molecule consists of two long , parallel chains ( strands ) which are
joined together by short crossbars at regular intervals.
x The two chains are spirally coiled around a common axis in a regular manner to form a double helix.
x The double helix is of constant diameter of 2 nanometers or 20angstorm and has major groove
about 22 A wide and minor groove about 12 A wide alternately.
x One complete spiral turn of the helix is 3.4 nm (34A) long and has 10 base pairs.
x The base face the interior of the double helix and are stacked 0.34 nm, 3.4.A apart.
DNA STRUCTURE
RIGHT-HANDED AND LEFT-HANDED HELICES
x Is your model a right-handed helix or a left-handed helix?
x If you hold it pointing away from you and it twists clockwise moving away, it is right-handed,
otherwise it is left-handed.
x These models are mirror images and can not be converted one into the other by rotation.
x The helix of normal DNA is right-handed.
x Left-handed helices have been produced experimentally and may be present in living cells.
Gene It’s Nature Expression and Regulation
28
RIGHT AND LEFT HANDED
DNA COMPOSITION
y 5 carbon deoxyribose sugar.
y Each deoxyribonucleotide unit consists of 3 different molecule.
y Phosphate( po4),
y Nitrogen gives the base its basic nature.
The nitrogenous base may be 9 membered double ringed purine ie adenine (A) , or guanine(G) ;
or 6 membered single ringed pyrimidine ie thymine or cytosine.
COMPONENTS OF DNA
y DNA is a polymer. The monomer units of DNA are nucleotides, and the polymer is known as a
"polynucleotide."
y Each nucleotide consists of a 5-carbon sugar (deoxyribose), a nitrogen containing base attached to
the sugar, and a phosphate group.
y There are four different types of nucleotides found in DNA, differing only in the nitrogenous base.
The four nucleotides are given one letter abbreviations as shorthand for the four bases.
y A is for adenine
y G is for guanine
y C is for cytosine
y T is for thymine
PURINE
y Adenine and guanine are purines. Purines are the larger of the two types of bases found in DNA.
y The 9 atoms that make up the fused rings (5 carbon, 4 nitrogen) are numbered 1-9. All ring atoms
lie in the same plane.
Gene It’s Nature Expression and Regulation
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- It's In Your DNA! What Is DNA? - Biology Book 6th Grade | Children's Biology BooksDa EverandIt's In Your DNA! What Is DNA? - Biology Book 6th Grade | Children's Biology BooksNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1 2Documento142 pagineLecture 1 2ngocnm.bi12-320Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology ProjectDocumento19 pagineBiology ProjectHussain Zohar0% (3)
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) : DNA: Structure, Function and DiscoveryDocumento18 pagineDeoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) : DNA: Structure, Function and DiscoveryHajar Zarguan (Full stack developer)Nessuna valutazione finora
- SodapdfDocumento49 pagineSodapdffaheem.ashrafNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12: Molecular GeneticsDocumento49 pagineChapter 12: Molecular GeneticsOttah Simon UdochiNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics BS - 6 Semester: Assignment # 1Documento20 pagineGenetics BS - 6 Semester: Assignment # 1Hassan JavedNessuna valutazione finora
- Sliced PDF CompressedDocumento49 pagineSliced PDF Compressedfaheem.ashrafNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7: Nucleic Acids: 7.1: DNA Structure and ReplicationDocumento5 pagineChapter 7: Nucleic Acids: 7.1: DNA Structure and ReplicationMariamNessuna valutazione finora
- Nucleic AcidsDocumento113 pagineNucleic AcidsBabak Nami100% (3)
- 6.molecular Basis of InheritanceDocumento62 pagine6.molecular Basis of InheritanceSubhashakti BeheraNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure and Properties of DNA and Genes: Using X-Rays To See Through DNADocumento4 pagineStructure and Properties of DNA and Genes: Using X-Rays To See Through DNAmoadhmoayedNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation Term Paper 2Documento13 paginePresentation Term Paper 2Satyam SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 8_ the DNA_ Structure, Function, And DiscoveryDocumento18 pagineCHAPTER 8_ the DNA_ Structure, Function, And Discoverybabylen bahalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide BiologyDocumento8 pagineStudy Guide BiologyBayron SaucedaNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocumento15 pagineDNA Structure and ReplicationYuli HdyNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics: For A Non-Technical Introduction To The Topic, See - For Other Uses, SeeDocumento8 pagineGenetics: For A Non-Technical Introduction To The Topic, See - For Other Uses, SeeElenaDiSavoiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Handouts Unit-IVDocumento11 pagineHandouts Unit-IVmukeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Nucleic Acids ChemistryDocumento68 pagineNucleic Acids ChemistryAlok DhelditNessuna valutazione finora
- Kuliah DnaDocumento47 pagineKuliah DnaRoby KieranNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1112 - DNA and ReplicationDocumento50 pagineLecture 1112 - DNA and ReplicationnizobellNessuna valutazione finora
- Discovery of DNADocumento6 pagineDiscovery of DNAamplicorNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular Basis-WPS OfficeDocumento33 pagineMolecular Basis-WPS OfficeShubhendu ChattopadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- Watson and Crick Model of DNADocumento22 pagineWatson and Crick Model of DNAGanesh V Gaonkar100% (1)
- Dna 20231115 214325 0000Documento16 pagineDna 20231115 214325 0000121320053030Nessuna valutazione finora
- 09NucAMO SuarezDocumento14 pagine09NucAMO SuarezscasuarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics 1Documento13 pagineGenetics 1Shivam PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 3. DNA Structure, Function and MetabolismDocumento19 pagineLec 3. DNA Structure, Function and MetabolismGajanan SaykhedkarNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA as the Genetic Blueprint of LifeDocumento26 pagineDNA as the Genetic Blueprint of LifeFernanda NúñezNessuna valutazione finora
- Nitrogenous Base Nucleoside DeoxynucleosideDocumento14 pagineNitrogenous Base Nucleoside DeoxynucleosideIan WongNessuna valutazione finora
- Background of GeneticsDocumento23 pagineBackground of GeneticsvubioNessuna valutazione finora
- Karthikeya XII-A Chemistry Project PDFDocumento45 pagineKarthikeya XII-A Chemistry Project PDFkarthikeya kakarlapudiNessuna valutazione finora
- Materi GenetikDocumento30 pagineMateri GenetikTavaelinova Princesia MabruriNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocumento61 pagineMolecular Basis of InheritanceGovind Mani Bhatt100% (1)
- Molecular BiologyDocumento20 pagineMolecular BiologyDaphne CuaresmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nucleic Acids.Documento18 pagineNucleic Acids.kasingabalyaandrewNessuna valutazione finora
- From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: Jump To Navigation Jump To Search Introduction To Genetics DNA (Disambiguation)Documento3 pagineFrom Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: Jump To Navigation Jump To Search Introduction To Genetics DNA (Disambiguation)Lali HajzeriNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.1-6.2 Genetics Intro (Student)Documento4 pagine6.1-6.2 Genetics Intro (Student)Meeriya NewtonNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Replication PDFDocumento7 pagineDNA Replication PDFPiyush ChandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To How DNA WorksDocumento15 pagineIntroduction To How DNA WorksYomi BrainNessuna valutazione finora
- LIfe Science 12 SchoolDocumento78 pagineLIfe Science 12 Schooljonathan otshudiNessuna valutazione finora
- Group Attached To The Sugar Molecule (Figure 1) - There Are Four Different DNA NucleotidesDocumento4 pagineGroup Attached To The Sugar Molecule (Figure 1) - There Are Four Different DNA Nucleotidespraneeth satishNessuna valutazione finora
- Xeroderma Pigmentosum Is Inherited Human Skin Diseases That Causes A Variety of Phenotype Change in Skin Cell Exposed To SunlighDocumento1 paginaXeroderma Pigmentosum Is Inherited Human Skin Diseases That Causes A Variety of Phenotype Change in Skin Cell Exposed To Sunlighסנאבל מוסאNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is DNA? Discovery Diagram DNA Structure Chargaff's Rule DNA Replication Function of DNA Why DNA Is Called A Polynucleotide Molecule?Documento5 pagineWhat Is DNA? Discovery Diagram DNA Structure Chargaff's Rule DNA Replication Function of DNA Why DNA Is Called A Polynucleotide Molecule?Hera ElykaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dna Structure and FunctionDocumento12 pagineDna Structure and FunctionAliah Aziz100% (1)
- 5.1DNA and RNADocumento26 pagine5.1DNA and RNAserficasoNessuna valutazione finora
- TOPIC 1 Organisation - Structure FunctionDocumento41 pagineTOPIC 1 Organisation - Structure FunctionsyuhadahNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture. (1), Introduction & Structure of Nucleic AcidDocumento64 pagineLecture. (1), Introduction & Structure of Nucleic Acidstudentactivity555Nessuna valutazione finora
- Watson & Crick DNA Model: Academic ScriptDocumento9 pagineWatson & Crick DNA Model: Academic ScriptMirunalini GobinathNessuna valutazione finora
- My Project On DNADocumento28 pagineMy Project On DNAAnokhi KashiparekhNessuna valutazione finora
- All About DnaDocumento65 pagineAll About DnaPeopwdNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA: The Warehouse/Storage of Genetic Information: by Librada M. RubioDocumento16 pagineDNA: The Warehouse/Storage of Genetic Information: by Librada M. RubioAbby SevillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Molecular Pathology - April 2012 - ZHDocumento55 pagineIntroduction To Molecular Pathology - April 2012 - ZHtoxiczarrar.pubgNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA - Level 1 18 Jan 2010Documento4 pagineDNA - Level 1 18 Jan 2010safemindNessuna valutazione finora
- Dna ANDYDocumento12 pagineDna ANDYAndy Morales100% (1)
- Nucleic Acids - Topic 7 HLDocumento28 pagineNucleic Acids - Topic 7 HLGracieNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes - Dna Protein Synthesis - Student 2000Documento14 pagineNotes - Dna Protein Synthesis - Student 2000api-270403367Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dna 053215Documento13 pagineDna 053215Baninla NerusNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)Documento5 pagineDNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)Sagar MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Orbital or Critical Velocity (V) :: Gravitation 3Documento1 paginaOrbital or Critical Velocity (V) :: Gravitation 3Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular Motion Forces and VelocitiesDocumento1 paginaCircular Motion Forces and VelocitiesAishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Interference & Diffraction-5Documento1 paginaInterference & Diffraction-5Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Interference & Diffraction-1Documento1 paginaInterference & Diffraction-1Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Synopsis Synopsis Synopsis Synopsis: D D D DDocumento1 paginaSynopsis Synopsis Synopsis Synopsis: D D D DAishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 4 MHT-CET - Part I (Std. 12)Documento1 pagina1 4 MHT-CET - Part I (Std. 12)Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- I. Variation of G' Just Above Earth's Surface:: 2 MHT-CET - Part I (Std. 12)Documento1 paginaI. Variation of G' Just Above Earth's Surface:: 2 MHT-CET - Part I (Std. 12)Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gravitation 5Documento1 paginaGravitation 5Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Binding Energy (B.E.) :: 4 MHT-CET - Part I (Std. 12)Documento1 paginaBinding Energy (B.E.) :: 4 MHT-CET - Part I (Std. 12)Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 2 MHT-CET - Part I (Std. 12) : Constant SpeedDocumento1 pagina1 2 MHT-CET - Part I (Std. 12) : Constant SpeedAishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular Motion-13Documento1 paginaCircular Motion-13Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circulation - Final PDF-4Documento2 pagineCirculation - Final PDF-4Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Synopsis Synopsis Synopsis Synopsis: 1. Gravitational Field: 3. Gravitational Intensity (E)Documento1 paginaSynopsis Synopsis Synopsis Synopsis: 1. Gravitational Field: 3. Gravitational Intensity (E)Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice Questions: Circular Motion 15Documento1 paginaMultiple Choice Questions: Circular Motion 15Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular Motion-11Documento1 paginaCircular Motion-11Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular Motion-5Documento1 paginaCircular Motion-5Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Potassium Permanganate Oxidation PropertiesDocumento3 paginePotassium Permanganate Oxidation PropertiesAishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular Motion-4Documento1 paginaCircular Motion-4Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- D and F Block Elements-2Documento3 pagineD and F Block Elements-2Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- D and F Block Elements-3Documento3 pagineD and F Block Elements-3Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circulation - Final PDF-2Documento2 pagineCirculation - Final PDF-2Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circulation - Final PDF-3Documento2 pagineCirculation - Final PDF-3Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circulation Systems ComparedDocumento2 pagineCirculation Systems ComparedAishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- d-Block Elements ConfigurationDocumento3 pagined-Block Elements ConfigurationAishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes-15Documento4 pagineHaloalkanes and Haloarenes-15Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes-14 PDFDocumento4 pagineHaloalkanes and Haloarenes-14 PDFAishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes-16Documento4 pagineHaloalkanes and Haloarenes-16Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 3Documento13 pagineLec 3Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec4 PDFDocumento8 pagineLec4 PDFAishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 2Documento12 pagineLec 2Aishwarya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Properties of Oil Palm Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Composites: A ReviewDocumento33 pagineMechanical Properties of Oil Palm Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Composites: A ReviewjaviergagocampusanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 4 - Chemical Bonding and Structure: Quick QuestionsDocumento4 pagineTopic 4 - Chemical Bonding and Structure: Quick QuestionsRafael Burgos CabanillaNessuna valutazione finora
- 10) Farming - Conventional and SustainableDocumento76 pagine10) Farming - Conventional and Sustainableeliseobravo572Nessuna valutazione finora
- Power Plant Engg Lab Manual BeDocumento32 paginePower Plant Engg Lab Manual Besinan2yilmazNessuna valutazione finora
- Material Safety Data Sheet - MSDS: Sulfuric Acid (Concentrated)Documento8 pagineMaterial Safety Data Sheet - MSDS: Sulfuric Acid (Concentrated)umair2kplus492Nessuna valutazione finora
- Class 7 Science Exam Paper March 2021-22Documento9 pagineClass 7 Science Exam Paper March 2021-22Riffat AamerNessuna valutazione finora
- Noble 2014Documento13 pagineNoble 2014Restu DanikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3Documento96 pagineChapter 3Sinclyr Valenciano100% (1)
- Microleakage and NanoleakgeDocumento61 pagineMicroleakage and NanoleakgemahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analiza Srotului de SoiaDocumento8 pagineAnaliza Srotului de SoiaKevin RmnNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 - HULGAN and HARTEINK - Recent Advances in Collagen Mimetic Peptide Structure and DesignDocumento15 pagine2022 - HULGAN and HARTEINK - Recent Advances in Collagen Mimetic Peptide Structure and DesignCarlos FerreiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaping PresentationDocumento24 pagineVaping PresentationDes0% (1)
- Experiment9 A011Documento35 pagineExperiment9 A011Manas GaikwadNessuna valutazione finora
- Rivet Edge Distance Guide - Key Factors for Aircraft DesignDocumento2 pagineRivet Edge Distance Guide - Key Factors for Aircraft Designnirlep_parikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Tanveer Maple Leaf IRDocumento55 pagineTanveer Maple Leaf IRsaqlain ahmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Oswaal CBSE 12th Chemistry Art IntegrationDocumento9 pagineOswaal CBSE 12th Chemistry Art Integrationhps3076Nessuna valutazione finora
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Sample PaperDocumento52 pagineRefrigeration and Air Conditioning Sample PaperkregdNessuna valutazione finora
- High viscosity acrylic polymer for hydro-alcoholic gelsDocumento2 pagineHigh viscosity acrylic polymer for hydro-alcoholic gelsCarlos SiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas CondensateDocumento10 pagineGas CondensateMurad RustamliNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Notes - CH - 5 Life Processes2Documento5 pagineBiology Notes - CH - 5 Life Processes2AISHA AMAL ANDIKATTILASSLAM ANDIKATTILNessuna valutazione finora
- Duron HP 15W-40: Safety Data SheetDocumento11 pagineDuron HP 15W-40: Safety Data SheetIng Kelvys GonzalezNessuna valutazione finora
- Remote Area Medical Equipment ChecklistDocumento47 pagineRemote Area Medical Equipment ChecklistEever Paul De LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Syed Shaheen ShahDocumento35 pagineSyed Shaheen ShahClaudia MunizNessuna valutazione finora
- Ceran-Xm-220 TDS v171128Documento2 pagineCeran-Xm-220 TDS v171128phucdc095041Nessuna valutazione finora
- DETAILED ANALYSIS OF ADULTERATED FOODDocumento9 pagineDETAILED ANALYSIS OF ADULTERATED FOODamritaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tractor Emulsion Shyne: Product BenefitsDocumento2 pagineTractor Emulsion Shyne: Product Benefitssumit gaurNessuna valutazione finora
- MakkuDocumento82 pagineMakkuParth PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Mistron VaproDocumento21 pagineMistron VaproChandrasekar KrishnamurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Wynn S Alto Al Humo Stop Smoke SDSDocumento7 pagineWynn S Alto Al Humo Stop Smoke SDSRamiro MarcaNessuna valutazione finora
- MSDS - Silky Serum Base PlusDocumento4 pagineMSDS - Silky Serum Base PlustopguitarNessuna valutazione finora